5 Configuring the Application Navigation
This chapter describes how to configure application navigation using the MAF application's springboard and navigation bar.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 5.1, "Introduction to the Display Behavior of MAF Applications"
-
Section 5.3, "What Happens When You Configure the Navigation Options"
-
Section 5.4, "What Happens When You Set the Animation for the Springboard"
-
Section 5.7, "What You May Need to Know About the Runtime Springboard Behavior"
-
Section 5.8, "Creating a Sliding Window in a MAF Application"
5.1 Introduction to the Display Behavior of MAF Applications
You can configure the mobile application to control the display behavior of the springboard and the navigation bar in the following ways:
-
Hide or show the springboard and navigation bar to enable the optimal usage of the mobile device's real estate. These options override the default display behavior for the navigation bar, which is shown by default unless otherwise specified by the application feature.
-
Enable the springboard to slide from the right. By default, the springboard does not occupy the entire display, but instead slides from the left, pushing the active content (which includes the navigation bar's Home button and application features) to the right.
5.2 Configuring Application Navigation
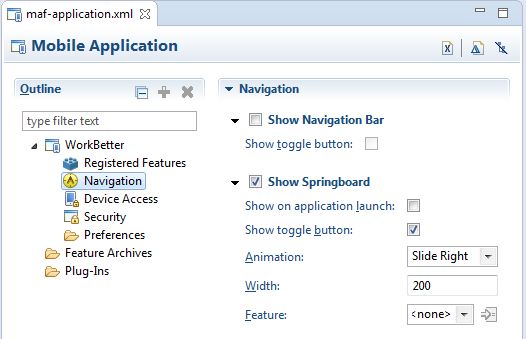
The Navigation options of the Applications page, shown in Figure 5-1, enable you to hide or show the navigation bar, select the type of springboard used by the application, and define how the springboard reacts when users page through applications.
You must select MAF Application Editor from assembly project > MAF in the Project Explorer to open maf-application.xml.
To set the display behavior for the navigation bar:
-
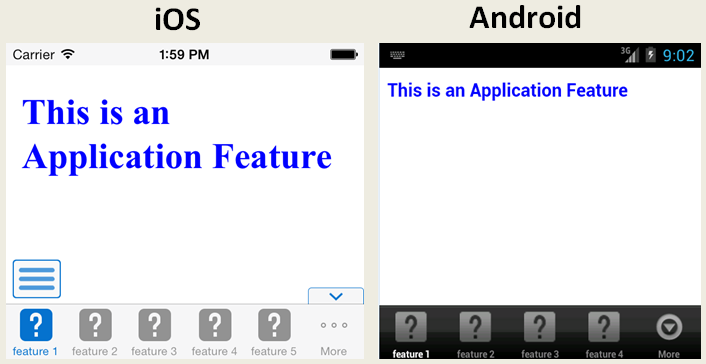
Select Show Navigation Bar to enable the mobile application to display its navigation bar (instead of the springboard), by default, as shown in Figure 5-2.
If you deselect Show Navigation Bar, then you hide the navigation bar when the application starts, presenting the user with the springboard as the only means of navigation. Because the navigation bar serves the same purpose as the springboard, hiding it can, in some cases, remove redundant functionality.
-
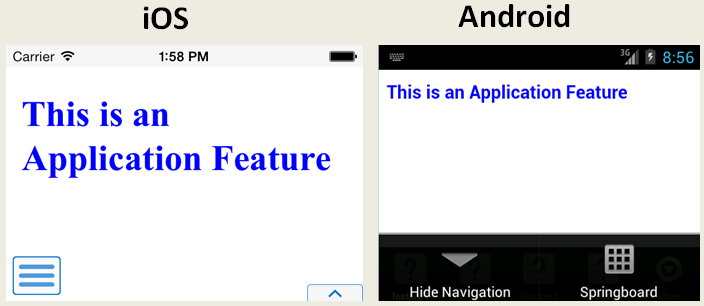
Select Show toggle button to hide the navigation bar when the content of a selected application feature is visible. Figure 5-3 illustrates this option, showing how the navigation bar illustrated in Figure 5-2 becomes hidden by the application feature content.
This option is selected by default; the navigation bar is shown by default if the show or hide state is not specified by the application feature.
To set the display behavior for the springboard:
-
To display the springboard select Show Springboard. This is selected by default.
-
Select Show on application launch to enable the mobile application to display the springboard to the end user after the mobile application has been launched.
-
Select Show Springboard Toggle Button to enable the display of the springboard button, shown in Figure 5-4, that displays within an application feature. Figure 5-2 shows this button within the context of an application feature.
