4 Deploying ADF Applications
This chapter includes the following sections:
For information about deploying ADF applications for development, see the Deploying Fusion Web Applications chapter of the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
Introduction to Deploying ADF Applications
JDeveloper can be used to develop an ADF application and create an EAR archive file to deploy to the target. There are several tools and methods used by the administrators to deploy ADF applications to the target.
Deployment is the process of packaging application files and artifacts and transferring them to a target application server to be run. During application development using JDeveloper, developers can test the application using the Integrated WebLogic Server that is built into the JDeveloper installation, or they can use JDeveloper to directly deploy to a standalone application server.
After the application has been developed, administrators can deploy the application to production application servers. The tools that the administrators use for production-level deployment are:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
-
WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) commands
-
Command scripts and Ant scripts
-
Oracle WebLogic Administration Console
This chapter describes the tools and methods that administrators use to deploy ADF applications. For information about deploying ADF applications for development and testing purposes using JDeveloper, see Deploying Fusion Web Applications of the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
If your application uses customizations, you may need to set up the MDS repository in the application server. For more information about MDS, see Managing the Metadata Repository of the Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Note:
Developers, Test, and QA personnel may also use these tools and the methods in this chapter to deploy ADF applications to staging application servers.
Preparing the Standalone Application Server for Deployment
To run ADF applications, you must install the standalone application server with the ADF runtime. You can include the ADF runtime during a new application server installation or you can install the ADF runtime into an existing application server installation.
Figure 4-1 shows the flow diagram for preparing a standalone application server for deployment. Note the following definitions used in the diagram:
-
OWSM: Oracle Web Services Manager
-
JRF: Java Required Files
-
RCU: Repository Creation Utility
-
MDS: Metadata Store
Figure 4-1 Preparing the Application Server Flow Diagram
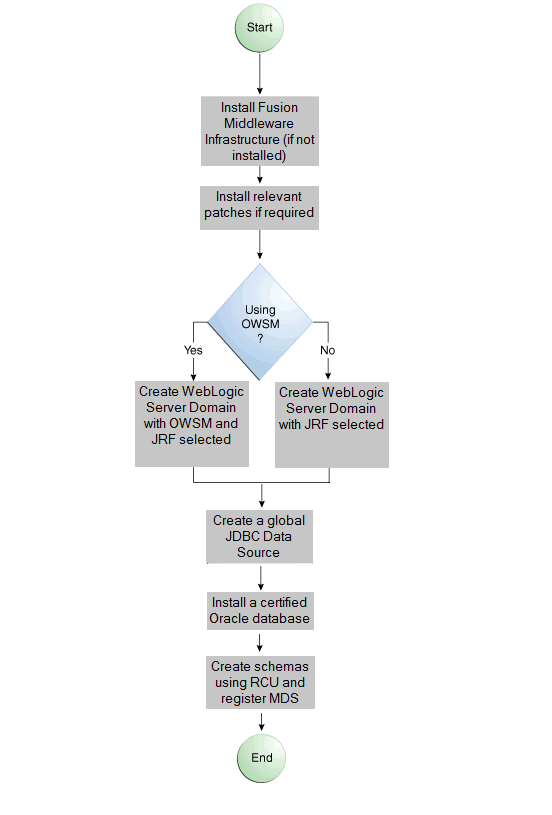
Description of "Figure 4-1 Preparing the Application Server Flow Diagram"
For WebLogic Server, the following points apply:
-
After you install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure, you can create a new WebLogic Server domain or you can extend an existing WebLogic Server domain for Oracle ADF.
-
If the Managed Servers are on a different host than the Administration Server, you must perform additional configuration tasks for the Managed Servers to enable them to host ADF applications.
-
An ADF application will use either a JDBC data source or a JDBC URL to access its data. You can configure WebLogic Server with the data source using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
For additional information about OPatch for patching your existing Oracle Fusion Middleware environment, see Patching Your Environment Using OPatch of the Patching with OPatch.
-
For additional information about creating and loading the schemas, see Creating Schemas in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
-
For the latest information about Oracle Application Development Framework and Oracle JDeveloper, see the Oracle JDeveloper Release Notes on Oracle Technology Network.
