Learn About the Cybersecurity Pillar in OCI
The following diagram illustrates the OCI Core Landing Zone reference architecture.
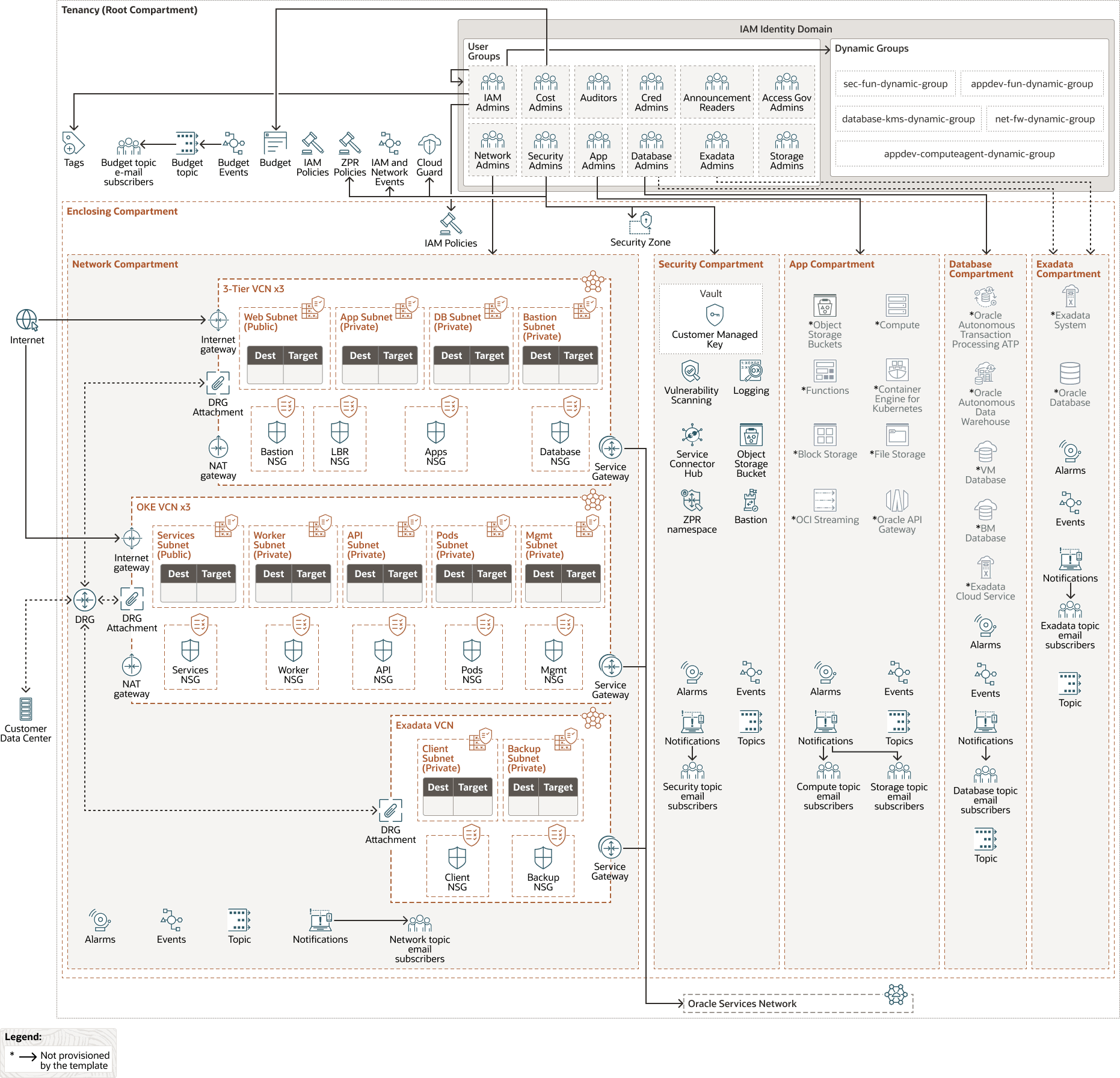
Description of the illustration oci-core-landingzone.png
oci-core-landingzone-oracle.zip
Landing zones are designed to help organizations efficiently deploy business-critical workloads. All essential technology components are included—covering identity, network, storage, compute, and security. Provisioning the landing zone is automated through Infrastructure as Code (IaC), so you can deploy everything with a single click.
The OCI Core Landing Zone integrates both the Oracle Enterprise Landing Zone (OELZ) and the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Landing Zone approaches. This unified landing zone provides a reference architecture for agility, scalability, and security in the cloud. Based on a modular OCI Landing Zone framework, it allows fast, scalable deployment and includes security best practices recommended by the CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark, helping you achieve a robust security posture and meet compliance requirements.
Cybersecurity covers the "Protect and Detect" phases of the NIST Cybersecurity model.
Recommendations for Preventative Controls
Preventative controls focus on three main areas: logical protection, network protection, and infrastructure/application protection. Secure your tenancy from unauthorized access and restrict network-level access to mitigate risks like ransomware. Protect your infrastructure and applications to strengthen your resilience against compromise.
Logical Protection
Tenancy Compartment Design
Design your compartment strategy to ensure protection from ransomware. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) provides robust identity management (authentication, SSO, lifecycle management) for Oracle Cloud and non-Oracle applications. It also supports secure access for employees, partners, and customers, whether on cloud or on-premises. OCI IAM integrates with existing identity stores and providers to streamline end user access for cloud applications and services. Follow these guidelines to design your compartment strategy:- Organize cloud resources into compartments, acting as logical containers within your tenancy.
- Structure compartments to isolate critical workloads and data, and allow for distributed administration, least-privilege access, and separation of duties.
- Group resources according to your operational model to distribute, limit role-based administrative privileges, and limit full tenancy administrative rights to emergency "break-glass" accounts.
- Compartments follow a zero-trust model and deny all access by default—access is only granted through explicit IAM policies.
OCI IAM Policies
Access to resources is denied by default; only permitted by explicit policies. Follow these guidelines to create OCI IAM policies:- Create explicit policies to grant access to groups and provide limited access to your cloud resources.
- Write fine-grained policies. For example, you can create a policy to
allow a group the ability to create and manage Object Storage buckets that are
commonly used to store backups but denies the ability to delete objects or
buckets. You can allow
Storage_Adminsto manage buckets in{tenancy OCID}whererequest.permission != 'DELETE'. - Assign separate identity domains to sensitive compartments (like vaults) to prevent credential reuse and enhance isolation. For example, you can create a Vault compartment to store copies of buckets, block volumes, and manual database backups and assign a separate identity domain to control access. This restricts anyone who has access to the main environment from using the same credentials to access the Vault compartment and provides isolation and protection of these assets.
- Independently federate identity domains with external providers for extra security. Use a separate identity provider for your Vault and Safe Restore enclaves to provide superior isolation from the identity provider used for your Production enclave.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Secure all local OCI accounts by enabling and mandating MFA. OCI IAM supports multiple methods for enabling MFA including security questions, mobile app passcode, mobile app notification, text message (SMS), email, bypass code, and Duo Security.
Network Protection
Traditional perimeter-driven cybersecurity is the foundation of the Cybersecurity pillar and uses Firewalls, Bastion hosts, perimeter next-generation firewalls, WAFs, and basic identity and access management practices. Traditional cybersecurity is table stakes, but without standard blocking and tackling mechanisms in this space perimeter security is compromised.
OCI provides multiple capabilities to help you implement controls to achieve a secure network. The VCN provides the foundation for all networking in OCI. By default, there is no network access to your tenancy. You must implement services to allow for ingress and egress, specify the direction, ports, and protocols that are allowed.
Design your network to prevent an attacker from gaining access to your network and prevent them from moving laterally if they happen to gain access. Follow these recommendations to configure network protection:
- Segmentation: Place sensitive workloads (such as databases) in dedicated VCNs. Use firewalls, SLs, and NSGs for control. You can granularly control access between and within a VCN and achieve the first layer of segmentation. By having your sensitive workload in its own dedicated VCN you can leverage Firewalls, Security Lists and Network Security Groups (NSGs) to filter and control access.
- Zero-Trust and Least Privilege: Apply the principles of zero-trust and least privilege, use Security Lists (SL), Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Zero Trust Packet Routing (ZPR) to achieve further segmentation and isolation between subnets and cloud resources. Use SLs, NSGs, and ZPR for subnet and resource isolation. OCI ZPR policies use intent-based and human-readable language, making them easy to audit, understand, and manage.
- SLs: SLs operate at the subnet level and control ingress and egress for the subnet.
- NSGs: Use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. NSGs provide isolation at the VNIC layer and allow you to implement micro-segmentation between individual VNIC equipped resources.
- NSGs over SLs: Prefer NSGs over SLs because NSGs support micro-segmentation at the VNIC level and separate security from network design.
- Restrict Traffic: Restrict ingress and egress traffic to only source and destination ports required for a given application to exercise the principle of least privilege. Tightly restrict worldwide access to sensitive ports such as RDP and SSH.
- OCI IAM Policies: Use OCI IAM policies to give permission to SLs and ensure that only those parties with responsibility for maintaining the lists based on their separation of duties can administer them.
- Network Firewall: Deploy OCI Network Firewall with hub-and-spoke architecture via DRG to regulate cross-VCN and on-premises traffic. OCI supports many third-party firewalls (such as Fortinet, Palo Alto, or Cisco).
- Use OCI gateways for secure, controlled internet access, and to
privately connect resources to OCI services.
- Internet Gateway: Controls ingress and egress (restrict for security).
- NAT Gateway: Allows controlled egress without exposing internal IPs.
- Service Gateway: Keeps resource communication within OCI's network.
- Private Connectivity: Use OCI FastConnect for high-speed, low-latency, private connection between your tenancy and your internal network. Consider MacSEC and/or IPSEC to provide encryption.
- Bastion Hosts: Use OCI Managed Bastion services for secure and ephemeral admin access to resources.
- Zero Trust Packet Routing: Make network security policies easier and more auditable.
Infrastructure and Application Protection
OCI provides several capabilities for protecting the infrastructure resources in your tenancy including:
- OCI IAM Policies: Remove sensitive permissions even from administrators. Limit full admin rights to a securely vaulted, break-glass account. For example, you can remove the ability to delete storage (Object, Block, and File) and backups and limit tenancy administrative rights to a break-glass account that can be vaulted.
- DDoS Protection: OCI provides default protection of the network against volumetric attacks, and Oracle also has solutions for providing layer-3 and 4 protection at the tenancy level.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Use OCI WAF with load balancers to protect public apps from threats, including Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 vulnerabilities. Restrict access by country if needed. OCI WAF should be deployed using OCI Load Balancing to inspect and protect web based traffic against OWASP attacks such as SQL Injection. Also consider restricting traffic by country based on usage and access requirements.
- Vulnerability and Patch Management: Use a combination of the OCI Vulnerability Scanning Service and Oracle OS Management Hub services.
- Use the OCI Vulnerability Scanning Service for compute nodes and registry images. Scan all your compute nodes and containers for both open ports and CVSS based vulnerabilities.
- Use Oracle OS Management Hub to automate and monitor OS patching. Identify missing OS and security patches and automate patching across your Oracle Linux and Windows compute nodes.
- Instance Security: Instance Security provides runtime security for workloads in compute, virtual, and bare metal hosts. Instance security expands Cloud Guard's scope from cloud security posture management to cloud workload protection. It ensures that security needs are met in one place with consistent visibility and a holistic understanding of the security state of your infrastructure.
- OCI Vault: Vault provides an HSM backed, full lifecycle management service for keys and secrets if you want to manage your own encryption keys and other critical credentials. There are multiple options for the Vault service to meet your needs.
- Security Zones: Provide guardrails for the creation and movement of cloud resources within your tenancy. Security zones are applied to compartments and operate at the control plane to prevent certain actions from taking place. For example, you can prevent the creation of public buckets, assignment of public IP addresses, and require that customer-managed encryption keys are used to secure all storage. Define custom security zones to meet your specific security posture and regulatory compliance requirements. Select the policy statements that are relevant for your needs and the target compartment.
OCI provides several services and capabilities that can assist you in properly securing your tenancy against ransomware type threats. While these controls significantly strengthen your OCI tenancy, no system is perfectly secure. Stay vigilant and continuously adapt your security posture as cyber threats evolve.
Recommendations for Detective Controls
You can use OCI services to help you identify and respond to potential ransomware threats in your tenancy. The fastest way to set up a secure OCI tenancy is by deploying the OCI Core Landing Zone, which follows OCI CIS Security Benchmarks and incorporates cybersecurity best practices.
Logging and Analytics
OCI Logging is a highly scalable and fully managed service that gives you a central view of all your logs. It collects logs from OCI resources and provides critical diagnostic details about how these resources are accessed and perform. There are three main types of logs you can use:
- Audit logs:
Audit logs capture every action within your tenancy, whether using the console, command line, or the API. The audit log contents are stored immutably and can't be altered or deleted. You can search the audit log from the console and turn entries into events that can then be sent using the OCI Notifications service to your security teams.
- Service logs:
Service logs are generated by OCI-native services like API Gateway, Load Balancer, Object Storage, Functions, and VCN flow logs. Each service offers predefined log categories that you can enable or disable as needed.
- Custom Logs:
Custom logs allow you to monitor and record diagnostic information from your custom applications, other cloud providers, or on-premises environments. Use the API to ingest these logs, or configure an OCI Compute instance or resource to directly upload custom logs from your compute resources using the Unified Monitoring Agent. Custom logs are supported both in a virtual machine and bare metal.
All log data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, and remains encrypted when archived or transferred to storage such as Object Storage. OCI Logging integrates with Connector Hub, so that you can easily forward your logs to Object Storage for archive storage, or the OCI Streaming service for ingestion by your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and other security analytics tools.
OCI Log Analytics
Consider using the OCI Log Analytics service to analyze your logs if you don't have a SIEM. The OCI Log Analytics service is an OCI-native solution that lets you index, enrich, aggregate, explore, search, analyze, correlate, visualize, and monitor log data from your cloud or on-premises applications and system infrastructure. The service provides multiple ways of gaining operational insights from your logs. With Log Analytics you can:
- Use an interactive log explorer UI
- Aggregate log information into dashboards
- Ingest and analyze data using APIs
- Integrate log data with other OCI services
The interactive visualizations provide several ways to slice and dice the data. You can use clustering features to reduce millions of log entries down to just the most interesting patterns, group features to spot anomalies, and track transactions. Use the Link feature to analyze logs in a transaction or identify anomalous patterns using the grouped view.
The Security monitoring solution in OCI Log Analytics is a set of curated dashboards that help you monitor and understand your cloud security posture. These dashboards turn complex log data into actionable security insights, and help you address security issues. This view saves you time, reduces risk, and improves your cloud security posture.
The three Oracle-defined views, VCN, OCI Compute, and OCI Audit are displayed in the Security Monitoring solution page.
Security Posture Management
While OCI Logging lets you visualize what's happening in your environment, it only provides disparate data points about the activity within it. Collecting contextual information enables you to spot potential threats and protect your environment from threats like ransomware. Traditional SIEM platforms provide the correlation and advanced analysis capabilities. However, they can be difficult to use and expensive to implement and maintain. OCI provides a cloud-native service that provides many of the same benefits:
Cloud Guard
A cloud-native service that helps you monitor your OCI environment, detect risky configurations or activities, and maintain a strong security posture. With Cloud Guard, you can:
- Examine your resources for configuration-related security weaknesses, and your users and operators for risky activities.
- Upon detection, suggest, assist, or take corrective actions, based on your configuration.
- Automatically convert audit log information into actionable security-related events and reduce the number of raw events that you have to sift through.
- Act on events from the Cloud Guard console and forward them to the OCI Streaming service and onward to your SIEM system.
- Clone and customize the Oracle-provided detector and responder recipes to tailor the security violations you want to be alerted to and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
- Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level for broad coverage and reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
- Use Managed Lists to include or exclude specific configurations from security scanning detectors.
Cloud Guard Threat Detector
Apply data science to quickly discover compromised environments. Automatically triage user behavior using machine learning, data science, and threat intelligence to reduce alert noise. Use Oracle's threat intelligence data to monitor targeted behavior models aligned with MITRE ATT&CK techniques. This uses known attacker behaviors and motivations to identify threat markers and combines those markers into a scoring algorithm based on attack progression.
Threat Detector also analyzes the OCI administrator's actions using machine learning and other techniques to help alert security operators of rogue users—someone whose credentials have been stolen or their allegiance compromised. Ensure that this detector is enabled and set up the Rogue User alert to notify authorized people on your team.
Cloud Guard Instance Security
Instance Security provides runtime security for workloads in OCI Compute virtual and bare metal hosts. It ensures that security needs are met in one place with consistent visibility. Instance Security provides a holistic understanding of the security state of infrastructure and helps you:
- Detect suspicious processes, open ports, and script executions at the OS level
- Receive actionable alerts on vulnerabilities and abnormal activity
- Use Oracle-managed detector recipes or create your own recipes for threat hunting
- Export logs to your third-party security tools with native integration OCI Logging
Database Security
Databases are primary targets for ransomware since they contain your organization's critical, sensitive, and regulated operational data. That's why it's critical to have real-time insights into your database security posture and protect your cloud infrastructure from ransomware and other attacks.
By default, OCI databases use Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) to protect sensitive data in tables and backups. TDE encrypts all data at rest and transparently decrypts it for authorized users or applications when they access this data. TDE protects data stored on media in the event that the storage media or data file is stolen.
Oracle Data Safe provides a unified Oracle Database console to help you understand your data's sensitivity, assess data risks, mask sensitive information, configure and monitor security controls, assess users, and monitor database activity. With Data Safe you can perform:
- Security risk assessments
- User assessments
- Activity audits
- Data discovery
- Data masking
Tip:
Register all your Oracle Databases with Data Safe to identify, categorize, and prioritize risks, and to generate comprehensive usage reports on security parameters, security controls, and user roles and privileges.Oracle Database Vault
Oracle Database Vault implements data security controls within your Oracle Database to restrict access to sensitive application data by privileged users. Reduce the risk of insider and outsider threats and address compliance requirements and separation of duties.
Secure new and existing Oracle Database environments without the need for expensive and time-consuming application changes. Database Vault is compatible with enterprise architectures, including Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC), Oracle GoldenGate, and Oracle Data Guard, all without the need to deploy additional servers and agents.
Oracle Database Vault offers the following features:
- Realms: Block unauthorized access to sensitive data by creating restricted application environments within your Oracle Database and Oracle Database Vault security controls. Help organizations address compliance with data privacy laws and standards such as the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), and numerous other regulations that require strong internal controls on access, disclosure, or modifications to sensitive information.
- Command Rules: Prevent malicious or accidental changes that
disrupt operations by privileged user accounts. Command controls prevent
unauthorized commands such as
DROP TABLEorALTER SYSTEMoutside of specific maintenance windows. - Trusted Paths: Enforce zero-trust access based on IP, application, user, and time of day, so attackers cannot easily use stolen credentials. Oracle Database Vault can block unauthorized access to sensitive data and generate high value alerts notifying administrators of suspicious data access activity and prevent data theft before it happens.
- Separation of Duties: Enforce checks and balances on privileged users, and prevent attackers from disabling security controls, creating rogue users, and accessing sensitive data using credentials from a privileged account.
Tip:
Implement Database Vault for all of your OCI databases.Events and Notifications
You can choose to be alerted about additional events that occur within your OCI tenancy that aren't covered by the described services. The OCI Events and Notifications services allow you to identify these events and send notifications to your team when an event occurs.OCI Events
Use OCI Events to create rules to send automated notifications based on state changes in your tenancy. Rules include a filter you define to specify events produced by the resources in your tenancy. Rules must also specify an action that will trigger when the filter finds a matching event.
Actions are responses you define for event matches. When the filter in the rule finds a match, the OCI Events service delivers the matching event to one or more of the destinations you identified in the rule. Destination services for events are Notifications, Streaming, and Functions.
OCI Notifications
Use OCI Notifications to send alerts when an event with your OCI resources triggers. You can configure
alarms, event rules, and service connectors, to send you human-readable messages
through supported endpoints, including email and text messages (SMS). You can also
automate tasks through custom HTTPS endpoints and OCI Functions. You can also directly publish messages.
The OCI Audit, Logging, Cloud Guard, and Data Safe services are all integrated with OCI Events and Notifications to enable you to notify your operations and security teams of security-related issues in your tenancy.