Cluster Configuration BUI View
The Configuration: Cluster view provides a graphical overview of the status of the cluster card, the cluster controller states, and the cluster resources.
The following figure shows cluster connections between two Oracle ZFS Storage ZS11-2 controllers:

The following figure shows cluster connections between two Oracle ZFS Storage ZS9-2 controllers:

The following figure shows cluster connections between two Oracle ZFS Storage ZS7-2, ZS5-x, ZS4-4, ZS3-4, or Sun ZFS Storage 7x20 controllers:
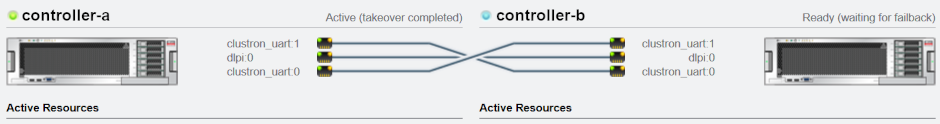
The following figure shows cluster connections between two Oracle ZFS Storage ZS3-2 controllers:

The interface contains the following objects:
-
A thumbnail picture of each controller. The controller that the user is currently logged into is on the left side of the view. Above each controller thumbnail, the controller name is on the left, and the current cluster state of the controller (such as Active or Ready) is on the right. For descriptions of controller states, see Clustered Controller States.
-
A line that represents each cluster card connection. These lines update dynamically with the hardware. A solid line indicates that the link is connected and active. A dashed line indicates that the link is broken in one of the following ways:
-
The other controller is restarting/rebooting.
-
The link is not cabled correctly or the cluster cables are not secure in their connectors. For cluster cabling instructions, see Connecting Cluster Cables in Oracle ZFS Storage Appliance Cabling Guide, Release OS8.8.x.
Ensure that all links are connected and active before you perform initial cluster setup. See Upgrading a Standalone Appliance to a Clustered Configuration (BUI).
-
-
Below each controller thumbnail is a list of the PRIVATE and SINGLETON resources that are currently assigned to that controller, and some attributes of those resources such as IP address or size.
-
For each resource, the owner of the resource is shown. The owner of the resource is the controller that will provide the resource when both controllers are in the CLUSTERED state. To change the owner, click the current owner name, select the peer controller, and then click the APPLY button at the top right of the view.
-
To the right of the owner is a restart icon
 that enables you to attempt to repair the resource.
that enables you to attempt to repair the resource.
-
For each resource, a lock icon
 indicates whether the resource is PRIVATE. When the current controller is in either the OWNER or CLUSTERED state, a resource can be locked to it (made PRIVATE) or unlocked (made a SINGLETON). To lock a resource to the controller or unlock the resource from the controller, click the lock icon, and then click the APPLY button at the top right of the view. Note that PRIVATE resources that belong to the remote peer are not displayed on either resource list.
indicates whether the resource is PRIVATE. When the current controller is in either the OWNER or CLUSTERED state, a resource can be locked to it (made PRIVATE) or unlocked (made a SINGLETON). To lock a resource to the controller or unlock the resource from the controller, click the lock icon, and then click the APPLY button at the top right of the view. Note that PRIVATE resources that belong to the remote peer are not displayed on either resource list.
The following table describes the buttons at the top of the Configuration: Cluster view.
Table 2-1 Cluster Interface Buttons
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
|
Setup |
The setup operation is a step in initial cluster configuration. See Upgrading a Standalone Appliance to a Clustered Configuration (BUI). |
|
Unconfig |
The unconfig operation configures a cluster node to standalone operation. See Unconfiguring a Cluster Node. |
|
Failback |
The failback operation changes the cluster configuration from OWNER-STRIPPED (active-passive) to CLUSTERED-CLUSTERED (active-active). See Upgrading a Standalone Appliance to a Clustered Configuration (BUI) and Cluster Takeover and Failback. |
|
Takeover |
Takeover is performed automatically in certain situations. Takeover can be performed manually, which can be useful for testing purposes. See Cluster Takeover and Failback. |
|
Revert |
If resource modifications are pending (resource rows are highlighted in yellow), revert those changes and show the current cluster configuration. |
|
Apply |
If resource modifications are pending (resource rows are highlighted in yellow), commit those changes to the cluster. |
Related Topics
-
Connecting Cluster Cables in Oracle ZFS Storage Appliance Cabling Guide, Release OS8.8.x
-
Upgrading a Standalone Appliance to a Clustered Configuration (BUI)