Release 9.0.1
Part Number A90150-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide Release 9.0.1 Part Number A90150-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to configure and use Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security for Secure Socket Layer (SSL) authentication. It contains the following topics:
A public-key infrastructure (PKI) includes various elements, such as a public key, bound into a digital certificate, a private key, and certain other security credentials. These credentials can be used for secure authentication over a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection, to establish a secure communication channel, and to generate and process digital certificates--including digital signatures. A complete PKI includes the following:
This section describes the PKI implementation provided by the following:
Oracle Advanced Security includes elements of a PKI, such as Oracle Wallet Manager, which creates and securely stores a user's public/private key pair, as well as the trust points (the list of root certificates the user trusts). The user's PKI credentials, stored in Oracle Wallet Manager, can be used to create a secure, authenticated session over SSL. However, Oracle Advanced Security does not provide certificate creation or certificate revocation status checking, which are important elements of a complete PKI.
For example, although Oracle Wallet Manager can generate a PKCS#10 certificate signing request, users must obtain certificate fulfillment from a certificate authority and load the resulting certificate into an Oracle wallet. Oracle wallets only support authentication to Oracle applications.
Entrust/PKI is a PKI product provided by Entrust Technologies, Inc. that provides certificate generation, certificate revocation, and key and certificate management.
The integration of Oracle Advanced Security with Entrust/PKI enables users of both Entrust and Oracle to utilize the extensive PKI capabilities of Entrust to enhance the security of their Oracle environment.
Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security provides:
Note:
http://www.entrust.com
Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security supports the use of Entrust credentials for X.509-based authentication and single sign-on. Instead of using an Oracle wallet to hold user PKI credentials, Oracle Advanced Security can access PKI credentials created by Entrust/Authority and held in an Entrust profile (an.epf file). Users who have deployed Entrust software within their enterprise are thus able to use it for authentication and single sign-on to Oracle9i.
Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security uses the extensive key management and rollover functionality provided by Entrust/PKI, which shield users from the complexity of a PKI deployment. For example, users are automatically notified when their certificates are expiring, and certificates are reissued according to administrator-configurable preferences.
Entrust provides a certificate authority component, which natively checks certificate revocation status and enables the revocation of certificates.
Users using Entrust credentials for authentication to Oracle are assured that the revocation status of the certificate is checked, and connections are prevented if the certificate is revoked.
This section describes the system components required for using Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security:
Entrust/PKI 5.0.2 for Oracle can be downloaded from the Entrust Web site:
http://www.entrust.com
Entrust/Toolkit Server Login and Entrust IPSEC Negotiator Toolkit can be downloaded from the Entrust Developer Network by registered members. Users can register for membership and download these products at the following Web address:
http://www.entrust.com//developer/memberships/registration.htm
Entrust/PKI 5.0.2 for Oracle requires a database for storing information about Entrust users and the infastructure, and a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)-compliant directory for information such as user names, public certificates, and certificate revocation lists.
Entrust/PKI 5.0.2 for Oracle is comprised of the following software components:
Entrust/Authority is the centerpiece of Entrust/PKI. It performs core certificate authority, certificate, and user management functions, such as creating users and user profiles containing the user's credentials.
|
Note: Oracle Corporation only supports the use of Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security with versions of Entrust/Authority that run on Oracle9i. |
|
See Also:
Chapter 7, Configuring Secure Sockets Layer Authentication, for information about certificate authorities. |
Entrust/Authority supports unattended login, also called Server Login, which eliminates the need for a Database Administrator (DBA) to repeatedly enter a password for the Entrust profile on the server. With unattended login, the DBA need only enter a password once to open the Entrust profile for the server to authenticate itself to multiple incoming connections.
Entrust/RA is the administrator's secure interface to Entrust/Authority.
Entrust/Entelligence provides support for user key management and single sign-on functionality on both clients and server by enabling Oracle9i server process access to incoming SSL connections.
Entrust/Toolkit Server Login Toolkit Release 5.0.2 is required for single sign-on functionality on servers operating on UNIX platforms.
Entrust/Server Login Toolkit provides single sign-on by enabling Oracle9i server process access to incoming SSL connections. Without this capability, a database administrator or other privileged user would have to enter the password for the Entrust profile on the server for every incoming connection.
You can download Entrust/Toolkit Server Login from the Entrust Web site:
http://www.entrust.com/developer/software/files/desc_serverlogin.cfm
The Entrust IPSEC Negotiator Toolkit Release 5.0.2 is required on both clients and servers for integrating the Oracle Advanced Security SSL stack with Entrust/PKI, enabling SSL authentication to use Entrust profiles.
