14 Instantiating Oracle GoldenGate with an Initial Load
The initial load can be done in Classic Architecture and in Microservices Architecture.
- Overview of the Initial-Load Procedure
- Initial Load in Classic Architecture
In Classic Architecture you can load data using various options. The processes and steps do so, are described in this topic.
Parent topic: Administering Oracle GoldenGate Classic Architecture
14.1 Overview of the Initial-Load Procedure
You can use Oracle GoldenGateto:
-
Perform a standalone batch load to populate database tables for migration or other purposes.
-
Load data into database tables as part of an initial synchronization run in preparation for change synchronization with Oracle GoldenGatee.
Parent topic: Instantiating Oracle GoldenGate with an Initial Load
14.1.1 Improving the Performance of an Initial Load
For all initial load methods except those performed with a database utility, you can load large databases more quickly by using parallel Oracle GoldenGate processes. To use parallel processing, take the following steps.
- Follow the directions in this chapter for creating an initial-load Extract and an initial-load Replicat for each set of parallel processes that you want to use.
- With the
TABLEandMAPparameters, specify a different set of tables for each pair of Extract-Replicat processes, or you can use theSQLPREDICATEoption ofTABLEto partition the rows of large tables among the different Extract processes.
For all initial load methods, testing has shown that using the TCPBUFSIZE option in the RMTHOST parameter produced three times faster throughput than loads performed without it. Do not use this parameter if the target system is NonStop.
Parent topic: Overview of the Initial-Load Procedure
14.1.2 Prerequisites for Initial Load
Verify that you meet the prerequisites for executing an initial load that are described in the following sections.
- Disable DDL Processing
- Prepare the Target Tables
- Configure the Manager Process
- Create a Data-definitions File
- Create Change-synchronization Groups
- Sharing Parameters between Process Groups
Parent topic: Overview of the Initial-Load Procedure
14.1.2.1 Disable DDL Processing
Before executing an initial load, disable DDL extraction and replication. DDL processing is controlled by the DDL parameter in the Extract and Replicat parameter files.
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.1.2.2 Prepare the Target Tables
The following are suggestions that can make the load go faster and help you to avoid errors.
-
Data: Make certain that the target tables are empty. Otherwise, there may be duplicate-row errors or conflicts between existing rows and rows that are being loaded.
-
Constraints: Disable foreign-key constraints and check constraints. Foreign-key constraints can cause errors, and check constraints can slow down the loading process. Constraints can be reactivated after the load concludes successfully.
-
Indexes: Remove indexes from the target tables. Indexes are not necessary for inserts. They will slow down the loading process significantly. For each row that is inserted into a table, the database will update every index on that table. You can add back the indexes after the load is finished.
Note:
A primary index is required for all applications that access DB2 for z/OS target tables. You can delete all other indexes from the target tables, except for the primary index.
-
Keys: For Oracle GoldenGate to reconcile the replicated incremental data changes with the results of the load, each target table must have a primary or unique key. If you cannot create a key through your application, use the
KEYCOLSoption of theTABLEandMAPparameters to specify columns as a substitute key for Oracle GoldenGate's purposes. A key helps identify which row to process. If you cannot create keys, the source database must be quiesced for the load.
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.1.2.3 Configure the Manager Process
On the source and target systems, configure and start a Manager process. One Manager can be used for the initial-load processes and the change-synchronization processes. See Configuring Manager and Network Communications for more information. For enhanced security, the target manager parameter file should have the following parameter for RMTTASK to access Replicat on target:
ACCESSRULE, PROG *, IPADDR *, ALLOW
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.1.2.4 Create a Data-definitions File
A data-definitions file is required if the source and target databases have dissimilar definitions. Oracle GoldenGate uses this file to convert the data to the format required by the target database.
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.1.2.5 Create Change-synchronization Groups
To prepare for the capture and replication of transactional changes during the initial load, create online Extract and Replicat groups. You will start these groups during the load procedure. See Configuring Online Change Synchronization for more information.
Note:
If the load is performed from a quiet source database and will not be followed by continuous change synchronization, you can omit these groups.
Do not start the Extract or Replicat groups until instructed to do so in the initial-load instructions. Change synchronization keeps track of transactional changes while the load is being applied, and then the target tables are reconciled with those changes.
Note:
The first time that Extract starts in a new Oracle GoldenGate configuration, any open transactions will be skipped. Only transactions that begin after Extract starts are captured.
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.1.2.6 Sharing Parameters between Process Groups
Some of the parameters that you use in a change-synchronization parameter file also are required in an initial-load Extract and initial-load Replicat parameter file. You can copy those parameters from one parameter file to another, or you can store them in a central file and use the OBEY parameter in each parameter file to retrieve them. Alternatively, you can create an Oracle GoldenGate macro for the shared parameters and then call the macro from each parameter file with the MACRO parameter.
See Getting Started with the Oracle GoldenGate Process Interfaces for more information about using OBEY and using macros.
Parent topic: Prerequisites for Initial Load
14.2 Initial Load in Classic Architecture
In Classic Architecture you can load data using various options. The processes and steps do so, are described in this topic.
