6 Adding Flexfields
This chapter describes support for flexfields in the BI Publisher data model.
This chapter includes the following sections:
6.1 About Flexfields
A flexfield is a flexible data field that your organization can customize to your business needs without programming. Oracle applications (Oracle E-Business Suite and Oracle Fusion Applications) use two types of flexfields: key flexfields and descriptive flexfields. A key flexfield is a field you can customize to enter multi-segment values such as part numbers, account numbers, and so on. A descriptive flexfield is a field you customize to enter additional information for which your Oracle applications product has not already provided a field.
If you are reporting on data from Oracle applications, use the Flexfield component of the data model to retrieve flexfield data. When BI Publisher is integrated with Oracle Fusion Applications, both key flexfields and descriptive flexfields are supported. When BI Publisher is integrated with Oracle E-Business Suite only key flexfields are supported.
Before including flexfields in your reports you should understand flexfields in your applications. See your Oracle E-Business Suite or Oracle Fusion Applications documentation.
6.1.1 Using Flexfields in Your Data Model
To use flexfields in your SQL-based data model:
-
Add the Flexfield component to the data model as described in this chapter.
-
Define the SQL SELECT statement against the applications data tables.
-
Within the SELECT statement, define each flexfield as a lexical. Use the &LEXICAL_TAG to embed flexfield related lexicals into the SELECT statement.
6.2 Adding Key Flexfields
You can use key flexfield references to replace the clauses appearing after SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ORDER BY, or HAVING. Use a flexfield reference when you want the parameter to replace multiple values at runtime. The data model editor supports the following flexfield types:
-
Where — This type of lexical is used in the WHERE section of the statement. It is used to modify the WHERE clause such that the SELECT statement can filter based on key flexfield segment data.
-
Order by — This type of lexical is used in the ORDER BY section of the statement. It returns a list of column expressions so that the resulting output can be sorted by the flex segment values.
-
Select — This type of lexical is used in the SELECT section of the statement. It is used to retrieve and process key flexfield (kff) code combination related data based on the lexical definition.
-
Filter — This type of lexical is used in the WHERE section of the statement. It is used to modify the WHERE clause such that the SELECT statement can filter based on Filter ID passed from Oracle Enterprise Scheduling Service.
-
Segment Metadata — Use this type of lexical to retrieve flexfield-related metadata. Using this lexical, you are not required to write PL/SQL code to retrieve this metadata. Instead, define a dummy SELECT statement, then use this lexical to get the metadata. This lexical should return a constant string.
After you set up the flexfield components of your data model, create a flexfield lexical reference in the SQL query using the following syntax:
&LEXICAL_TAG ALIAS_NAME
for example:
&FLEX_GL_BALANCING alias_gl_balancing
After entering the SQL query, when you click OK
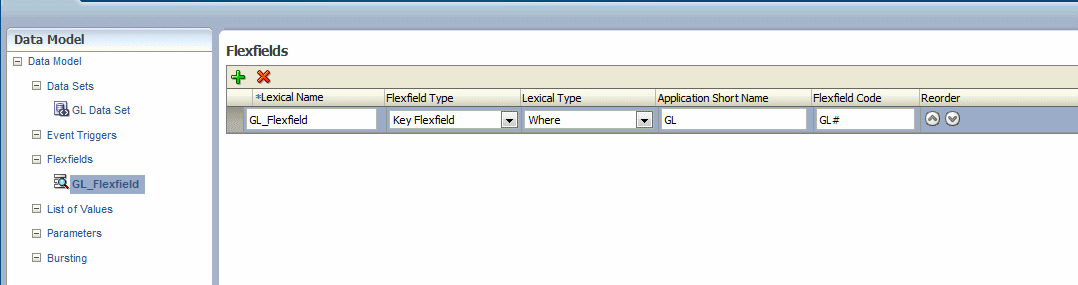
To add a key flexfield:
-
Enter the following:
-
Lexical Name — Enter a name for the flexfield component.
-
Flexfield Type — Select Key Flexfield.
-
Lexical Type — Select the type from the list. Your selection here determines the additional fields required. See Section 6.2.1, "Entering Flexfield Details."
-
Application Short Name — Enter the short name of the Oracle Application that owns this flexfield (for example, GL).
