Sonoco: On-Premises Supply Chain Solution Deployment on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
In 2019, Sonoco completed their on-premises migration of a legacy system, replacing it with Oracle E-Business Suite. As Sonoco accelerated on its growth path, the information technology (IT) team explored migrating their on-premises deployment to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Sonoco is a leading green consumer packaging and construction material supplier. Founded in 1899, it provides diversified consumer packaging, industrial product, protective packaging, and packaging supply chain services. They're also world's largest supplier of composite canes tubes and cords. With net sales of $4.9B, Sonoco has 20,000 employees and more than 335 operations in 33 worldwide locations, serving more than 85 countries. Sonoco is based out of South Carolina, USA.
The first step, deployment on-premises, included the following components:
- Oracle E-Business Suite, version 12.1.3
- Oracle Advance Supply Chain Planning
- Service-oriented architecture
- Oracle GoldenGate
- Advanced Data Guard
- Oracle Transportation Management
- Agile
- Custom applications
The following factors drove the decision to move to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Transformative growth required changes in the way Sonoco IT deployed and managed their solutions on-premises.
- Changes were needed in overall deployment strategy to take advantage of speed, scalability, and readily available security offered in the cloud to fulfill business growth needs.
- They needed the ability to meet requirements for future workloads and to quickly and cost-effectively accommodate any changes in these requirements.
- They needed to troubleshoot the ecosystem using a single pane of glass. The ecosystem links are connected and unified with Oracle.
Sonoco considered several cloud vendors, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure met the technological and cost requirements, including the following features:
- Secure and flexible infrastructure design to run Oracle and non-Oracle workloads with required segregation and security controls
- Oracle applications on Oracle hardware provided best performance in a cost-effective way
- Options to use virtual machine (VM) or bare metal servers (required by some work loads) with dynamic CPU and memory scaling
- Exadata Cloud Service, which not only provided unmatched performance and on-demand scaling, but minimized operational tasks, such as patches and updates, when compared to on-premises deployment
- 17% performance improvement in applications, which increased significantly after performance tuning
- Oracle E-Business Suite upgrade and migration from 12.1.3 to 12.2.9, achieved smoothly and quickly with minimal challenges
- Cost control mechanism that ensured resources and new features were being deployed and utilized only when needed resulting in significant cost reduction
- Disaster recovery set-up with low-latency, high-speed private connection
So, what's next for Sonoco? 2020 was about migrations, and 2021 onwards is about growth. Sonoco has only migrated one-third of their overall data center facilities to cloud. So, they plan a lot more cloud migrations for existing applications and solutions. Sonoco is also rolling out new applications, such as AP automation, OTM , OPM, and upgrading and deploying cloud version of SOA. Sonoco looks forward to continuing this work in partnership with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure team.
Architecture
This architecture shows Sonoco's multi-region disaster recovery architecture on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
One of the key requirements of the migration was to have fast, redundant, and reliable connection to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, so they use FastConnect as the primary connection. Sonoco also uses Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's native connectivity option to Azure for seamless and quick access to applications deployed in Azure.