Installing the ADF Runtime to the Application Server Installation
The application server requires the ADF runtime to run ADF applications.
Installing the ADF runtime is not required if you are using JDeveloper to run applications in Integrated WebLogic Server.
For WebLogic Server, you can install the ADF runtime using the following installers:
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Application Developer Infrastructure Installer: Installs the ADF runtime and Oracle Enterprise Manager. You should use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Installer if you want to use Oracle Enterprise Manager to manage standalone ADF applications (without Oracle SOA Suite or Oracle WebCenter Portal components). For more information, see Planning the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Installation of the Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
Note:
The Oracle JDeveloper Installer can also be used to install the ADF runtime to the application server installation. However, it does not include all the components that are typically needed for production and full test environments. Therefore, this installer should not be used for anything other than for development purposes. For information about the obtaining and using the installer, see Installing the Oracle JDeveloper Software of the Installing Oracle JDeveloper.
Using the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Installer
You can use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Installer to install the ADF runtime and Enterprise Manager.
Install Oracle WebLogic Server. You must also have obtained the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Installer.
Use the instructions in Preparing for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation of the Planning an Installation of Oracle Fusion Middleware to obtain the software, start the installer, and to complete the installation.
In the installer you will perform several tasks including:
-
Adding any software updates
-
Selecting the WebLogic Server directory for installation
-
Verifying installation information
After you have installed the ADF runtime, follow the instructions in Creating and Extending Oracle WebLogic Server Domains to use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard to create or extend the Oracle WebLogic Server domain.
Installing Relevant Patches
You may need to install patches and other updates to your software distribution. For more information, see Patching Your Environment Using OPatch of the Patching with OPatch.
To enable existing sessions to continue to run while OPatchAuto updates the servers, use -plan wls-zdt-rollout . Note that Oracle WebLogic Server domain must be configured with a Load Balancer like Oracle HTTP Server, for example. For more information, see ZDT Patching Restrictions.
If Oracle WebLogic Server Domain is not configured with Load Balancer, you can use the -plan rolling OpatchAuto option. Note that this option is not related to zero downtime technology and causes existing sessions to be terminated as patching proceeds.
Creating and Extending Oracle WebLogic Server Domains
You need to create and configure the Oracle WebLogic Server domain to accept ADF applications. If you do not already have a domain, you need to create one. If you already have a domain, you must extend the domain before it can run ADF applications.
If you are using Managed Servers to run your applications, you may need to configure your Managed Server. For more information about configuring a Managed Server on Oracle WebLogic Server, see Managed Servers of the Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
If you are setting up Managed Servers for ADF where the Managed Servers are on the same host as the Administration Server, follow the instructions described in this section.
If you are setting up to deploy to Managed Servers that are on a different host than the Administration Server, perform the additional steps described in Setting Up Remote WebLogic Managed Servers for Oracle ADF.
Creating an Oracle WebLogic Server Domain for Oracle ADF
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the options that are available to you when you create a WebLogic Server domain for Oracle ADF. For more information, see Preparing the Standalone Application Server for Deployment.
To create a new Oracle WebLogic Server domain:
-
Start the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration wizard as described in Configuring Your WebLogic Domain of the Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
Follow the directions as described in that guide but consider the following steps.
-
In the Welcome page, select Create a New Domain and click Next.
-
In the Templates page, select Create Domain Using Product Templates.
The option Basic WebLogic Server Domain - 12.2.1 [wlserver] is already selected.
Select Oracle JRF - 12.2.1 [oracle_common]. If you are using Oracle Web Services, select Oracle WSM Policy Manager 12.2.1 [oracle_common] and click Next.
-
Continue to follow the directions in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
Extending the Oracle WebLogic Server Domain for Oracle ADF
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the options that are available to you when you extend the WebLogic Server domain for Oracle ADF. For more information, see Preparing the Standalone Application Server for Deployment.
You will need to create an Oracle WebLogic Server domain with the ADF runtime installed.
