2 weblogic.Server Command-Line Reference
weblogic.Server class is the main class for a WebLogic Server instance. You start a server instance by invoking weblogic.Server in a Java command.You can invoke the class directly in a command prompt (shell), indirectly through scripts, or through Node Manager.
Oracle recommends using java weblogic.Server primarily for initial development but not as a standard mechanism for starting production systems for the following reasons:
-
java weblogic.Serverwill not function if you select a product directory outside of theORACLE_HOMEdirectory. -
When executing
java weblogic.Server, patches will not be recognized by the WebLogic Server run time.
The following sections explain how to use the weblogic.Server class to start WebLogic Server:
For information about using scripts to start an instance of WebLogic Server, see Starting an Administration Server with a Startup Script and Starting Managed Servers With a Startup Script in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server.
For information about using the Node Manager to start an instance of WebLogic Server, see Using Node Manager to Control Servers in the Administering Node Manager for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Required Environment and Syntax for weblogic.Server
Before you can use the weblogic.Server class to start a WebLogic Server instance, you must install WebLogic Server, set the CLASSPATH environment variable, and include a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in your PATH environment variable.
Modifying the Classpath
After installation, WebLogic Server's classpath is already set, but you may choose to modify it for a number of reasons such as adding a patch to WebLogic Server, updating the version of Derby you are using, or adding support for Log4j logging.
To apply a patch to ALL of your WebLogic Server domains without the need to modify the classpath of a domain, give the patch JAR file the name, weblogic_sp.jar, and copy it into the WL_HOME/server/lib directory. The commEnv.cmd/sh script will automatically include a JAR named weblogic_sp on the classpath for you.
If you would rather not use the name weblogic_sp.jar for your patch file or you would just like to make sure a JAR file, such as one mentioned below, comes before weblogic.jar on the classpath:
-
For ALL domains, edit the
commEnv.cmd/shscript inWL_HOME/common/binand prepend your JAR file to theWEBLOGIC_CLASSPATHenvironment variable. -
To apply a patch to a SPECIFIC WebLogic Server domain, edit the
setDomainEnv.cmd/shscript in that domain'sbindirectory, and prepend the JAR file to thePRE_CLASSPATHenvironment variable.Note:
setDomainEnvis designed to be sourced from other scripts, such as thestartWebLogicscript.setDomainEnvshould not be called directly from within an interactive shell. Doing so can cause unpredictable issues in the domain.
If you use Derby, the open-source all-Java database management system included with Oracle WebLogic Server for use by the sample applications and code examples, include the following files on the classpath:
-
WL_HOME/common/derby/lib/derbyclient.jar- for the driver on the client side -
WL_HOME/common/derby/lib/derbynet.jarandWL_HOME/common/derby/lib/derby.jar - for running the Derby network server
If you use WebLogic Enterprise Connectivity, include the following files on the classpath:
WL_HOME/server/lib/wlepool.jar WL_HOME/server/lib/wleorb.jar
If you use Log4j logging, include the following file on the classpath:
WL_HOME/server/lib/log4j.jar
Note:
The use of Log4j with the WebLogic logging service, as an alternative to Java logging, is deprecated as of WebLogic Server 12.1.3.The shell environment in which you run a server determines which character you use to separate path elements. On Windows, you typically use a semicolon (;). In a BASH shell, you typically use a colon (:).
Default Behavior
Understand the default sequence of operations that occur when a WebLogic Server instance is started without any options having been passed to the weblogic.Server class.
If you have set up the required environment described in Environment, when you enter the command java weblogic.Server with no options, WebLogic Server does the following:
-
Looks in the
domain_name/configdirectory for a file namedconfig.xml. -
If
config.xmlexists in thedomain_name/configdirectory, WebLogic Server does the following:-
If only one server instance is defined in
config/config.xml, it starts that server instance.For example, if you issue
java weblogic.ServerfromORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\medrec, WebLogic Server starts the MedRec server. -
If there are multiple server instances defined in
config/config.xml:-
If an Administration Server is defined, it looks for the server with that name.
-
If an Administration Server is not defined, it looks for a server configuration named
myserver. If it finds such a server configuration, it starts themyserverinstance. -
If it does not find a server named
myserver, WebLogic Server exits theweblogic.Serverprocess and generates an error message.
-
-
-
If there is no
config.xmlfile in the current directory, WebLogic Server prompts you to create one. If you respondy, WebLogic Server does the following:-
Creates a server configuration named
myserver, and persists the configuration in a file namedconfig/config.xml.Any options that you specify are persisted to the
config.xmlfile. For example, if you specify-Dweblogic.ListenPort=8001, then WebLogic Server saves8001in theconfig.xmlfile. For any options that you do not specify, the server instance uses default values.You can configure WebLogic Server to make backup copies of the configuration files. This facilitates recovery in cases where configuration changes need to be reversed or the unlikely case that configuration files become corrupted. See Configuration File Archiving in Understanding Domain Configuration for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
Uses the username and password that you supply to create a user with administrative privileges. It stores the definition of this user along with other basic, security-related data in
domain_name/securityfiles namedDefaultAuthenticatorInit.ldift,DefaultRoleMapperInit.ldift, andSerializedSystemIni.dat.WebLogic Server also encrypts and stores your username and password in a
server_name/security/boot.propertiesfile, which enables you to bypass the login prompt during subsequent instantiations of the server. See Boot Identity Files in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. -
Creates two scripts,
bin/startWebLogic.cmdandbin/startWebLogic.sh, which you can use to start subsequent instantiations of the server. You can use a text editor to modify startup options such as whether the server starts in production mode or development mode. ThestartWebLogicscript contains comments that describe each option.
Note that the server starts as an Administration Server in a new domain. There are no other servers in this domain, nor are any of your deployments or third-party solutions included. You can add them as you would add them to any WebLogic domain.
-
weblogic.Server Configuration Options
weblogic.Server options to configure the attributes of a server instance. The following attributes are commonly used when starting a server instance:
WebLogic Server provides other startup options that enable you to temporarily override a server's saved configuration. For information about these startup options, see Options that Override a Server's Configuration.
Unless you are creating a new domain as described in Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Create a Domain, all startup options apply to the current server instantiation; they do not modify the persisted values in an existing config.xml file. Use the WebLogic Server Administration Console or WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) to modify the config.xml file. See Creating Domains Using WLST Offline in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool.
For information on verifying the WebLogic Server attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
JVM Parameters
Table 2-1 describes frequently used options that configure the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in which the server instance runs. For a complete list of JVM options, see the documentation for your specific JVM. For a list of JVMs that can be used with WebLogic Server, see Supported Configurations.
Table 2-1 Frequently Used Options for Setting JVM Parameters
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Xms and -Xmx |
Specify the minimum and maximum values (in megabytes) for Java heap memory. For example, you might want to start the server with the default allocation of 256 megabytes of Java heap memory to the WebLogic Server. To do so, start the server using the The values assigned to these parameters can dramatically affect the performance of your WebLogic Server and are provided here only as general defaults. In a production environment you should carefully consider the correct memory heap size to use for your applications and environment. |
-classpath |
The minimum content for this option is described under Modifying the Classpath. Instead of using this argument, you can use the |
-client
-server |
Used by some JVMs to start a HotSpot virtual machine, which enhances performance. For a list of JVMs that can be used with WebLogic Server, see Supported Configurations. |
-Dfile.encoding=Canonical Name weblogic.Server |
To display special characters on Linux browsers, set the JVM java -Dfile.encoding=ISO8859_1 weblogic.ServerFor a complete listing, see the Supported Encodings page available at |
Location of Configuration Data
All server instances must have access to configuration data. Table 2-2 provides options for indicating the location of this data.