To set the slide out behavior for the springboard:
-
Select
Slide Rightfor Animation. The springboard occupies an area determined by the number of pixels (or the percent) entered for the Width option. If you select<none>, then the springboard cannot slide from the right (that is, MAF does not provide the animation to enable this action). The springboard takes the entire display area. -
Set the width (in pixels). The default width of a springboard on an iOS-powered device is 320 pixels. On Android-powered devices, the springboard occupies the entire screen by default, thereby taking up all of the available width.
Note:
If the springboard does not occupy the entire area of the display, then an active application feature occupies the remainder of the display. For more information, see Section 5.4, "What Happens When You Set the Animation for the Springboard."
5.3 What Happens When You Configure the Navigation Options
Setting the springboard and navigation bar options updates or adds elements to the maf-application.xml file's <adfmf:navigation> element. For example, selecting None results in the code updated with <springboard enabled="false"> as illustrated below.
<adfmf:application>
...
<adfmf:navigation>
<adfmf:navigationBar enabled="true"/>
<adfmf:springboard enabled="false"/>
</adfmf:navigation>
</adfmf:application>
Tip:
By default, the navigation bar is enabled, but the springboard is not. If you update the XML manually, you can enable the springboard as follows:
<adfmf:application>
...
<adfmf:navigation>
<adfmf:springboard enabled="true"/>
</adfmf:navigation>
...
</adfmf:application>
The example below illustrates how the enabled attribute is set to true when you select Default.
Note:
Because the springboard fills the entire screen of the device, the navigation bar and the springboard do not appear simultaneously.
adfmf:application>
...
<adfmf:navigation>
<adfmf:navigationBar enabled="true"/>
<adfmf:springboard enabled="true"/>
</adfmf:navigation>
</adfmf:application>
5.4 What Happens When You Set the Animation for the Springboard
The example below shows the navigation block of the maf-application.xml file, where the springboard is set to slide out and occupy a specified area of the display (213 pixels).
<adfmf:navigation>
<adfmf:navigationBar enabled="true"
displayHideShowNavigationBarControl="true"/>
<!-- default interpretation of width is pixels -->
<adfmf:springboard enabled="true"
animation="slideright"
width="213"
showSpringbaordAtStartup="true"/>
</adfmf:navigation>
The following line disables the animation:
<adfmf:springboard enabled="true" animation="none"/>
The following line sets the springboard to occupy 100 pixels from the left of the display area and also enables the active application feature to occupy the remaining portion of the display:
<adfmf:springboard enabled="true" animation="slideright" width="100px"/>
In addition to the animation, the example above demonstrates the following:
-
The use of the
showSpringboardAtStartupattribute, which defines whether the springboard displays when the application starts. (By default, the springboard is displayed.) -
The use of the
navigationBar'sdisplayHideShowNavigationBarControlattribute.
To prevent the springboard from displaying, set the enabled attribute to false.
5.5 What You May Need to Know About Custom Springboard Application Features with HTML Content
The default HTML springboard page provided by MAF uses the following technologies, which you may also want to include in a customized login page:
-
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)—Defines the colors and layout.
-
JavaScript—The
<script>tag embedded within the springboard page contains references to the methods described in Chapter 16073296, "Local HTML and Application Container APIs" that call the Apache Cordova APIs. In addition, the HTML page uses JavaScript to respond to the callbacks and to detect page swipes. When swipe events are detected, JavaScript enables the dynamic modification of the style sheets to animate the page motions.A springboard authored in HTML (or any custom HTML page) can leverage the Apache Cordova APIs by including a
<script>tag that references thebase.jslibrary. You can determine the location of this library (or other JavaScript libraries) by first deploying an MAF application and then locating thewww/jsdirectory within platform-specific artifacts in thedeploydirectory. For an Android application, thewww/jsdirectory is located within the Android application package (.apk) file at:application workspace directory/deploy/deployment profile name/deployment profile name.apk/assets/www/js
For iOS, this library is located at:
application workspace directory/deploy/deployment profile name/temporary_xcode_project/www/js
For more information, see Section B.1, "Using MAF APIs to Create a Custom HTML Springboard Application Feature."
-
WebKit—Provides smooth animation of the icons during transitions between layouts as well as between different springboard pages. For more information on the WebKit rendering engine, see
http://www.webkit.org/.
Springboards written in HTML are application features declared in the maf-feature.xml file and referenced in the maf-application.xml file.
5.6 What You May Need to Know About Custom Springboard Application Features with MAF AMX Content
Like their HTML counterparts, springboards written using MAF AMX are application features that are referenced by the mobile application, as described in Section 4.2.1, "How to Designate the Content for a Mobile Application." Because a springboard is typically written as a single MAF AMX page rather than as a task flow, it uses the gotoFeature method, illustrated by the method expression in the example below, to launch the embedded application features.
Note:
A custom springboard page (authored in either HTML or MAF AMX) must reside within a view controller project which also contains themaf-feature.xml file. For more information, see Section 4.2.1, "How to Designate the Content for a Mobile Application."The default springboard (adfmf.default.springboard.jar) is an MAF AMX page that is bundled in a Feature Archive (FAR) JAR file and deployed with other FARs that are included in the mobile application. This JAR file includes all of the artifacts associated with a springboard, such as the DataBindings.cpx and PageDef.xml files. This file is only available after you select Default as the springboard option in the maf-application.xml file. Selecting this option also adds this FAR to the application classpath. For more information, see Section 27.3, "Deploying Feature Archive Files (FARs)."
The default springboard (springboard.amx, illustrated below) is implemented as an MAF AMX application feature.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<amx:view xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:amx="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf/amx"
xmlns:dvtm="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf/amx/dvt">
<amx:panelPage id="pp1">
<amx:facet name="header">
<amx:outputText value="#{bindings.name.inputValue}" id="ot3"/>
</amx:facet>
<amx:listView var="row"
value="#{bindings.features.collectionModel}"
fetchSize="#{bindings.features.rangeSize}"
id="lv1"
styleClass="amx-springboard">
<amx:listItem showLinkIcon="false"
id="li1"
actionListener="#{bindings.gotoFeature.execute}">
<amx:tableLayout id="tl1"
width="100%">
<amx:rowLayout id="rl1">
<amx:cellFormat id="cf11"
width="46px"
halign="center">
<amx:image source="#{row.image}"
id="i1"
inlineStyle="width:36px;height:36px"/>
</amx:cellFormat>
<amx:cellFormat id="cf12"
width="100%"
height="43px">
<amx:outputText value="#{row.name}"
id="ot2"/>
</amx:cellFormat>
</amx:rowLayout>
</amx:tableLayout>
<amx:setPropertyListener from="#{row.id}"
to="#{pageFlowScope.FeatureId}"/>
</amx:listItem>
</amx:listView>
</amx:panelPage>
</amx:view>
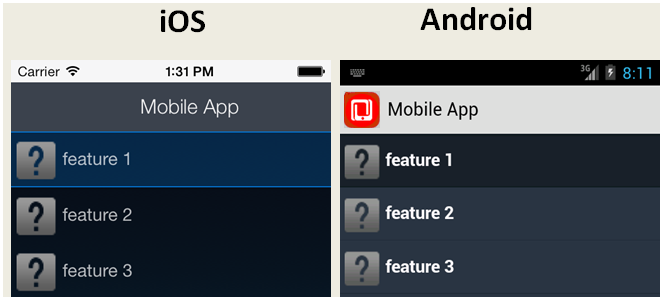
As shown in Figure 5-5, an MAF AMX file defines the springboard using a List View whose List Items are the mobile application's embedded application features. These application features, once deployed, are displayed by their names and associated icons. The gotoFeature method of the AdfmfContainerUtilities API provides the page's navigation functions. For a description of using this method to display a specific application feature, see Section B.2.6, "gotoFeature." See also Section 13.3.15, "How to Use List View and List Item Components."
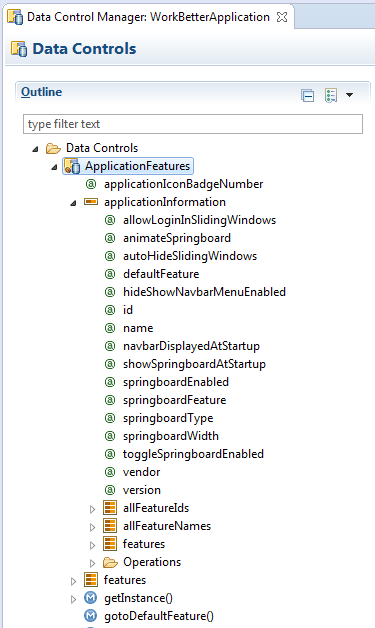
MAF provides the basic tools to create a custom springboard (or augment the default one) in the ApplicationFeatures data control. This data control, illustrated in Figure 5-6, enables you to declaratively build a springboard page using its data collections of attributes that describe both the mobile application and its application features. For an example of a custom springboard page, see the APIDemo sample application. For more information on this application (and other samples that ship with MAF), see Appendix G, "MAF Sample Applications."
The methods of the ApplicationFeatures data control enable you to add navigation functions. These adfmf.containerUtilities methods are described in Table 5-1. For more information, see Section B.2, "The MAF Container Utilities API." See also Chapter 14, "Using Bindings and Creating Data Controls in MAF AMX."
