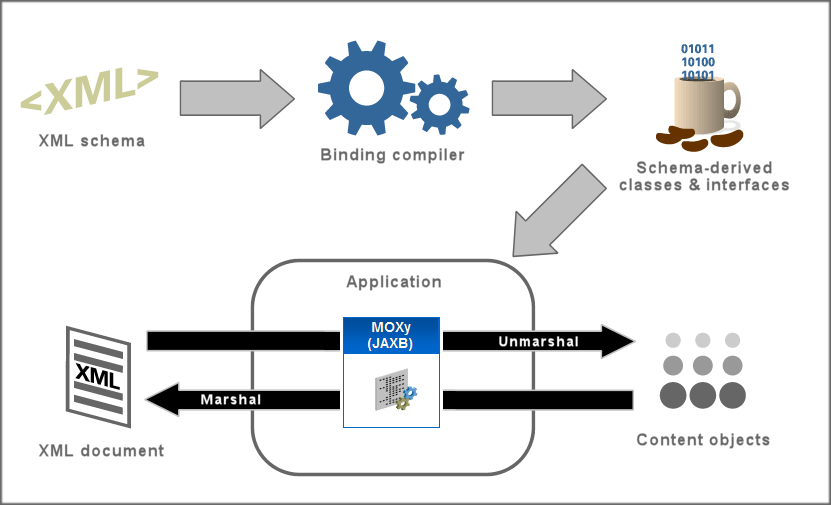
1 Introduction
JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding – JSR 222) is the standard for XML Binding in Java. JAXB covers 100% of XML Schema concepts and EclipseLink provides a JAXB implementation with many extensions. See http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=222 for complete information on the JAXB specification.
Oracle TopLink includes EclipseLink, and its JAXB provider: EclipseLink MOXy.
The EclipseLink MOXy component enables developers to efficiently bind Java classes to XML schemas and JSON documents. MOXy implements JAXB, allowing developers to provide their mapping information through annotations as well as providing support for storing the mappings in XML and JSON formats.
This chapter includes the following topics:
1.1 About EclipseLink MOXy
When using EclipseLink MOXy as the JAXB provider, no metadata is required to convert your existing object model to XML or JSON. You can supply metadata (using annotations, XML, or JSON) only when fine-tuning of the XML or JSON representation is required.
EclipseLink MOXy includes many advanced mappings that allows you to handle complex XML structures without having to mirror the schema in the Java class model.
1.2 Solving Object-XML Impedance Mismatch
Although XML is a common format for the exchange of data, for many applications objects are the preferred programmatic representation – not XML. In order to work at the object-level, the XML data needs to be converted to object form. The mismatch between XML and objects is known as object-xml impedance mismatch.
JAXB allows you to interact with XML data by using domain-like objects. Unlike DOM objects, the JAXB content model provides insight into the XML document based on the XML schema. For example, if the XML schema defines XML documents that contain customer information, your content model will contain objects such as Customer, Address, and PhoneNumber. Each type in the XML schema will have a corresponding Java class.
With EclipseLink MOXy (included with TopLink), you can efficiently bind Java classes to XML schemas or JSON documents. MOXy implements JAXB by allowing you to provide mapping information through annotations as well as storing the mappings in XML or JSON. By using these mappings, you can manage complex XML structures without having to mirror the schema in your Java class model.
1.3 About This Documentation
Oracle TopLink includes EclipseLink, the reference implementation of the Java Persistence (JPA) specification, as its persistence provider. It also includes many enhancements and extensions.
1.3.1 Other Resources
For more information, see:
-
Oracle TopLink on the Oracle Technology Network (OTN).
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/toplink/overview/index.html -
EclipseLink documentation center
http://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/documentation/ -
The EclipseLink API reference documentation (Javadoc) for complete information on core JAXB plus the EclipseLink enhancements
http://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/api/ -
Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB) specification
http://www.jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=222 -
Examples that display the use of a number of JAXB and EclipseLink MOXy features
http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink/Examples/MOXy -
JAXB Tutorial
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/javase/index-140168.html