2 Modeling Approach and Methodology
This chapter discusses Oracle's approach to business process modeling and analysis, and explains the methodology and organization of process models.
This chapter includes the following sections:
2.1 Oracle's Approach to Business Process Modeling and Analysis (BPA)
Oracle combines the business view of the business analyst with a glimpse of the technical view of the technical analyst. A standard modeling method is used with technical artifacts added to the models at the lowest level of decomposition.
2.2 Methodology and Organization
Oracle uses accepted standard modeling methods and notation and adds Oracle-specific information on the most detailed level of the models. Oracle models:
-
Use horizontal, role-based swimlane workflow modeling method based on the Rummler-Brache diagramming technique.
-
Are BPMN-compliant at the lowest level.
-
Include both human and system lanes.
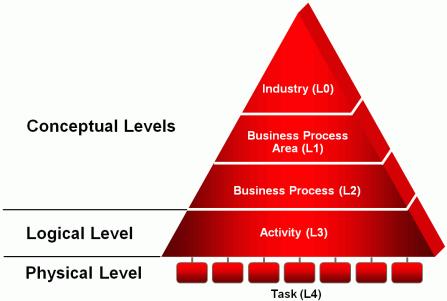
Oracle has organized its model content using four levels of hierarchical decomposition as shown in Figure 2-1.
-
The top three levels are conceptual.
-
The conceptualization of SOA services can be observed on the third level.
-
The fourth level is implementation-specific.
-
Process integration points and AIA artifacts appear on lowest level.
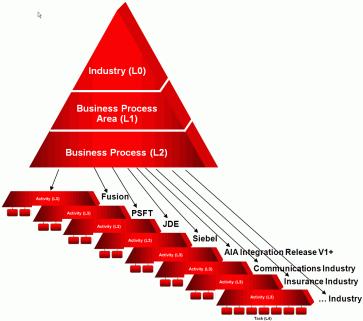
Oracle has created many sets of the lowest level models that correspond to particular implementation solutions, as shown in Figure 2-2. AIA provides solutions that join together pieces of application functionality between two or more Oracle product families.
Oracle has also created industry-specific variations of their models for many of the industries that Oracle supports.
Oracle creates and delivers the following types of models:
-
Reference Process Models (RPMs): horizontal, functionally scoped business process models that depict all of the aspects of the processes supporting a particular function (Marketing, Sales, and Order Fulfillment, for example).
-
Industry Reference Process Models: industry-specific business process models that combine industry processes with relevant horizontal processes and variations of horizontal processes.
-
Composite Business Flows: end-to-end processes that are comprised of parts of several functional business processes (Order to Cash, Procure to Pay, and Design to Release, for example).
2.2.1 Authoritative and Guiding Sources for Industry Process Best Practices
The TeleManagement Forum enhanced Telecom Operations Map® (eTOM®) was used as a reference to frame the conceptual levels of the Communications industry business process models.
Oracle continues to determine current external best practice and governing sources and uses them as references to frame and influence our business process models, including:
-
Supply Chain Council (SCOR).
-
Value-Chain Group (VCG).
-
Federal Enterprise Architecture Business Reference Model (FEA).
-
Other external industry best practice sources.