Enabling Cloud Guard in your Tenancy
Cloud Guard is a cloud security posture service in OCI giving you visibility into potential security issues in your cloud setup. Once enabled in your tenancy (or on particular sub-compartment), Cloud Guard uses Detectors to identify common misconfigurations, activities and threats, and then helps with remediation through Responder Rules and Recipes. Cloud Guard is a free OCI service and it’s recommended it be enabled in OCI tenancies.
What Does Cloud Guard Look For?
At the time of writing, Cloud Guard scans for issues with three broad classes of detectors. To get the latest detectors, review the documentation here.
1. Configuration Detectors
These detectors look for potential misconfigurations in their targets. Example detectors include:
- Instance has a public IP address
- API key is too old
- VCN Security list allows traffic to non-public port from all sources (0.0.0.0/0)
- Bucket is public
2. Activity Detectors
Activity detectors call out actions of potential concern, including:
- Export Image (for Compute)
- Suspicious Ip Activity
- VCN Security List ingress rules changed
3. Threat Detectors
Threat detectors look for more specific malicious threat activities in a tenancy, such as those conducted by a ‘Rogue User’. This is when a user has performed activities that generate a problematic risk score, such as through Impossible Travel or Password Spraying.
Setting Up Cloud Guard
You can find Cloud Guard in the ‘Identity & Security’ section of the menu.
The first time you visit Cloud Guard, you’ll need to Enable it within the tenancy.

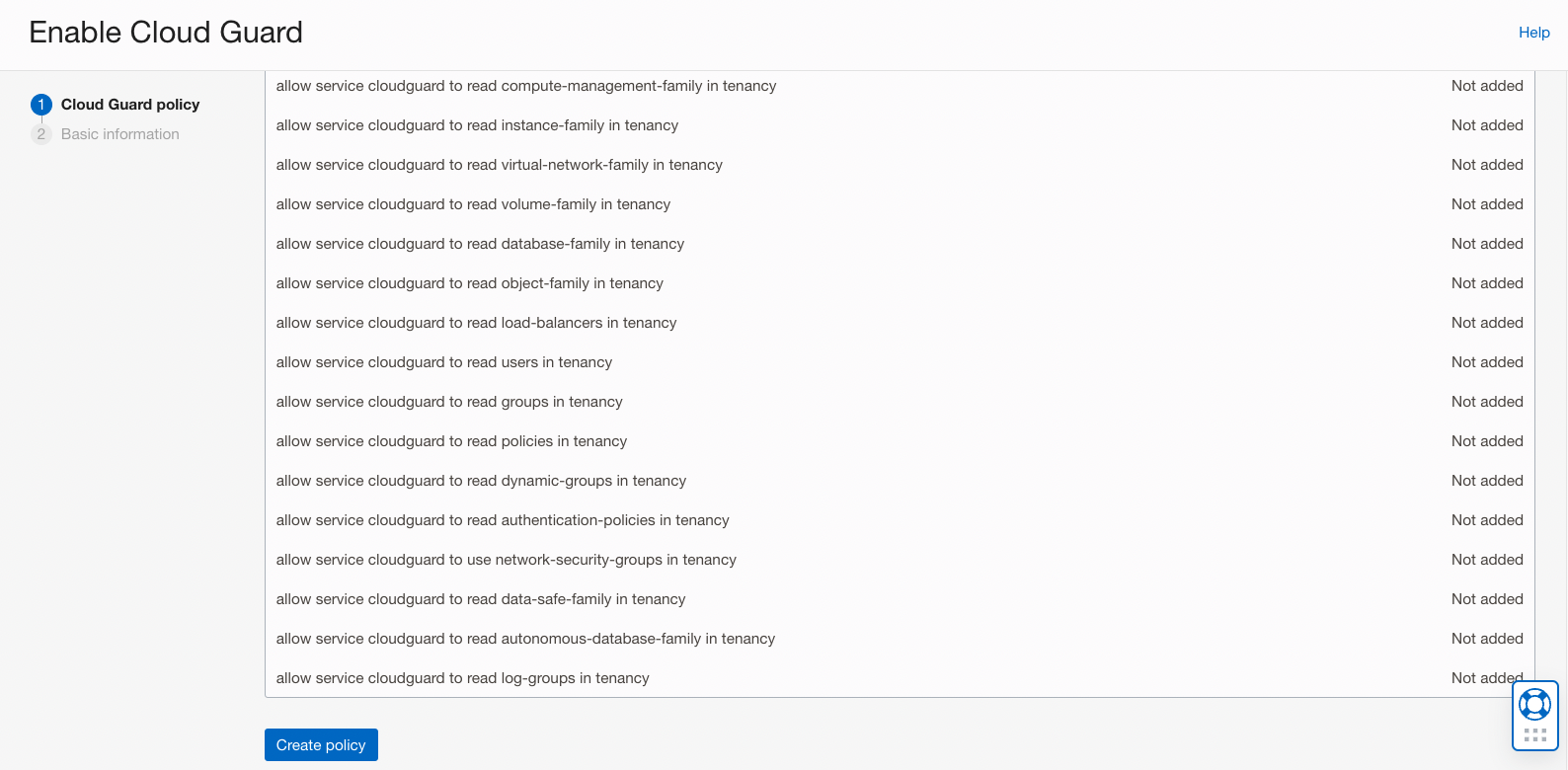
After clicking ‘Enable’, you’re brought to the setup screen. Setting up Cloud Guard requires creating a Policy for the cloudguard service so that it may interact with target services and components. The console outlines the policy rules that will be added, and automatically creates these by clicking the “Create policy” button. After creating, you can view the rules in the “Policies” page.
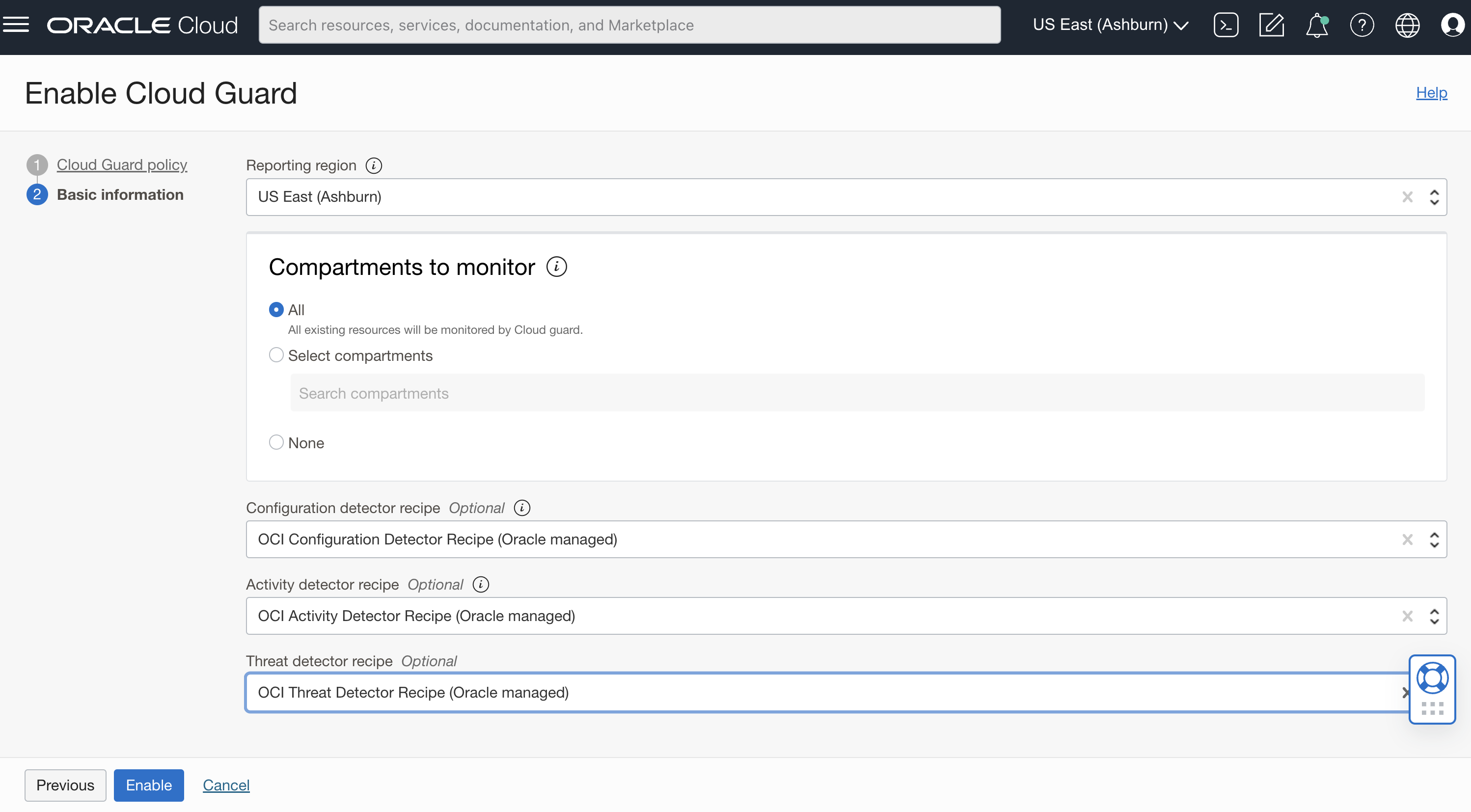
On the next (and final) page of Cloud Guard setup you select:
- The Reporting Region
- Note, this choice may be important for compliance/governance reasons, and cannot be changed without re-creating Cloud Guard in the tenancy.