- Loading Data with Oracle Data Pump
- Loading Data from File to Replicat
- Loading Data with an Oracle GoldenGate Direct Load
- Loading Data with a Direct Bulk Load to SQL*Loader
Parent topic: Instantiating Oracle GoldenGate with an Initial Load
14.2.1 Loading Data with Oracle Data Pump
This method uses the Oracle Data Pump utility to establish the target data. After you apply the copy to the target, you record the SCN at which the copy stopped. Transactions that were included in the copy are skipped to avoid collisions from integrity violations. With the data pump method, Replicat has the information about the consistent SCN from the export of each table. Replicat will ignore changes that belongs to transactions up to this SCN. Transactions after this SCN will be applied. No initial-load Oracle GoldenGate processes are required for these methods.
Parent topic: Initial Load in Classic Architecture
14.2.1.1 Using Automatic Per Table Instantiation
On the Source Database
You can automatically instantiate per table CSN filtering for Oracle Database with Oracle data pump, which avoids having all of your tables at the same SCN.
-
Use
ADD TRANDATAandADD SCHEMATRANDATA.ADD TRANDATA/SCHEMATRANDATA.PREPARECSNautomatically prepares the tables at the source so the Oracle data pump export dump file includes instantiation CSNs. Replicat uses the per table instantiation CSN set by the Oracle data pump (on import) to filter out trail records.UseINFO TRANDATAto make sure that your table is prepared for instantiation and at what point it was done. Here's a sample of the report file:2016-09-29 15:30:00 INFO OGG-10154 Schema level PREPARECSN set to mode NOWAIT on schema SCOTT -
Stop Replicat on the target database.
-
Start Extract with the correct
TABLEstatement.
The EXPORT datapump option
FLASHBACK_SCN is not needed as the tables have been prepared
earlier.
On the Target Database
-
Import your exported tables using Oracle data pump, which populates system tables and views with instantiation SCNs, as well as the specified table data.
-
Start Replicat using one of the following:
Set the
DBOPTIONS ENABLE_INSTANTIATION_FILTERINGparameter in the Replicat parameter file to enable table-level instantiation filtering.You can remove this parameter when replicat has processed all transactions beyond the instantiation SCN.
For all other Replicats, set the
DBOPTIONSsource_dbase_nameglobal_nameparameter in the Replicat parameter file whereglobal_nameis the global name of the Oracle source database that the trail is coming from.Note:
When the source has no
DOMAIN, do not specify aDOMAINfor the downstream database.Replicat queries the instantiation SCN on any new mapping and filter records accordingly. For example, see the following report file output:2015-06-29 17:12:39 INFO OGG-10155 Oracle GoldenGate Delivery for Oracle, r1.prm: Instantiation CSN filtering is enabled on table SCOTT.EMP at CSN 1,851,797.
create table as a select
command or RMAN. It's steps are:
-
Use
create tablewith anat SCN ofparameter, using the following command:SET_INSTANTIATION_CSN SCN for object from global_nameFor example:SET_INSTANTIATION_CSN 1 FOR u1.t1 FROM DBS1.REGRESS.RDBMS.DEV.US.ORACLE.COM - If you want to remove the manual setting of the instantiation
CSN later, you can use the following
command:
CLEAR_INSTANTIATION_CSN for object from global_name
Parent topic: Loading Data with Oracle Data Pump
14.2.1.2 Using Oracle Data Pump Table Instantiation
To perform instantiation with Oracle Data Pump, see My Oracle Support document 1276058.1. To obtain this document, do the following:
- Go to http://support.oracle.com.
- Under Sign In, select your language and then log in with your Oracle Single Sign-On (SSO).
- On the Dashboard, expand the Knowledge Base heading.
- Under Enter Search Terms, paste or type the document ID of
1276058.1and then click Search. - In the search results, select Oracle GoldenGate Best Practices: Instantiation from an Oracle Source Database [Article ID 1276058.1].
- Click the link under Attachments to open the article.
Parent topic: Loading Data with Oracle Data Pump
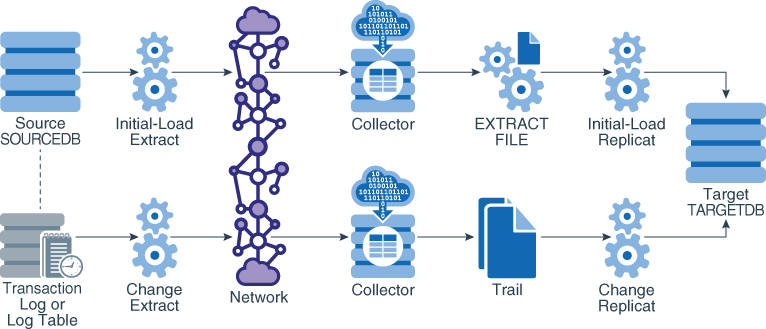
14.2.2 Loading Data from File to Replicat
To use Replicat to establish the target data, you use an initial-load Extract to extract source records from the source tables and write them to an extract file in canonical format. From the file, an initial-load Replicat loads the data using the database interface. During the load, the change-synchronization groups extract and replicate incremental changes, which are then reconciled with the results of the load.
