A WebCenter Configuration
The main configuration files for Oracle WebCenter applications are adf-config.xml and connections.xml. This appendix describes both these files, how to locate them in a WebCenter application deployment, and also when to configure these files and which tools to use. Other configuration files, such as web.xml, are described here too. See also, Section 1.3.5, "Oracle WebCenter Configuration Considerations."
This appendix also outlines how to tune configuration properties for the operating system on which WebCenter applications are installed, WebCenter applications, and their back-end components.
This appendix includes the following sections:
A.1 Configuration Files
adf-config.xml, connections.xml, and web.xml are used to configure WebCenter applications and their back-end services. This section describes how WebCenter applications use each file and the location of these files post deployment. This section includes the following sub sections:
A.1.1 adf-config.xml and connections.xml
adf-config.xml and connections.xml both store design time configuration information, such as the discussions server, mail server, or Oracle Content Server that is used by the WebCenter application in the development environment:
-
adf-config.xml - Stores application-level settings, such as the which discussions server or mail server the WebCenter application is currently using.
See also, Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
connections.xml - Stores connection details for WebCenter services.
See also, Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
After you deploy a WebCenter application to a production environment, you can use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST commands to reconfigure some properties to meet your production requirements. For example, you can modify connection details to point to production server instances.
Any configuration changes that you make, post deployment, are stored as customizations in the WebCenter application's Oracle Metadata Services (MDS) repository. MDS uses the original deployed versions of adf-config.xml and connections.xml as base documents and stores all subsequent customizations separately into MDS using a single customization layer.
When a WebCenter application starts up, customizations stored in MDS are applied to the appropriate base documents and the WebCenter application uses the merged documents (base documents with customizations) as the final set of configuration properties.
For information on MDS customizations, see "Understanding the MDS Repository" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
adf-config.xml and connections.xml are both located in the /META-INF folder for your application. In a WebCenter application deployment (.ear), you will find the base documents of these files under:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name
For example, if the DOMAIN_HOME is MW_HOME/wlshome/ /domains/wc_domain/, both configuration files are located under MW_HOME/wlshome/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/WLS_Spaces.
To determine the exact location, search for the configuration file under this folder. For example, enter the following at a command prompt:
> cd MW_HOME/wlshome/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/WLS_Spaces
> find . -name adf-config.xml
A sample response, for this particular example, is as follows: ./tmp/_WL_user/webcenter/8gco54/adf/META-INF/adf-config.xml
You can locate connections.xml in a similar way.
Reviewing Post Deployment Customizations in MDS
Post deployment, always use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST commands to review the latest configuration or make configuration changes. In Fusion Middleware Control you will mostly use WebCenter application configuration screens but a useful Systems MBean Browser is also available for reviewing configuration settings. These tools always show you the current configuration so, typically, there is no need for you to examine or change the content of base documents or MDS customization data for files such as adf-config.xml and connections.xml.
At times it might be useful to 'see' the information in MDS. If for any reason you must extract or examine configuration file customizations that are stored in MDS, use the WLST command exportMetadata.
See also:
For detailed syntax and examples, see "exportMetadata" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.For example, to determine MDS customizations for connections.xml in WebCenter Spaces, where application name is always webcenter, the managed server is always WLS_Spaces, and the file name and location is always /META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare/connections.xml.xml, you might specify:
exportMetadata(application='webcenter', server='WLS_Spaces', toLocation='/tmp/mydata', docs='/META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare/connections.xml.xml')
And similarly, to determine MDS customizations for adf-config.xml:
exportMetadata(application='webcenter', server='WLS_Spaces', toLocation='/tmp/mydata', docs='/META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare/adf-config.xml.xml')
You choose where to save file customizations by specifying toLocation. If, for example, toLocation is set to /tmp/mydata, then the requested file is saved to /tmp/mydata/META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare.
If no customizations exist for the requested file, then nothing is saved to the specified location—previously extracted customizations at the same location are not overwritten.
Handling Configuration Conflicts
MDS customizations use references to elements in the base document to call out which elements must be inserted/deleted/replaced, and at what location. If an element is inadvertently removed from a future redeployment and MDS contains a reference to that element, then the WebCenter application's configuration appears corrupt. You are unlikely to face this problem but should a previously deployed application appear corrupt after making changes to adf-config.xml or connections.xml you have the following options:
-
Delete MDS customizations for
adf-config.xmlorconnections.xml, deploy the new EAR file, and reconfigure your application from scratch using Fusion Middleware Control or WLST.See below for detailed steps, "Deleting MDS Customizations for adf-config.xml or connections.xml".