- The Target compartments
- You may want to have at least one Target set to the ‘Root’ compartment.
- The Detector Recipes
- By default the Oracle managed recipes are available. These can be cloned and modified into User managed recipes for more customized control.
How to Use Cloud Guard in your Tenancy
After enabling, Cloud Guard monitors the selected target and highlights problems according to the selected detectors.
Review Problems
In the absence of configured automated alerts and responses, you should periodically check Cloud Guard for problems.
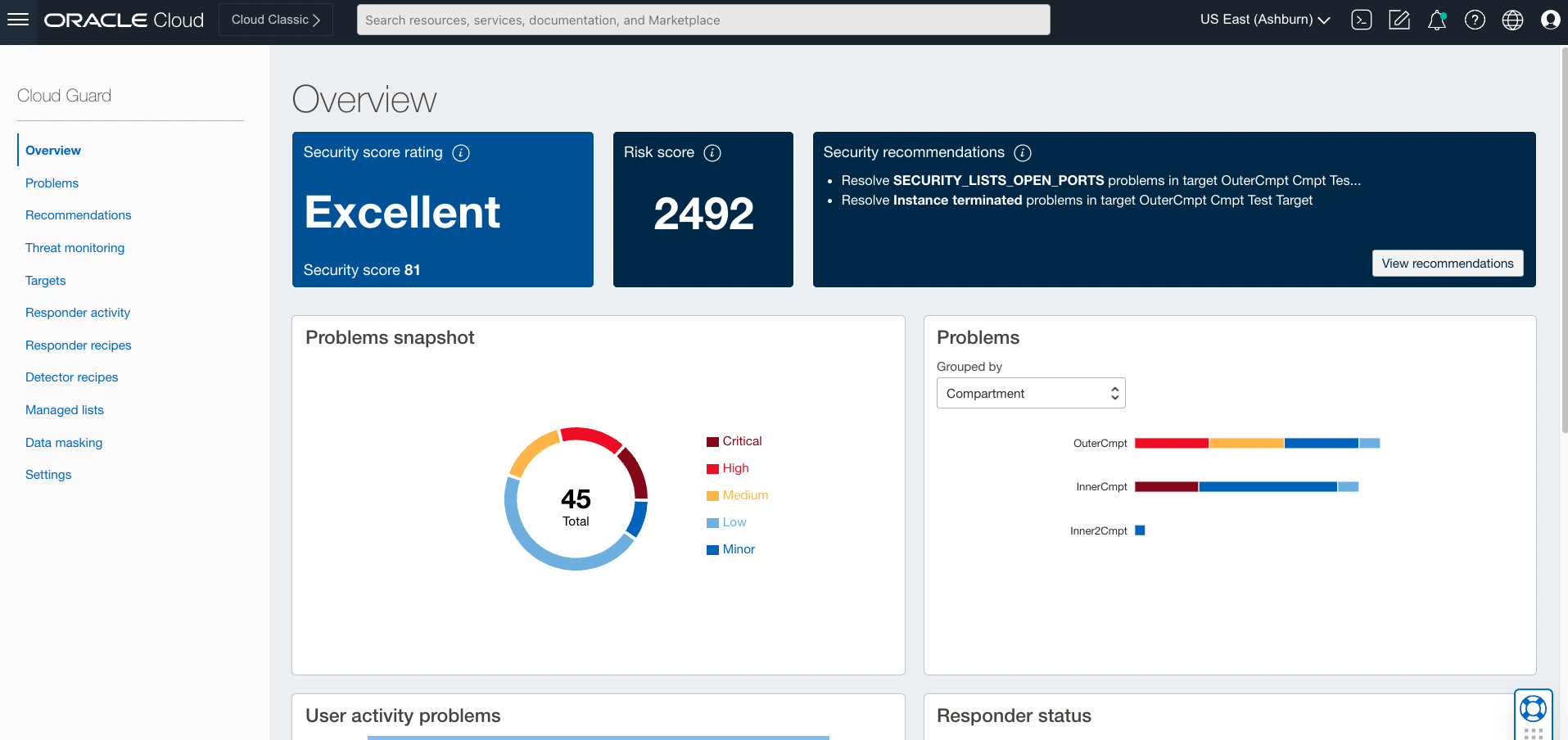
The Cloud Guard “Overview” page gives a snapshot of the overall security posture of your tenancy (or other selected targets).
