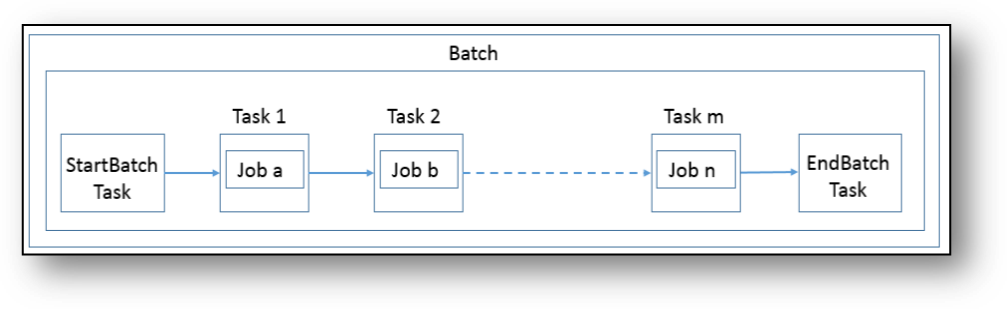
Transaction Monitoring uses Scheduler to create, schedule, execute and manage batches in Transaction Monitoring. A batch is a combination of tasks that are scheduled to run at a defined interval of time. A batch contains a StartBatch, Endbatch, and other tasks.
Figure 32: Flow of Batch

Transaction Monitoring contains certain pre-configured batches that can be used to run the default data. You must create new batches to run customer-specific data.
To execute the batches, you must use Schedule Batch feature in the Scheduler Service. For more information, see Scheduler Service.
Transaction Monitoring contains the following pre-configured batches that must be executed in the following sequence:
Table 20: Pre-configured Batches and their Sequences
Sequence |
Batch Name |
1 |
AMLRedaction |
2 |
Ingestion |
3 |
TMScenario |
4 |
TM_ECMExpress |
The Ingestion batch runs the data pipelines, filters the data and prepares the data for further processing. Therefore, Ingestion batch must be run first.
This batch loads the data from staging to the business table in the specified order. The loading process receives, transforms, and loads Market, Business, and Reference data that is required for event detection.
The following table provides the tasks that are configured for the Ingestion batch. These tasks must be executed in the following sequence:
Table 22: Ingestion Batch Details
Sequence |
Tasks for Ingestion Batch |
Jobs for Ingestion Batch |
Pipelines for Ingestion Batch |
1 |
StartBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
2 |
ACCTTRXNINT |
Load Intermediate Account and Transaction Data |
Load Intermediate Account and Transaction Data |
3 |
WatchList |
WatchList Load Data |
Load and Prepare Watchlist |
4 |
Customer |
Load Customer Data |
Load Customer Data |
5 |
CustomerAddData |
Load Customer Additional Data |
Load Customer Additional Data |
6 |
AnticipatoryProfile |
Load Customer Anticipatory Profile Data |
Load Customer Anticipatory Profile Data |
7 |
Account |
Load Account Data |
Load Account Data |
8 |
AccountGroup |
Load Account Group Data |
Load Account Group Data |
9 |
AccountAddData |
Load Account Additional Data |
Load Account Additional Data |
10 |
AcctAnticipatoryProfile |
Load Account Anticipatory Profile Data |
Load Account Anticipatory Profile Data |
11 |
CustMapData |
Load Customer Mapping Data |
Load Customer Mapping Data |
12 |
SupplyInfo |
Derive Risk and Load Supplementary Information |
Derive Risk and Load Supplementary Information |
13 |
Transaction |
Transaction Load Data |
Load Transactions and derives Risk and External Entity |
14 |
TrustedPair |
Load Trusted Pair |
Load Trusted Pair |
15 |
EndBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
The TMScenario batch makes use of the data that is prepared during ingestion and executes the scenario pipelines in the configured sequence and generates events. For more information on scenarios configured in Transaction Monitoring, see TSD Documentation.
NOTE |
You cannot run the TMScenario batch before running the TMIngestion batch. |
The following table provides the tasks that are configured for the TMScenario batch.