You can download the IPSEC Negotiator Toolkit from the Entrust Web site:
http://www.entrust.com/developer/software/index.htm
Figure 8-1 illustrates the following Entrust authentication process:
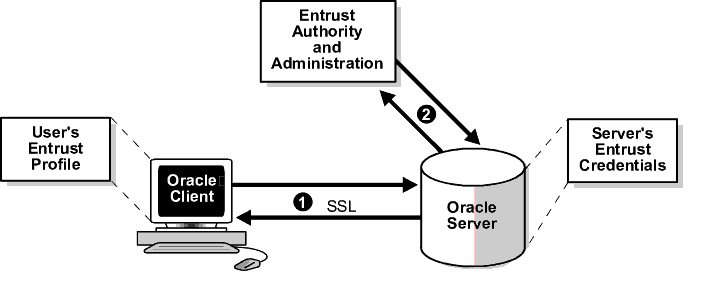
This section describes the following tasks that enable Entrust-enabled Oracle Advanced Security SSL authentication:
This section describes how to create Entrust profiles. Entrust profiles can be created by either administrators or users. On UNIX platforms, administrators create the Entrust profiles for all clients. On Windows NT platforms, users can be permitted to create their Entrust profiles.
Administrators create Entrust profiles as follows:
.epf file.
Entrust users create their own Entrust profiles as follows:
Start>Programs>Entrust>Entrust Profiles>Create Entrust Profiles
.epf file, and the Entrust initialization file.
For Oracle Advanced Security Release 9.0.1, Entrust support installs in Typical mode. A single Oracle installation supports the use of both Oracle Wallets and Entrust Profiles.
|
Notes:
|
Configure SSL on the client and server.
|
See Also:
Chapter 7, Configuring Secure Sockets Layer Authentication, for information about configuring SSL on the client and server; skip the section that describes the Oracle wallet location. |
The steps for configuring Entrust on the client vary according to the type of platform:
If the client resides on a non-Windows NT platform, perform the following steps:
JAVA_HOME variable to JDK or JRE location.
For example:
>setenv JAVA_HOME $ORACLE_HOME/JRE
WALLET_LOCATION in the sqlnet.ora file.
For example:
WALLET_LOCATION =(SOURCE =(METHOD = ENTR)(METHOD_DATA =(PROFILE =profile_location)(INIFILE =initialization_file_location)))
If the client resides on a Windows NT platform, ensure that the Entrust/Entelligence component is installed on the client and perform the following steps to set up the entrust credentials.
WALLET_LOCATION in the sqlnet.ora file.
For example:
WALLET_LOCATION =(SOURCE =(METHOD = ENTR)(METHOD_DATA =(INIFILE =initialization_file_location)))
where initialization_file_location is typically c:\WinNT.
The steps for configuring Entrust on the server vary according to the type of platform:
If the server is a UNIX platform, ensure that the Entrust/Server Login Toolkit component is installed on the server and perform the following steps:
wallet_location parameter in the sqlnet.ora and listener.ora files to specify the paths to the server's profile and the Entrust initialization file:
WALLET_LOCATION =(SOURCE =(METHOD = ENTR)(METHOD_DATA =(PROFILE =profile_location)(INIFILE =initialization_file_location)))
.ual files.
For example:
binder
If the server is a Windows NT platform, ensure that the Entrust/Entelligence component is installed on the client and perform the following steps:
wallet_location parameter in the sqlnet.ora and listener.ora files to specify the paths to the server's profile and the Entrust initialization file:
WALLET_LOCATION =(SOURCE =(METHOD = ENTR)(METHOD_DATA =(PROFILE =profile_location)(INIFILE =initialization_file_location)))
.ual files as follows:
Start>Programs>Entrust Toolkit>Server Login>Entrust Binder
Create global user in the database based on the distinguished name (DN) of each Entrust user.
For example:
SQL> create user jdoe identified globally as 'cn=jdoe,o=oracle,c=us';
where "cn=jdoe, o=oracle, c=us" is the Entrust distinguished name of the user.
sqlplus /@tns_service_name
where tns_service_name is the service name of the Oracle instance.
The Entrust_Login dialog box appears.
WALLET_LOCATION parameter, you are prompted to enter the path to the Entrust initialization file.
The Entrust-ready designation from Entrust typically requires that a partner product integration with Entrust is done using an Entrust toolkit. This means that an application must be specifically modified to work with Entrust.
For example, Oracle has modified its SSL libraries to access an Entrust profile instead of an Oracle wallet. Accordingly, the Entrust profile is not accessible from standard SSL libraries.
In addition, the following restrictions apply:
This section describes how to diagnose errors returned from Entrust to Oracle Advanced Security users.
SQLPLUS login on an Entrust-enabled Oracle client errors out with the following generic error message:
ORA-28890 Entrust Login Failed
To get more detail on the exact Entrust error, turn on TRACING for SQLPLUS by specifying the following parameters in sqlnet.ora:
Search for the word IKMP within the created TRACE file. The TRACE file contains information about the exact error code returned by Entrust API.
sqlnet.ora, the Entrust initialization file (entrust.ini) must reside in c:\WINNT.
The software authentication filed. (error code - 162).
Contact Entrust support to resolve this issue.
Algorithm self-test failed. (error code - 176).
Contact Entrust support to resolve this issue.
IdentityLibrary = location
where location is the location of libidapi.so, including the file name.
\\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Entrust Technologies\Toolkits\Version\IPSec
to be "5.0.1" (or "5.0.2").
Contact Oracle Support to obtain an Installer patch that resolves this issue.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|