3 Monitoring an Oracle GoldenGate Instance
This topic describes how to monitor and Oracle GoldenGate instance. It contains the following information:
3.1 Overview of the Monitoring Workspace
The following tabs show real-time monitoring information and historical data to use for troubleshooting and tuning the Oracle GoldenGate replication solution. Anyone with any security role can view these tabs.
-
The Metrics and Alerts tab is the main monitoring console of Oracle GoldenGate Monitor. It focuses on objects that are not in a normal state, such as those that have an error status. See Monitoring the Oracle GoldenGate System.
-
The History tab focuses on historical and logged data for the attributes that are associated with a selected Oracle GoldenGate object. Working with History Information.
3.2 Monitoring the Oracle GoldenGate System
Use the Metrics and Alerts tab as your main monitoring area within Oracle GoldenGate Monitor. This tab combines all of the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor tools to provide several different ways to get information about your configuration quickly. You can view:
-
All of your Oracle GoldenGate Instances, their processes, their files, and their associated databases.
-
The logical relationship of the Oracle GoldenGate components to one another.
-
Information about each component, such as process status, performance statistics, and error conditions. This information is captured in a set of attributes that, together, provide an accurate view of the overall condition of the Oracle GoldenGate environment. See About the Metrics.
-
Expand the Navigation Tree nodes to navigate to the Oracle GoldenGate object or group of objects that you want to monitor. See About the Objects.
-
On the tree nodes, check for alerts and status indicators that indicate whether there is a potential problem or state change that applies to the selected node. An alert or status indicator on any container node or Oracle GoldenGate Instance node indicates that you should drill down further to locate the object that is affected. See About the Status Indicators.
-
Select any object in the tree for which you want more information. The Navigation Tree works with the Diagram View to show the selected object along with other objects to which it has a logical relationship. For example, if you selected a Host node, you will see all of the Oracle GoldenGate components on that system, in their correct context. You can use the toolbar to navigate the diagram, if needed. See About the Diagram View.
-
In the diagram, check for alerts and status indicators, and evaluate the summary attributes, not only for the selected object but also for the other objects. Those objects might be the cause of, or might also be affected by, the condition that you are observing.
Note:
You can click any area of the Overview panel to focus on a specific part of the diagram. -
Select any object in the diagram (or tree) and then view the Metrics Panel to get detailed data for all of the attributes that are associated with the object. See About the Metrics.
Note:
You can sort the attributes by the Name column. You can double-click the header area, or click the embedded arrow, to expand or collapse the panel. -
(Optional) In the Metrics Panel, click the history icon (
 ) next to any attribute. This will open the History tab and show historical data for that attribute. See Working with History Information.
) next to any attribute. This will open the History tab and show historical data for that attribute. See Working with History Information. -
Select any object in the diagram (or tree) and then view the Alerts Panel to get details about any active alerts that were triggered for the object, including the text of the alert, the time that it occurred, and the condition that triggered it. See About Alerts.
Note:
You might have to double-click the Alerts header area to expand the panel to view it. You can double-click the header area, or click the embedded arrow, to expand or collapse the panel. -
(Optional) Focus on objects that have warning or error conditions. See Viewing Warning or Error Conditions.
Viewing Warning or Error Conditions
3.3 Viewing Warning or Error Conditions
Use the Metrics and Alerts tab get a quick overview of Oracle GoldenGate components that have warning or error conditions, without the need to drill down through the Navigation Tree. The objects are displayed in a large Diagram View, so that you can quickly identify the ones that need the most attention. The Diagram view shows the objects in their logical relationship to one another.
To view information about a problem:
-
Select any object in the diagram. You can click any area of the Overview panel to focus on a specific part of the diagram. Use the diagram tools in the toolbar to interact with the diagram. See About the Diagram View.
-
View the Metrics Panel to get detailed data for all of the attributes that are associated with the object. See About the Metrics.
Note:
You can sort the attributes by the Name column. You can double-click the header area, or click the embedded arrow, to expand or collapse the panel. -
(Optional) In the Metrics Panel, click the history icon next to any metric for which you want to view historical data on the History tab. See Working with History Information.
-
View the Alerts Panel to get details about any active alerts that were triggered for the object, including the text of the alert, the time that it occurred, and the condition that triggered it. See About Alerts.
Note:
You might have to double-click the Alerts header area to expand the panel to view it. You can double-click the header area, or click the embedded arrow, to expand or collapse the panel.