These tasks must be executed in the following sequence:
Table 23: TMScenario Batch Details
Sequence |
Tasks for TMScenario Batch |
Jobs for TMScenario Batch |
Pipelines for TMScenario Batch |
1 |
StartBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
2 |
CALENDAR |
Load Calendar Data |
Load Calendar Data |
3 |
HRECUST |
HRE Customer Focused Scenario |
Focal High Risk Entity - Customer Focused |
4 |
HRGACCT |
HRG Account Focused Scenario |
High Risk Geography Account Focused |
5 |
POSSIBLECTRCUST |
Possible CTR Customer Focused Scenario |
Possible CTR Customer Focused |
6 |
LRTCUST |
Large Reportable Transaction Customer Focused Scenario |
Large Reportable Transaction Customer Focused |
7 |
FTNINTCUST |
FTN Internal Customer Focused Scenario |
FTN Internal -- Customer Focused |
8 |
RMFCUST |
RMF Customer Focused Scenario |
Rapid Movement of Fund Customer Focused |
9 |
LDACCT |
Large Account Depreciation Account Focused |
Large Depreciation of Account Value |
10 |
HREEE |
Focal High Risk Entity External Entity Focused |
Focal High Risk Entity External Entity Focused |
11 |
HRGEE |
High Risk Geography EE Focused |
High Risk Geography External Entity Focused |
12 |
LRTEE |
Large Reportable Transaction External Entity |
Large Reportable Transaction External Entity |
13 |
POSSIBLECTREE |
Possible CTR External Entity Focused |
Possible CTR External Entity Focused |
14 |
FTNEXTCUST |
FTN External - Customer Focused |
FTN External - Customer Focused |
15 |
HUBSPOKE |
Hub and Spoke Customer Focused |
Hub and Spoke Customer Focused |
16 |
EndBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
DM Utility in CMExpress moves data from AM to CM tables. It loads Event, Business as well as Evented related tables. Once the data is moved to consolidation tables then it is used for Correlation. Cases are generated after correlation.
You must perform certain pre batch configurations before executing the CMExpress batch. For more information, see Pre Batch Execution Configuration.
The following table provides the tasks that are configured for the CMExpress batch. These tasks must be executed in the following sequence:
Table 24: CMExpress Batch Details
Sequence |
Tasks for CMExpress Batch |
Jobs for CMExpress Batch |
Pipelines for CMExpress Batch |
1 |
ECMSRTBTH |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
2 |
PL_SRT |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
3 |
SCRLOAD |
Load Scenario data from AM to CM |
Load Scenario data from AM to CM |
4 |
BCUSTLOAD |
Customer Business data load AM to CM |
Load Customer and Customer-related business data from AM to CM |
5 |
BACCTLOAD |
Account Business data load AM to CM |
Load account and account-related business data from AM to CM |
6 |
BTRXNLOAD |
Transaction business data load AM to CM |
Load Transaction business data from AM to CM |
7 |
BEXTENLOAD |
External Entity Business data load AM to CM |
Load External Entity and Derive Address business data from AM to CM |
8 |
EVNTPOP |
Events Load AM to CM |
Load Events and Event-related data from AM to CM |
9 |
EVCUSTLOAD |
Customer Evented data load AM to CM |
Load Evented Customer data from AM to CM |
10 |
EVACCTLOAD |
Account Evented data load AM to CM |
Load Evented Account data from AM to CM |
11 |
EVTRXNLOAD |
Transaction Evented data load AM to CM |
Load Evented Transaction data from AM to CM |
12 |
EVEXTELOAD |
External Entity Evented data load AM to CM |
Load Evented External Entity and Derive Address data from AM to CM |
13 |
EVCORR |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
14 |
CASEGEN |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
15 |
CASELOAD |
Load Case Related data |
Load Case Related data |
16 |
PRECSUPDT |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
17 |
ECMECND |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
The AMLRedaction batch runs the data redaction.
The following table provides the tasks that are configured for the AMLRedaction batch. These tasks must be executed in the following sequence:
Table 21: AMLRedaction Batch
Sequence |
Tasks for AMLRedaction Batch |
Jobs for Ingestion Batch |
Pipelines for Ingestion Batch |
1 |
StartBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
2 |
REDACT |
Apply Redact Policy |
Apply Redact Policy |
3 |
EndBatch |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
You must perform the following pre batch configurations before executing the CMExpress Batch.
· Configuring Correlation Rules
· Correlation Case Type Mapping
Follow these steps before starting a batch:
1. To add parameters for the ECMSRTBTH task in CMExpress Batch, follow these steps:
a. Navigate to the Transaction Monitoring page.
b. Click  to
access the Navigation List. The Navigation
List displays the list of modules.
to
access the Navigation List. The Navigation
List displays the list of modules.
c. Click Scheduler in the Navigation List. The Scheduler Service page opens in a new window.
d. Define tasks for the ECMSRTBTH task in the CMExpress Batch. For more information on defining tasks to batches, see the Define Tasks section.
e. Add the following parameters to the ECMSRTBTH task in CMExpress Batch.
Table 25: Parameters in CMExpress Batch
Parameter Name |
Expected Value |
DATAORIGIN |
MAN |
FICMISDATE |
FICMISDATE |
BATCHTYPE |
DATA |
BATCHRUNID |
BATCHRUNID |
component |
ALL |
dataorigin |
MAN |
sourcebatch |
- |
currentbatch |
ALL |
2. When the Start Batch run is executed, it loads the data to the FCC_CM_BATCH_RUN table.
After events are correlated to business entities, the event-to-business entity relationships are used to correlate events to each other. Events are grouped into a correlation if they share common business entities, and if they meet the criteria defined in the Event Correlation Rules. The logic of an Event Correlation Rule is defined in the FCC_CM_CORRELATION_RULE table.
