There are several reports you can generate in Oracle Policy Modeling to check the dependencies between rules. To check the structure of rules, you use the Rule Browser.
Check connections between rules
Using the top and base level attribute reports in Oracle Policy Modeling you can check if there are any intermediate attributes which have unintentionally become top or base level attributes because they have not been correctly constructed to fit into the rule hierarchy.
A top level attributes report shows a list of attributes in the rulebase which are only proved by other attributes in the rulebase (ie they don't prove other attributes in the rulebase).
To run a top level attributes report, select Reports | Top Level Attributes.
A base level attributes report generates a list of attributes in the rulebase which are not proved by any other normal rules (forward chaining only rules). These are the attributes which will be presented to users as questions during interviews (if running the rules interactively), and which will be the basis for all decisions made with the rulebase.
Generating the base level attributes report for your rules assists you in reviewing all of these attributes and determining whether or not they are at an appropriate level of granularity.
To run a base level attributes report, select Reports | Base Level Attributes.
An additional use of the base level attributes report is to determine whether any structural attributes have not been connected to base attributes properly. Structural attributes are those which refer to structural elements of your rules, such as "Section 1 is satisfied", "Paragraph 1(a) is satisfied", and which are typically generated automatically by Oracle Policy Modeling.
A common error in rule formatting is to write similar but not exactly the same structural attributes, creating duplicate attributes. Whilst you intend for these attributes to be identical, their textual difference means that they are added as separate attributes to your model. The consequence of this is that these attributes become accidental base level or top level attributes.
When you have completed work on a section of rules, you should generate the base level attributes report and review the list to ensure that attributes have not unintentionally been duplicated through the use of inconsistent text forms.
The dependent base attributes report generates a list of base level attributes which go towards proving a particular inferred attribute. This report can be very useful when working with large rule models.
To generate the report, select an attribute in the Build Model, then select Reports | Dependent Base Attributes from the main menu.
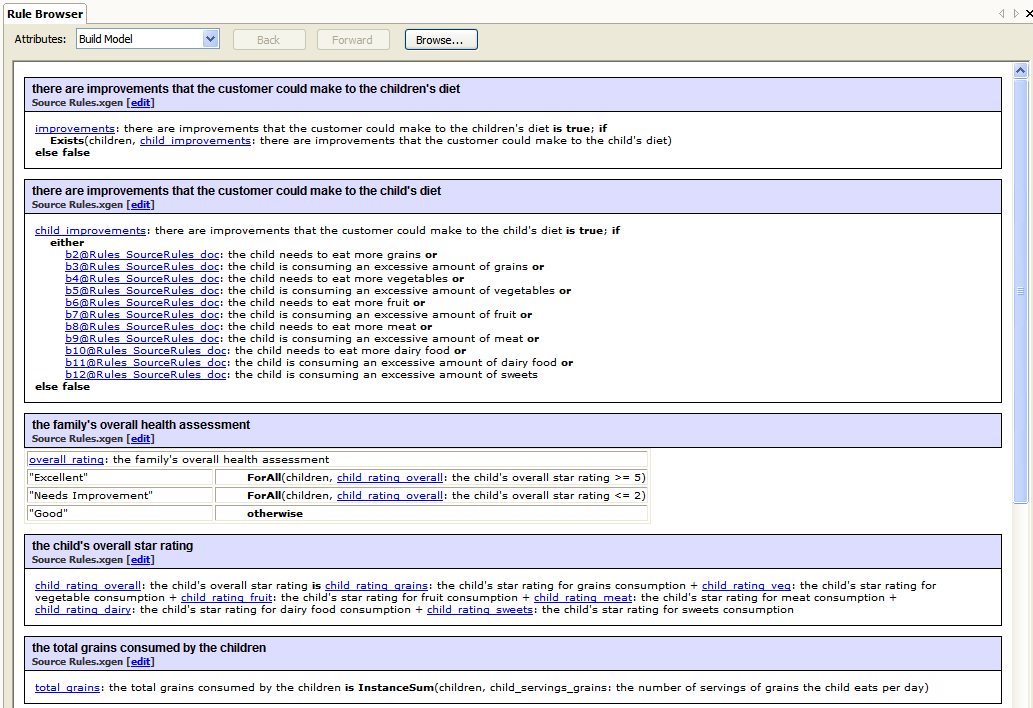
The Rule Browser is a helpful way to understand the links between rules across your rule documents.
To launch the Rule Browser, right-click on a rule document in the Project Explorer and select Open Rule Browser. You can also right-click on an attribute in the Build Model view (View | Build Model) and select Rule Browser.
In the Rule Browser linked attributes are displayed as hyperlinks, allowing you to jump from rule to rule to check the rule structure.
The Attributes drop down list allows you to specify the attribute ID format displayed:

To quickly jump to a rule within a Word document, click on the Edit link in the Rule Browser. For rules defined in Word documents, this will open the document and jump to the rule. For rules defined in Excel documents, the Rule Editor is opened (although note that the rule may not actually be modified in this view).