To extend an Oracle WebLogic Server domain for ADF:
-
Start the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration wizard as described in Configuring Your WebLogic Domain of the Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
Follow the directions as described in that guide but consider the following steps.
-
In the Welcome page, select Update an existing domain.
-
Select the location of the domain you want to update for Oracle ADF, and click Next.
-
In the Templates page, select Update Domain Using Product Templates.
The option Basic WebLogic Server Domain - 12.2.1 [wlserver] is already selected.
Select Oracle JRF - 12.2.1 [oracle_common]. If you are using Oracle Web Services, select Oracle WSM Policy Manager 12.2.1 [oracle_common] and click Next.
-
Continue to follow the directions in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
This configures the rest of the runtime .jar files using the manifest file.
Note:
Your application's EAR file must have a weblogic-application.xml file containing a reference to the adf.oracle.domain shared library.
You can now start Oracle WebLogic Server by running the command-line script ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\domain_name\bin\startWebLogic.cmd, and you can stop the server using the stopWebLogic.cmd script in the same directory. For Linux platforms, use \bin\startWebLogic.sh and stopWebLogic.sh respectively.
Access the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console using the URL http://localhost:7001/console.
Setting Up Remote WebLogic Managed Servers for Oracle ADF
If the WebLogic Managed Servers are on a different host than the Administration Server, you need to perform additional steps.
You will need to set up Managed Servers for Oracle ADF on the host with the Administration Server, pack the JRF template, copy it to the remote host, and unpack the template.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the options that are available to you when you create remote WebLogic Managed Servers for Oracle ADF. For more information, see Preparing the Standalone Application Server for Deployment.
For more information about using pack and unpack commands to set up managed servers, see pack and unpack Command Reference of the Creating Templates and Domains Using the Pack and Unpack Commands.
You will need to complete this task:
-
Set up Managed Servers for Oracle ADF on the host with the Administration Server.
-
Pack the JRF template.
-
Copy the template to the remote host.
-
Unpack the template
To set up remote Managed Servers for Oracle ADF:
-
Use the Oracle Installer for JDeveloper to install Oracle WebLogic Server installations on both the local and remote hosts, if not already installed. If you are not installing JDeveloper Studio, you need to select the Application Development Framework Runtime option in the installer. The local host is the host with the Administration Server.
Or, if there are existing Weblogic Server installations, use the Oracle Installer for JDeveloper to install the ADF runtime into the WebLogic Server installations on both hosts by selecting the Application Development Framework Runtime option. For more information on installation, see Installing the ADF Runtime to the Application Server Installation.
-
Run the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard to create a new Oracle WebLogic Server domain. In the wizard, select the Oracle JRF option, as described in Creating an Oracle WebLogic Server Domain for Oracle ADF.
-
On the local host, run the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard to create Managed Servers.
-
On the local host, start the Administration Server and the Managed Server.
For example,
cd ORACLE_HOME/user_projects/domain/base_domain/bin ./startWeblogic.sh ./startManagedWebLogic.sh ManagedServer_1 http://localhost:7001
-
On the local host, pack the Managed Server configuration information into a JAR and then copy the JAR to the remote host. This JAR contains the JRF template information.
For example,
cd ORACLE_HOME/oracle_home/common/bin ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=../../../user_projects/domains/base_domain -template=../../../base_domain_managed.jar -template_name= "Base Managed Server Domain" cp ../../../base_domain_managed.jarremote_machine_ORACLE_HOME/ -
On the remote host, unpack the Managed Server configuration JAR.
For example,
cd ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin ./unpack.sh -domain=../../../user_projects/domains/base_domain -template=../../../base_domain_managed.jarIf the Managed Server was created after the domain was, you must delete the entire domain configuration directory of the Managed Server before running
unpack. -
On the remote host, start the Node Manager.
For example,
cd ORACLE_HOME/wlserver_10.3/server/bin ./startNodeManager.sh
-
On the remote host, if the Managed Server was not created with the JRF template applied, run the
applyJRFWLST command to extend the Managed Server with the JRF template.Also, if the Managed Server was created after the domain was, you must delete the entire domain configuration directory of the Managed Server before running
applyJRF. -
On the both hosts, start the Managed Servers.