Monitoring the Oracle GoldenGate System
3.4 Viewing Logged Information
You can view logged information about an instance from the Metrics subtab of the History tab. This display shows the report and discard files generated for each Extract or Replicat session. Every time you start an Extract or Replicat session, data is collected and a report generated and stored. You can view these reports from the Metrics and Alert tab in the Report subtab of the Logs subtab. Meanwhile, a runtime error log is also compiled and is displayed in the Ggserr Log subtab. The report location on your local system is specified at the bottom of this tab. The Logs subtab contains these three tabs (not all tabs must appear):
3.4.1 Report Subtab
The Report tab shows run-time reports generated for a specific Extract or Replicat instance. These reports contain the following information:
-
Version information and select environmental settings
-
Runtime parameters
-
Runtime Messages and statistics
The Report tab is divided into two sections:
-
The report list, on the left, which lists each report (where the naming format is GROUPNAMEnn.rpt, where GROUPNAME represents Extract (EXT) or Replicat (REP), and nn is a sequential number identifying the where report falls among all reports collected; for example, EXTAA.rpt, EXTAA0.rpt. EXTAA1.rpt and so on. Note that, as demonstrated in the preceding examples, the most current report will not have a sequence number).
-
The actual report content on the right.
Additionally, the bottom of the panel shows the full path and file name, size of the file in bytes, and a time stamp for when the data was collected is displayed.
-
Select the Extract or Replicat instance from either the Navigation Tree or the Diagram Area.
-
Select the Logs subtab on the Metrics and Alerts tab; the default sub tab of the Logs subtab is the Report subtab.
-
Select the specific report from the reports list.
3.4.2 Discard File Subtab
Discard files contains information about data that failed the respective Extract or Replicat session.
The Discard subtab is divided into two sections:
-
The discard disk, on the left, which lists each report (where the naming format is GROUPNAMEnn.rpt, where GROUPNAME represents Extract (ext) or Replicat (rep) and nn is a sequential number identifying the where report falls among all reports collected; for example, repaa.dsc, repaa0.dsc, repaa1.dsc, and so on. Note that, as demonstrated in the preceding examples, the most current report will not have a sequence number).
-
The actual report content on the right; for example:
Oracle GoldenGate Delivery for Oracle process started, group REPAA discard file opened: 2014-04-14 17:43:49.382279 Oracle GoldenGate Delivery for Oracle process stopped, group REPAA : 2014-04-14 17:52:20.212009
Additionally, bottom of the panel shows the full path and file name, size of the file in bytes, and a time stamp for when the data was collected.
3.4.3 Ggserr Log Subtab
This subtab displays the Oracle GoldenGate error log file; for example:
2014-04-15 05:42:08 INFO OGG-01738 Oracle GoldenGate Capture for Oracle, extaa.prm: BOUNDED RECOVERY: CHECKPOINT: for object pool 1: p31714_extr: start=SeqNo: 263, RBA: 29534736, SCN: 0.6146203 (6146203), Timestamp: 2014-04-15 05:41:09.000000, Thread: 1, end=SeqNo: 263, RBA: 29536256, SCN: 0.6146203 (6146203), Timestamp: 2014-04-15 05:41:09.000000, Thread: 1. 2014-04-15 01:42:00 INFO OGG-01738 Oracle GoldenGate Capture for Oracle, extaa.prm: BOUNDED RECOVERY: CHECKPOINT: for object pool 1: p31714_extr: start=SeqNo: 263, RBA: 23313936, SCN: 0.6138834 (6138834), Timestamp: 2014-04-15 01:40:11.000000, Thread: 1, end=SeqNo: 263, RBA: 23316480, SCN: 0.6138834 (6138834), Timestamp: 2014-04-15 01:40:11.000000, Thread: 1. 2014-04-14 21:41:54 INFO OGG-01738 Oracle GoldenGate Capture for Oracle, extaa.prm: BOUNDED RECOVERY: CHECKPOINT: for object pool 1: p31714_extr: start=SeqNo: 262, RBA: 23449104, SCN: 0.6123109 (6123109), Timestamp: 2014-04-14 21:40:57.000000, Thread: 1, end=SeqNo: 262, RBA: 23450112, SCN: 0.6123109 (6123109), Timestamp: 2014-04-14 21:40:57.000000, Thread: 1. 2014-04-14 17:54:50 INFO OGG-00987 Oracle GoldenGate Command Interpreter for Oracle: GGSCI command (espear): info repaa detail. 2014-04-14 17:52:24 INFO OGG-03522 Oracle GoldenGate Delivery for Oracle, repaa.prm: Setting session time zone to source database time zone 'GMT'.
Each line of the error log contains time stamp, severity, error code, process reporting the message, and the actual message. This enables you to track an error or warning to data on the associated report.
To download the Ggserr.log file:
You can download the error log file in order to save or view it by clicking Download complete Ggserr.log, at the bottom of the Ggserr Log subtab. The parenthetical number next to the download link indicates the current size of the error log file.
3.5 Working with History Information
The History tab contains the Metrics and Alerts subtabs that enable you to view performance statistics, event messages, lag, and other information that occurred over a specific time period. You can analyze this data to identify persistent trouble spots or processes that need performance tuning. Historical data can be obtained for any metric of an Oracle GoldenGate component. See About the Metrics.