-
Flexfield Code — Enter the flexfield code defined for this flexfield. In Oracle E-Business Suite this code is defined in the Register Key Flexfield form (for example, GL#).
-
ID Flex Number — Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM.
-
6.2.1 Entering Flexfield Details
The Details region displays appropriate fields depending on the Lexical Type you chose.
Fields for Key Flexfield Type: Segment Metadata
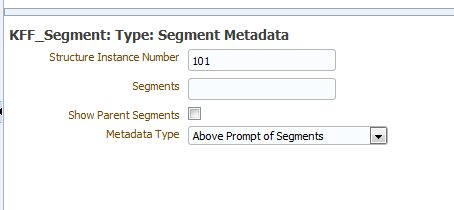
Table 6-1 Detail Fields for Segment Metadata
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Structure Instance Number |
Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM. |
|
Segments |
(Optional) Identifies for which segments this data is requested. Default value is "ALL". See Oracle E-Business Suite Developer's Guide for syntax. |
|
Show Parent Segments |
Select this box to automatically display the parent segments of dependent segments even if it is specified as not displayed in the segments attribute. |
|
Metadata Type |
Select the type of metadata to return: Above Prompt of Segments — Above prompt of segment(s). Left Prompt of Segments — Left prompt of segment(s) |
Fields for Key Flexfield Type: Select
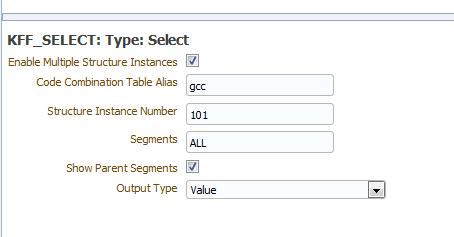
Table 6-2 shows the detail fields for the Select flexfield type.
Table 6-2 Detail Fields for Select
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable Multiple Structure Instances |
Indicates whether this lexical supports multiple structures. Checking this box indicates all structures are potentially used for data reporting. The data engine uses <code_combination_table_alias>.<set_defining_column_name> to retrieve the structure number. |
|
Code Combination Table Alias |
Specify the table alias to prefix to the column names. Use TABLEALIAS if your SELECT joins to other flexfield tables or uses a self-join. |
|
Structure Instance Number |
Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM. |
|
Segments |
(Optional) Identifies for which segments this data is requested. Default value is "ALL". See Oracle E-Business Suite Developer's Guide for syntax. |
|
Show Parent Segments |
Select this box to automatically display the parent segments of dependent segments even if it is specified as not displayed in the segments attribute. |
|
Output Type |
Select from the following:
|
Fields for Key Flexfield Type: Where
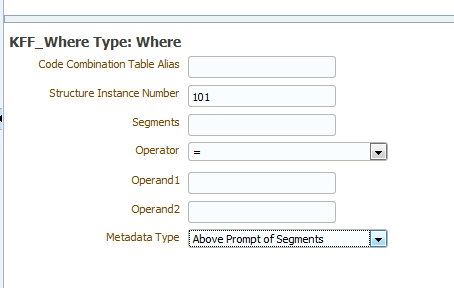
Table 6-3 shows the detail fields for the Where key flexfield type.
Table 6-3 Detail Fields for Where
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Code Combination Table Alias |
Specify the table alias to prefix to the column names. You use TABLEALIAS if your SELECT joins to other flexfield tables or uses a self-join. |
|
Structure Instance Number |
Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM. |
|
Segments |
(Optional) Identifies for which segments this data is requested. Default value is "ALL". See Oracle E-Business Suite Developer's Guide for syntax. |
|
Operator |
Select the appropriate operator. |
|
Operand1 |
Enter the value to use on the right side of the conditional operator. |
|
Operand2 |
(Optional) High value for the BETWEEN operator. |
Fields for Key Flexfield Type: Order By
Table 6-4 shows the detail fields for the Order by flexfield type.
Table 6-4 Detail Fields for Order By
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable Multiple Structure Instances |
Indicates whether this lexical supports multiple structures. Selecting this box indicates all structures are potentially used for data reporting. The data engine uses <code_combination_table_alias>.<set_defining_column_name> to retrieve the structure number. |
|
Structure Instance Number |
Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM. |
|
Code Combination Table Alias |
Specify the table alias to prefix to the column names. You use TABLEALIAS if your SELECT joins to other flexfield tables or uses a self-join. |
|
Segments |
(Optional) Identifies for which segments this data is requested. Default value is "ALL". See Oracle E-Business Suite Developer's Guide for syntax. |
|
Show Parent Segments |
Select this box to automatically display the parent segments of dependent segments even if it is specified as not displayed in the segments attribute. |
Fields for Key Flexfield Type: Filter
Table 6-5 shows the detail fields for the Filter flexfield type.