Table 2-2 Options for Indicating the Location of Configuration Data
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.home=WL_HOME |
Specifies the location of the WebLogic home directory, which contains essential information. By default, |
-Dweblogic.RootDirectory=path |
Specifies the server's root directory. See A Server's Root Directory in Understanding Domain Configuration for Oracle WebLogic Server. By default, the root directory is the directory from which you issue the start command. |
-Dweblogic.management.GenerateDefaultConfig=true |
Prevents the Valid only if you invoke |
-Dweblogic.Domain=domain |
Specifies the name of the domain. If you are using In addition, this option supports a directory structure that WebLogic Server required in releases prior to 7.0 and continues to support in current releases. Prior to 7.0, all configuration files were required to be located in the following pathname: .../config/domain_name/config.xmlIn this pathname, If your domain's configuration file conforms to that pathname, and if you invoke the |
For information on how a Managed Server retrieves its configuration data, see the -Dweblogic.management.server entry in Table 2-3.
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Example
The following example starts a Managed Server instance named SimpleManagedServer. Specifying a config.xml file is not valid because Managed Servers contact the Administration Server for their configuration data. Multiple instances of WebLogic Server can use the same root directory. However, if your server instances share a root directory, make sure that all relative filenames are unique. In this example, SimpleManagedServer shares its root directory with SimpleServer. The command itself is issued from the D:\ directory after running WL_HOME\server\bin\setWLSEnv.cmd:
D:\> java -Dweblogic.Name=SimpleManagedServer -Dweblogic.management.server=http://localhost:7001 -Dweblogic.RootDirectory=c:\my_domains\SimpleDomain weblogic.Server
Options that Override a Server's Configuration
In most cases, you do not use startup options to override the configuration that is saved in the domain's config.xml file. However, in some extraordinary cases you might need to do so.
Tip:
When you use a startup option to override a configuration value, the server instance uses this value for the duration of its life cycle. Even if you use the WebLogic Server Administration Console, the WebLogic Scripting Tool, or some other utility to change the value in the configuration, the value will remain overridden until you restart the server without using the override.
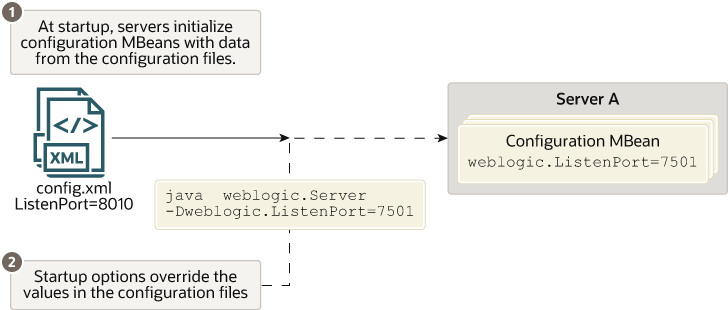
For example, in a production environment, your organization might have a policy against modifying the domain's config.xml file, but you need to shut down the Administration Server and restart it using a temporary listen port. In this case, when you use the weblogic.Server command to start the Administration Server, you can include the -Dweblogic.ListenPort=7501 startup option to change the listen port for the current server session. The server instance initializes its configuration MBeans from the config.xml file but substitutes 7501 as the value of its listen port. When you subsequently restart the server without passing the startup option, it will revert to using the value from the config.xml file, 8010. (See Figure 2-1.)
The following options temporarily override a server's configuration:
Server Communication
Table 2-3 describes the options for configuring how servers communicate.