The historical data of an metric can be represented either as a chart, as a table, or both, depending on the type of metric.
-
The table view displays the selected metric data in a tabular format. The column names vary, depending on the metric that was selected.
-
The chart view has two independent charts to allow comparison between different date ranges for the given metric. The tools on the tool bar control the navigation in this view and the display format of the historical data. See History Tab Toolbar.
You can use the following icons, located at the top right-hand corner of the tab, to toggle between chart and table view (if valid for the metric).
| Chart View | |
| Table View |
To work with history information:
-
Select an Oracle GoldenGate object in the Navigation Tree. The name of that object will be displayed in the header area of the Metrics subtab. See About the Objects.
-
For Attribute, select an metric for which you want historical data to be retrieved. The Attribute list contains only the appropriate attributes for the selected object, and only those for which there is historical data. If an metric cannot be displayed in chart view, it will not be displayed in the Attribute list when chart view is enabled. To view that metric, switch to table view. (Any metric that can be displayed in chart view can be displayed in table view.)
-
For Date Range Type, select the date range for which you want the history to be retrieved. If you select Custom, additional From and To fields are displayed, where you can type a date range or select dates by clicking the calendar icon. The date format is MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM {AM | PM}. (If you click in a field, an example of the correct format is displayed.)
-
Click Get Data.
Monitoring the Oracle GoldenGate System
Viewing Warning or Error Conditions
3.5.1 History Tab Toolbar
Navigation Tools on the Metrics Subtab
| Zoom-in
Zooms in to focus on an area. |
|
| Zoom-out
Zooms out to view a larger area. |
|
| Fit-to-screen
Fits the image to your monitor screen. |
|
| Zoom-to-area
Zooms in to a specific area when you depress and hold the mouse button, and then drag the selection box to enclose the zoom area. |
|
| Pan
Moves the image within the visible area when you depress and hold the mouse button, and then drag the mouse. |
The following are the chart styles that you can use to view the trend of the historical data over time. You can switch between chart styles as needed.
| Line chart style | |
| Area chart style | |
| Histogram chart style |
You can choose the following color schemes for the chart style that you selected.
| Complementary colors | |
| Monochromatic colors | |
| Contrasting colors |
3.6 Purging Historical Data
Over time, historical data and old alerts will accumulate in the database repository. A user with at least the Power User role can purge old metrics and alerts with the Purge Data control.
Note:
Purge Data removes the metrics and alerts permanently from the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor database.-
Log in with at least the Power User role.
-
On the Utility Bar, click Purge Data.
The Purge Data dialog box appears.
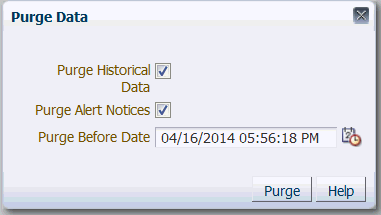
Description of the illustration ''purge_data.gif''
-
Select the kind of data to purge: Historical Data, Alert Notices, or both.
-
For Purge Before Date, enter a date that represents the oldest data that you want to keep (using the date-time format shown), or click the calendar icon to select the date from a calendar. All of the selected data before that date will be deleted permanently. You can purge just one kind of data the first time, and then you can purge the other kind using a different purge date.
-
Click Purge. You are not prompted to confirm this action.
-
Click OK on the confirmation. You are returned to the Purge Data dialog box to do additional purging, if desired.
3.7 Viewing Alerts
Use the Alerts subtab of the History tab to view a history of alerts. By analyzing alert history, you can determine how often certain conditions occur, so that you can make adjustments to the Oracle GoldenGate configuration or the underlying hosts.
The alert history goes back in time to the point where it was last purged by the Super Administrator, Administrator, or Power User.
-
Select an object in the Navigation Tree. The closer to the root level of the tree that you go, the more alerts that will be displayed, because the selection encompasses alerts for all of the objects within the sub-nodes.
-
View the alerts on the Alerts subtab. This table displays the name of the alert (as specified in the alert definition), the actual notification message (which is the same as that which is sent to email, SNMP, or CLI clients if active), and the time that the alert was generated. You can sort the Alert Name column in ascending or descending order.
3.8 Running GGSCI Commands
Use the GGSCI subtab of the Metrics and Alerts tab to run any supported commands without leaving within Oracle GoldenGate Monitor. Enter the command you want to run with any associated options in the GGSCI Command field the click Run. The results are displayed for you to review.
You cannot edit parameter files using GGSCI commands with this subtab.
The list of unsupported GGSCI Commands follows:
-
sh -
edit -
view -
stop jagent -
start jagent -
obey -
fc -
set editor -
shell -
info marker -
edit params