To investigate specific problems, you can click into reports from the Overview, or navigate to the “Problems” page.
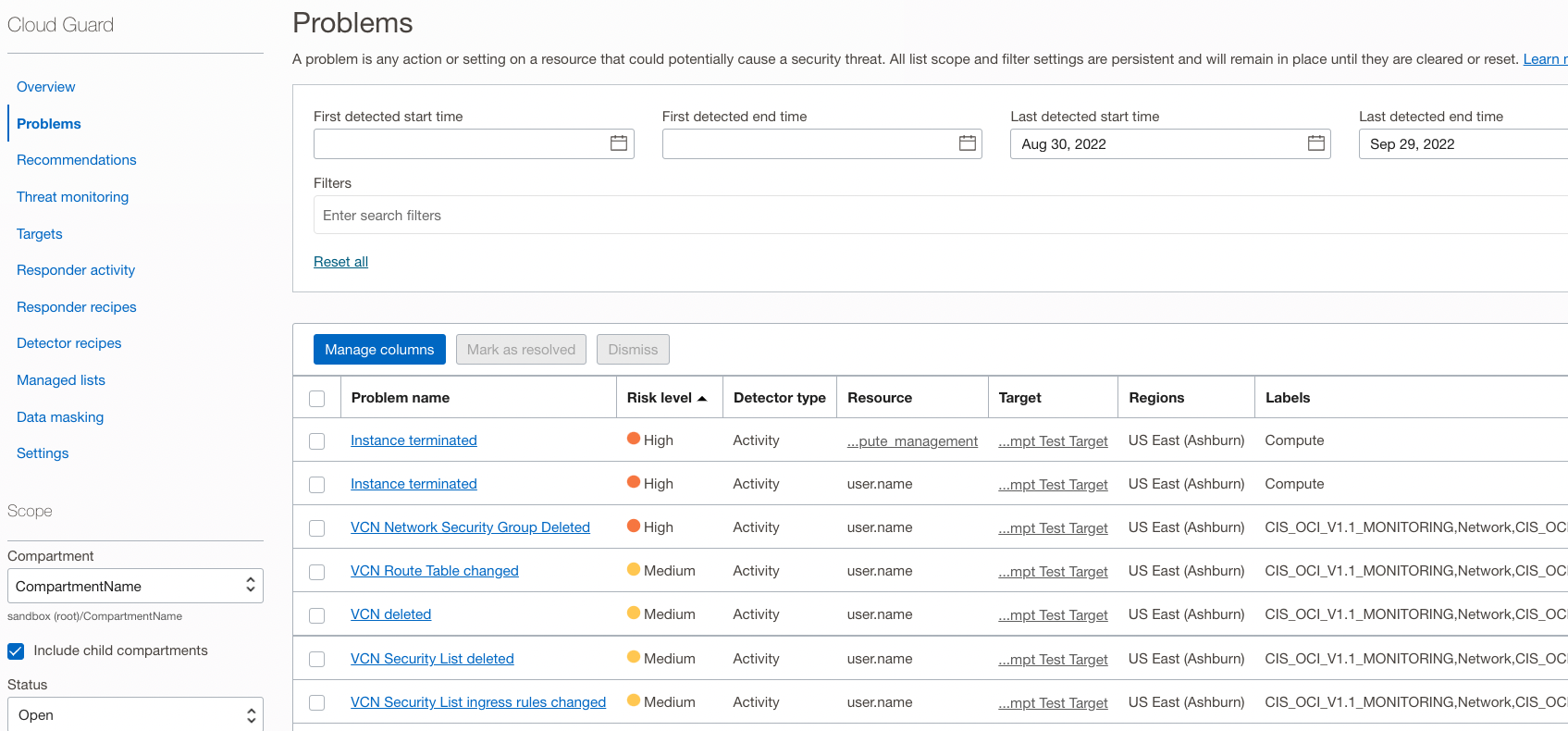
This page shows problems sorted by Risk level, and other information needed to respond. If you click a problem name you’ll be brought to a “Problem Details” page where you can find out more information and respond in 1 of 3 ways (see next section).