Table 2-3 Options for Configuring Server Communication
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.management.server=[protocol://]Admin-host:port |
Starts a server instance as a Managed Server and specifies the Administration Server that will configure and manage the server instance. The domain's configuration file does not specify whether a server configuration is an Administration Server or a Managed Server. You determine whether a server instance is in the role of Administration Server or Managed Server with the options that you use to start the instance. If you omit the For Note: Regardless of which protocol you specify, the initial download of a Managed Server's configuration is over HTTP or HTTPS. After the RMI subsystem initializes, the server instance can use the T3 or T3S protocol. For For See Configuring Managed Server Connections to the Administration Server in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.ListenAddress=host |
Specifies the address at which this server instance listens for requests. The This startup option overrides any listen address value specified in the See Configure listen addresses in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help and Creating Domains Using WLST Offline in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool. |
-Dweblogic.ListenPort=portnumber |
Enables and specifies the plain-text (non-SSL) listen port for the server instance. This startup option overrides any listen port value specified in the The default listen port is 7001. See Configure listen ports in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help and Creating Domains Using WLST Offline in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool. |
-Dweblogic.ssl.ListenPort=portnumber |
Enables and specifies the port at which this WebLogic Server instance listens for SSL connection requests. This startup option overrides any SSL listen port value specified in the The default SSL listen port is 7002. See Configure listen ports in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help and Creating Domains Using WLST Offline in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool. |
-Dweblogic.management.discover={true|false} |
Note: This option was removed as of WebLogic Server 9.0. Determines whether an Administration Server recovers control of a domain after the server fails and is restarted. A A false value prevents an Administration Server from communicating with any Managed Servers that are currently active in the domain. Tip: Specify In WebLogic Server 9.0, this command is deprecated because if an Administration Server stops running while the Managed Servers in the domain continue to run, each Managed Server will periodically attempt to reconnect to the Administration Server at the interval specified by the |
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
SSL
Each Weblogic Server instance uses an instance of weblogic.management.configuration.SSLMBean to represent its SSL configuration.
All of the options in the following table that start with -Dweblogic.security.SSL modify the configuration of the server's SSLMBean. For example, the -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification option sets the value of the SSLMBean's ignoreHostnameVerification attribute.
Table 2-4 describes the options for configuring a server to communicate using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Note:
As of WebLogic Server version 12.1.1, JSSE is the only SSL implementation that is supported. The Certicom-based SSL implementation is removed and is no longer supported in WebLogic Server.
Table 2-4 Options for Configuring SSL
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification=true |
Disables host name verification, which enables you to use the demonstration digital certificates that are shipped with WebLogic Server. By default, when a WebLogic Server instance is in the role of SSL client (it is trying to connect to some other server or application via SSL), it verifies that the host name that the SSL server returns in its digital certificate matches the host name of the URL used to connect to the SSL server. If the host names do not match, the connection is dropped. If you disable host name verification, either by using this option or by modifying the server's configuration in the Note: Oracle does not recommend using the demonstration digital certificates or turning off host name verification in a production environment. This startup option overrides any host name verification setting in the See Using Host Name Verification in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.HostnameVerifier=hostnameverifierimplementation |
Specifies the name of a custom host name verifier class. The class must implement the |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.sessionCache.ttl=sessionCacheTimeToLive |
Modifies the default server-session time-to-live for SSL session caching. The For
|
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.CertificateCallback=callback-handler |
Specifies a certificate callback handler class, which evaluates details contained the end-user certificate passed in a secure connection request to WebLogic Server. Depending on the details contained in the certificate, the callback handler returns a Note: If you use a certificate callback implementation in WebLogic Server, a callback is generated whenever a request is received over a secure port. As a result, using certificate callbacks may impose a performance overhead that should be taken into consideration. See Checking the Validity of End User Certificates in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.management.pkpassword=pkpassword |
Specifies the password for retrieving SSL private keys from an encrypted flat file. Use this option if you store private keys in an encrypted flat file. |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.trustedCAKeyStore=path |
Specifies the trusted keystore to use in either of these use cases:
The Oracle recommends that you do not use the demonstration certificate authorities in any type of production deployment. See Configuring SSL in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.trustedCAkeystorePassPhrase=password |
Specifies the password to use if you specified a PKCS12 trust keystore using the When running a WebLogic client such as WLST, if the type of trust keystore specified by |
-Dsecurity.use.interopCA=true |
If you are using WebLogic Server together with a version of WebLogic Server prior to 12.1.2, be aware that the demo trust keystore of the previous versions does not contain the demo CA certificate used as of version 12.1.2. Therefore, if an instance of WebLogic Server sends its public certificate to an instance of WebLogic Server running a prior version, that public certificate will not automatically be trusted. Use this system property to generate interoperable demo certificates signed by the previous demo CA certificate. |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.protocolVersion=protocol |
Specifies the protocol that is used for SSL connections. The
See Using the weblogic.security.SSL.protocolVersion System Property in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.security.SSL.minimumProtocolVersion=protocol |
Specifies the minimum protocol version that is used for SSL connections. The
Note:
See Using the weblogic.security.SSL.minimumProtocolVersion System Property in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.security.ssl.sslcontext.protocol=protocol |
Specifies the For some JSSE providers, there is a correlation between the Note: When using the IBM JSSE provider, WebLogic Server attempts to select ajavax.net.ssl.SSLContext algorithm equivalent to the default TLS.