The following is an example of the rule logic defined in FCC_CM_CORRELATION_RULE table:
Table 26: FCC_CM_CORRELATION_RULE table
Column Name |
Column Type |
Nullable |
N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY |
NUMBER(22) |
No |
V_RULE_NAME |
VARCHAR2(1020) |
Yes |
N_PATH_PRECEDENCE |
NUMBER(22) |
Yes |
V_EVENT_FILTER_OPERATIONS |
VARCHAR2(4000) |
Yes |
V_EVENT_LINK_OPERATIONS |
VARCHAR2(4000) |
Yes |
N_LOOKBACK_VALUE |
NUMBER(22) |
Yes |
V_LOOKBACK_UNIT |
VARCHAR2(40) |
Yes |
F_EXTEND_FLAG |
VARCHAR2(40) |
Yes |
V_CASE_STATUS |
VARCHAR2(4000) |
Yes |
V_STATUS |
VARCHAR2(40) |
Yes |
F_CORRELATION_REQUIRED_FLAG |
VARCHAR2(4) |
Yes |
F_LOOKBACK_PROCESS_IND |
NUMBER(22) |
Yes |
· N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY (optional): This is the correlation rule unique Identification number.
· V_RULE_NAME (required): Defines the name of the correlation rule.
· N_PATH_PRECEDENCE (required): Number indicating the maximum precedence value that a business entity shared between events must have to be considered a correlation by this rule. The lower the precedence number the stronger the relationship. Events are not considered for the correlation unless the precedence number associated with the business entity-to-event is less than or equal to (<=) the value defined.
· V_EVENT_FILTER_OPERATIONS and V_EVENT_LINK_OPERATIONS (required): Defines operations used to further constrain the events to be used for correlation. An operation consists of an event attribute compared to a numerical value, such as from event and to an event which can be correlated if they both have V_EVENT_TYPE='AML', represented by source.V_EVENT_TYPE='AML', or a from event and to event which can be correlated if source.V_DATA_ORIGIN='SIN'. The set of supported comparison operators are: =, !=, <, >, <=, >=, IN, and NOT IN.
NOTE |
Because the N_SCENARIO_ID attribute of both events and correlations can potentially have multiple values, only the IN and NOT IN operators should be used in expressions involving N_SCENARIO_ID. The rest of the operators can only support single value operands. Also, there should be no space in the scenario ID list specified. For example, source.N_SCENARIO_ID IN (115600002,114690101). |
· Multiple operations can be joined together by logical AND and OR operators and operation precedence can be defined with parentheses.
· N_LOOKBACK_VALUE (required): The number attribute indicates the number of days to lookback from the current date or time to create a time window to consider events for correlation. This is a create timestamp of the event.
NOTE |
If lookback value is defined, then the lookback unit is also required. |
· V_LOOKBACK_UNIT (required): The unit attribute identifies the unit of the lookback number. Possible values are D and CM for days and current month, respectively. All of these require a valid number value except for CM, which essentially makes the lookback the first of the current month, such as if the current date is October 14, we will lookback to October 1 if the CM unit is selected. The create timestamp of the event is used to determine whether or not an event falls within the lookback period.
NOTE |
Do not use a unitless granular than a day in rules intended for batch events. |
· F_EXTEND_FLAG (required): Defines the conditions for extending existing correlations. When a new correlation is discovered, it is possible that it is a superset (with only the triggering event not already included in the existing correlation) of a correlation that is previously identified. F_EXTEND_FLAG defines whether this correlation rule can result in extending an existing correlation. If this is set to FALSE (do not extend) then a new correlation is created when this condition is identified. If F_EXTEND_FLAG is set to TRUE then the existing correlation is added to unless it is already promoted to a case that has a status identified in the V_CASE_STATUS tags of NonExtendableCaseStatuses.
· F_CORRELATION_REQUIRED_FLAG (required): Defines the conditions for correlation required. You can set this as Y or N. If this is set to N, then every event is self-linked and promoted to the case. If this is set to Y, then multiple events are linked if they have a common business entity and promoted to the case.
· F_LOOKBACK_PROCESS_IND (required): Indicates if the date of lookback is event processing date or sysdate. If this is set to 1, then the processing date is picked. If this is set to 0, then the event created date is picked.
· V_STATUS (required): Defines the status of correlation rule. By default, the correlation rule is Active.
§ To deactivate a correlation rule, modify the V_STATUS value to INACT.
