Deploy Oracle Key Vault with Oracle Exadata Database Service (Oracle Database@Azure)
Oracle Database@Azure provides customers with a new option for managing encryption keys, Oracle wallets, Java Keystores (JKS), Java Cryptography Extension Keystores (JCEKS), and credential files, which include SSH private keys, regardless of the cloud in which they are operating.
Oracle Key Vault is a fault-tolerant, continuously available and highly scalable key management system that has been purpose-built to provide key management for highly consolidated Oracle database deployments, for example Oracle Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@Azure.
While Oracle and Azure are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure supporting Oracle Database@Azure, customers are responsible for implementing the required security controls in their applications and any configuration mechanisms to meet their security and compliance mandates. Utilizing Oracle Key Vault with Oracle Exadata Database Service (Oracle Database@Azure) provides customers the following benefits:
- Fault tolerance
- High availability
- Scalability
- Security
- Standards-compliance
Security objects that you can manage with Oracle Key Vault include encryption keys, Oracle wallets, Java Keystores (JKS), Java Cryptography Extension Keystores (JCEKS), and credential files. Credential files can include SSH private keys, used for public key authentication to remote servers (on-premises or in any cloud), or database account passwords for unattended execution of regularly scheduled maintenance scripts. Oracle Key Vault is optimized for the Oracle Cloud Stack (database, middleware, systems), and advanced security transparent data encryption (TDE). In addition, it complies with the industry standard OASIS Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP) for compatibility with KMIP-based clients. Oracle Key Vault works with endpoints, an endpoint is a computer system such as a database server, an application server, and other information systems. Endpoints must be registered and enrolled so that they can communicate with Oracle Key Vault. Enrolled endpoints can upload their keys, share them with other endpoints, and download them to access their data. Keys are used to access encrypted data and credentials are used to authenticate to other systems. For database servers hosting one or more Oracle databases, each Oracle database will be at least one endpoint. Oracle Key Vault streamlines day-to-day operations with encrypted databases deployed as RAC or with Active Data Guard, pluggable databases, OCI GoldenGate, as well as globally distributed (sharded) databases. Oracle Key Vault facilitates the movement of encrypted data using Oracle Data Pump and transportable tablespaces, a key feature of Oracle Database.
Before You Begin
To take advantage of this reference architecture, the following are required:
Oracle Database@Azure
- Access to an Azure subscription and directory
- Access to an OCI tenancy
- Active Oracle Database@Azure multicloud link between the Azure and OCI clouds
- Prior to provisioning, ensure adequate Oracle Exadata Database
Service limits and OCI service limits
- In the OCI menu, click Governance & Administration.
- Under Tenancy Management, click Limits, Quotas and Usage.
- From the Service dropdown, select Database.
- Plan your network topology:
- Requires at least one Azure Virtual Network (VNet) that can be paired with a corresponding OCI virtual cloud network (VCN)
- The CIDR blocks for any Azure VNet and OCI VCNs must not overlap
- Access to an Oracle Key Vault image, built on-premises from the corresponding ISO file
- Oracle Key Vault installation requirements
- Setting up NTP is required
Architecture
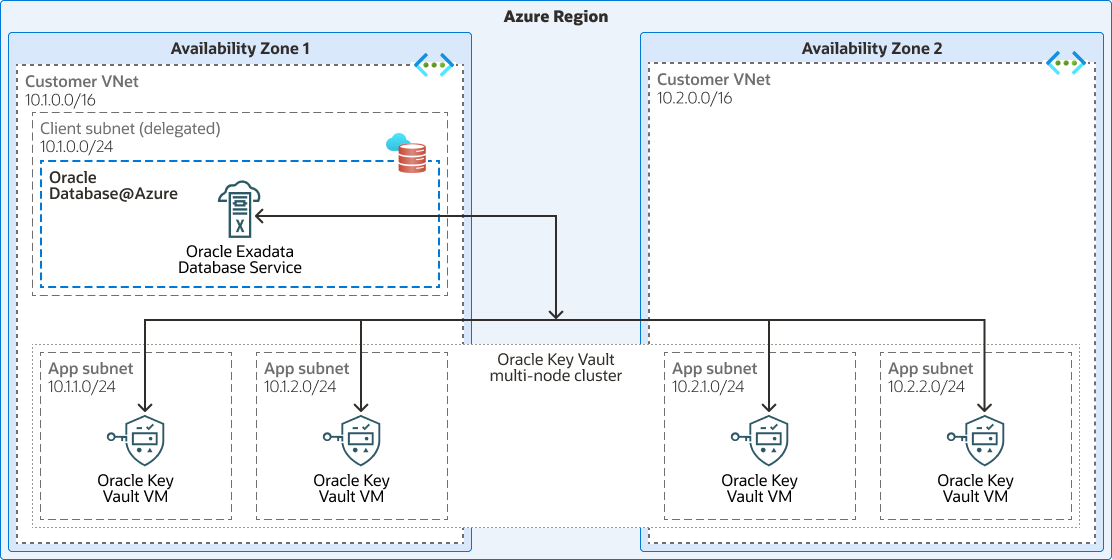
This architecture shows how to deploy Oracle Key Vault on an Microsoft Azure virtual machine (VM) as a secure long-term external key management storage for Oracle Exadata Database Service encryption keys in Oracle Database@Azure.