Standard supported values are See Using the weblogic.security.ssl.sslcontext.protocol System Property in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Setting Additional SSL Attributes
To set additional SSL attributes from the startup command, do the following:
For example, the SSLMBean exposes its Enabled attribute with the following setter method:
setEnabled()
To enable SSL for a server instance named MedRecServer, use the following command when you start MedRecServer:
java -Dweblogic.Name=MedRecServer
-Dweblogic.ssl.Enabled=true weblogic.Server
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
HTTP Strict Transport Security
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a web security policy mechanism that allows a web server to be configured so that web browsers, or other user agents, can access the server using only secure connections, such as HTTPS. Web servers declare this policy using the Strict-Transport-Security HTTP response header field.
For more information about HSTS, see Using HTTP Strict Transport Security in Developing Web Applications, Servlets, and JSPs for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Table 2-5 describes the system properties that you add to WebLogic Server domain start up scripts to enable HSTS and customize the response header.
Table 2-5 Options for Configuring HSTS
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.http.headers.enableHSTS={true|false} |
Specifies whether the server is configured to use HSTS. The default value of this system property is Set this property to
The values specified in this response are the minimum values required by the HSTS preload submission web site You can customize these values using the system properties described in the following rows of this table. |
-Dweblogic.http.headers.hsts.maxage=max-age-seconds |
Specifies the time, in seconds, that the browser remembers that a site is only to be accessed using HTTPS. The default value is 31536000 seconds (one year). |
-Dweblogic.http.headers.hsts.includesubdomains={true|false} |
Specifies whether the HSTS policy applies to this HSTS host as well as any subdomains of the host's domain name. If this directive is not specified, the property defaults to |
-Dweblogic.http.headers.hsts.preload={true|false} |
Specifies that the site is requesting inclusion in the HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) preload list, which is a list of sites that are hardcoded into Chrome (and other browsers) as using HTTPS only. If this directive is not specified, the property defaults to Ensure that your site meets all the necessary requirements before including the |
Security
Table 2-6 describes the options for configuring general security parameters.