-
Redeploy the EAR file on a new partition or a partition where older customizations are deleted. In either case, all data previously stored in MDS for the application is lost, including any customizations for
adf-config.xmlorconnections.xml, and all user personalizations. You must reconfigure your application from scratch too, using Fusion Middleware Control or WLST.See also, "deleteMetadata" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Deleting MDS Customizations for adf-config.xml or connections.xml
-
Delete customizations for
connections.xml, using WLST. For example:deleteMetadata(application='webcenter', server='WLS_Spaces', docs='/META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare/connections.xml.xml')
-
Delete customizations for
adf-config.xml, using WLST. For example:deleteMetadata (application='webcenter', server='WLS_Spaces', docs='/META-INF/mdssys/cust/adfshare/adfshare/adf-config.xml.xml')
-
Restart the WebCenter application.
-
Reconfigure your application from scratch using Fusion Middleware Control or WLST.
A.1.2 web.xml
web.xml is a standard J2EE application deployment descriptor file and it is located in the /META-INF directory for your application. Typical run-time settings in web.xml include initialization parameters, custom tag library locations, and security settings.
Unlike connections.xml and adf-config.xml, web.xml does not store post deployment customizations in MDS.
To determine the exact location of web.xml in a particular WebCenter application deployment, search for the configuration file under:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name
For example, if the DOMAIN_HOME is MW_HOME/wlshome/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/, web.xml is located under MW_HOME/wlshome/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/WLS_Spaces.
For example, enter the following at a command prompt:
> cd MW_HOME/wlshome/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/WLS_Spaces
> find . -name web.xml
A sample response, for this particular example, is as follows:
./tmp/_WL_user/webcenter/8gco54/adf/META-INF/web.xml
You cannot use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST to modify web.xml in an existing WebCenter application deployment. If you must modify settings in web.xml you will have to do so manually, as described in Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually".
The are several instance where you might be required to modify web.xml, for example, if you must change:
-
Content repository upload parameters:
UPLOAD_MAX_MEMORY,UPLOAD_MAX_DISK_SPACE, andUPLOAD_TEMP_DIR. For details, see Section 11.9, "Changing the Maximum File Upload Size". -
Time after which HTTP sessions expire. For details, see Appendix A, "Setting HTTP Session Timeout".
-
JSP page timeout value. For details, see Appendix A, "Setting JSP Page Timeout".
A.2 Cluster Configuration
All post deployment configuration through Fusion Middleware Control, WLST, or the Systems MBean Browser is stored as customizations in the MDS repository. In a cluster environment, all configuration changes are visible to all nodes in the cluster. To effect configuration changes that are not dynamic, all nodes in the cluster must be restarted. See also Section 8.2, "Starting and Stopping Managed Servers for WebCenter Application Deployments".
In WebCenter applications most configuration changes that you make, through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST, are not dynamic. For example, when you add or modify connection details for Web services (Announcements, Discussions, Documents, Mail, Instant Messaging and Presence, Search, Worklists) you must restart the application's managed server.There are several exceptions; portlet producer and external application registration is dynamic. Any new portlet producers and external applications that you register are immediately available in your WebCenter application and any changes that you make to existing connections take effect immediately too.
If you edit configuration file manually in a cluster environment, then you must ensure that identical changes are made in each cluster member so that the overall cluster configuration remains synchronized.
A.3 Configuration Tools
Oracle offers a range of tools for configuring WebCenter application deployments. This section outline which tools are available and in case you cannot use these tools, describes how to edit configuration files manually.
Note:
Most of the WebCenter configuration parameters are immutable and cannot be changed at run time unless otherwise specified.This section includes the following sub sections:
A.3.1 Configuration Through Fusion Middleware Control, WLST Commands, and System MBeans Browser
Post deployment, always use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST commands to review the latest configuration or make configuration changes. In Fusion Middleware Control you will mostly use WebCenter application configuration screens but a useful Systems MBean Browser is also available for reviewing and modifying configuration settings.
For more information about these tools, read:
These tools always show you the current configuration so, typically, there is no need for you to examine or manually change the content of configuration files or MDS customization data for files such as adf-config.xml or connections.xml.
If you must edit these files directly, to set concurrency options for example, follow instructions in Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually" carefully.
A.3.2 Editing Configuration Files Manually
A few configuration settings, such as those stored in web.xml, are not exposed through MBeans, and therefore, you cannot use Fusion Middleware Control, WLST commands, or the System MBeans Browser for post deployment configuration.
If you must modify these settings, Oracle recommends that you re-create the WebCenter application deployment .ear file with the desired configuration, and redeploy the application. Sometimes this is not feasible or desirable—maybe you do not have access to the .ear file, or perhaps you must configure properties uniquely based on where the file is deployed—in this case, follow the manual steps below, using WLST:
-
Prevent the Weblogic Server from re-staging the WebCenter application, except at deployment time. From the WLST shell, type:
connect() edit() startEdit() cd("DeploymentConfiguration/<domain_name>") cmo.setRestageOnlyOnRedeploy(true) activate() -
Open the configuration file in a text editor and modify configuration properties manually, as required.
Read Locating Base Documents to find out how to determine the exact location of
adf-config.xml,connections.xml, orweb.xml. -
Restart the managed server on which the WebCenter application is deployed.
See, "Starting and Stopping WebLogic Managed Servers Using the Command Line" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
Caution:
If you redeploy the WebCenter application in the future you must edit the configuration file again.A.4 Tuning Environment Configuration
This section describes how to tune the operating system on which WebCenter applications are deployed. It provides information on configuring system limit, JDBC data source, and JRockit virtual machine (JVM) arguments.
A.4.1 Setting System Limit
To run a WebCenter application at moderate load, set the open-files-limit to 4096. If you encounter errors, such as running out of file descriptors, then increase the system limit.
For example, on Linux, you can use this command:
ulimit -n 8192
Refer to your operating system documentation to find out how to change this system limit.
A.4.2 Setting JDBC Data Source
The following data source settings are recommended for MDSDS and WebCenterDS. These settings can be adjusted depending on the application's usage pattern and load.
<jdbc-connection-pool-params>
<initial-capacity>10</initial-capacity>
<max-capacity>200</max-capacity>
<capacity-increment>1</capacity-increment>
<shrink-frequency-seconds>0</shrink-frequency-seconds>
<highest-num-waiters>2147483647</highest-num-waiters>
<connection-creation-retry-frequency-seconds>0</connection-creation-retry-frequency-seconds>
<connection-reserve-timeout-seconds>60</connection-reserve-timeout-seconds>
<test-frequency-seconds>0</test-frequency-seconds>
<test-connections-on-reserve>true</test-connections-on-reserve>
<ignore-in-use-connections-enabled>true</ignore-in-use-connections-enabled>
<inactive-connection-timeout-seconds>0</inactive-connection-timeout-seconds>
<test-table-name>SQL SELECT 1 FROM DUAL</test-table-name>
<login-delay-seconds>0</login-delay-seconds>
<statement-cache-size>50</statement-cache-size>
<statement-cache-type>LRU</statement-cache-type>
<remove-infected-connections>true</remove-infected-connections>
<seconds-to-trust-an-idle-pool-connection>60</seconds-to-trust-an-idle-pool-connection>
<statement-timeout>-1</statement-timeout>
<pinned-to-thread>false</pinned-to-thread>
</jdbc-connection-pool-params>
To edit JDBC data source settings:
-
Login to WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
From the Home page, select Summary of JDBC Data Sources, Settings for mds-SpacesDS, and then the Connection Pool tab.
-
Edit properties, as required.
See also "Configuring JDBC Data Sources" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring and Managing JDBC for Oracle WebLogic Server.
A.4.3 Setting JRockit Virtual Machine (JVM) Arguments
JVM arguments are set in the setDomainEnv.sh file.
-
WebLogic Server production mode: To enable WebLogic Server production mode through WebLogic Administration Console, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring Server Environments for Oracle WebLogic Server. The parameter is:
-Dweblogic.ProductionModeEnabled=true
-
Heap size: If the system is overloaded, that is, garbage is collected or out of memory error occurs frequently, then increase the heap size as appropriate to your system's available physical memory. The parameter is:
-Xms2048M -Xmx2048M -Xns512M
-
Memory size: Default memory sizes for custom WebCenter applications are set as follows:
-Xmx512M -XX:PermSize=128M -XX:MaxPermSize512M
This is an out-of-the-box setting.
-
Garbage collector behavior: To maximize throughput in an application, set the following JVM option for the application's garbage collector behavior:
-Xgcprio:throughput -Djrockit.codegen.newlockmatching=true
This is an out-of-the-box setting.
-
Security: The following JVM arguments improve performance of WebCenter application's security layer. These are out-of-box settings.
-DUSE_JAAS=false -Djps.policystore.hybrid.mode=false -Djps.combiner.optimize.lazyeval=true -Djps.combiner.optimize=true -Djps.auth=ACC
-
Log output: This option reduces the log output in some WebCenter application-dependent components. This is an out-of-box setting:
-Djbo.debugoutput=silent
A.5 Tuning WebCenter Application Configuration
This section describes parameters that enable administrators to tune performance of WebCenter applications.
This section includes the following:
A.5.1 Setting HTTP Session Timeout
To manage over resource usage, adjust the session timeout value, in minutes, in the web.xml file.