The architecture diagram depicts the recommended Oracle Key Vault multi-master cluster in Azure to provide continuously available, extremely scalable, and fault-tolerant key management for the Oracle Database in Oracle Exadata Database Service (Oracle Database@Azure).
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
key-vault-database-azure-diagram-oracle.zip
Oracle Key Vault for Oracle Database@Azure can be deployed on-premises, in Azure, or any other cloud, as long as network connectivity can be established. Stretched Oracle Key Vault clusters (on-premises to cloud, or across cloud providers) are also possible, giving you maximum deployment flexibility and local availability of your encryption keys. Oracle Key Vault provides "hold your own key" functionality out of the box, without the need for an additional, expensive third-party key management appliance.
The architecture has the following components:
- Azure region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
An Azure region is a geographical area in which one or more physical Azure data centers, called availability zones, reside. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
Azure and OCI regions are localized geographic areas. For Oracle Database@Azure, an Azure region is connected to an OCI region, with availability zones (AZs) in Azure connected to availability domains (ADs) in OCI. Azure and OCI region pairs are selected to minimize distance and latency.
- Azure availability zone
An availability zone is a physically separate data center within a region that is designed to be available and fault tolerant. Availability zones are close enough to have low-latency connections to other availability zones.
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Network
Microsoft Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the fundamental building block for your private network in Azure. VNet enables many types of Azure resources, such as Azure virtual machines (VM), to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks.
- Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service delivers proven Oracle Database capabilities on purpose-built, optimized Oracle Exadata infrastructure in the public cloud. Built-in cloud automation, elastic resource scaling, security, and fast performance for OLTP, in-memory analytics, and converged Oracle Database workloads help simplify management and reduce costs.
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure X9M brings more CPU cores, increased storage, and a faster network fabric to the public cloud. Exadata X9M storage servers include Exadata RDMA Memory (XRMEM), creating an additional tier of storage, boosting overall system performance. Exadata X9M combines XRMEM with innovative RDMA algorithms that bypass the network and I/O stack, eliminating expensive CPU interrupts and context switches.
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure X9M increases the throughput of its 100 Gbps active-active Remote Direct Memory Access over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) internal network fabric, providing a faster interconnect than previous generations with extremely low-latency between all compute and storage servers.
- Oracle Database@Azure
Oracle Database@Azure is the Oracle Database service (Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure or Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless) running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), deployed in Microsoft Azure data centers. The service offers features and price parity with OCI. Users purchase the service on Azure Marketplace.
Oracle Database@Azure integrates Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC), and Oracle Data Guard technologies into the Azure platform. Oracle Database@Azure service offers the same low latency as other Azure-native services and meets mission-critical workloads and cloud-native development needs. Users manage the service on the Azure console and with Azure automation tools. The service is deployed in Azure Virtual Network (VNet) and integrated with the Azure identity and access management system. The OCI and Oracle Database metrics and audit logs are natively available in Azure. The service requires that users have an Azure tenancy and an OCI tenancy.