Table 2-6 Options for General Security Parameters
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.management.username=username |
Specifies the username under which the server instance will run. As of WebLogic Server 12.1.1, the boot username property As an alternative, Oracle recommends that you use the See Provide User Credentials to Start and Stop Servers in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.management.password=password |
Specifies the user password. As of WebLogic Server 12.1.1, the boot password system property As an alternative, Oracle recommends that you use the See Provide User Credentials to Start and Stop Servers in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.system.StoreBootIdentity=true |
Creates a Do not specify this argument in a server's Oracle recommends that you do not add this argument to a startup script. Instead, use it only when you want to create a See Boot Identity Files in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.system.BootIdentityFile=filename |
Specifies a boot identity file that contains a username and password. The -Dweblogic.system.BootIdentityFile=
WL_HOME\mydomain\servers\myserver\security
\boot.propertiesIf you do not specify a filename, a server instance, or the WLST If there is no boot identity file, when starting a server, the server instance prompts you to enter a username and password. |
-Dweblogic.system.RemoveBootIdentity=true |
Removes the boot identity file after a server starts. |
-Dweblogic.security.anonymousUserName=name |
Assigns a user ID to anonymous users. By default, all anonymous users are identified with the string To emulate the security behavior of WebLogic Server 6.x, specify See Users, Groups, and Security Roles in Securing Resources Using Roles and Policies for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
|
|
Standard Java EE options that enable the Java Security Manager and specify a filename (using a relative or fully-qualified pathname) that contains Java 2 security policies. To use the WebLogic Server sample policy file, specify Using Note: The WebLogic JACC provider does not require the Java Security Manager to be enabled. See Using the Java Security Manager to Protect WebLogic Resources in Developing Applications with the WebLogic Security Service. |
-Dweblogic.security.fullyDelegateAuthorization=true |
By default, roles and security policies cannot be set for an EJB or Web application through the WebLogic Server Administration Console unless security constraints were defined in the deployment descriptor for the EJB or Web application. Use this option when starting WebLogic Server to override this problem. This startup option does not work with EJBs or EJB methods that use |
-Dweblogic.management.anonymousAdminLookupEnabled=true
|
Enables you to retrieve an If you retrieve This startup option overrides the Anonymous Admin Lookup Enabled setting on the domain_name > Security > General page in the WebLogic Server Administration Console. By default, the |
-Dweblogic.security.identityAssertionTTL=seconds |
Configures the number of seconds that the Identity Assertion cache stores a Subject. When using an Identity Assertion provider (either for an X.509 certificate or some other type of token), Subjects are cached within the server. This greatly enhances performance for servlets and EJB methods with By default, Subjects remain in the cache for 300 seconds, which is also the maximum allowed value. Setting the value to Setting a high value generally improves the performance of identity assertion, but makes the Identity Assertion provider less responsive to changes in the configured Authentication provider. For example, a change in the user's group will not be reflected until the Subject is flushed from the cache and recreated. |
|
|
Defining these three system properties is required to enable the use of the Java Authorization Contract for Containers in the security realm. When these providers are in use, JACC handles authorization decisions for the EJB and servlet containers for external applications. Any other authorization decisions for internal applications are handled by the authorization in the WebLogic Security framework. Note: JACC authorization does not require the use of Java SE security. The WebLogic JACC implementation expects that the policy object is the default When starting, WebLogic Server attempts to locate and instantiate the classes specified by the JACC startup properties and fails if it cannot find or instantiate them (if, for example, the files specified by the startup properties are not valid classes). See Using the Java Authorization Contract for Containers in Developing Applications with the WebLogic Security Service |
-Dweblogic.security.ldap.
maxSize=<max bytes> |
Limits the size of the data file used by the embedded LDAP server. When the data file exceeds the specified size, WebLogic Server eliminates from the data file space occupied by deleted entries. |
-Dweblogic.security.ldap.changeLogThreshold=<number of entries> |
Limits the size of the change log file used by the embedded LDAP server. When the change log file exceeds the specified number of entries, WebLogic Server truncates the change log by removing all entries that have been sent to all Managed Servers. |
-Dweblogic.security.providers.authentication.ldap.socketTimeout=seconds |
Sets a timeout value for the LDAP Authentication provider connection to an LDAP server. If multiple LDAP servers are specified in the Note that the |
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. See Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Message Output and Logging
Table 2-7 describes options for configuring a server instance's message output.