If you must modify this property, post deployment, you must edit web.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually".
The following is a sample snippet of web.xml:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>
45
</session-timeout>
</session-config>
A.5.2 Setting JSP Page Timeout
You can specify an integer value, in seconds, after which any JSP page will be removed from memory if it has not been requested in the web.xml file. This frees up resources in situations where some pages are called infrequently.
Increasing the value reduces user response time, and decreasing it reduces application memory foot print. The default value is 0, for no timeout.
If you must modify this property, post deployment, you must edit web.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of web.xml:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>
oraclejsp
<init-param>
<param-name>
jsp_timeout
</param-name>
<param-value>
600
</param-value>
</init-param>
A.5.3 Setting ADF Client State Token
Through this setting, you can control the number of pages users can navigate using the browser Back button without losing information. To reduce CPU and memory usage, you can decrease the value in the web.xml file.
If you must modify this property, post deployment, you must edit web.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of web.xml:
<context-param>
<param-name>
org.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CLIENT_STATE_MAX_TOKENS
</param-name>
<param-value>
3
</param-value>
</context-param>
A.5.4 Setting MDS Cache Size and Purge Rate
The default MDS cache size is 100MB. If you encounter the error message, JOC region full, then you can increase the MDS cache size in the adf-config.xml file.
Post deployment, modify these properties through the System MBeans Browser. For more information, see the section "Changing MDS Configuration Attributes for Deployed Applications" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<cache-config> <max-size-kb>150000</max-size-kb> </cache-config>
MDS purges old version of metadata automatically every hour. If excessive metadata is accumulated and each purge is very expensive, reduce this interval in the adf-config.xml file.
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<auto-purge seconds-to-live="3600"/>
A.5.5 Configuring Concurrency Management
Concurrency management includes global settings that impact entire WebCenter and service- and resource-specific settings that only impact a particular service.
You can define deployment-specific overrides or additional configuration in the adf-config.xml file. For example, you can specify resource-specific (producers) values that are appropriate for a particular deployment.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, you must edit adf-config.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following describes the format of the global, service, and resource entries in adf-config.xml:
<concurrent:adf-service-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/concurrent/config">
<global
queueSize="SIZE"
poolCoreSize="SIZE"
poolMaxSize="SIZE"
poolKeepAlivePeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutMinPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutMaxPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutDefaultPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutMonitorFrequency="TIMEPERIOD"
hangMonitorFrequeny="TIMEPERIOD"
hangAcceptableStopPeriod="TIMEPERIOD" />
<service
service="SERVICENAME"
timeoutMinPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutMaxPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutDefaultPeriod="TIMEPERIOD" />
<resource
service="SERVICENAME"
resource="RESOURCENAME"
timeoutMinPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutMaxPeriod="TIMEPERIOD"
timeoutDefaultPeriod="TIMEPERIOD" />
</concurrent:adf-service-config>
Where:
SIZE: A positive integer. For example: 20.
TIMEPERIOD: Any positive integer followed by a suffix indicating the time unit, which must be one of: ms for milliseconds, s for seconds, m for minutes, or h for hours. For example: 50ms, 10s, 3m, or 1h. The following are examples of default settings for different services. These settings are overwritten with any service-specific configurations in connections.xml or adf-config.xml files:
<concurrent:adf-service-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/concurrent/config">
<resource service="oracle.webcenter.community"
resource="oracle.webcenter.doclib"
timeoutMinPeriod="2s" timeoutMaxPeriod="10s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="5s"/>
<resource service="oracle.webcenter.community"
resource="oracle.webcenter.collab.calendar.community"
timeoutMinPeriod="2s" timeoutMaxPeriod="10s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="5s"/>
<resource service="oracle.webcenter.community"
resource="oracle.webcenter.collab.rtc"
timeoutMinPeriod="2s" timeoutMaxPeriod="10s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="5s"/>
<resource service="oracle.webcenter.community"
resource="oracle.webcenter.list"
timeoutMinPeriod="2s" timeoutMaxPeriod="10s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="5s"/>
<resource service="oracle.webcenter.community"
resource="oracle.webcenter.collab.tasks"
timeoutMinPeriod="2s" timeoutMaxPeriod="10s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="5s"/>
</concurrent:adf-service-config>
Note:
All of the attributes exceptservice and resource are optional, and therefore, for example, the following tags are valid:
<global queueSize="20"/>
<resource service="foo" resource="bar" timeoutMaxPeriod="5s"/>
A.5.6 Configuring CRUD APIs (Create, Read, Update and Delete)
CRUD API configuration for WebCenter update is defined in the adf-config.xml file. You can adjust the timeout to manage overall resource usage.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, you must edit adf-config.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<!-- The following entry configures the timeout for Webcenter Application CRUD APIs --> <concurrent:service service="oracle.webcenter.community" timeoutMinPeriod="100ms" timeoutMaxPeriod="4s" timeoutDefaultPeriod="2s"/> <!-- Webcenter Application configuration END -->
A.6 Tuning Back-End Component Configuration
This section describes performance configuration for back-end services used by WebCenter applications. Performance of back-end servers, for example, Worklists, Oracle Content Server, and so on, should be tuned as described in guidelines for those back-ends.
