Learn About Migrating with Oracle Recovery Manager
This architecture diagram shows an example of the solution for using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to migrate an on-premises database to Exadata Cloud at Customer.
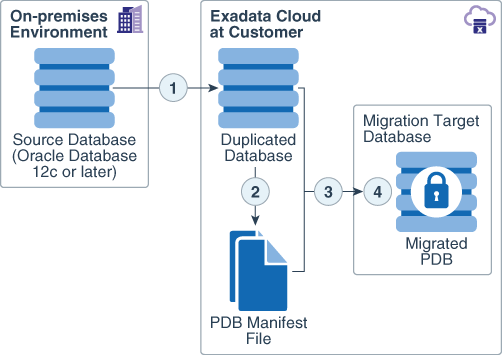
Description of the illustration png-architecture-migrating-premises-database-exadata-cloud-customer.png
-
The first phase of the migration involves duplicating and transporting the source database to Exadata Cloud at Customer. This phase is achieved using the Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN)
DUPLICATE DATABASEcommand. -
After the source database is duplicated, it is prepared so that it can be plugged into the migration target database. During this phase a pluggable database (PDB) manifest file is created.
-
The duplicated database is plugged into the migration target database.
-
Oracle Transparent Database Encryption (TDE) is configured on the migrated PDB, and the migrated data is encrypted to protect it while it resides in Oracle Cloud at Customer.
Considerations for Migrating a Database Using RMAN
You can migrate your Oracle Database to Oracle Cloud Services by using various tools and technologies, and each migration approach has its benefits and limitations.
Consider migrating with RMAN only if your source database meets the following requirements:
-
The database is a non-CDB database, which does not use the Oracle multitenant architecture.
-
The database host platform uses little-endian byte ordering. Query
V$TRANSPORTABLE_PLATFORMto view the byte ordering for different platforms.
Consider an alternative migration procedure if:
-
You cannot tolerate any downtime for migration or your maintenance windows are not large enough to accommodate the procedure.
-
You wish to physically reorganize the database objects as you move the data between platforms.