To satisfy security requirements, multiple virtual cloud networks (VCNs) with multiple private subnets are used to segregate applications and provide secure access to these applications. Sonoco also uses multiple load balancers to access servers deployed in different tiers. This ensure traffic is equally distributed so that no server is overloaded. Sonoco uses Exadata Cloud Service for database and deployed it in multiple private subnets.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage provides multiple applications servers a file system with shared mount points. Database backups use Oracle Cloud service gateway and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage service, and Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery. The disaster recovery site uses Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's high-speed, low-latency private backbone, which was a critical requirement. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volumes provides more storage for compute instances.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
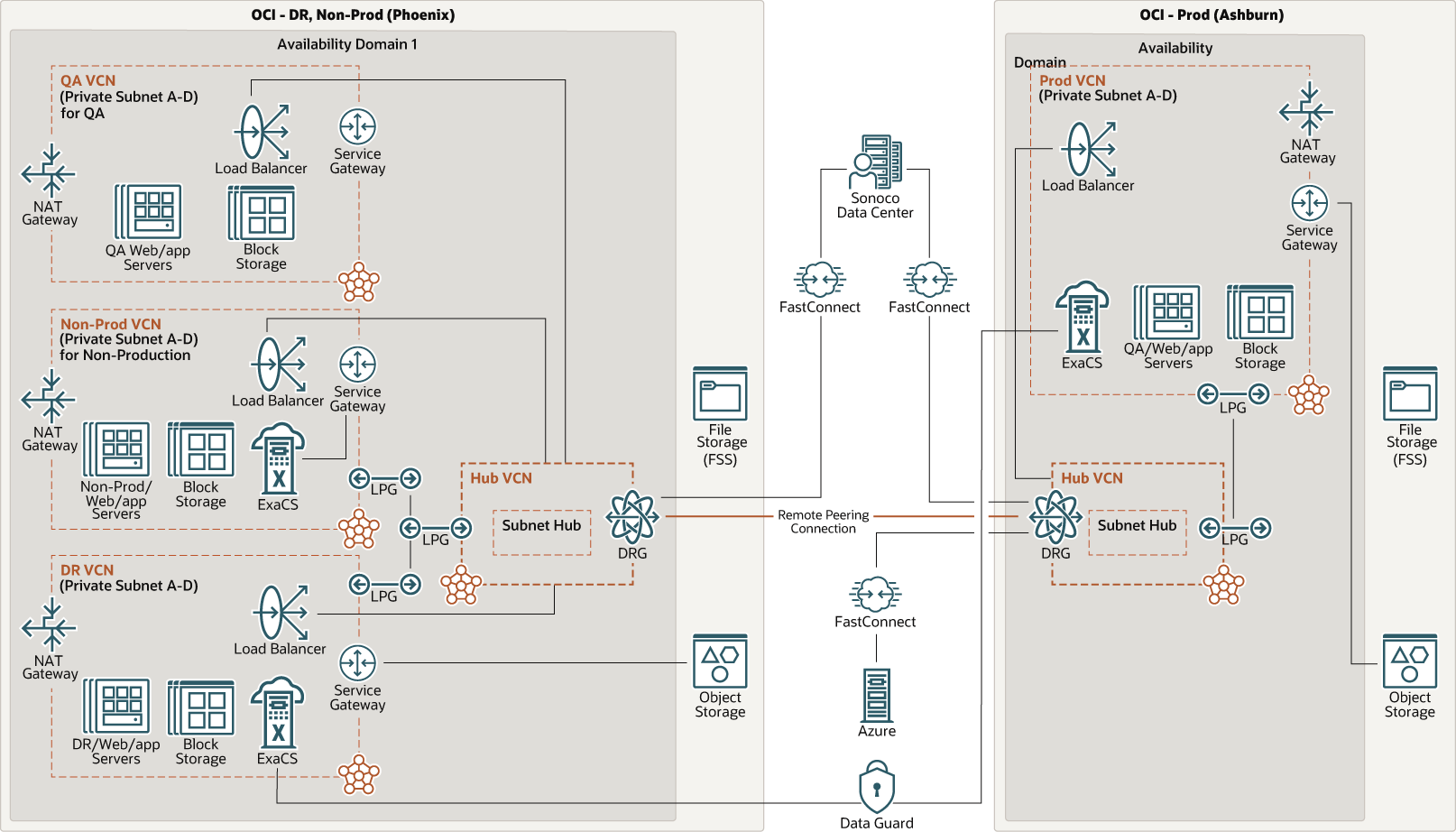
Description of the illustration sonoco-ebs-dr-oci.png
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
All the resources in this architecture are deployed in a single region.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
All the resources in this architecture are deployed in a single availability domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Hub VCN
The hub VCN is a centralized network. It provides secure connectivity to all spoke VCNs, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services, public endpoints and clients, and on-premises data center networks.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
This architecture includes a public load balancer.
- Security lists
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route tables
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
The VCN that's used for the data tier in this architecture has a DRG to enable private connectivity to your on-premises data center using FastConnect or VPN Connect.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
The VCN that's used for the data tier in this architecture has a service gateway.
- Network address translation (NAT) gateway
A NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Local peering gateway (LPG)
An LPG enables you to peer one VCN with another VCN in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network.
- Remote peering
Remote peering allows the VCNs' resources to communicate using private IP addresses without routing the traffic over the internet or through your on-premises network. Remote peering eliminates the need for an internet gateway and public IP addresses for the instances that need to communicate with another VCN in a different region.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Exadata DB systems
Exadata Cloud Service enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. You can provision flexible X8M systems that allow you to add database compute servers and storage servers to your system as your needs grow. X8M systems offer RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) networking for high bandwidth and low latency, persistent memory (PMEM) modules, and intelligent Exadata software. You can provision X8M systems by using a shape that's equivalent to a quarter-rack X8 system, and then add database and storage servers at any time after provisioning.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Get Featured in Built and Deployed
Want to show off what you built on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Care to share your lessons learned, best practices, and reference architectures with our global community of cloud architects? Let us help you get started.
- Download the template (PPTX)
Illustrate your own reference architecture by dragging and dropping the icons into the sample wireframe.
- Watch the architecture tutorial
Get step by step instructions on how to create a reference architecture.
- Submit your diagram
Send us an email with your diagram. Our cloud architects will review your diagram and contact you to discuss your architecture.