This section includes the following sub sections:
A.6.1 Tuning Performance of the Announcements Service
To manage overall resource usage for the Announcements service, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 10 seconds
-
Minimum: 0 seconds
-
Maximum: 45 seconds
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 12.5.1, "Modifying Discussions Server Connection Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 12.5.2, "Modifying Discussions Server Connection Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<Reference name="Jive-7777" className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.Announcement. AnnouncementConnection">
<Factory className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.forum.ForumConnectionFactory"/>
<StringRefAddr addrType="connection.time.out">
<Contents>5</Contents>
</StringRefAddr>
</RefAddresses>
</Reference>
A.6.2 Tuning Performance of the Discussions Service
To manage overall resource usage for the Discussions service, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 10 seconds
-
Minimum: 0 seconds
-
Maximum: 45 seconds
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 12.5.1, "Modifying Discussions Server Connection Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 12.5.2, "Modifying Discussions Server Connection Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<Reference name="Jive-7777" className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.forum.ForumConnection">
<Factory className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.forum.ForumConnectionFactory"/>
<RefAddresses>
<StringRefAddr addrType="forum.url">
<Contents>http://[machine]:[port]/owc_discussions_5520</Contents>
<StringRefAddr addrType="connection.time.out">
<Contents>5</Contents>
</StringRefAddr>
</RefAddresses>
</Reference>
A.6.3 Tuning Performance of the Instant Messaging and Presence (IMP) Service
To manage overall resource usage for the IMP service, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 10 seconds
-
Minimum: 0 seconds
-
Maximum: 45 seconds
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<Reference name="IMPService-OWLCS"
className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.rtc.RtcConnection">
<Factory className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.rtc.RtcConnectionFactory"/>
<RefAddresses>
<StringRefAddr addrType="connection.time.out">
<Contents>5</Contents>
</StringRefAddr>
</RefAddresses>
</Reference>
A.6.4 Tuning Performance of the Mail Service
To manage overall resource usage for the Mail service, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 10 seconds
-
Minimum: 0 seconds
-
Maximum: 45 seconds
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 15.5.1, "Modifying Mail Server Connection Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 15.5.2, "Modifying Mail Server Connection Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<Reference name="MailConnection"
className="oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.webcenter.mail.MailConnection">
<StringRefAddr addrType="connection.time.out">
<Contents>5</Contents>
</StringRefAddr>
</Reference>
A.6.5 Tuning Performance of the RSS News Feed Service
To manage overall resource usage for the RSS News Feed service, you can adjust the refresh interval and timeout in the adf-config.xml file.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, use the System MBeans Browser.
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<rssC:adf-rss-config>
<rssC:RefreshSecs>3600</rssC:RefreshSecs>
<rssC:TimeoutSecs>3</rssC:TimeoutSecs>
<rssC:Configured>true</rssC:Configured>
</rssC:adf-rss-config>
A.6.6 Tuning Performance of the Search Service
To manage overall resource usage and user response time for searching, you can adjust the number of saved searches displayed, the number of results displayed, and these timeout values:
-
prepareTimeoutMs- Maximum time that a service is allowed to initialize a search (in ms). -
timeoutMs- Maximum time that a service is allowed to execute a search (in ms). -
showAllTimeoutMs- Maximum time that a service is allowed to display search all results (in ms).
