Deploy Microsoft Remote Desktop Services on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
The Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) platform allows you to build virtualization solutions—including those that deliver individual virtualized applications—that provide secure remote desktop access and allow end users to run their applications and desktops from the cloud.
This reference architecture describes on a high-level how you can leverage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) services to deploy a secure and highly available RDS environment in the cloud.
Architecture
A standard RDS deployment includes various remote desktop services running on Windows Server VMs. The diagram below represents some of the components, including Remote Desktop Web and Remote Desktop Gateway, which sit on private subnets and are exposed to the internet via two network load balancers.
Note:
This reference architecture focuses on the infrastructure components of OCI that can support the deployment of RDS. For software configuration guidance refer to the Microsoft documentation.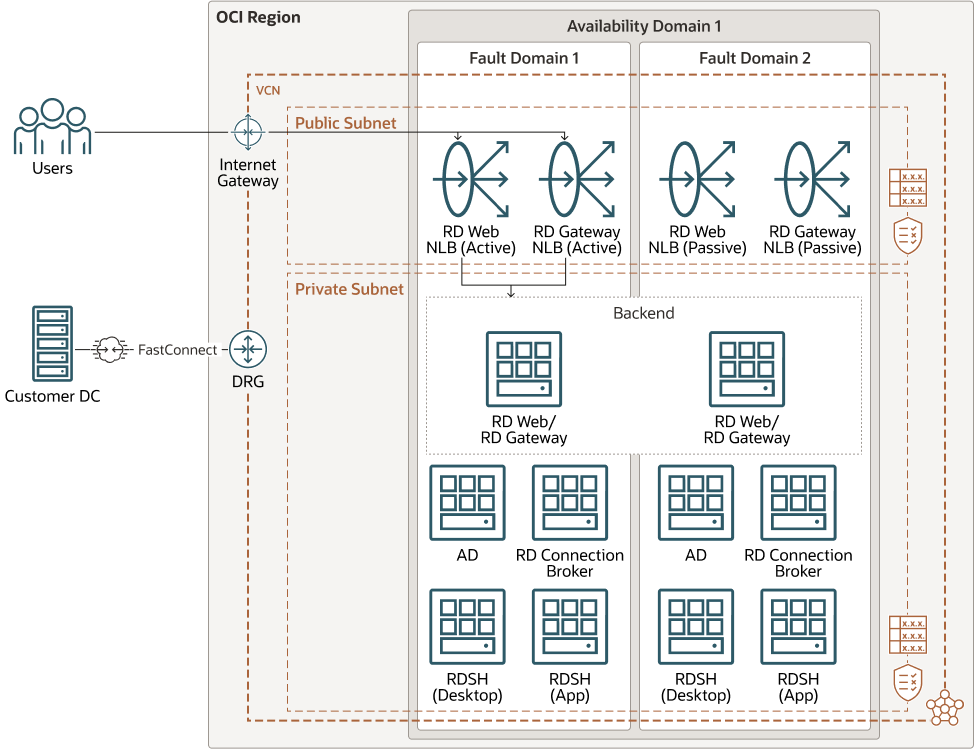
Description of the illustration rds_on_oci.png
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Remote Desktop Web Access (RD Web)
An RD Web provides users access to a web page where they can authenticate and access Windows desktops and applications hosted on the session hosts.
- Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway)
An RD Gateway provides secure access to Windows desktops and applications for clients on the internet. The RD Gateway uses SSL to provide encrypted communications between clients and the server.
- Active Directory (AD)
This is the Active Directory Domain Services server that contains all user accounts in the domain and is joined by all virtual machines. The server can be either standalone, for the cloud environment, or a replica of an existing on-premises server leveraging FastConnect.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RD Connection Broker)
The RD Connection Broker manages incoming connections to the RD Session Host server farms.
- Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host)
The RD Session Host provides users access to session-based desktops and applications.
- Flexible Network Load balancer
The OCI flexible network load balancer provides automated traffic distribution from one entry point to multiple, backend servers in your virtual cloud networks. It operates at the connection level and load balances incoming client connections to healthy backend servers based on Layer3/Layer4 (IP protocol) data.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- FastConnect Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Use regional subnets.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Availability
To provide higher availability, consider using different Fault Domains when deploying multiple instances of each Remote Desktop Services role.
- Licensing
OCI provides licenses for Compute instances running Microsoft Windows Server. For additional licensing requirements consult your Microsoft representative.