Learn How to Convert Monolithic Apps Into Containerized Services on Oracle Cloud
By their nature, monolithic applications are fixed and linear, making them difficult to manage and update over time.
Because monolithic architectural patterns are used to design and develop a complete application as a single unit, reliability can be a major problem, especially in cases involving entanglement and coupling. That’s because if one thing goes wrong in any module, it might make the entire application unusable.
If your application requires scalability, reliability, agility and autonomy, then you should consider adopting a microservices architecture. In contrast to the fixed and linear monoliths, a microservices architecture hinges on designing, developing, and deploying an application as a collection of loosely coupled services that can be independently deployed and tested.
One of the biggest benefits of microservices architectures is that they will not affect the development and deployment of other services and their capabilities. You can scale a particular microservice independently of other microservices, and you have the liberty of choosing a technology stack and programming language for each particular service.
Architecture
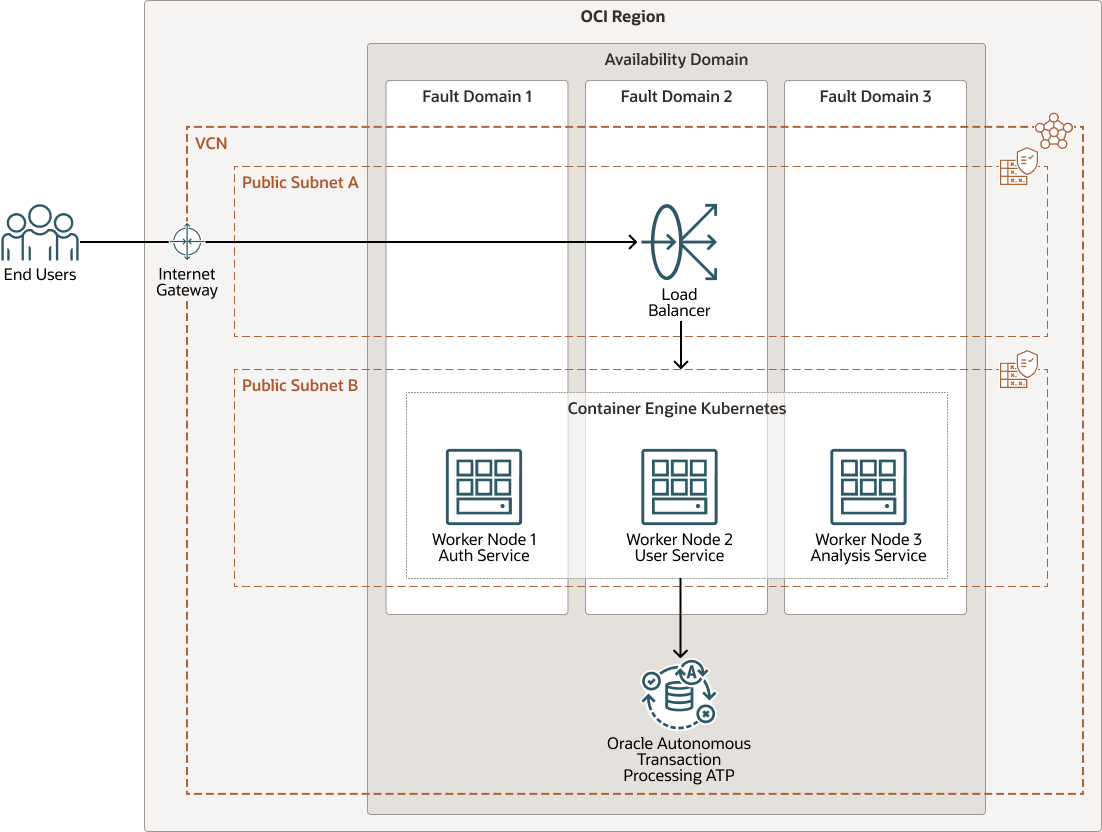
The architecture diagram below shows the final deployment with the containerized applications running independently from one another.
apps-multiservices-arch-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy. A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domain
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Container Engine for Kubernetes
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes is a fully managed, scalable, and highly available service that you can use to deploy your containerized applications to the cloud. You specify the compute resources that your applications require, and Container Engine for Kubernetes provisions them on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure in an existing tenancy. Container Engine for Kubernetes uses Kubernetes to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across clusters of hosts.
- Compute
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service enables you to provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
- Autonomous Transaction
Processing
Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing is a self-driving, self-securing, self-repairing database service that is optimized for transaction processing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.