Post deployment, modify timeout properties through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 18.3.3.1, "Modifying Oracle SES Connection Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 18.3.3.2, "Modifying Oracle SES Connection Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<searchC:adf-search-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/search/config">
<display-properties>
<common numSavedSearches="25"/>
<region-specific>
<usage id="simpleSearchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="searchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="localToolbarRegion" numServiceRows="5"/>
</region-specific>
</display-properties>
<execution-properties prepareTimeoutMs="1000" timeoutMs="3000" showAllTimeoutMs="20000" />
</execution-properties>
</searchC:adf-search-config>
A.6.7 Tuning Performance of WSRP Producers
To manage overall resource usage for a WSRP producer, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 30000 ms
-
Minimum: 5000 ms
-
Maximum: 60000 ms
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 21.6.1, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 21.6.2, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<wsrpproducerconnection producerName="wc-RichText" wsConnection="wc-RichText-wsconn" timeout="30"/>
<wsrpproducerconnection producerName="wc-WSRPTools" wsConnection="wc-WSRPTools-wsconn" timeout="30"/>
A.6.8 Tuning Performance of Oracle PDK-Java Producers
To manage overall resource usage for a Web producer, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 30000 ms
-
Minimum: 5000 ms
-
Maximum: 60000 ms
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 21.6.1, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 21.6.2, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<webproducerconnection producerName="wc-WebClipping" urlConnection="wc-WebClipping-urlconn" timeout="10000" establishSession="true" mapUser="false"/>
A.6.9 Tuning Performance of OmniPortlet
To manage overall resource usage for OmniPortlets, you can tune the Connection Timeout property:
-
Default: 30000 ms
-
Minimum: 5000 ms
-
Maximum: 60000 ms
Post deployment, modify the Connection Timeout property through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST. For details, see:
-
Section 21.6.1, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using Fusion Middleware Control"
-
Section 21.6.2, "Editing Producer Registration Details Using WLST"
The following is a sample snippet of connections.xml:
<webproducerconnection producerName="wc-OmniPortlet" urlConnection="wc-OmniPortlet-urlconn" timeout="10000" establishSession="false" mapUser="false"/>
A.6.10 Tuning Performance of the Portlet Service
To manage overall resource usage and user response time, you can remove unnecessary locale support, modify portlet timeout and cache size in the adf-config.xml file.
For the Portlet service, 28 supported locales are defined out-of-the-box. You can remove the locales that are unnecessary for your application.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, you must edit adf-config.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<portletC:adf-portlet-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/portlet/config">
<supportedLocales>
<value>es</value>
<value>ko</value>
<value>ru</value>
<value>ar</value>
<value>fi</value>
<value>nl</value>
<value>sk</value>
<value>cs</value>
<value>fr</value>
<value>no</value>
<value>sv</value>
<value>da</value>
<value>hu</value>
<value>pl</value>
<value>th</value>
<value>de</value>
<value>it</value>
<value>pt</value>
<value>tr</value>
<value>el</value>
<value>iw</value>
<value>pt_BR</value>
<value>zh_CN</value>
<value>en</value>
<value>ja</value>
<value>ro</value>
<value>zh_TW</value>
</supportedLocales>
<defaultTimeout>20</defaultTimeout>
<minimumTimeout>1</minimumTimeout>
<maximumTimeout>60</maximumTimeout>
<parallelPoolSize>10</parallelPoolSize>
<parallelQueueSize>20</parallelQueueSize>
<cacheSettings enabled="true">
<maxSize>10000000</maxSize>
</cacheSettings>
</portletC:adf-portlet-config>
A.6.11 Configuring Portlet Cache Size
You can modify the portlet cache size in the adf-config.xml file. The default portlet cache size is set to 10 MB.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, you must edit adf-config.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<adf-portlet-config>
....
<supportedLocales>
<cacheSettings enabled="true">
<maxSize>10000000</maxSize>
</cacheSettings>
<adf-portlet-config>
A.6.12 Configuring Portlet Timeout
You can modify the portlet timeout value in the adf-portlet-config element of the adf-config.xml file. Default: 10 seconds, minimum: 0.1 seconds, maximum: 60 seconds.
If you must modify these properties, post deployment, you must edit adf-config.xml manually. See Appendix A, "Editing Configuration Files Manually."
The following is a sample snippet of adf-config.xml:
<adf-portlet-config>
....
<defaultTimeout>5</defaultTimeout>
<minimumTimeout>2</minimumTimeout>
<maximumTimeout>100</maximumTimeout>
<adf-portlet-config>
A.7 Troubleshooting WebCenter Application Configuration Issues
This section includes the following sub sections:
-
WebCenter Does Not Display in the Application Deployment Menu in Fusion Middleware Control
-
Configuration Performed in One Application Reflects in Another
A.7.1 WebCenter Does Not Display in the Application Deployment Menu in Fusion Middleware Control
After logging into Fusion Middleware Control, you cannot find the WebCenter option in the Application Deployment menu.
Ensure the following:
-
Deployed application is an ADF application.
The WebCenter option does not display for applications that are not developed using ADF.
-
Deployed application is up and running.
-
Deployed application contains accurate information about the MDS repository and partition, and the MDS repository is accessible to the application. To verify this information, check the
metadata-store-usagessection in theadf-config.xmlfile. For information on MDS, see "Understanding the MDS Repository" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide. -
Application is packaged with required artifacts to support configuration:
-
adf-jndi-configname space is configured in the application'sadf-config.xmlfile. This is provisioned at design time. The following is an example (the text in bold) of theadf-jndi-configname space:<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config" xmlns:jndiC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/jndi/config" xmlns:ns2="http://xmlns.oracle.com/mds/config" xmlns:ns3="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config"> ... ... </adf-config> -
MDSBackingStoreis configured in the application'sadf-config.xmlfile. This is provisioned at design time. This section can exist anywhere in the upperadf-configelement, for instance, after the end tag ofadf-mds-config. For example, see the text in bold in the following snippet:<jndiC:adf-jndi-config> <jndiC:ConnectionsJndiContext initialContextFactoryClass="oracle.adf.share.jndi.InitialContextFactoryImpl" backingStoreURL="META-INF/connections.xml" backingStoreClass="oracle.adf.share.jndi.MDSBackingStore"> <jndiC:contextEnv value="true" name="cache_application_scope"/> </jndiC:ConnectionsJndiContext> </jndiC:adf-jndi-config>
-
Appropriate listeners exist in the
web.xmlfile to register the MBeans. This is provisioned at design time. For example, see the text in bold in the following snippet of theweb.xmlfile:<listener> <description>ADF Config MBeans</description> <display-name>ADF Config MBeans</display-name> <listener-class>oracle.adf.mbean.share.config.ADFConfigLifeCycleCallBack</listener-class> </listener> <listener> <description>ADF Connection MBeans</description> <display-name>ADF Connection MBeans</display-name> <listener-class>oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.ADFConnectionLifeCycleCallBack</listener-class> </listener>
-
-
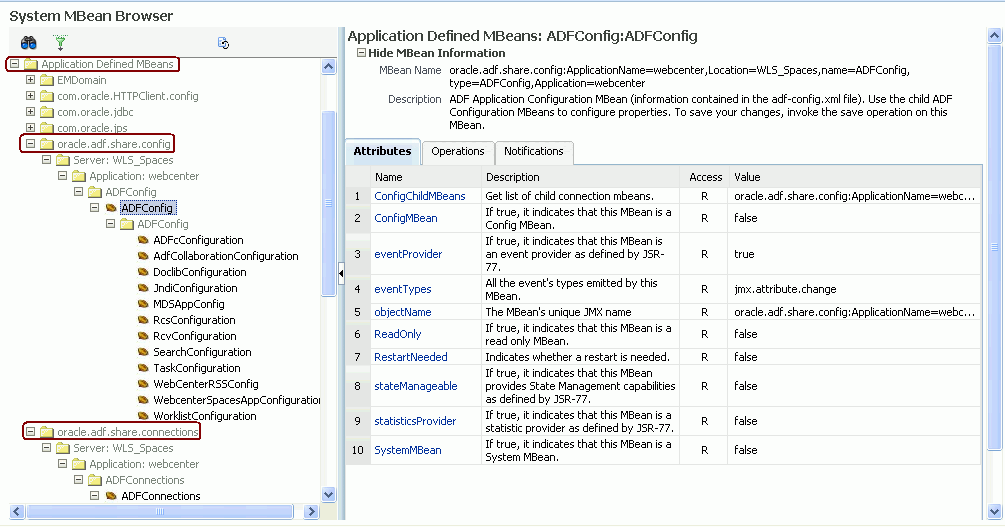
MBeans is registered for the WebCenter application. To verify this:
-
In Fusion Middleware Control, from the Application Deployment menu, select System MBean Browser.
-
Locate connection MBeans for your application under Application Defined MBeans > oracle.adf.mbean.share.connection.
-
Similarly, locate
adf-configMBeans for your application under Application Defined MBeans > oracle.adf.mbean.share.config. Figure A-1 shows how the Application Defined MBeans section looks in Fusion Middleware Control.If your application consumes producers, then locate the Producer Manager Mbean.
-
-
Check the application's diagnostic logs, analyze messages for the modules
oracle.adf.mbean.share.connectionandoracle.adf.mbean.share.config, and determine what must be done.
A.7.2 Configuration Options Unavailable
When you try to configure an application in Fusion Middleware Control, the following message displays:
Configuration options currently unavailable. The application application_name might be down, did not start-up properly, or is incorrectly packaged.
Check the log files for further details.
For information on how to resolve this issue, see Section A.7.1, "WebCenter Does Not Display in the Application Deployment Menu in Fusion Middleware Control."
A.7.3 Configuration Performed in One Application Reflects in Another
You configured a WebCenter application, but those configurations also show in another application.
This happens when multiple applications share the MDS partition in the same schema. To resolve this problem, deploy these applications again and ensure that each application uses its own MDS schema and partition combination. For information about creating a MDS repository or configuring an existing WebCenter application to use a different MDS repository or partition, see section "Managing the Oracle Metadata Repository" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
A.7.4 WebCenter Spaces Logs Indicate Too Many Open Files
WebCenter Spaces is inaccessible or displaying error messages and the diagnostic log files indicates that there is an issue with 'too many open files'.
Do the following:
-
Check the number of file handles configured on each of the back-end servers, primarily the database, and increase appropriately.
-
If the problem persists after increasing the file handles, check the value of
fs.file-maxin the/etc/sysctl.conffile and increase the value appropriately.
A.8 Troubleshooting WLST Command Issues
This section includes the following sub sections:
-
WLST Shell is Not Connected to the Oracle WebLogic Managed Server Instance
-
Application with the Same Name Already Exists on a Managed Server
A.8.1 None of the WLST Commands Work
You are unable to run any WLST commands.
Ensure the following:
-
No files other than Python are stored in the WLST source directory:
WC_ORACLE_HOME/common/bin/wlst. This directory must contains files with the.pyextension only.The default set of files in this location contain legal Python files from Oracle. It is possible that a user copied some non-python script to this directory, for example, a backup file or a test python file with syntax errors.
-
webcenter-wlst.jaris located atWC_ORACLE_HOME/common/bin/wlst/lib.
A.8.2 WLST Commands Do Not Work for a Particular Service
You are unable to run WLST commands for a particular service, and therefore, you cannot configure that service.
First, run generic non-WebCenter commands, for example, listApplications() and displayMetricTableNames()to verify whether these commands work. If generic commands do not work, then apply the solution described in Section A.8.1, "None of the WLST Commands Work."
If generic commands work, then run test commands to check WebCenter-specific commands for syntax errors. Run the appropriate WSLT check command (see Table A-1).
See also, Section 1.12.3.1, "Running Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Commands."
Table A-1 File Names and WLST Commands for WebCenter Service
| Service Name | File Name | WLST Command |
|---|---|---|
|
Discussions and Announcements |
|
|
|
Documents |
|
|
|
External Applications |
|
|
|
Group Space Events |
|
|
|
Instant Messaging and Presence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Producer Help |
|
|
|
WSRP Producers |
|
|
|
PDK Producers |
|
|
|
RSS News Feed |
|
|
|
Search |
|
|
|
Worklist |
|
|
|
WebCenter Spaces and SOA |
|
|
|
Export/Import - WebCenter application |
|
|
|
Export/Import - Group Spaces and Template |
|
|
|
WebCenter Help |
|
|
A.8.3 A Connection with the Name Connection_Name Already Exists
You are unable to create a connection with the name connection_name. The following message displays:
A connection with name Connection_Name already exists.
Connection names are unique across WebCenter applications. This error occurs when you try to create a connection with a name that is in use. Ensure that you use a unique name for your connection.
A.8.4 WLST Shell is Not Connected to the Oracle WebLogic Managed Server Instance
The WLST shell is not connected to the managed server on which you want to run WLST commands.
Run the following command to connect the WLST shell to the managed server:
connect(username, password , serverhost:serverport)
See also, Section 1.12.3.1, "Running Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Commands."
A.8.5 Application with the Same Name Already Exists in a Domain
You are unable to register a producer application. The following message displays:
Another application named "YourApplicationName" exists. Specify the Server on which your application is deployed. Use: server="YourServerName".
There are multiple applications with the same name in the domain in which you are trying to register your application. This usually happens in a cluster environment, where the same application is deployed to multiple managed servers. If this is the case, specify the name of the server in which you are trying to register this application. For example, run the registerWSRPProducer WLST command with the server argument:
registerWSRPProducer(appName='myApp', name='MyWSRPSamples',url='http://host:port/application_name/portlets/wsrp2?WSDL', server=server_name)
For command syntax and examples, see "registerWSRPProducer" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
See also, Section 1.12.3.1, "Running Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Commands."
A.8.6 Application with the Same Name Already Exists on a Managed Server
You are unable to register a producer application. The following message displays:
Another application named "application_name" exists on the server managedServerName.
There are multiple applications with the same name on the managed server in which you are trying to register your application. This usually happens when applications are assigned different versions. If this is the case, specify the version of the application you want to register. For example, run the registerWSRPProducer WLST command with the arguments server and applicationVersion:
registerWSRPProducer(appName='myApp', name='MyWSRPSamples',url='http://host:port/application_name/portlets/wsrp2?WSDL', server=server_name applicationVersion=version of the application)
For command syntax and examples, see "registerWSRPProducer" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
See also, Section 1.12.3.1, "Running Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Commands."