4 Creating the Source Files for an ADF Skin
This chapter describes how to create the source files for an ADF skin in the ADF Skin Editor and in JDeveloper. Information on how to open an application or project in the ADF Skin Editor that was created in a prior release of JDeveloper and how to import an ADF skin from an ADF Library JAR file is also provided.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.2, "Creating ADF Skin Applications and ADF Skin Projects"
-
Section 4.4, "Importing One or More ADF Skins Into the Current ADF Skin"
-
Section 4.6, "Opening an Application Created Outside of the ADF Skin Editor"
4.1 About Creating an ADF Skin
An ADF skin defines the properties for the selectors that ADF Faces and ADF Data Visualization components expose. Using the editor in JDeveloper or the ADF Skin Editor, you can create a source file for an ADF skin. As a source file for an ADF skin is a type of CSS file, you could create it without using an editor. However, when you use the editor, associated configuration files get created (the first time that you create an ADF skin) or modified (when you create subsequent ADF skins). For more information about these configuration files, see Section 12.2, "Configuration Files for an ADF Skin."
4.2 Creating ADF Skin Applications and ADF Skin Projects
New ADF skin applications and ADF skin projects can be created in the ADF Skin Editor.
4.2.1 How to Create an ADF Skin Application
This section describes how to create an ADF skin application and a project within the application in the ADF Skin Editor.
To create a new ADF skin application:
-
From the main menu, choose File > New > ADF Skin Application.
-
In the Create ADF Skin Application dialog, enter application details like the name and directory. For help with the wizard, press F1.
-
Click Next to open the ADF Skin Project page where you specify the name of your ADF skin project and the directory to store it.
-
In the Target Application Release list, select the release of Oracle ADF that the application you want to skin uses.
The ADF Skin Editor configures your ADF skin project appropriately for the release you specify. For example, the ADF Skin Editor filters the list of ADF skins that you can extend from, as described in Section 4.3.1, "How to Create an ADF Skin in the ADF Skin Editor." The ADF Skin Editor also filters the list of skin selectors to display only those that the release you target supports. It will not display a skin selector introduced in a later release if you target your ADF skin project at an earlier release.
-
When you are done, click Finish.
4.2.2 How to Create a New ADF Skin Project
You use the Applications window to keep track of the ADF skin projects (collections of source files for ADF skins, images, and related files) you use while developing your ADF skin application.
You can create a new empty ADF skin project in an ADF skin application.
All ADF skin projects inherit the settings specified in the Default Project Properties dialog. As soon as you create the ADF skin project, it is added to the active ADF skin application.
To create a new ADF skin project:
-
In the Applications window, select the ADF skin application within which the project will appear.
-
Open the Create ADF Skin Project dialog by choosing File > New > ADF Skin Project.
-
In the Create ADF Skin Project dialog, enter project details like the name and directory.
-
In the Target Application Release list, select the release of Oracle ADF that the application you want to skin uses.
The ADF Skin Editor configures your ADF skin project appropriately for the release you specify. For example, the ADF Skin Editor filters the list of ADF skins that you can extend from, as described in Section 4.3.1, "How to Create an ADF Skin in the ADF Skin Editor." The ADF Skin Editor also filters the list of skin selectors to display only those that the release you target supports. It will not display a skin selector introduced in a later release if you target your ADF skin project at an earlier release.
-
When you are done, click Finish.
The new ADF skin project appears in the Applications window. It inherits whatever default properties you have already set. To alter project properties for this project, either double-click the project node or right-click and choose Project Properties.
4.3 Creating an ADF Skin File
You can create an ADF skin file in the ADF Skin Editor or in JDeveloper that defines how ADF Faces and ADF Data Visualization components render at runtime. The ADF skin that you create must extend either one of the ADF skins that Oracle ADF provides or from an existing ADF skin that you created. The ADF skins that Oracle ADF provides vary in the level of customization that they define for ADF Faces and ADF Data Visualization components. For information about the inheritance relationship between the ADF skins that Oracle ADF provides, see Section 1.4, "Inheritance Relationship of the ADF Skins Provided by Oracle ADF." For information about the levels of customization in the ADF skins provided by Oracle ADF and for a recommendation about the ADF skin to extend, see Section 12.3, "ADF Skins Provided by Oracle ADF."
By default, the design and selectors editors in the ADF Skin Editor and in JDeveloper create ADF skins for the org.apache.myfaces.trinidad.desktop render kit. A render kit defines how ADF Faces components map to component tags that are appropriate for a particular client.
After you create an ADF skin, you can use the design editor and the other provided editors to modify the values for the selectors that the ADF Faces and ADF Data Visualization components expose. Otherwise, the ADF skin that you create defines the same appearance as the ADF skin from which it extends. For more information, see Chapter 5, "Working with Component-Specific Selectors."
If you create an ADF skin that extends from the Skyros or Fusion Simple families of ADF skins, you enable the design editor. This tab provides an overview pane where you can use controls to set properties for many frequently-used selectors. If the ADF skin that you create extends from the Fusion Simple family of ADF skins, you enable the images editor in addition to the design editor. The images editor provides extra functionality to manage the images associated with the Fusion Simple family of ADF skins. The images editor does not appear if your ADF skin extends from the Skyros family of ADF skins. For more information about using the images editor, see Section 6.5, "Working with the Images Editor." For more information about using the design editor, see Section 3.2, "Working with the ADF Skin Design Editor."
4.3.1 How to Create an ADF Skin in the ADF Skin Editor
You can create an ADF skin in the ADF Skin Editor.
To create an ADF skin in the ADF Skin Editor:
-
In the Applications window, right-click the project where you want to create the new ADF skin and choose New > ADF Skin File.
-
In the Skin File page of the Create ADF Skin dialog, enter the following:
-
File Name: Enter a file name for the new ADF skin.
-
Directory: Enter the path to the directory where you store the CSS source file for the ADF skin or accept the default directory proposed by the editor.
-
Family: Enter a value for the family name of your skin.
You can enter a new name or specify an existing family name. If you specify an existing value, you may need to version ADF skins, as described in Section 12.4, "Versioning ADF Skins," to distinguish between ADF skins that have the same value for family.
The value you enter is set as the value for the
<family>element in thetrinidad-skins.xmlwhere you register the ADF skin that you create. At runtime, the<skin-family>element in an application'strinidad-config.xmlfile uses this value to identify the ADF skin that an application uses. For more information, see Section 11.4, "Applying an ADF Skin to Your Web Application." -
Use as the default skin family for this project: Clear this checkbox if you do not want to make the ADF skin the default for your project immediately.
-
-
In the Base Skin page of the Create ADF Skin dialog, specify the following:
-
Show Latest Versions Only: Clear this checkbox to show all available versions of ADF skins.
-
Available Skins: Select the ADF skin that you want to extend. ADF Faces provides a number of ADF skins that you can extend. The list also includes any ADF skins that you created previously in this project. For more information and a recommendation on the ADF skin to extend, see Section 12.3, "ADF Skins Provided by Oracle ADF."
Note:
The value you select for Target Application Release, as described in Section 4.2, "Creating ADF Skin Applications and ADF Skin Projects," determines the list of ADF skins from which you can extend.
-
Skin Id: A read-only field that displays a concatenation of the value you enter in File Name and the ID of the render kit (
desktop) for which you create your ADF skin. You select this value from the Extends list if you want to create another ADF skin that extends from this one.The ADF Skin Editor writes the value to the
<id>element in thetrinidad-skins.xmlfile.
-
-
Click Finish.
4.3.2 How to Create an ADF Skin in JDeveloper
You can create an ADF skin in JDeveloper.
To create an ADF skin in JDeveloper:
-
In the Applications window, right-click the project that contains the code for the user interface and choose New.
-
In the New Gallery, expand Web Tier, select JSF/Facelets and then ADF Skin, and click OK.
-
In the Skin File page of the Create ADF Skin dialog, enter the following:
-
File Name: Enter a file name for the new ADF skin.
-
Directory: Enter the path to the directory where you store the CSS source file for the ADF skin or accept the default directory proposed by the editor.
-
Family: Enter a value for the family name of your skin.
You can enter a new name or specify an existing family name. If you specify an existing value, you may need to version ADF skins, as described in Section 12.4, "Versioning ADF Skins," to distinguish between ADF skins that have the same value for family.
The value you enter is set as the value for the
<family>element in thetrinidad-skins.xmlwhere you register the ADF skin that you create. At runtime, the<skin-family>element in an application'strinidad-config.xmlfile uses this value to identify the ADF skin that an application uses. For more information, see Section 11.4, "Applying an ADF Skin to Your Web Application." -
Use as the default skin family for this project: Deselect this checkbox if you do not want to make the ADF skin the default for your project immediately. If you select the checkbox, the
trinidad-config.xmlfile is updated, as described in Section 4.3.3, "What Happens When You Create an ADF Skin."
-
-
In the Base Skin page of the Create ADF Skin dialog, specify the following:
-
Show Latest Versions Only: Clear this checkbox to show all available versions of ADF skins.
-
Available Skins: Select the ADF skin that you want to extend. ADF Faces provides a number of ADF skins that you can extend. The list also includes any ADF skins that you created previously in this project. For more information and a recommendation on the ADF skin to extend, see Section 12.3, "ADF Skins Provided by Oracle ADF."
-
Skin Id: A read-only field that displays a concatenation of the value you enter in File Name and the ID of the render kit (
desktop) for which you create your ADF skin. You select this value from the Extends list if you want to create another ADF skin that extends from this one.JDeveloper writes the value to the
<id>element in thetrinidad-skins.xmlfile.
-
-
Click Finish.
4.3.3 What Happens When You Create an ADF Skin
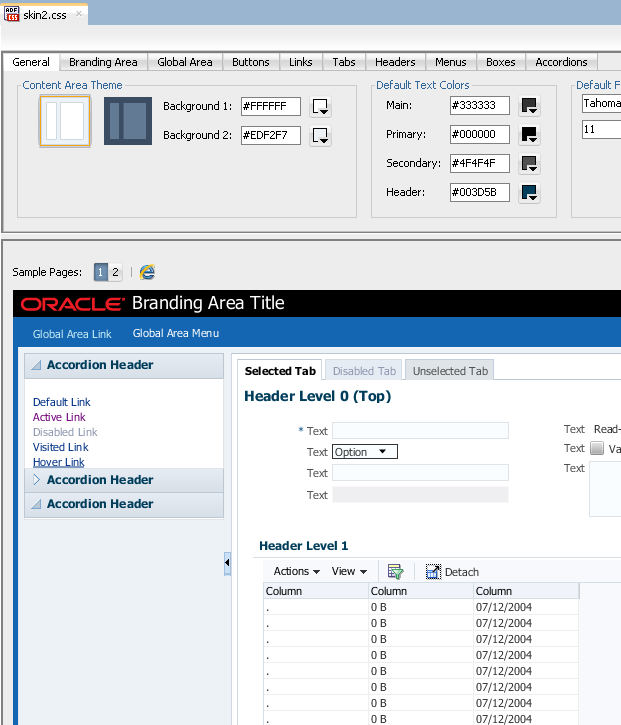
If you accepted the default value proposed for the Directory field, a file with the extension .css is generated in a subdirectory of the skins directory in your project. An ADF skin that extends the Fusion Simple or Skyros family of ADF skins opens in the design editor, as illustrated in Figure 4-1.
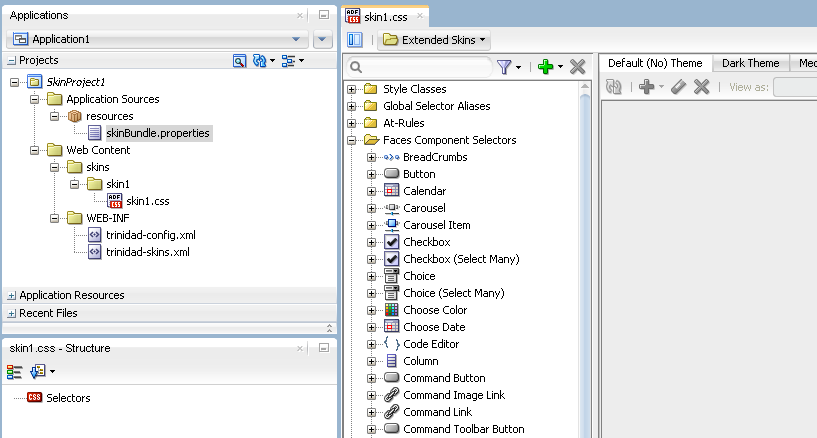
An ADF skin that extends an ADF skin not from the Skyros or Fusion Simple families of ADF skin opens in the selectors editor, as illustrated in Figure 4-2. This selectors editor is also available if you create an ADF skin that extends from the Skyros or Fusion Simple family of ADF skin.
The trinidad-skins.xml file is modified to include metadata for the ADF skin that you create, as illustrated in Example 4-1, which shows entries for an ADF skin that extends from the Skyros family of ADF skins. Example 4-1 also contains values that specify the render kit and the resource bundle associated with this ADF skin. For more information about resource bundles, see Chapter 7, "Working With Text in an ADF Skin."
Example 4-1 trinidad-skins.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252"?>
<skins xmlns="http://myfaces.apache.org/trinidad/skin">
....
<skin>
<id>skin2.desktop</id>
<family>skin2</family>
<extends>skyros-v1.desktop</extends>
<render-kit-id>org.apache.myfaces.trinidad.desktop</render-kit-id>
<style-sheet-name>skins/skin2/skin2.css</style-sheet-name>
<bundle-name>resources.skinBundle</bundle-name>
</skin>
</skins>
If you select the Use as the default skin family for this project check box in the Create ADF Skin dialog, the trinidad-config.xml file is modified to make the new ADF skin the default skin for your application. This means that if you run the application from JDeveloper, the application uses the newly-created ADF skin. For more information, see Section 11.4, "Applying an ADF Skin to Your Web Application." Example 4-2 shows a trinidad-config.xml file that makes the ADF skin in Example 4-1 the default for an application.