Table 5-1 ApplicationFeature Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Navigates to default application feature. |
|
|
Navigates to a specific application as designated by the parameter that is passed to this method. |
|
|
Navigates to the springboard. |
|
|
Hides the navigation bar. |
|
|
Displays the navigation bar (if it is hidden). |
|
|
Resets the application feature that is designated by the parameter passed to this method. |
5.7 What You May Need to Know About the Runtime Springboard Behavior
If you chose the Show on application launch option and defined the slideout width to full size of the screen, then MAF loads the default application feature in the background at startup. When the mobile application hibernates, MAF hides the springboard.
5.8 Creating a Sliding Window in a MAF Application
You can render an application feature as a sliding window. This makes the application feature display concurrently with the other application features that display within the navigation bar or springboard. You might use a sliding window to display content that is always present within the application, such as a global tool bar, or for temporary (pop-up) content, such as a help window.
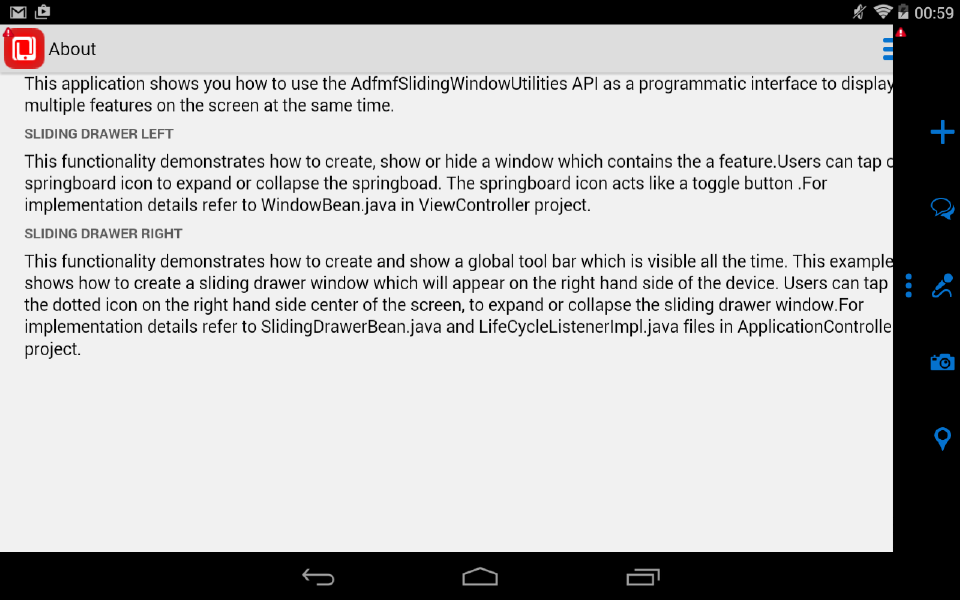
Figure 5-7 shows the SlidingDrawer application feature from the SlidingWindow sample application, described in Appendix G, "MAF Sample Applications." This application feature appears on the right of an application screen while overlaying other application features.
If you choose to render an application feature as a sliding window, you must set its Show on Navigation Bar and Show on Springboard properties to false.
You create a sliding window by invoking a combination of the oracle.adfmf.framework.api.AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions and AdfmfSlidingWindowUtilities classes, either from a managed bean or lifecycle listener within your application.
The example below demonstrates how the SlidingWindow sample application creates the sliding window shown in Figure 5-7 from the activate method of LifeCycleListenerImpl.java. After creating the sliding window, the SlidingWindow sample application uses SlidingDrawerBean.java to manage the display of the sliding window.
...
public void activate() {
// The argument you pass to the create method is the refId of the
// feature in the maf-application.xml. For example,
// <adfmf:featureReference id="fr4" refId="SlidingDrawer" showOnNavigationBar="false"
// showOnSpringboard="false"/>
String slidingWindowDrawer = AdfmfSlidingWindowUtilities.create("SlidingDrawer");
// Note also that both showOn... values must be set to false in the config
// file for the sliding window to appear
SlidingDrawerBean.slidingDrawerWindow=slidingWindowDrawer;
AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions options = new AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions();
options.setDirection(AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions.DIRECTION_RIGHT);
options.setStyle(AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions.STYLE_OVERLAID);
options.setSize("0");
}
For information about how to access the complete SlidingWindow sample application discussed here, see Appendix G, "MAF Sample Applications."
For more information about AdfmfSlidingWindowUtilities and AdfmfSlidingWindowOptions, see the Java API Reference for Oracle Mobile Application Framework. For more information about using lifecycle listeners, see Chapter 11, "Using Lifecycle Listeners in MAF Applications."