Learn About Different Ways to Connect to Oracle Services
Connect Privately From VM to Services
Service Gateway provides private access to the VMs in a private subnet for the supported Oracle services within the region. You can create a service gateway in your private subnets and enable their traffic to reach to a public Oracle service, such as ADW/ATP and Object Storage. Connections can be initiated from the VMs in a subnet.
For service private endpoints, you can run the service privately in your own VCN and can be accessed by any resource which has access to that VCN. As a service user, create a service private endpoint in your own VCN and consume the Oracle services privately without opening any access control lists (ACLs) to any public IP address space.
Connect Privately with FastConnect or VPN
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure allows consumers to route traffic from on premises systems to their service gateway, using FastConnect or VPN based private connectivity. This provides the on premises systems a private and more secure path to accessing the service, as compared to internet-based access.
With Service gateway, data travels over a FastConnect private virtual circuit or Site to Site VPN, transits through a VCN, and then through a service gateway to your Oracle service.
With service private endpoints, the resources are accessible over a private IP address in consumer’s VCN, enabling connectivity from on premises through Fastconnect and/or Site to Site VPN. The network configuration is kept secure by not opening it up to public IP addresses. You can simplify the configuration in the corporate firewalls and route tables to allow access only to the private IP address.
Scenario 1: Forward connection to the Oracle Services
You can request the Oracle service provider to create a service private endpoint (VNIC) in your private network. Your consumer will use this VNIC to access the service. You'll go through the usual onboarding workflow offered by the Service. In addition to the details required for service instance creation, you'll need to provide your preference to access the service using a service private endpoint including the specific VCN and subnet in which the endpoint will be created. The service provider creates an instance and creates a service private endpoint in consumer VCN/subnet.
Description of the illustration forward_connection_to_services.png
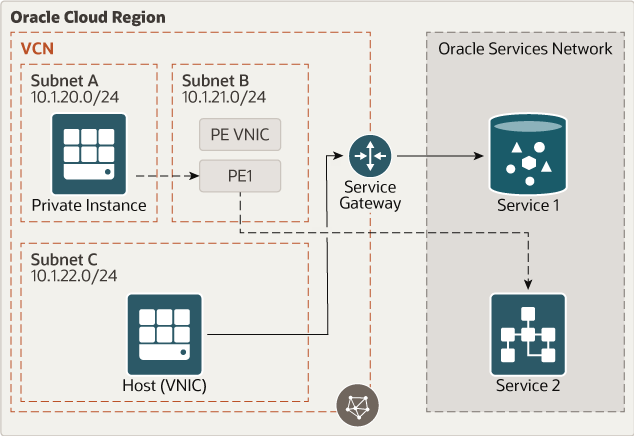
The consumer’s private instance connectivity experience on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is the same as with any other private IP in the consumer’s VCN. There is a Service 2 instance, which has a service private endpoint in the consumer's VCN. The VCN includes three subnets: Subnet A (CIDR 10.1.20.0/24), Subnet B (CIDR 10.1.21.0/24) and Subnet C (CIDR 10.1.22.0/24).
- Service Private Endpoint
- From the private instance in subnet A the traffic reaches the service private endpoint in subnet B with a private IP address inside the consumer’s VCN.
- Data flows to the service 2 based on the subnet security rules or network security groups configured per service private endpoint.
- Service Gateway
- From host on subnet C, data will go to a service gateway on the consumer’s VCN.
- From consumer VCN, it flows to Oracle Services and reaches Service 1.
For service private endpoint, once an Oracle resource is mapped to a service private endpoint, the connectivity works out of the box for private instance in subnet A without any additional configurations on route tables and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Network Security Groups.
If you need a private access from your data center to Oracle Cloud, you can use either Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect or IPSec VPN. You can extend your on premises network to consumer's VCN for higher bandwidth, lower latency, and flexibility of the type of peering such as private, public or both. From your consumer VCN, you can connect to service provider.

Description of the illustration fastconnect_vpn_connection.png
- In Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, the FastConnect virtual circuit terminates at DRG, which is attached to a virtual cloud network (VCN).
- Traffic from the consumer VCN to the service VCN is routed through the private IP address. Traffic in the opposite direction is routed through the DRG. In both directions, the traffic never leaves the private network.
- You can connect to service VCN publicly from on premises using public DNS name of the service.
Scenario 2: Reverse connection from Oracle Services
A set of services need to initiate connections back into the consumer network. For example, you may want your Oracle Analytics Cloud to connect to consumer database endpoints, which can be in the VCN or on premises, to ingest data and build the required dashboards/reports. Consumers do not want these data sources to be accessed over the Internet and want to limit access to Oracle Analytics Cloud. Reverse connections functionality in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service private endpoint enables service providers to privately access endpoints in the consumer’s network. The service instances in the Oracle Services can access a consumer-specified workload without traversing the Internet.

Description of the illustration reverse_connection_from_services.png
Note:
Service Gateway does not support reverse connections.This product extends private connectivity from service instances in Oracle Services to consumer's VCN, on premises network, and to other networks that are accessible via the consumer’s VCN. Service providers can create multiple service private endpoints each providing connectivity to a different consumer network.