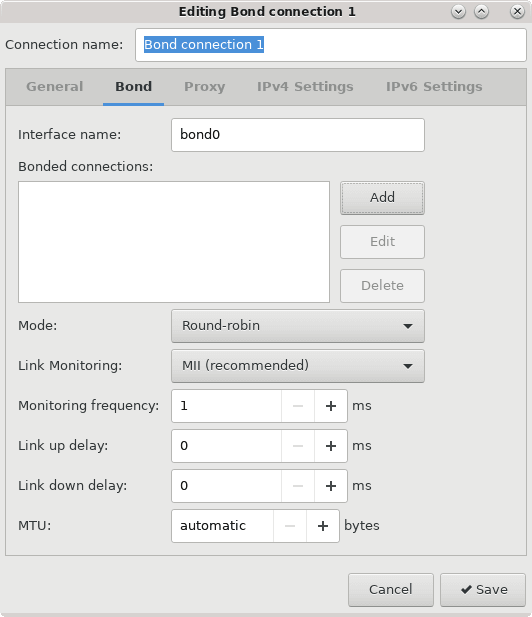
Network Bonding
A system's physical network interfaces that are connected to a network switch can be grouped together into a single logical interface to provide better throughput or availability. This grouping, or aggregation, of physical network interfaces is known as a network bond.
A bonded network interface can increase data throughput by load balancing or can provide redundancy by activating failover from one component device to another. By default, a bonded interface appears similar to a normal network device to the kernel, but it sends out network packets over the available secondary devices by using a round-robin scheduler. You can configure bonding module parameters in the bonded interface's configuration file to alter the behavior of load-balancing and device failover.
The network bonding driver within the kernel can be used to configure the network bond in different modes to take advantage of different bonding features, depending on the requirements and the available network infrastructure. For example, the balance-rr mode can be used to provide basic round-robin load-balancing and fault tolerance across a set of physical network interfaces; while the active-backup mode provides basic fault tolerance for high availability configurations. Some bonding modes, such as 802.3ad, or dynamic link aggregation, require particular hardware features and configuration on the switch that the physical interfaces connect to. Basic load-balancing modes (balance-rr and balance-xor) work with any switch that supports EtherChannel or trunking. Advanced load-balancing modes (balance-tlb and balance-alb) don't impose requirements on the switching hardware, but do require that the device driver for each component interfaces implement certain specific features such as support for ethtool or the ability to change the hardware address while the device is active.
For more information on the kernel bonding driver, see the upstream documentation at https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/bonding.txt or included at /usr/share/doc/iputils-*/README.bonding.
Note:
For network configurations where systems are directly cabled together for high availability, a switch is required to support certain network interface bonding features such as automatic failover. Otherwise, the mechanism might not work.Configuring Network Bonding Using the Command Line
nmcli command line tool.