Another useful display is the “Recommendations” tab, which shows the top 10 recommendations for your tenancy.
Resolve Problems
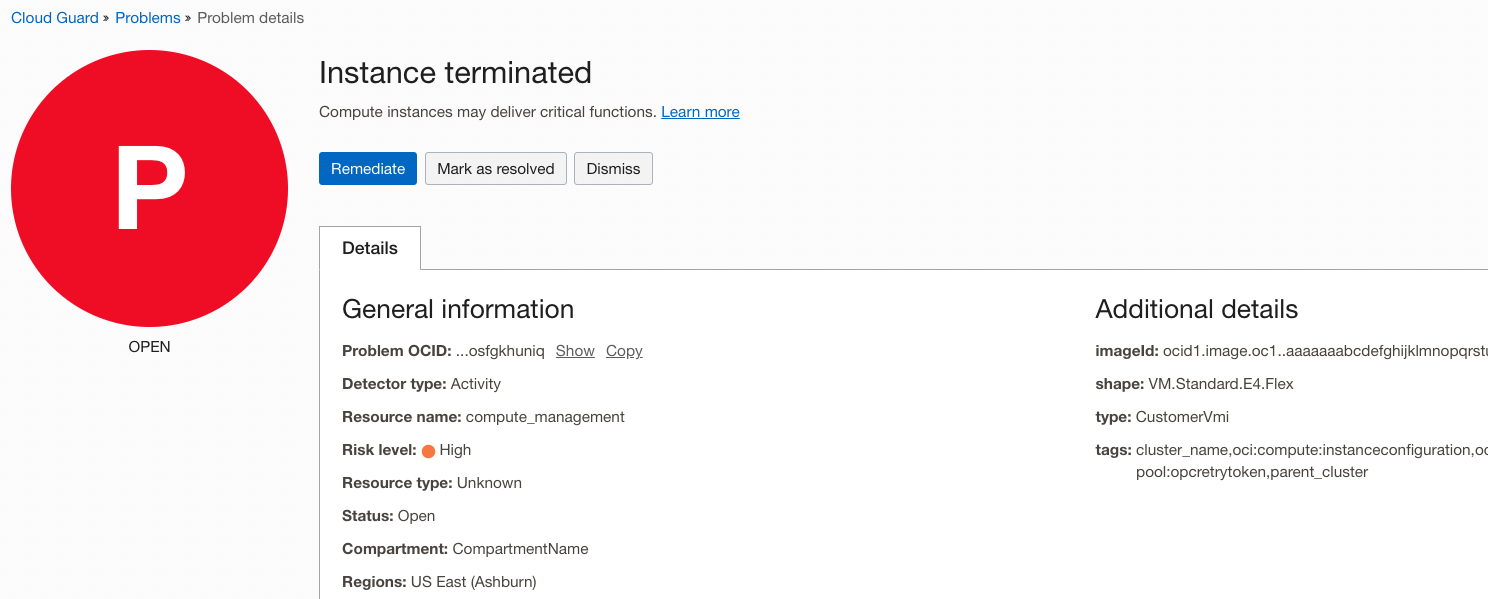
From the “Problem Details” page you have three ways to respond:
- Remediate: Fix using a Cloud Guard Responder.
- Responders are automated (or semi-automated) resolutions.
- They may require additional policies that give the cloudguard service permission to carry out the response (and this can be added directly from the remediation page).
