What Are a Predictive Model's Related Datasets?
When you run the data flow to create the Oracle Analytics predictive model's training model, Oracle Analytics creates a set of related datasets. You can open and create workbooks on these datasets to learn about the accuracy of the model.
Depending on the algorithm you chose for your model, related datasets contain details about the model such as prediction rules, accuracy metrics, confusion matrix, and key drivers for prediction. You can use this information to fine tune the model to get better results, and you can use related datasets to compare models and decide which model is more accurate.
For example, you can open a Drivers dataset to discover which columns have a strong positive or negative influence on the model. By examining those columns, you find that some columns aren't treated as model variables because they aren't realistic inputs or that they're too granular for the forecast. You use the data flow editor to open the model and based on the information you discovered, you remove the irrelevant or too-granular columns, and regenerate the model. You check the Quality and Results tab and verify if the model accuracy is improved. You continue this process until you're satisfied with the model's accuracy and it's ready to score a new dataset.
Different algorithms generate similar related datasets. Individual parameters and column names may change in the dataset depending on the type of algorithm, but the functionality of the dataset stays the same. For example, the column names in a statistics dataset may change from Linear Regression to Logistic Regression, but the statistics dataset contains accuracy metrics of the model.
Related Datasets for AutoML Models
When you train a predictive model using AutoML, Oracle Analytics creates additional datasets that contain useful information about the model. The number of datasets created depends on the model algorithm. For example, for Naive Bayes models, Oracle Analytics creates a dataset providing information about conditional probabilities. For a decision tree model, the dataset provides information about decision tree statistics. When you inspect an AutoML-generated model using the generalized linear model (GLM) algorithm, you see entries prefixed with GLM* for the model-specific datasets that contain metadata information about the model.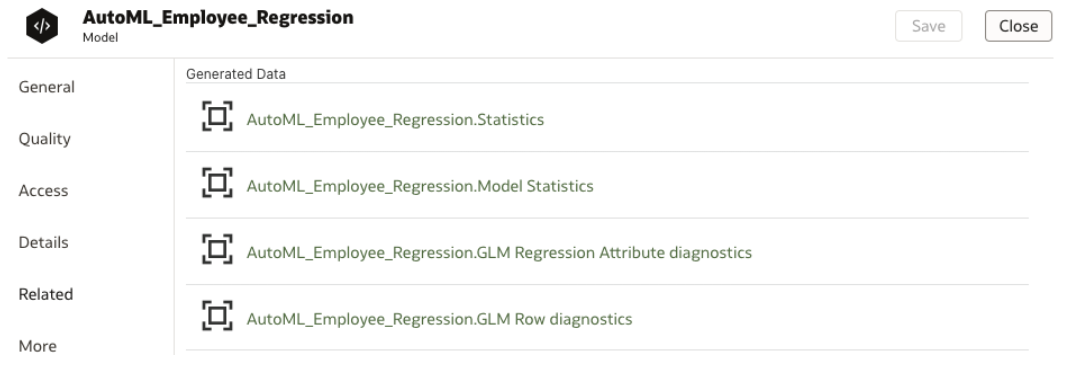
Description of the illustration automl-related-datasets.png
Related Datasets
Note:
Oracle Analytics appends the dataflow's output name to the related dataset type. For example, for a CART model, if the data flow's output is named cart_model2, then the dataset is named cart_model2_CART.CART
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the CART (Classification and Regression Tree) related dataset, which contains columns that represent the conditions and the conditions' criteria in the decision tree, a prediction for each group, and prediction confidence. Use the tree diagram visualization to visualize this decision tree.
The CART dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Numeric | CART for Numeric Prediction |
| Binary Classification | CART |
| Multi Classification | CART |
Classification Report
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Classification Report related dataset. For example, if the target column can have the two distinct values, Yes or No, this dataset shows accuracy metrics like F1, Precision, Recall, and Support (the number of rows in the training dataset with this value) for every distinct value of the target column.
The Classification dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Binary Classification |
Naive Bayes Neural Network Support Vector Machine |
| Multi Classification |
Naive Bayes Neural Network Support Vector Machine |
Confusion Matrix
Oracle Analytics creates a pivot table for the Confusion Matrix related dataset, which is also called an error matrix. Each row represents an instance of a predicted class, and each column represents an instance in an actual class. This table reports the number of false positives, false negatives, true positives, and true negatives, which are used to compute precision, recall, and F1 accuracy metrics.
The Confusion Matrix dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Binary Classification |
Logistics Regression CART (Decision Tree) Naive Bayes Neural Network Random Forest Support Vector Machine |
| Multi Classification |
CART (Decision Tree) Naive Bayes Neural Network Random Forest Support Vector Machine |
Drivers
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Drivers related dataset, which contains information about the columns that determine the target column values. Linear regressions are used to identify these columns. Each column is assigned coefficient and correlation values. The coefficient value describes the column's weight-age used to determine the target column's value. The correlation value indicates the relationship direction between the target column and dependent column. For example, if the target column's value increases or decreases based on the dependent column.
The Drivers dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Numeric |
Linear Regression Elastic Net Linear Regression |
| Binary Classification |
Logistics Regression Support Vector Machine |
| Multi Classification | Support Vector Machine |
Hitmap
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Hitmap related dataset, which contains information about the decision tree's leaf nodes. Each row in the table represents a leaf node and contains information describing what that leaf node represents, such as segment size, confidence, and expected number of rows. For example, expected number of correct predictions = Segment Size * Confidence.
The Hitmap dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Numeric | CART for Numeric Prediction |
Residuals
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Residuals related dataset, which contains information about the quality of the residual predictions. A residual is the difference between the measured value and the predicted value of a regression model. This dataset contains an aggregated sum value of absolute difference between the actual and predicted values for all columns in the dataset.
The Residuals dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Numerics |
Linear Regression Elastic Net Linear Regression CART for Numeric Prediction |
| Binary Classification | CART (Decision Tree) |
| Multi Classificatin | CART (Decision Tree) |
Statistics
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Statistics related dataset. This dataset's metrics depend upon the algorithm used to generate it. Note this list of metrics based on algorithm:
- Linear Regression, CART for Numeric Prediction, Elastic Net Linear Regression - These algorithms contain R-Square, R-Square Adjusted, Mean Absolute Error(MAE), Mean Squared Error(MSE), Relative Absolute Error(RAE), Related Squared Error(RSE), Root Mean Squared Error(RMSE).
- CART(Classification And Regression Trees), Naive Bayes Classification, Neural Network, Support Vector Machine(SVM), Random Forest, Logistic Regression - These algorithms contain Accuracy, Total F1.
This dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Numeric |
Linear Regression Elastic Net Linear Regression CART for Numeric Prediction |
| Binary Classification |
Logistics Regression CART (Decision Tree) Naive Bayes Neural Network Random Forest Support Vector Machine |
| Multi Classification |
Naive Bayes Neural Network Random Forest Support Vector Machine |
Summary
Oracle Analytics creates a table for the Summary related dataset, which contains information such as Target name and Model name.
The Summary dataset is created when you select these model and algorithm combinations.
| Model | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| Binary Classification |
Naive Bayes Neural Network Support Vector Machine |
| Multi Classification |
Naive Bayes Neural Network Support Vector Machine |