Using Virtual NICs on Virtual Networks
The Oracle Solaris 11 OS enables you to define virtual networks that consist of virtual network interface cards (VNICs), virtual switches, and etherstubs. Oracle Solaris Zones virtualize operating system services and provide isolated and secure environments for running applications within the same Oracle Solaris OS instance of a logical domain.
Oracle Solaris 11 improves on the Oracle Solaris 10 “shared IP” zone model in which zones inherit network properties from the global zone and cannot set their own network address or other properties. Now, by using zones with virtual network devices, you can configure multiple isolated virtual NICs, associate zones with each virtual network, and establish rules for isolation, connectivity, and quality of service (QoS).
For more information, see the networking books in the Oracle Solaris 11.4 information library (http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37838_01/).
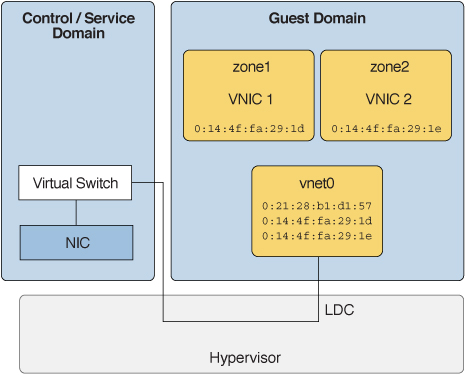
A virtual network device in a logical domain can support multiple Oracle Solaris 11 virtual NICs. The virtual network device must be configured to support multiple MAC addresses, one for each virtual NIC it will support. Oracle Solaris zones in the logical domain connect to the virtual NICs.
Within the domain1 domain are Oracle Solaris 11 zones: zone1 and zone2. Each zone is connected to the network by a virtual NIC based on the vnet0 virtual network device.
Virtual NICs on Virtual Network Devices
The following sections describe the configuring of virtual NICs on virtual network devices and the creating of zones in the domain with the virtual NICs:
For information about using virtual NICs on Ethernet SR-IOV virtual functions, see the following sections: