Configuring a Virtual Switch and the Service Domain for NAT and Routing
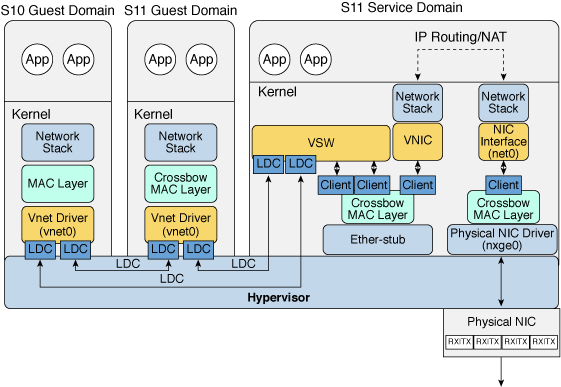
The Oracle Solaris 11 network virtualization features include etherstub, which is a pseudo network device. This device provides functionality similar to physical network devices but only for private communications with its clients. This pseudo device can be used as a network back-end device for a virtual switch that provides the private communications between virtual networks. By using the etherstub device as a back-end device, guest domains can also communicate with VNICs on the same etherstub device. Using the etherstub device in this way enables guest domains to communicate with network endpoints, including zones, in the service domain. By enabling IP routing in the service domain, virtual networks can communicate outside the machine by using the service domain as a router. Subsequently, configure NAT in the service domain to provide external connectivity to guest domains by means of a private IP address that is not externally routable. Use the dladm create-etherstub command to create an etherstub device.
The following diagram shows how virtual switches, etherstub devices, and VNICs can be used to set up Network Address Translation (NAT) in a service domain.
Virtual Network Routing