Plan
| Sequence | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Enable Immutability and Zero Data Loss of Oracle Databases IM-2: Use the Recovery Service for Oracle cloud databases. |
| 2 |
Configure immutable buckets and enable IAM principal of least privilege IM-1: Configuration of immutable bucket for unstructured data. ZT-1: Privately configured bucket with secure permissions configured for IAM specialized recovery accounts only. |
| 3 |
Enable Threat Detection related to Cyber Resiliency threats TD-1: Cloud Guard Verify bucket rules (public/private) and bucket logging. |
| 4 |
Start to test movement of data into immutable buckets IM-3: Use OCI CLI script to copy OCI FSS to immutable object storage. BR-1: Backup OCI Custom Image to immutable bucket. |
Protect Databases with Autonomous Recovery Service
Start a pilot for a new development and test database. Sample questions include, but are not limited to:
- Which databases platforms and software versions are required?
- Are your Databases using OCI for DNS? If not investigate DNS conditional forwarding.
- Do you need to increase existing OCI limits?
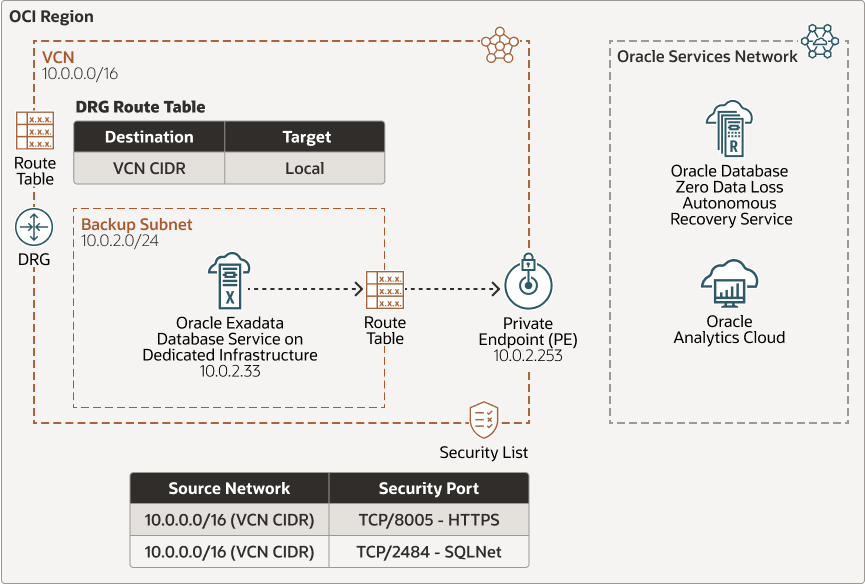
- Did you enable the security lists to permit your databases to connect to the Autonomous Recovery Service?
- Did you enable all the required IAM policy statements to authorize the service?
The following diagram shows an example of an OCI recovery subnet connecting to the Oracle Database Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service:
Now that your databases are protected, focus on protecting your unstructured data (Boot, Block, File systems, and so on) using the following recommendations:
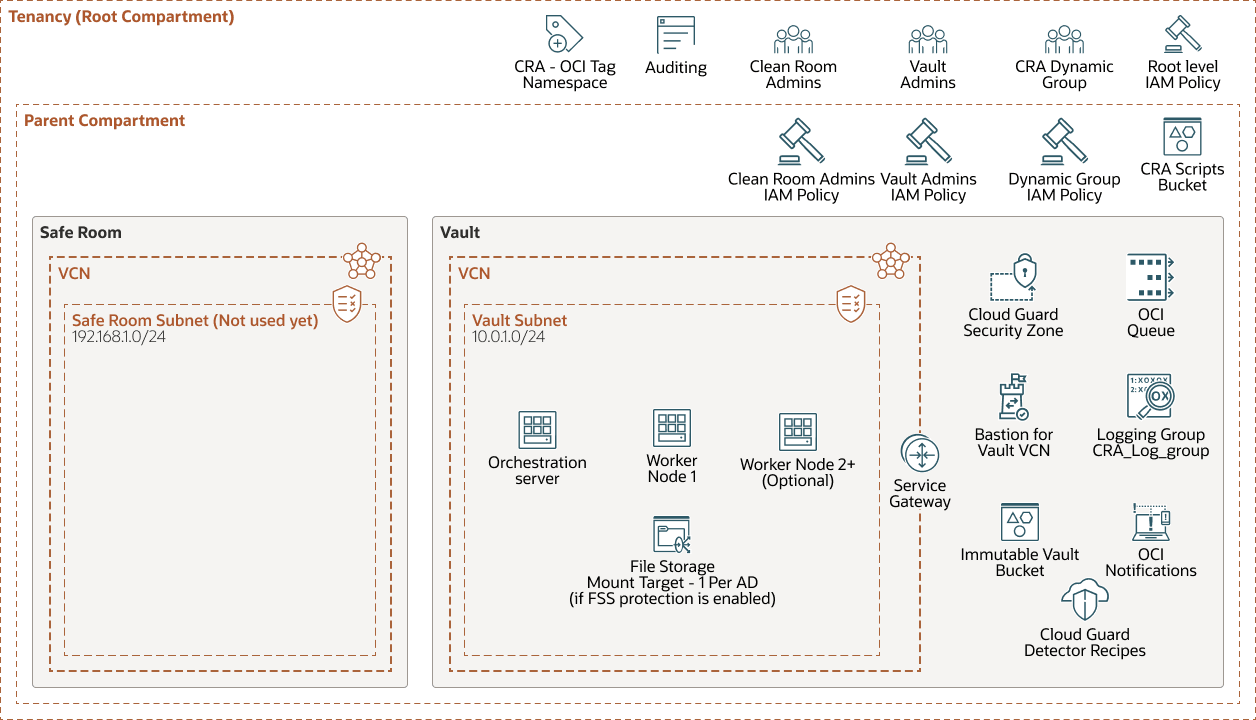
- Create a nested compartment structure or creating a new OCI tenancy to act as your Vault enclave or Safe Restore enclave.
- Create an Object Storage bucket, add retention rules, and lock the rules after you test your retention policies.
- Verify that IAM policies restrict group memberships and only provide access to backup or storage administrators. If needed, you could also use a different IAM domain.
- Make sure that Oracle Cloud Guard and OCI security zones ensure that your bucket can't be made public, and that no one can disable your backup and recovery services. A security zone policy forbids the creation of public buckets in OCI Object Storage. For example, you can set up a security zone policy to prevent anyone from creating a public bucket or modifying an existing storage bucket and making it public.
Backup to an Immutable Vault
There are open-source and commercial tools available that enable replicating, synchronizing, and moving data across platforms. Review The right tool for the job section of the Migrating data blog. There are multiple tools and techniques for copying your data into the Immutable Vault Bucket.
In a cyber resilience pilot, you can deploy an architecture in which you can use an orchestration server that resides in the Immutable Vault. The Orchestration Server discovers resources to backup and sends backup jobs into the OCI Queue service. Worker nodes then listen for backup jobs and start processing tasks immediately. In this model, you can copy the data from the Production enclave and then upload the data into the immutable vault bucket.
Summary of Critical Controls by Domain
| Domain | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Immutability | IM-1: Configuration of immutable bucket for
unstructured data.
IM-2: Use of the Recovery Service for Oracle cloud databases. IM-3: If using OCI File Storage, copy OCI File Storage to immutable object storage. |
| Zero Trust | ZT-1: Privately configured bucket with secure permissions configured for IAM specialized recovery accounts only. Leverage OAG to determine effective permissions on immutable bucket(s). |
| Backup and Recovery | BR-1: Backup OCI Custom Image to immutable bucket. |
| Threat Detection | TD-1: Cloud Guard bucket rules (public/private). Bucket logging. Threat Detector rule enabled. |