3 Configuring EDQ Case Management
This chapter describes how to configure EDQ to use Case Management.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Case Management supports the manual investigation of results from data quality processes. Using Case Management, privileged users can manage and review matching results using highly configurable workflows.
The complete set of Case Management extended attributes that are used on an EDQ server are configured in the flags.xml file in the oedq_local_home/casemanagement directory. This file must be modified to add new extended attributes, and to define rules for how these attributes are populated.
An additional property file named flags.properties accompanies the base flags.xml file and specifies the labels for the extended attributes as they will appear in the graphical user interface (GUI). The settings in this file may be overridden for a specific client language by the creation of additional property files with an ISO 639-1 language code, such as flags_en.properties (for English) or flags_de.properties (for German). This language code is described at the ISO website found at http://www.iso.org/iso/home/standards/language_codes.htm.
If Oracle Watchlist Screening is installed, these files may already exist.
To ensure that Case Management publication works correctly, the flags.xml file is overwritten whenever a Case Source is imported using the Case Management Administration application. This is because Case Sources have a dependency on the format of the flags.xml file and requires the flags to be indexed and specified in the same way as on the server where the Case Source was defined. Oracle recommends that you back up the file before importing a Case Source in case there are any existing extended attributes in the flags.xml file on the server that need to be re-added once the import is complete.
3.1 Understanding and Adding Extended Attributes
This section describes the different types of extended attributes and how to add them for use in Case Management.
3.1.1 Default Extended Attributes
In an initial EDQ installation, the flags.xml file contains the following two extended attribute (flag) example definitions:
<f:flag index="1" label="%escalation" type="boolean" default="false" notnull="true"/>
<f:flag index="2" label="%priority.score" type="number" readonly="true"/>
Note:
The order in which these properties appear in each line may not match this example. The order of properties is immaterial. Also, if Oracle Watchlist Screening is installed, the contents of theflags.xml file is different.3.1.2 Adding New Extended Attributes
To add a new extended attribute, add a line immediately after the existing attribute definitions in the flags.xml file, following the same syntax as the existing lines and using the following notes for each property:
| Property | Allowed Values | Notes |
|---|---|---|
index |
Integer | Must be unique for each entry in the file |
label |
Any | The% character is used to indicate that the label for the UI should be retrieved from the flags.properties file for the client locale. If the% character is not used, the label will always be exactly as stated (in all languages). |
type |
number, boolean, or string |
Controls the data type of the column. |
readonly |
true or false |
Controls whether or not privileged users can edit the value of the extended attribute when editing a Case or Alert |
notnull |
true or false |
Controls whether or not Null values are allowed in the extended attribute. If this is undefined, Null values are allowed (the same as the 'false' setting). |
default |
Any permissible value | Sets the default value of the extended attribute if not set to a specific value. |
There is a character limit of 80 characters for extended attributes with a type of 'string'. Values longer than this cannot be inserted as values.
3.2 Configuring Data Entry Validation
You can restrict the format of user-specified data for an extended attribute. The restriction is checked when users edit extended attributes in the Case Management GUI, and when defining possible values to set for an extended attribute in the Workflow editor in Case Management Administration.
The restriction is not checked when cases and alerts are written to Case Management from a process, so it is possible to write invalid values into an extended attribute. The invalid values will appear in error, with an appropriate error message. This designed behavior protects the system against unnecessary job failure.
Restrictions are defined as part of the flags.xml file. There are two types of possible restrictions:
-
Predefined list means that the data to be written is checked against a predefined list of allowed values.
-
Regular expression means that the data to be written is checked against a regular expression.
3.2.1 Checking Predefined List Restrictions
To check that the data being entered into the extended attribute matches a predefined list of possible values, add XML elements in the following format after the definition of the extended attribute (flag):
<f:restrictions> <f:predefined> <f:value>first value</f:value> <f:value>second value</f:value> <f:value>third value</f:value> </f:predefined> </f:restrictions> </f:flag>
For example, the following XML fragment defines a custom 'Status' extended attribute that allows only the values 'active' and 'inactive':
<f:flag index="6" label="Status" type="string" readonly="false"> <f:restrictions> <f:predefined> <f:value>active</f:value> <f:value>inactive</f:value> </f:predefined> </f:restrictions> </f:flag>
The extended attribute appears with a list of the valid values in the Case Management Edit Case (or Edit Alert) dialog:
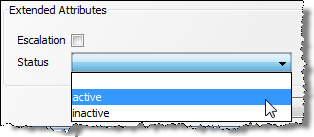
Description of the illustration ''ext_attr_picklist.png''
Tip:
In this case, the user can specify a Null value for theStatus field (as a 'notnull' condition was not set).3.2.2 Checking Regular Expression Restriction
To check that data being entered into the extended attribute matches a regular expression, add XML elements in the following format after the definition of the extended attribute (flag):
<f:restrictions> <f:regex ignorecase="false" matchby="w"> <f:value></f:value> </f:regex> </f:restrictions>
Where: the value property defines the regular expression, and the ignorecase and matchby properties defines how it is matched. The possible values for the matchby condition are as follows:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
w |
WHOLE - The whole value must match the Regular Expression. |
s |
STARTS - The beginning of the value must match the Regular Expression. |
e |
ENDS - The end of the value must match the Regular Expression. |
c |
CONTAINS - The value must contain a string that matches the Regular Expression. |
For example, the following XML fragment defines a custom 'National ID' extended attribute that allows only values in the format NN-NN-NNN (2 digits, hyphen, 2 digits, hyphen, 3 digits):
<f:flag index="7" label="National ID" type="string" readonly="false" notnull="true">
<f:restrictions>
<f:regex ignorecase="false" matchby="w">
<f:value>\d{2}-\d{2}-\d{3}</f:value>
</f:regex>
</f:restrictions>
</f:flag>
The following shows the error message displayed when a user attempts to add a value that does not match the regular expression:
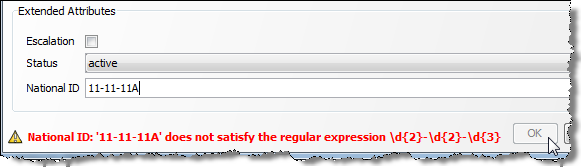
Description of the illustration ''ext_attr_regex.png''
It is also possible to customize this error message with the errormessage attribute. Either enter a simple text string to be displayed as the error message, or begin the string with a percent (%) symbol to direct the application to look in the flags.properties file for a localized value.
For example, the following XML fragment causes the e1.message error message to be retrieved from the flags.properties file when an error occurs:
<f:restrictions><f:regex ignorecase="false" matchby="w" errormessage="%e1.message"><f:value>\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}</f:value></f:regex></f:restrictions>
3.3 Understanding Case Management Configuration Properties
This section lists the main parameters in director.properties that are used to configure Case Management.
| Parameter | Description0 |
|---|---|
case.management.fail.on.long.flags |
This property controls the Case Management behavior when flag values that are longer than 80 characters are generated. If this property is set to true, the process will generate an error and will stop. If it is set to false, long flag values will be truncated and a warning will be written to the log file. This property is set to false by default. |
cm.index.queue.limit |
This property controls the maximum size of the index queue limit. |
index.directory |
This property allows an absolute path for the Lucene index directories to be configured. By default, the index directories are always created within the localhome directory. In some circumstances, these directories can become very large, and storing them in a separate location may facilitate better management of disk space. |