For example,
cd ORACLE_HOME/user_projects/domains/base_domain/bin./startManagedWebLogic.sh ManagedServer_2 http://<adminServerHost>:7001
Creating a JDBC Data Source for Oracle WebLogic Server
Use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to set up a JDBC data source in the WebLogic Server instance for your applications.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the options that are available to you when you create a JDBC data source. For more information, see Preparing the Standalone Application Server for Deployment.
To configure Oracle WebLogic Server for a JDBC data source:
Once the data source has been created in Oracle WebLogic Server, it can be used by an application module.
Deploying Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
You can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control to deploy the EAR file created in JDeveloper. Fusion Middleware Control is a web browser-based, graphical user interface that you can use to monitor and administer a server farm.
For more information about deploying using Fusion Middleware Control, see Deploying Oracle ADF Applications in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Deploying Using Scripting Commands
Applications or modules can be deployed from JDeveloper without starting the JDeveloper IDE. You can run WLST commands from the command line or sequence them in scripts to run as a batch.
Before deploying from the command line, there must be deployment profiles for the application (EAR) or project (JAR or WAR). JDeveloper creates these deployment profiles automatically for certain types of applications, but before using commands for deployment, it is important to verify that the deployment profile(s) exist. To verify that the profiles exist, choose the Deployment node from either the Application Properties or Project Properties dialogs in JDeveloper. For more information about deployment profiles, see How to Create Deployment Profiles in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
JDeveloper can also be used to deploy an application's EAR, WAR, or JAR files. The same scripts that are used for deployment via a command line are also used to deploy via JDeveloper, but JDeveloper creates the syntax and provides a user interface for the deployment.
There are specific WLST commands (WebLogic) for working with ADF applications. For a list of these commands, see Working with WLST Commands for ADF Applications.
For more information about using WLST scripts, see the WLST Command Reference for Infrastructure Components.
Deploying Using Scripts and Ant
You can deploy the application using commands and scripts. You create a script to deploy the application using the ojdeploy command and use the ojaudit command to audit projects, workspaces, or source files of the application.
You can also set up the script to run automatically, for instance, whenever a developer checks in new changes.
ojdeploy scripts and Ant scripts can be used together or separately:
-
Create an
ojdeployscript to compile, package, and deploy the application. -
Create an
ojdeployscript to compile and package the application. Then use an Ant script (such asWLDeploy) to deploy the application. -
Create an Ant script to compile, package, and deploy the application. The Ant does not need to use
ojdeploy.
For more information about the ojdeploy and ojaudit commands, see the JDeveloper online help.
You can deploy to most application servers from JDeveloper, or use tools provided by the application server vendor. You may also use Ant to package and deploy applications. The build.xml file, which contains the deployment commands for Ant, may vary depending on the target application server.
For deployment to other application servers, see the application server's documentation. If your application server does not provide specific Ant tasks, you may be able to use generic Ant tasks. For example, the generic ear task creates an EAR file for you.
For information about Ant, see http://ant.apache.org.
Deploying Using the Application Server Administration Tool
JDeveloper can be used to develop an ADF application and create an EAR archive file to deploy to the target. Use Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to deploy the EAR file to the target.
For Oracle WebLogic Server, you can use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to deploy the EAR file created in JDeveloper.
For more information, see Introduction and Roadmap of the Deploying Applications to Oracle WebLogic Server.
Deploying Using Oracle Java Cloud Service
There are different tools and options to deploy ADF applications to a WebLogic Server instance in Oracle Java Cloud Service. You can use JDeveloper, WebLogic Server Administration Console, or Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control to deploy ADF applications.
You can deploy an application to a WebLogic Server instance in Oracle Java Cloud Service using any option listed below:
-
from Oracle JDeveloper through a secure shell (SSH) tunnel
-
from WebLogic Server Administration Console through a menu on the Oracle Java Cloud Service cloud portal
-
from Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control for WebLogic Server through a menu on the Oracle Java Cloud Service cloud portal
-
from WebLogic Scripting Tool through an SSH client
For more information, see the documentation provided with Oracle Java Cloud Service.