Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A90125-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A90125-01 |
|
Functions, 15 of 166
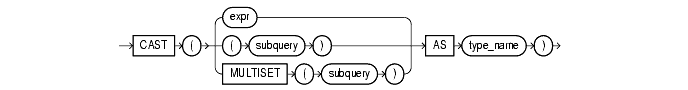
cast::=
cast
A CAST function converts one built-in datatype or collection-typed value into another built-in datatype or collection-typed value.
CAST lets you convert built-in datatypes or collection-typed values of one type into another built-in datatype or collection type. You can cast an unnamed operand (such as a date or the result set of a subquery) or a named collection (such as a varray or a nested table) into a type-compatible datatype or named collection. The type_name must be the name of a built-in datatype or collection type and the operand must be a built-in datatype or must evaluate to a collection value.
For the operand, expr can be either a built-in datatype or a collection type, and subquery must return a single value of collection type or built-in type. MULTISET informs Oracle to take the result set of the subquery and return a collection value. Table 6-9 shows which built-in datatypes can be cast into which other built-in datatypes. (CAST does not support LONG, LONG RAW, any of the LOB datatypes, or the Oracle-supplied types.)
If you want to cast a named collection type into another named collection type, the elements of both collections must be of the same type.
If the result set of subquery can evaluate to multiple rows, you must specify the MULTISET keyword. The rows resulting from the subquery form the elements of the collection value into which they are cast. Without the MULTISET keyword, the subquery is treated as a scalar subquery.
The following examples use the CAST function with scalar datatypes:
SELECT CAST('22-OCT-1997' AS DATE) FROM dual; SELECT product_id, CAST(ad_sourcetext AS VARCHAR2(30)) FROM print_media;
The CAST examples that follow use the following user-defined types and tables:
CREATE TYPE address_t AS OBJECT (no NUMBER, street CHAR(31), city CHAR(21), state CHAR(2)); / CREATE TYPE address_book_t AS TABLE OF address_t; / CREATE TYPE address_array_t AS VARRAY(3) OF address_t; CREATE TABLE emp_address (empno NUMBER, no NUMBER, street CHAR(31), city CHAR(21), state CHAR(2)); CREATE TABLE employees (empno NUMBER, name CHAR(31)); CREATE TABLE depts (dno NUMBER, addresses address_array_t);
This example casts a subquery:
SELECT e.empno, e.name, CAST(MULTISET(SELECT ea.no, ea.street, ea.city, ea.state FROM emp_address ea WHERE ea.empno = e.empno) AS address_book_t) FROM employees e;
CAST converts a varray type column into a nested table:
SELECT CAST(d.addresses AS address_book_t) FROM depts d WHERE d.dno = 111;
The following example casts a MULTISET expression with an ORDER BY clause:
CREATE TABLE projects (empid NUMBER, projname VARCHAR2(10)); CREATE TABLE emps (empid NUMBER, ename VARCHAR2(10)); CREATE TYPE projname_table_type AS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(10); /
An example of a MULTISET expression with the above schema is:
SELECT e.ename, CAST(MULTISET(SELECT p.projname FROM projects p WHERE p.empid=e.empid ORDER BY p.projname) AS projname_table_type) FROM emps e;
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|