Release 1 (9.0.1) for Windows
Part Number A90371-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i OLAP Services Concepts and Administration Guide for Windows Release 1 (9.0.1) for Windows Part Number A90371-01 |
|
Configuring Your Data Warehouse, 5 of 11
Creating OLAP metadata is one of several data administration tasks that you can perform through Oracle Enterprise Manager. Using its OLAP management tool, you create the metadata that defines the multidimensional objects required by the OLAP Services. Oracle Enterprise Manager enables you to map columns in your star or snowflake schema to dimensions, measures, and attributes. Even if you have other types of metadata in your database to support other types of applications, you must create OLAP metadata for OLAP Services.
You generate the SQL statements that create the metadata primarily by following the steps presented by a wizard or by completing a property sheet. If you wish, you can display the SQL statements before executing them.
Note: You may have already created the required metadata with an ETT tool as part of creating your data warehouse. If so, you can check and modify this metadata using OLAP management in Oracle Enterprise Manager.
To run OLAP management, you must have installed Oracle Enterprise Manager Client.
If Oracle Enterprise Manager Client is installed on the same computer with Oracle9i and OLAP Services, then a service name has already been defined as part of the installation. Otherwise, you may need to define a service name using Oracle Net Assistant so that Oracle Enterprise Manager Client can open a connection with the database.
To create OLAP metadata, you must be able to log into your database through Oracle Enterprise Manager with credentials that have been granted the OLAP_DBA role. The OLAP_DBA role is necessary to create metadata through Oracle Enterprise Manager as described in this chapter, and to administer OLAP Services as described in Chapter 3.
The OLAP_DBA role has system privileges associated with it, such as the ability to create and drop tables, indexes, and dimensions. For a list of these privileges, follow these steps:
If you have the system DBA role, then you also have the OLAP_DBA role. You must also have the CONNECT role.
Note: To view existing metadata, you only need the CONNECT and SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE roles.
Follow these steps to start Oracle Enterprise Manager and access OLAP management:
You see the main page.
You see the list of service names for Oracle databases on your network.
You see the Database Connect Information dialog box.
Tip: Select the Save as preferred credentials box if you wish to eliminate this step in future sessions. Your user name and encrypted password will be saved in a local file. For security, make sure that only you can run Oracle Enterprise Manager with your stored credentials. Later, if you wish to change this information, then choose Edit Local Preferred Credentials from the Configuration menu.
The tree view will expand to show the various tools available for administering the database.
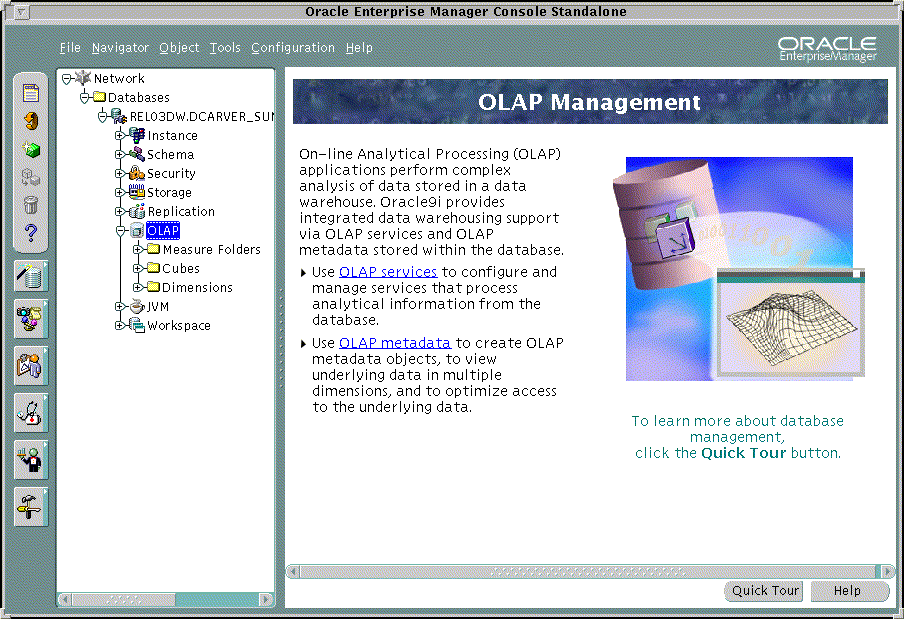
You see the types of objects that you can create, as shown in "Figure: Location of OLAP management". This part of the Oracle Enterprise Manager tree is for OLAP management.
The following figure identifies the location of OLAP management in Oracle Enterprise Manager.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|