About the Implementation Architecture
This architecture shows Oracle Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@AWS with an Active Data Guard deployment with primary and standby databases across two different regions.
Architecture
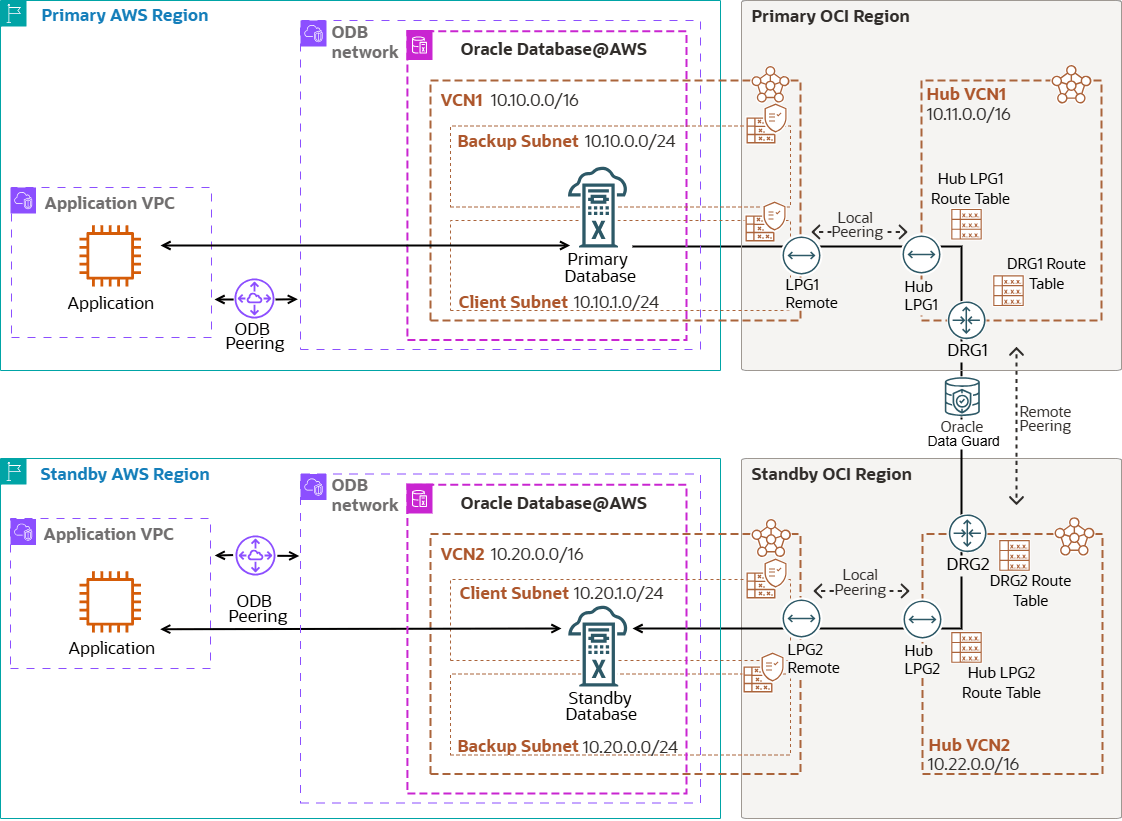
The following diagram illustrates this architecture.
db-aws-dr-cross-region-oracle.zip
The Oracle Database runs in an Exadata VM Cluster in the primary region. For data protection and disaster recovery, Oracle Active Data Guard replicates the data to a different region (remote standby). A remote standby database setup ensures data protection against regional failures and can also be used to offload read-only query processing. You should also replicate the application across regions to avoid higher latency after the standby database becomes the primary.
You can route Active Data Guard traffic through the AWS network. However, this architecture directs Active Data Guard network traffic through the OCI network to optimize network throughput and latency. The VCNs on the OCI site are created after the Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure VM clusters on Oracle Database@AWS are created for the primary and standby databases.
The Oracle Exadata Database Service on the Oracle Database@AWS network is connected to the Exadata client subnet using a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG) managed by Oracle. A DRG is also required to create a peer connection between Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs) in different regions. Because only one DRG is allowed per VCN in OCI, a second VCN acting as a Hub VCN with its own DRG is required to connect the primary and standby VCNs in each region.
In this architecture:
- The primary Exadata VM Cluster is deployed in the primary region in
VCN1with CIDR10.10.0.0/16and client subnet CIDR10.10.1.0/24. VCN1has a Local Peering GatewayLPG1remote.- The hub VCN in the primary region is
HubVCN1with CIDR10.11.0.0/16. HubVCN1has a Local Peering GatewayHubLPG1and Dynamic Routing GatewayDRG1.VCN1andHubVCN1are peered with a Local Peering Connection viaLPG1remoteandHubLPG1.- The standby Exadata VM Cluster is deployed in the standby region in
VCN2with CIDR10.20.0.0/16and client subnet CIDR10.20.1.0/24. VCN2has a Local Peering GatewayLPG2remote.- The hub VCN in the standby region is
HubVCN2with CIDR10.22.0.0/16. HubVCN2has a Local Peering GatewayHubLPG2and Dynamic Routing GatewayDRG2.VCN2andHubVCN2are peered with a Local Peering Connection viaLPG2remoteandHubLPG2.HubVCN1andHubVCN2are peered with a Romete Peering Connection viaDRG1andDRG2.
AWS providesthe following components:
- AWS availability zone
Availability zones are highly available data centers within each AWS region.
- ODB network
An ODB network is a private network that hosts Oracle Database@AWS in a specified availability zone. You can set up an ODB peering connection between an ODB network and a VPC to connect to your Oracle databases.
- AWS region
AWS regions are separate geographic areas. They consist of multiple, physically separated, and isolated availability zones that are connected with low latency, high throughput, highly redundant networking.
- Amazon virtual private cloud and subnet
Amazon virtual private cloud (VPC) enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network you've defined. This virtual network resembles a traditional network that you operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS. After you create an VPC, you can add subnets.
A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your Amazon VPC. You can create AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances, in specific subnets.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides the following components:
- Oracle Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard and Oracle Active Data Guard provide a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases and that enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database by using in-memory replication. If the production database becomes unavailable due to a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage. Oracle Active Data Guard provides the additional ability to offload read-mostly workloads to standby databases and also provides advanced data protection features.
- Dynamic routing gateway
(DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated
Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. Oracle Exadata Database Service delivers proven Oracle Database capabilities on purpose-built, optimized Oracle Exadata infrastructure in the public cloud. Built-in cloud automation, elastic resource scaling, security, and fast performance for all Oracle Database workloads helps you simplify management and reduce costs.
- Local Peering Group (LPG)
An LPG provides peering between VCNs in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network.
- Network security group
(NSG)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of OCI you control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of virtual network interface cards (VNICs) in a single VCN.
- OCI region
An OCI region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, hosting availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Remote
peering
Remote peering allows resources within different VCNs to communicate using private IP addresses. Remote peering eliminates the need for an internet gateway or public IP addresses for instances that need to communicate with another VCN in a different region.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- OCI virtual cloud
network and subnet
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an OCI region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
Recommendations
- Use Active Data Guard for comprehensive data corruption prevention with automatic block repair, online upgrades and migrations, and offload workload to standby with read-mostly scale-out.
- Enable Application Continuity to mask database outages during planned and unplanned events from end-users and ensure uninterrupted applications.
- Set up automatic backup to Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery Service (in OCI), even though the data is protected by Oracle Data Guard, to minimize the backup workload on the database by implementing the incremental forever backup strategy that eliminates weekly full backups. Alternatively, customers can use AWS S3 Object Storage for automatic backups.
- Enable backups from standby to achieve backup replication across regions.
- Use OCI Full Stack Disaster Recovery to orchestrate database switchover and failover operations.
- Use OCI Vault to store the database's Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) keys using customer-managed keys.
Considerations
When implementing disaster recovery for Oracle Exadata Database Service on Oracle Database@AWS with a remote Data Guard standby database, consider the following:
- When Exadata VM Clusters are created in the Oracle Database@AWS child site, each Exadata VM Cluster is created within its own OCI VCN. Data Guard requires that the databases communicate with each other to ship
redodata. The VCNs need to be peered to enable this communication. Hence, the Exadata VM Cluster VCNs must not share overlapping IP CIDR ranges. - Network latency across regions is usually higher than most mission-critical applications can tolerate. Therefore, you should use Data Guard maximum performance protection mode and async replication. Use Active Data Guard Far Sync to ensure zero data loss across regions.
- OCI is the preferred network for achieving better performance, measured by latency and throughput, and for achieving reduced cost, including the first 10 TB/month egress for free.
- You can create up to six standby databases for a primary database via cloud tooling.