The single table inheritance strategy results in a single table containing records for two or more different classes in an inheritance hierarchy. Similarly, using the joined strategy results in the superclass table holding records for superclass instances as well as for the superclass state of subclass instances. When selecting data, EJB needs a way to differentiate a row representing an object of one class from a row representing an object of another. That is the job of the discriminator column.
The discriminator column is always in the table of the base entity. It holds a different value for records of each class, allowing the EJB persistence runtime to determine what class of object each row represents.
The DiscriminatorColumn annotation represents
a discriminator column. It has these properties:
String name: The column name. Defaults toDTYPE.length: For string discriminator values, the length of the column. Defaults to 31.String columnDefinition: This property has the same meaning as thecolumnDefinitionproperty on theColumnannotation, described in Section 12.3, “Column”.DiscriminatorType discriminatorType: Enum value declaring the discriminator strategy of the hierarchy.
The corresponding XML element is
discriminator-column.
Its attribues mirror the annotation properties above:
namelengthcolumn-definitiondiscriminator-type: One ofSTRING,CHAR, orINTEGER.
The DiscriminatorValue annotation specifies the
discriminator value for each class. Though this annotation's value is
always a string, the implementation will parse it according to the
DiscriminatorColumn's discriminatorType
property above. The type defaults to
DiscriminatorType.STRING, but may be
DiscriminatorType.CHAR or
DiscriminatorType.INTEGER. If you do not specify a
DiscriminatorValue, the provider will choose an
appropriate default.
The corresponding XML element is discriminator-value.
The text within this element is parsed as the discriminator value.
![[Note]](img/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
Kodo assumes your model employs a discriminator column if any of the following are true:
Only Kodo defines additional discriminator strategies; see Section 7.7, “Additional JPA Mappings” in the Reference Guide for details. Kodo also supports final entity classes. Kodo does not use a discriminator on final classes. |
We can now translate our newfound knowledge of EJB discriminators into concrete EJB mappings. We first extend our diagram with discriminator columns:
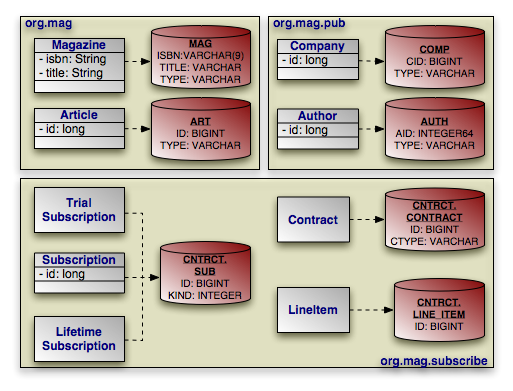
Next, we present the updated mapping document. Notice that in this
version, we have removed explicit inheritance annotations when the
defaults sufficed. Also, notice that entities using the default
DTYPE discriminator column mapping do not need an
explicit DiscriminatorColumn annotation.
Example 12.9. Discriminator Mapping
package org.mag;
@Entity
@IdClass(Magazine.MagazineId.class)
@Table(name="MAG")
@DiscriminatorValue("Mag")
public class Magazine
{
@Column(length=9)
@Id private String isbn;
@Id private String title;
...
public static class MagazineId
{
...
}
}
@Entity
@Table(name="ART", uniqueConstraints=@Unique(columnNames="TITLE"))
@SequenceGenerator(name="ArticleSeq", sequenceName="ART_SEQ")
public class Article
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator="ArticleSeq")
private long id;
...
}
package org.mag.pub;
@Entity
@Table(name="COMP")
public class Company
{
@Column(name="CID")
@Id private long id;
...
}
@Entity
@Table(name="AUTH")
public class Author
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.TABLE, generator="AuthorGen")
@TableGenerator(name="AuthorGen", table="AUTH_GEN", pkColumnName="PK",
valueColumnName="AID")
@Column(name="AID", columnDefinition="INTEGER64")
private long id;
...
}
@Embeddable
public class Address
{
...
}
package org.mag.subscribe;
@MappedSuperclass
public abstract class Document
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
...
}
@Entity
@Table(schema="CNTRCT")
@Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.JOINED)
@DiscriminatorColumn(name="CTYPE")
public class Contract
extends Document
{
...
}
@Entity
@Table(name="SUB", schema="CNTRCT")
@DiscriminatorColumn(name="KIND", discriminatorType=DiscriminatorType.INTEGER)
@DiscriminatorValue("1")
public class Subscription
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
...
@Entity
@Table(name="LINE_ITEM", schema="CNTRCT")
public static class LineItem
extends Contract
{
...
}
}
@Entity(name="Lifetime")
@DiscriminatorValue("2")
public class LifetimeSubscription
extends Subscription
{
...
}
@Entity(name="Trial")
@DiscriminatorValue("3")
public class TrialSubscription
extends Subscription
{
...
}
The same metadata expressed in XML:
<entity-mappings xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm orm_1_0.xsd"
version="1.0">
<mapped-superclass class="org.mag.subscribe.Document">
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<generated-value strategy="IDENTITY"/>
</id>
...
</attributes>
</mapped-superclass>
<entity class="org.mag.Magazine">
<table name="MAG"/>
<id-class="org.mag.Magazine.MagazineId"/>
<discriminator-value>Mag</discriminator-value>
<attributes>
<id name="isbn">
<column length="9"/>
</id>
<id name="title"/>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.Article">
<table name="ART">
<unique-constraint>
<column-name>TITLE</column-name>
</unique-constraint>
</table>
<sequence-generator name="ArticleSeq" sequence-name="ART_SEQ"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<generated-value strategy="SEQUENCE" generator="ArticleSeq"/>
</id>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.pub.Company">
<table name="COMP"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<column name="CID"/>
</id>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.pub.Author">
<table name="AUTH"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<column name="AID" column-definition="INTEGER64"/>
<generated-value strategy="TABLE" generator="AuthorGen"/>
<table-generator name="AuthorGen" table="AUTH_GEN"
pk-column-name="PK" value-column-name="AID"/>
</id>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.subcribe.Contract">
<table schema="CNTRCT"/>
<inheritance strategy="JOINED"/>
<discriminator-column name="CTYPE"/>
<attributes>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.subcribe.Subscription">
<table name="SUB" schema="CNTRCT"/>
<inheritance strategy="SINGLE_TABLE"/>
<discriminator-value>1</discriminator-value>
<discriminator-column name="KIND" discriminator-type="INTEGER"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<generated-value strategy="IDENTITY"/>
</id>
...
</attributes>
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.subscribe.Subscription.LineItem">
<table name="LINE_ITEM" schema="CNTRCT"/>
<primary-key-join-column name="ID" referenced-column-name="PK"/>
...
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.subscribe.LifetimeSubscription" name="Lifetime">
<discriminator-value>2</discriminator-value>
...
</entity>
<entity class="org.mag.subscribe.TrialSubscription" name="Trial">
<discriminator-value>3</discriminator-value>
...
</entity>
</entity-mappings>