Table 2-7 Options for Configuring Message Output
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.Stdout="filename" |
Redirects the server and JVM standard output stream to a file. You can specify a pathname that is fully qualified or relative to the WebLogic Server root directory. See Redirect JVM output in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. |
-Dweblogic.Stderr="filename" |
Redirects the server and JVM standard error stream to a file. You can specify a pathname that is fully qualified or relative to the WebLogic Server root directory. See Redirecting JVM Output in Configuring Log Files and Filtering Log Messages for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.AdministrationMBeanAuditingEnabled={true|false} |
Determines whether the Administration Server emits configuration auditing log messages when a user changes the configuration or invokes management operations on any resource within a domain. By default, the Administration Server does not emit configuration auditing messages. See Enable configuration auditing in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. |
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Setting Logging Attributes
Each Weblogic Server instance uses an instance of weblogic.management.configuration.LogMBean to represent the configuration of its logging services.
To set values for LogMBean attributes from the startup command, do the following:
The LogMBean exposes its FileName attribute with the following setter method:
setFileName()
To specify the name of the MedRecServer instance's local log file, use the following command when you start MedRecServer:
java -Dweblogic.Name=MedRecServer
-Dweblogic.log.FileName="C:\logfiles\myServer.log"
weblogic.Server
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Clusters
Table 2-8 describes options for configuring additional attributes of a cluster.
Table 2-8 Options for Configuring Cluster Attributes
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.cluster.multicastAddress |
Determines the Multicast Address that clustered servers use to send and receive cluster-related communications. By default, a clustered server refers to the Multicast Address that is defined in the Note: The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line. Regardless of how you set the Multicast Address, all servers in a cluster must communicate at the same Multicast Address. |
Deployment
Table 2-9 describes options for configuring additional attributes for deployment.
Table 2-9 Options for Configuring Deployment Attributes
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.deployment.IgnorePrepareStateFailures=true |
Overrides the default deployment behavior by allowing a server to transition to Note: This server level flag may cause inconsistent deployment behavior within clusters, such as issues with HttpSessionReplication or SFSB replication. |
Other Server Configuration Options
Table 2-10 describes options for configuring additional attributes of a server instance.
Table 2-10 Options for Configuring Server Attributes
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-Dweblogic.Name=servername |
Specifies the name of the server instance that you want to start. The specified value must refer to the name of a server that has been defined in the domain's |
-Dweblogic.ProductionModeEnabled={true|false} |
This attribute is deprecated in WebLogic Server 9.0. Determines whether a server starts in production mode. A If you do not specify this option, the assumed value is To enable production mode, you can use WLST to set Note: It is recommended that you enable production mode via the WebLogic Server Administration Console, in Note: It is important to note that when ProductionModeEnabled is set from the command line on the Administration Server, this value is propagated to all Managed Servers. |
-Dweblogic.management.startupMode=MODE |
The argument
Specifying the startup mode startup option overrides any startup mode setting in the If a system property is specified on the server startup:
|
-Dweblogic.apache.xerces.maxentityrefs=numerical-value |
Limits the number of entities in an XML document that the WebLogic XML parser resolves. If you do not specify this option, the XML parser that WebLogic Server installs resolves 10,000 entity references in an XML document, regardless of how many an XML document contains. |
-Dweblogic.jsp.windows.caseSensitive=true |
Causes the JSP compiler on Windows systems to preserve case when it creates output files names. See Using the WebLogic JSP Compiler in Developing Web Applications, Servlets, and JSPs for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.servlet.optimisticSerialization=true |
When This means that you must make sure that the attributes common to Web applications are scoped to a common parent classloader (application scoped) or you must place them in the system classpath if the two Web applications do not belong to the same application. When The optimistic-serialization value can also be specified at domain level in the The default value is false. |
-Dweblogic.servlet.maxLoggingURILength=length |