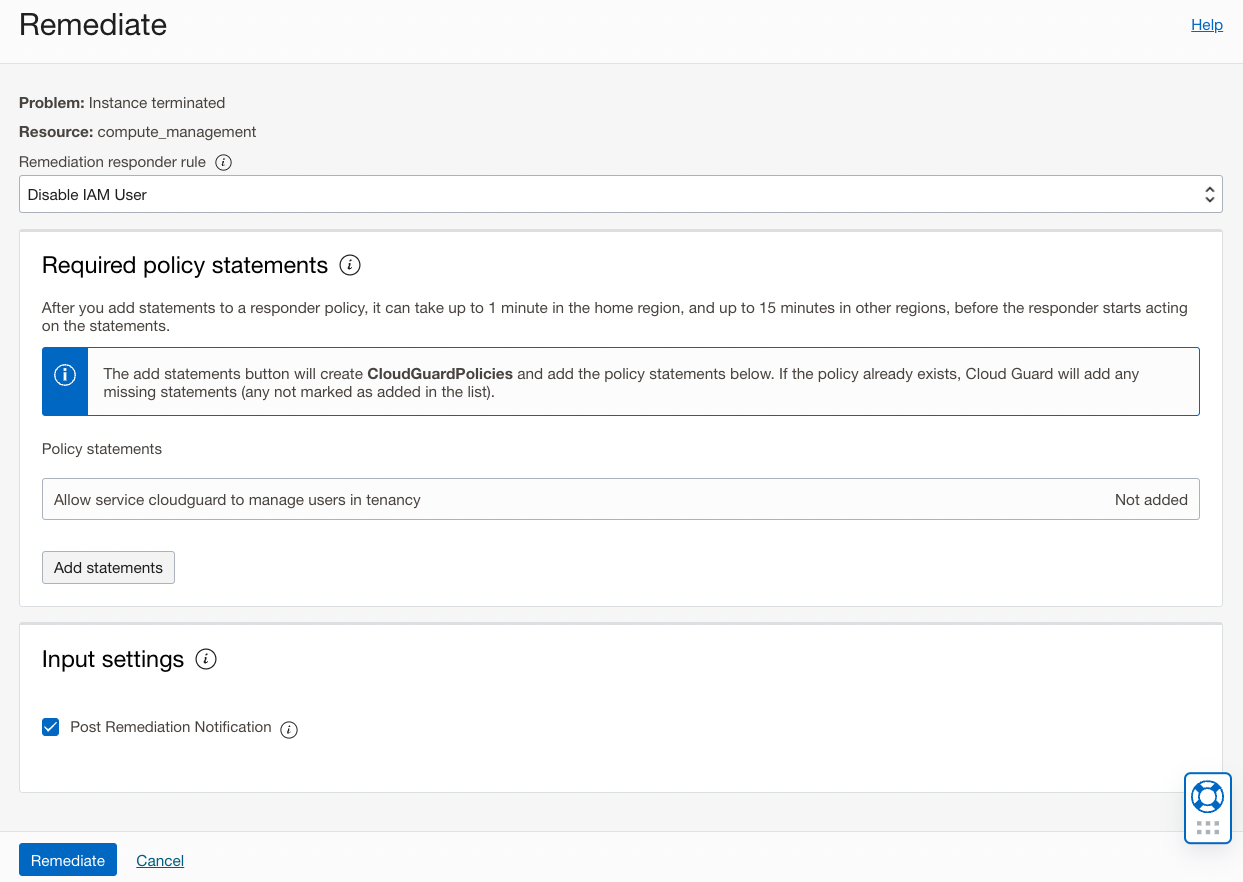
- Mark as resolved: Fixed by another process
- In the case where the issue has been addressed means other than a Cloud Guard Responder (such as making a change manually in the tenancy), you can mark the process as “Resolved”
- Dismiss: Ignore and Close
- Should the problem be a false positive, or one you’re not interested in resolving, you can ‘Dismiss’ the warning outright.
In all cases, you should be aware of how each resolution reacts when the same problem occurs or re-occurs in the future by reading and understanding the table here.
Working with Cloud Guard
Customize Detector and Responder Recipes
- By default, Detectors and Responders are “Oracle managed”. These cannot be modified.
- Customization may be desired to omit particular detectors/responders that are not applicable, change the risk level of a detector or customize the steps a responder takes.
- In these cases, you can create a “User managed” recipe by cloning the original and customizing as needed.
- Note, you’ll need to update your Targets to use the newly cloned recipes.
Automated problem resolution
- With sufficient policies in place, Responders can be fully automated by setting the Rule Trigger in a responder to “Execute Automatically”.
- For full details, see the steps outlined here.
Setup email notifiers
- Using the Notifications and Events services you can send alerts from Oracle Cloud Guard.
- This Blog outlines the steps. Note: Slack integration is optional and you can just as easily setup an ‘email’ notification subscription instead.
FAQs
- For more information, see the Cloud Guard FAQs.
Enabling Cloud Guard in your Tenancy
F72097-01
April 2023
Copyright © 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates.