About Cloud Core
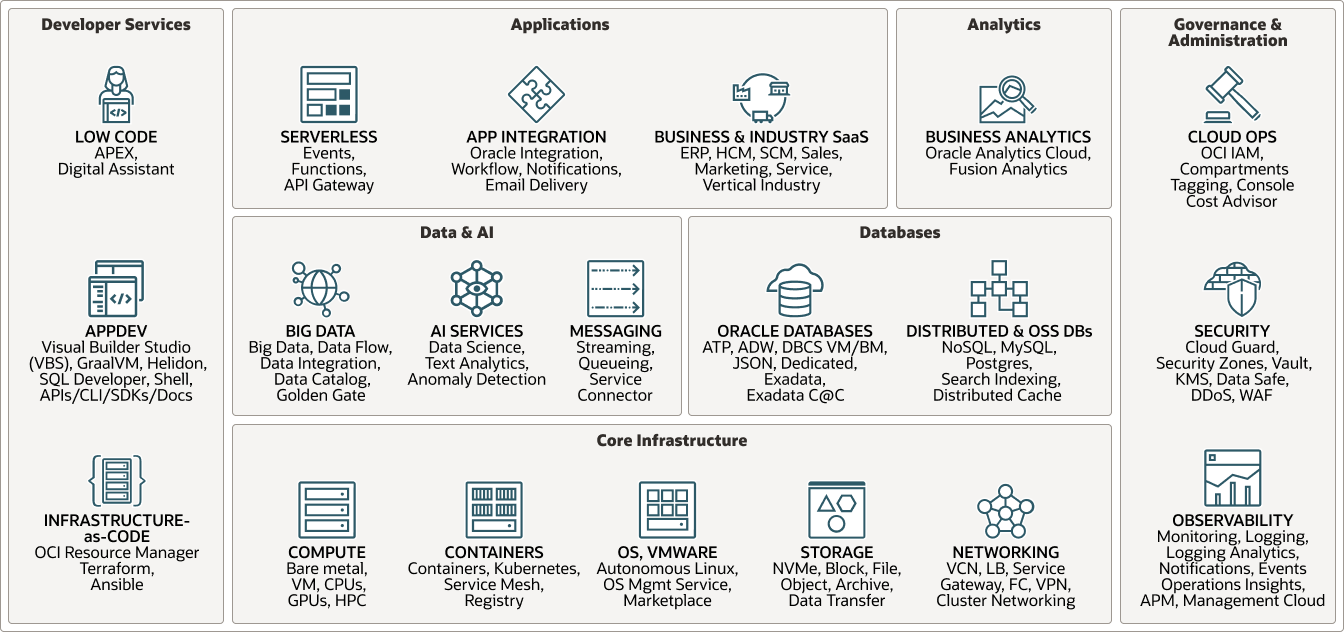
The cloud core consists of the following components: Compute, Storage, Functions, Containers, and Database Services.
OCI services portfolio offers a range of options to implement your cloud strategy. You can choose OCI services to be consumed from public or government regions, or get a dedicated OCI region just for your organization with all the services. Oracle Database Exadata Cloud at Customer comes with a cloud operating model and gives you full control over the physical Oracle Exadata Database Machine. Services like Azure Interconnect and the Oracle Database service for Azure give you the choice to use best services across clouds.
The following diagram shows the portfolio of cloud core infrastructure and components:
OCI includes a large portfolio of services and provides various choices for your multicloud solutions. Organizations can leverage the OCI core infrastructure services like compute, storage, and networking as required, and also to choose from database services with an optimized infrastructure, or as a fully-automated PaaS service. You can build multicloud solutions with Data and AI services from OCI that provide the ability to create simple low-code applications, or run business analytics on large data sets. OCI provides all these services in multicloud solution architectures with the ability for governance and administration across cloud providers.
About Application and Database Multicloud Architecture
A multicloud solution can be single-stack or split-stack architecture depending on the cloud providers you choose and the cloud services available in the region.