By default, when using extended log format in HTTP access logs, the maximum logged URI length is 256 characters. If the URI exceeds that length, the logged URI is truncated. You can use this property to increase the length of the URI that is logged. See DNS Related Fields in Administering Server Environments for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.jdbc.qualifyRMName=false |
When set, restores pre-WebLogic Server 11gR1 (10.3.1) behavior of not qualifying the JTA registration name with the domain name. |
-Dweblogic.ScatteredReadsEnabled=trueand -Dweblogic.GatheredWritesEnabled=true |
When each is set to true, increases efficiency during I/O in environments with high network throughput. These command options are used together to optimize WebLogic Server performance for use with Oracle Exalogic. See the Oracle Exalogic Enterprise Deployment Guide. |
-Dweblogic.replication.enableLazyDeserialization= true |
When set to true, increases efficiency with session replication. This command option is used to optimize WebLogic Server performance for use with Oracle Exalogic. See the Oracle Exalogic Enterprise Deployment Guide. |
-Dweblogic.resourcepool.max_test_wait_secs=seconds |
The amount of time, in seconds, WebLogic Server waits before considering a connection test failed. By default, a server instance is assigned a value of 10 seconds. If set to zero, the server instance waits indefinitely. |
-Dweblogic.wsee.client.ssl.usejdk=true |
When set to true, switches from By default, WebLogic Server Web services use the The |
-Dweblogic.http.URIDecodeEncoding=charset-name |
The argument See Determining the Encoding of an HTTP Request in Developing Web Applications, Servlets, and JSPs for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
-Dweblogic.utils.http.requestparams.useArrayMap= true |
When set to true in the server startup command, HTTP request parameters are stored using an ArrayMap. By default, HTTP request parameters are stored in a TreeMap. |
The WebLogic Server Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Start a Server Instance
The basic procedure to start a WebLogic Server instance is to run the setWLSEnv script to set the environment, change to the root directory of a domain, and enter the java weblogic.Server command.
Complete the following steps:
Note:
If you are using the demo certificates in a multi-server domain, Managed Server instances will fail to boot if you specify the fully-qualified DNS name of the Administration Server host machine, as in the argument url-for-Administration Server. See Limitation on CertGen Usage in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Create a Domain
weblogic.Server class to create a domain that contains a single server instance. However, you cannot invoke the weblogic.Server class either to add Managed Server instances to a domain, or to modify an existing domain.
As described in Default Behavior, if weblogic.Server is unable to find a config.xml file, it offers to create the file. Any command option that you specify and that corresponds to an attribute that is persisted in the config.xml file will be persisted. For example, the -Dweblogic.Name and -Dweblogic.Domain options specify the name of a server configuration and the name of a domain. If weblogic.Server is unable to find a config.xml file, both of these values are persisted in config.xml. However, the -Dweblogic.system.BootIdentityFile option, which specifies a file that contains user credentials for starting a server instance, is not an attribute that the config.xml file persists.
To create and instantiate a simple example domain and server, do the following:
After you enter this command, WebLogic Server asks if you want to create a new config.xml file. If you enter y, it then instantiates a domain named SimpleDomain. The domain's Administration Server is configured as follows:
-
The name of the Administration Server is SimpleServer.
-
The domain's security realm defines one administrative user,
weblogic, with a password of password. -
For the listen address of the Administration Server, you can use
localhost, the IP address of the host computer, or the DNS name of the host computer. See Configure listen addresses in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. -
The Administration Server listens on port 7001.
Entering the weblogic.Server command as described in this section creates the following files:
-
config.xml -
DefaultAuthenticatorInit.ldift,DefaultRoleMapperInit.ldift, andSerializedSystemIni.dat, which store basic security-related data. -
boot.propertiesfile, which contains the username and password in an encrypted format. This file enables you to bypass the prompt for username and password when you start the server. See Boot Identity Files in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server. -
startWebLogic.cmdandstartWebLogic.sh, that you can use to start subsequent instantiations of the server.Note:
Invoking
weblogic.Serverin an empty directory results in implicit domain creation which uses the same configuration process as WLST offline and the Configuration Wizard and thus ensures that you always see uniform domains. As a result, implicitly creating a domain in an empty directory usingweblogic.Servermay take around 15 seconds.
Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line
See Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tooland Understanding WebLogic Server MBeans in Developing Custom Management Utilities Using JMX for Oracle WebLogic Server.