§ To activate a correlation rule, modify the V_STATUS value to ACT.
§ Changes made to the metadata are effective immediately and are utilized the next time correlation is run.
Define the Case Type mapping before executing the batch. This is performed using FCC_CM_CORRELATION_CASE_TYPE_MAP table.
Table 27: FCC_CM_CORRELATION_CASE_TYPE_MAP table
Column Name |
Column Type |
Nullable |
N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY |
NUMBER(22) |
No |
V_CASE_TYPE |
VARCHAR2(60 CHAR) |
No |
· N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY: This is the correlation rule unique Identification number.
· V_CASE_TYPE: This is the type of case. The entry should be the same as mentioned in fcc_cm_case_type_b table.
To perform this activity, follow these steps:
Add a new entry in FCC_CM_CORRELATION_CASE_TYPE_MAP table. For example, N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY can be 1, 2, 3 and V_CASE_TYPE can be AML_DD, AML_TER, AML_PAT.
NOTE |
The value of the N_CORRELATION_RULE_SKEY column (rule number) should be the same as defined in the FCC_CM_CORRELATION_RULE table. |
You must create new batches to run customer-specific data.
To create and configure a new batch, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the Transaction Monitoring page.
2. Click  to
access the Navigation List. The Navigation
List displays the list of modules.
to
access the Navigation List. The Navigation
List displays the list of modules.
3. Click Scheduler in the Navigation List. The Scheduler Service page opens in a new window.
4. Define a batch. This option enables you to create a new batch. For more information, see the Define Batch section. For information on defining batches in Transaction Monitoring , see Defining Tasks for Transaction Monitoring Batches.
5. Define a task. This option enables you to add new tasks to the selected batch definition.
For more information, see the Define Tasks section.
For information on configuring tasks for batches in Transaction Monitoring batches, see Defining Tasks section.
6. Schedule a batch. This option enables you to run a batch. For more information, see the Schedule Batch section.
7. Monitor a batch. This option enables you to view the status of the executed Batch along with the details of the task. For more information, see the Monitor Batch section.
To define batches for Transaction Monitoring, you must configure the Transaction Monitoring batches as follows:
Table 28: Defining Batches for Transaction Monitoring
Field Name |
Description |
Batches for Data Redaction |
Batches for Data Pipeline |
Batches for Scenario Pipeline |
Batches for Case Management |
Batch Name |
Indicates the batch name. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Batch Description |
Indicates the batch description. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Service URL Name |
Indicates the Service URL name. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Service URL |
Indicates the Service URL. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
NOTE |
You cannot run a data and scenario pipeline in the same batch. |
Table 29: Parameter Details for Defining the Transaction Monitoring Batches
Param Name |
Description |
Batches for Data Redaction |
Batches for Data Pipeline |
Batches for Scenario Pipeline |
Batches for Case Management |
$LOADRUNID$ |
Indicates the load run ID. |
Not Applicable |
To be configured |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
$GROUPNAME$ |
Indicates the group name. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Not Applicable |
$DATAORIGIN$ |
Indicates the type of the source of the data. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Pre-configured |
$RUNTYPE$ |
Indicates the run type. |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
To be configured |
Not Applicable |
$FICMISDATE$ |
Indicates the date on which you want to run the batch. |
To be configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
$BATCHTYPE$ |
Indicates the type of pipeline to run as part of this batch. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Pre-configured |
$PREVMISDATE$ |
Indicates the date previous to the FICMISDATE |
Not applicable |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Not Applicable |
$BATCHRUNID$ |
Indicates the batch run ID. |
To be configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
To define tasks for Transaction Monitoring, you must configure the Transaction Monitoring batches as follows:
Table 30: Task Details for Defining the Transaction Monitoring Batches
Field Name |
Description |
StartBatch Task |
EndBatch Task |
Other Task |
Task Name |
Indicates the task name. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Task Description |
Indicates the task description. |
To be configured |
To be configured |
To be configured |
Task Type |
Indicates the task type. |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Batch Service URL |
Indicates the batch service URL. |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Pre-configured |
Task Service URL |
Indicates the task service URL. |
To be configured as /StartBatch |
To be configured as /EndBatch |
To be configured as /ExecutePipeline |
Parameter Name |
Parameter Value |
$GROUPNAME$ |
These values are obtained from the Batch Configuration. |
$DATAORIGIN$ |
|
$FICMISDATE$ |
|
$BATCHTYPE$ |
|
$PREVMISDATE$ |
|
$BATCHRUNID$ |
|
$JOBNAME$ |
You must add this parameter and mention the corresponding job name that you want to execute as part of this task. |
component |
This is applicable only for ECM start batch task. For more information, see Start a Batch. |
dataorigin |
|
sourcebatch |
|
currentbatch |