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) transparently encrypts data at rest in an Oracle Database. It stops unauthorized attempts from the operating system to access database data stored in files, without impacting how applications access the data using SQL. TDE is fully integrated with Oracle Database and can encrypt entire database backups (RMAN), Data Pump exports, entire application tablespaces, or specific sensitive columns. Encrypted data remains encrypted in the database, whether it is in tablespace storage files, temporary tablespaces, undo tablespaces, or other files such as redo logs.
- Key Vault
Oracle Key Vault securely stores encryption keys, Oracle Wallets, Java KeyStores, SSH key pairs, and other secrets in a scalable, fault-tolerant cluster that supports the OASIS KMIP standard and deploys in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services as well as on-premises on dedicated hardware or virtual machines.
Recommendations
- Oracle Key Vault ISO
To build the right Oracle Key Vault solution, make sure to use the latest Oracle Key Vault installation medium. See Explore More for the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud link.
- Oracle Key Vault image building
To build the Oracle Key Vault image from the ISO, do so on a local system with at least 1 TB of storage with at least 32 GB in RAM. Create the virtual hard disk as Fixed size and in the VHD format.
- Multi-node cluster
Deploy Oracle Key Vault as a multi-node cluster to achieve maximum availability and reliability with read-write pairs of Oracle Key Vault nodes.
Oracle Key Vault multi-master cluster is created with a first node, then additional nodes can e subsequently inducted to eventually form a multi-node cluster with up to 8 read-write pairs.
The initial node is in read-only restricted mode and no critical data can be added to it. Oracle recommends to deploy a second node to form a read-write pair with the first node. After which, the cluster can be expanded with read-write pairs so that both critical and non-critical data can be added to the read-write nodes. Read-only nodes can help with load balancing or operation continuity during maintenance operations.
Consult the documentation to learn how a multi-master cluster affects endpoints, both in the way an endpoint connects and with restrictions.
For large deployments, install at least four Oracle Key Vault servers. Endpoints should be enrolled by making them unique and balanced across the four servers to ensure high availability. For example, if a data center has 1,000 database endpoints to register, and you have four Oracle Key Vault servers to accommodate them, then enroll 250 endpoints across each of the four servers.
Ensure that the system clocks of the endpoint host and the Oracle Key Vault server are in sync. For Oracle Key Vault server, setting up NTP is required.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Performance
For optimum performance and load balancing, add more read-write pairs.
Multiple read-only nodes can be added to a cluster, but for optimum performance and load balancing, you must have more read-write pairs to prevent the cluster from being overloaded.
Oracle Key Vault multi-master cluster requires at least one read-write pair to be fully operational. It can have a maximum of eight read-write pairs.
- Availability
The multi-node cluster provides high availability, disaster recovery, load distribution, and geographic distribution to an Oracle Key Vault environment. It provides a mechanism to create read-write pairs of Oracle Key Vault nodes for maximum availability and reliability.
After you initialize the cluster, you can expand it by adding up to 15 more nodes, as either read-write pairs or read-only nodes. A multi-master cluster can contain a minimum of two nodes and a maximum of 16 nodes.
You can add read-only Oracle Key Vault nodes to the cluster to provide even greater availability to endpoints that need Oracle wallets, encryption keys, Java keystores, certificates, credential files, and other objects.
Explore More
Learn more about managing encryption in Oracle Database@Azure with Oracle Key Vault.
Review these additional resources:
- Creating Oracle Key Vault Image in Microsoft Azure in Oracle Key Vault Administrator's Guide
- Best practices framework for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle Database@Azure
- Oracle Key Vault Concepts
- Enrolling and Upgrading Endpoints for Oracle Key Vault in Oracle Key Vault Administrator's Guide
- Oracle Key Vault General System Administration in Oracle Key Vault Administrator's Guide
- Oracle Software Delivery Cloud
- Learn about Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture for Oracle Database@Azure
- Move to Oracle Database@Azure with Oracle Zero Downtime Migration
- Migration of File based TDE to OKV for ExaDB-D Using Automation via REST