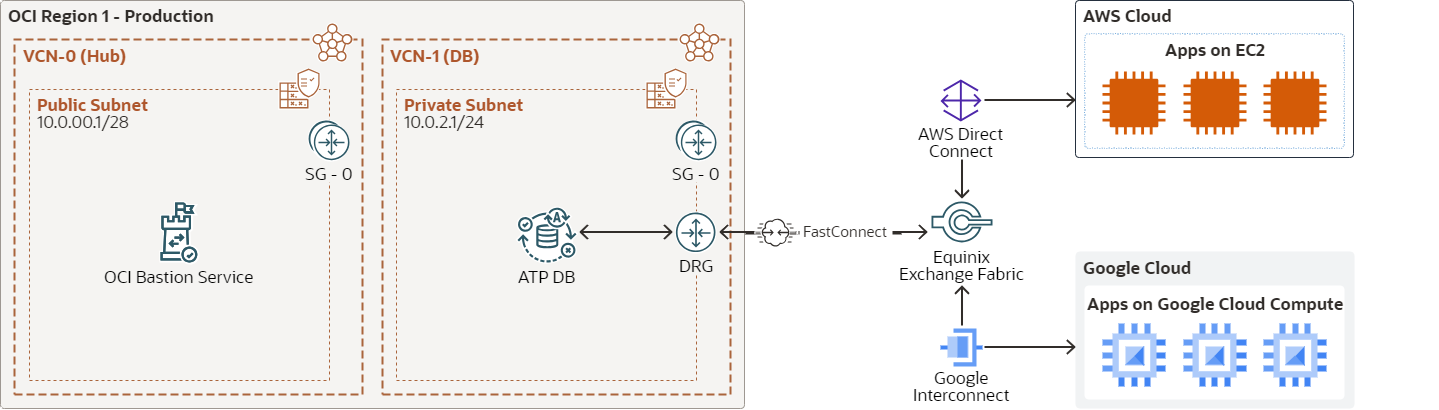
The following diagram shows a common multicloud use case for application and database split-stack architecture. The application tier runs on AWS and the database runs on OCI. The OCI FastConnect partners, such as Equinix, connect OCI FastConnect to AWS Direct Connect to provide the private, dedicated network connection between the application and database. Google Cloud and Azure offer additional network connection options to OCI that will be discussed in details later.
oci-aws-gcp-split-stack-arch-oracle.zip
The Oracle Database service provides a variety of options leveraging OCI for these architecture types. Organizations can run Oracle Database on OCI to get the best performance and price point.
- You can use the fully managed Oracle Autonomous Database (ADB) where automation and minimum database management are key requirements.
- You can also get Oracle Exadata Database Service for scalability and high performance when you need to run business critical applications in cloud.
- You can choose a Oracle Base Database service on OCI for simple workloads or deploy RAC (real application clusters) for high availability.
About Oracle Database@Azure
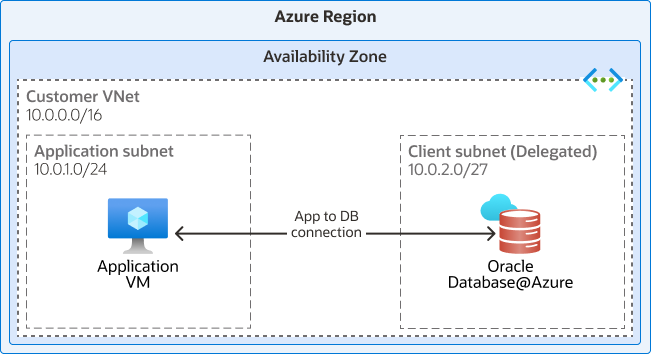
The following diagram shows Oracle Database@Azure service running on OCI colocated in a Microsoft Azure data center:
oracle-db-azure-colocated-data-centers-oracle.zip
Oracle Database@Azure brings Oracle technologies, such as Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless, Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC), and Oracle Data Guard, into the Azure platform. The solution uses Azure networking and Azure Virtual Network (VNet) access. You can manage the service on the Azure console or using Azure automation tools. Oracle Database@Azure consists of a fully-managed Autonomous Database and a co-managed Oracle Exadata Database Service. Both services are natively integrated in Azure providing a simple, secure, and low latency operating environment. Microsoft Entra ID provides federated identity and access management for Oracle Database@Azure. The solution is deployable across multiple Azure availability zones (AZs) and regions to ensure business continuity and cloud resilience.