During the load, the records are applied to the target database one record at a time, so this method is considerably slower than any of the other initial load methods. This method permits data transformation to be done on either the source or target system.
You can also use the Microservices Architecture to load data from file to Replicat. See Loading Data from File to Replicat in Microservices Architecture.
To Load Data From File to Replicat
Parent topic: Initial Load in Classic Architecture
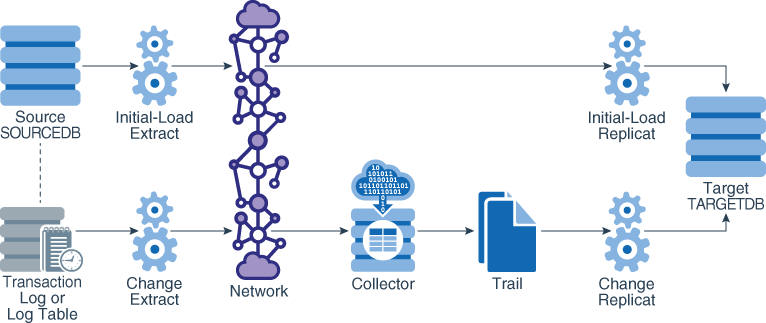
14.2.3 Loading Data with an Oracle GoldenGate Direct Load
To use an Oracle GoldenGate direct load, you run an Oracle GoldenGate initial-load Extract to extract the source records and send them directly to an initial-load Replicat task. A task is started dynamically by the Manager process and does not require the use of a Collector process or file. The initial-load Replicat task delivers the load in large blocks to the target database. Transformation and mapping can be done by Extract, Replicat, or both. During the load, the change-synchronization groups extract and replicate incremental changes, which are then reconciled with the results of the load.
To control which port is used by Replicat, and to speed up the search and bind process, use the DYNAMICPORTLIST parameter in the Manager parameter file. Manager passes the list of port numbers that are specified with this parameter to the Replicat task process. Replicat first searches for a port from this list, and only if no ports are available from the list does Replicat begin scanning in ascending order from the default Manager port number until it finds an available port.
This method supports standard character, numeric, and datetime data types, as well as CLOB, NCLOB, BLOB, LONG, XML, and user-defined datatypes (UDT) embedded with the following attributes: CHAR, NCHAR, VARCHAR, NVARCHAR, RAW, NUMBER, DATE, FLOAT, TIMESTAMP, CLOB, BLOB, XML, and UDT. Character sets are converted between source and target where applicable.
This method supports Oracle internal tables, but does not convert between the source and target character sets during the load.
To Load Data with an Oracle GoldenGate Direct Load
Parent topic: Initial Load in Classic Architecture
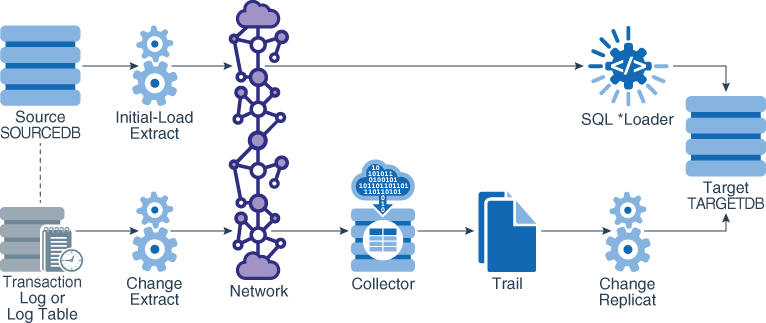
14.2.4 Loading Data with a Direct Bulk Load to SQL*Loader
To use Oracle's SQL*Loader utility to establish the target data, you run an Oracle GoldenGate initial-load Extract to extract the source records and send them directly to an initial-load Replicat task. A task is a process that is started dynamically by the Manager process and does not require the use of a Collector process or file. The initial-load Replicat task interfaces with the API of SQL*Loader to load data as a direct-path bulk load. Data mapping and transformation can be done by either the initial-load Extract or initial-load Replicat, or both. During the load, the change-synchronization groups extract and replicate incremental changes, which are then reconciled with the results of the load.
To control which port is used by Replicat, and to speed up the search and bind process, use the DYNAMICPORTLIST parameter in the Manager parameter file. Manager passes the list of port numbers that are specified with this parameter to the Replicat task process. Replicat first searches for a port from this list, and only if no ports are available from the list does Replicat begin scanning in ascending order from the default Manager port number until it finds an available port.
This method supports standard character, numeric, and datetime data types, as well as CLOB, NCLOB, BLOB, LONG, XML, and user-defined datatypes (UDT) embedded with the following attributes: CHAR, NCHAR, VARCHAR, NVARCHAR, RAW, NUMBER, DATE, FLOAT, TIMESTAMP, CLOB, BLOB, XML, and UDT. VARRAYS are not supported. Character sets are converted between source and target where applicable.
This method supports Oracle internal tables, but does not convert between the source and target character sets during the load.
To Load Data With a Direct Bulk Load to SQL*Loader
Parent topic: Initial Load in Classic Architecture