Table 6-5 Detail Fields for Filter
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Code Combination Table Alias |
Specify the table alias to prefix to the column names. You use TABLEALIAS if your SELECT joins to other flexfield tables or uses a self-join. |
|
Structure Instance Number |
Enter the name of the source column or parameter that contains the flexfield structure information. For example: 101. To use a parameter, prefix the parameter name with a colon, for example, :PARAM_STRUCT_NUM. |
6.3 Adding Descriptive Flexfields
Reporting on descriptive flexfields is supported only for Oracle Fusion Applications.
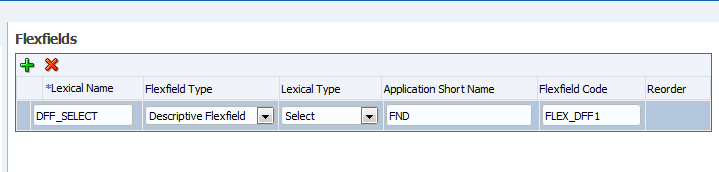
To add a descriptive flexfield:
-
Enter the basic flexfield information:
-
Name — Enter a name for the flexfield component.
-
Flexfield Type — Select Descriptive Flexfield.
-
Lexical Type - only Select is supported.
-
Application Short Name — Enter the short name of the Oracle Application that owns this flexfield (for example, FND).
-
Flexfield Code — Enter the flexfield code defined for this flexfield in the Register Descriptive Flexfield form (for example, FND_DFF1).
-
-
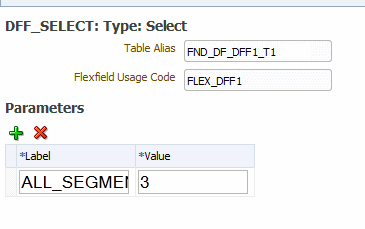
Enter the flexfield details:
-
Table Alias - Specify the table alias to prefix to the column names. Use TABLEALIAS if your SELECT joins to other flexfield tables or uses a self-join.
-
Flexfield Usage Code - (Optional) Identifies for which segments this data is requested. Default value is "ALL".
-
-
If your descriptive flexfield definition includes parameters, you can enter the parameters in the Parameters region.
To enter parameters, click + to add each parameter. Enter a Label and a Value for each parameter. The Label must match exactly the label in the descriptive flexfield definition.
6.3.1 Including Descriptive Flexfield Reference in SQL Queries
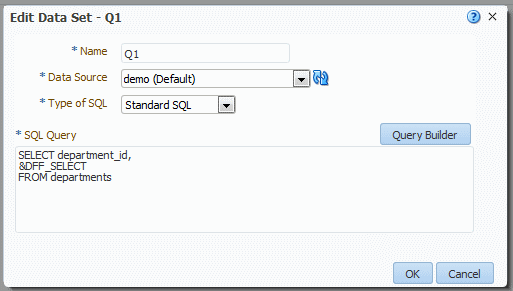
When you create the SQL data set, include the descriptive flexfield using the ampersand symbol, for example:
&DFF_SELECT
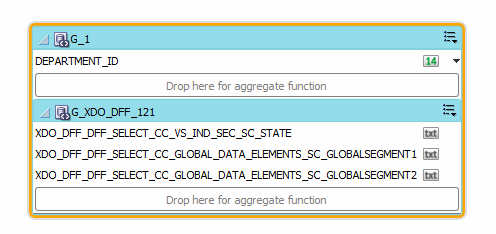
an example is shown in Figure 6-5.
When you click OK, the diagram of your data set shows the columns that are returned from your descriptive flexfield as shown in Figure 6-6.
The columns that are returned from the key flexfield have the following limitations:
-
Element properties are disabled
-
In the data model Structure tab, you cannot edit the following fields: XML Tag Name, Value if Null, Display Name, Data Type
-
Subgrouping of descriptive flexfield elements is not supported
-
Element linking is not supported