Example 4-2 trinidad-config.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252"?> <trinidad-config xmlns="http://myfaces.apache.org/trinidad/config"> <skin-family>skin2</skin-family> </trinidad-config>
The source file for the ADF skin contains a comment and namespace references, as illustrated in Example 4-3. These entries in the source file for the ADF skin distinguish the file from non-ADF skin files with the .css file extension. A source file for an ADF skin requires these entries in order to open in the design or selectors editors for the ADF skin.
Example 4-3 Default Entries for a Newly-Created ADF Skin File
/**ADFFaces_Skin_File / DO NOT REMOVE**/ @namespace af "http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/rich"; @namespace dvt "http://xmlns.oracle.com/dss/adf/faces";
The first time that you create an ADF skin in your project, a resource bundle file (skinBundle.properties) is generated, as illustrated in Figure 4-2. For more information about using resource bundles, see Chapter 7, "Working With Text in an ADF Skin."
4.4 Importing One or More ADF Skins Into the Current ADF Skin
You can import another ADF skin that is in your ADF skin project into your ADF skin using the @import rule. This makes the style properties defined in the latter ADF skin available to your ADF skin. The following examples demonstrate the valid syntax to import an ADF skin (skinA) into the current ADF skin:
/** Use the following syntax if skinA.css is in the same directory **/
@import "skinA.css";
@import url("skinA.css");
/** Use the following syntax if skinA.css is in another directory **/
@import "../skinA/skinA.css";
@import url("../skinA/skinA.css");
The @import rule(s) must follow all @charset rules and precede all other at-rules and rule sets in an ADF skin, as shown in the following example that imports two ADF skins into the current ADF skin:
@charset "UTF-8";
@import url("../skinA/skinA.css");
@import url("../skinB/skinB.css");
/**ADFFaces_Skin_File / DO NOT REMOVE**/
@namespace af "http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/rich";
@namespace dvt "http://xmlns.oracle.com/dss/adf/faces";
af|inputText{
background-color: Green;
}
...
4.5 Importing ADF Skins from an ADF Library JAR
You can import ADF skins that have been packaged in a JAR file into your ADF skin project. When you import an ADF skin from a JAR file into your project, the imported ADF skin is available to extend from when you create a new ADF skin, as described in Section 4.3, "Creating an ADF Skin File."
The recommended type of JAR file to use to package an ADF skin is an ADF Library JAR file. For information about how to package an ADF skin into this type of JAR file, see Section 11.3, "Packaging an ADF Skin into an ADF Library JAR."
4.5.1 How to Import an ADF Skin from an ADF Library JAR
You can import ADF skins into your project that have been packaged in a JAR file.
To import an ADF skin from an ADF Library JAR:
-
From the main menu, choose Application > Project Properties.
-
In the Project Properties dialog, select the Libraries and Classpath page and click Add JAR/Directory.
-
In the Add Archive or Directory dialog, navigate to the JAR file that contains the ADF skin you want to import and click Select.
The JAR file appears in the Classpath Entries list.
-
When finished, click OK.
4.5.2 What Happens When You Import an ADF Skin from an ADF Library JAR
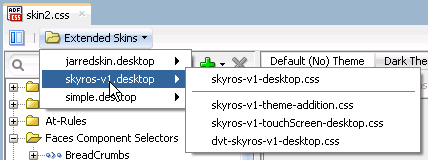
The ADF skin(s) that you import from the JAR file appear in the Extends list when you create a new ADF skin, as described in Section 4.3, "Creating an ADF Skin File." After you create a new ADF skin by extending an ADF skin that you imported from a JAR file, the Extended Skins list in the selectors editor's Preview Pane displays the name of the ADF skin that you imported. For example, in Figure 4-3 the skin2.css ADF skin has been created by extending the ADF skin, jarredskin.css, that was imported into the project from a JAR file.
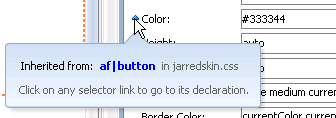
Properties that have been defined in the ADF skin that you imported appear with a blue upward pointing arrow in the Properties window. An information tip about the inheritance relationship displays when you hover the mouse over the property, as illustrated in Figure 4-4.
4.6 Opening an Application Created Outside of the ADF Skin Editor
When you open an application or project that was created in a prior release of JDeveloper, the ADF Skin Editor prompts you to migrate the project to JDeveloper 12c format. Depending on the content of the project, the ADF Skin Editor may display additional prompts to migrate some specific source files as well. Oracle recommends that you make a backup copy of your projects before you open them in the ADF Skin Editor or migrate them using the ADF Skin Editor.