7 Administering Benefits
This chapter contains the following topics:
7.1 Understanding the Benefits Administration Process
As part of a total compensation package, companies typically provide benefit plans for their employees. Benefit plans vary among companies, organizations, and industries. However, most benefit plans include medical insurance, life insurance, and retirement and investment programs. Additionally, a company might offer various plan options.
You enroll employees in benefits plans so that they can participate in the benefit that the organization offers. Depending on how you set up benefit plans and the eligibility standards for employees or groups of employees, you can use one or more of these methods to enroll employees in the plans:
-
Enrollment with eligibility
-
Enrollment overrides
-
Batch enrollment
-
Self service enrollment
When you enroll employees in benefit plans that have eligibility requirements, you typically use the enrollment with eligibility method. With this method, the system verifies that employees meet the eligibility requirements before it enrolls them in a plan. You can also use batch enrollment to globally enroll employees who are eligible for enrollment. You typically use batch enrollment to enroll employees in mandatory and default plans.
In some cases, you might need to waive eligibility requirements for an employee. For example, suppose that you rehire an employee who previously worked for the organization for 10 years. In that case, you might waive the eligibility requirements for the employee. When you enroll the employee in benefit plans, you use enrollment overrides to waive the eligibility requirements of those plans.
You can provide an additional service to employees and reduce data entry by enabling self service benefits enrollment. With self service enrollment, employees use a website on the company's intranet to enroll in or change their own benefits during an open enrollment period—or when they are hired or have life changes, such as marriage. The system stores the changes that employees make in work files, which the system then updates to the live benefits tables.
You need to maintain accurate and current information to successfully administer benefit plans for all employees in the company. After you enroll employees in benefit plans, you can perform these tasks:
-
Correct or change employee and enrollment information.
-
Manage plan changes and open enrollment.
For each employee, you can produce a benefits statement that indicates the amount that both the employee and the company have contributed to the employee's benefits, taxes, and other compensation.
7.1.1 (USA) Administering Benefits for the U.S.
After a company has determined which standard, government-mandated, and supplemental benefits it will incorporate into its benefit package, benefit professionals must administer the plans. This task can be time-consuming and require paperwork. It generally involves close interaction with health insurance companies, state unemployment insurance offices, and pension plan administrators. Therefore, many companies hire a third-party administrator to assist them in administering the plans, maintaining plan compliance, and submitting regulatory reports to the appropriate administrators.
In addition to maintaining the benefit plans, benefit administrators must enroll employees in these plans. Many factors affect how employee enrollment is administered, such as eligibility requirements and enrollment periods. Most benefit plans have eligibility criteria—such as age, length of service, and employment status—that employees must meet before they are allowed to participate. For example, a pension plan might stipulate that for an employee to participate in the plan, the employee must be at least 21 years old, work a minimum of 20 hours per week, and have been employed by the company for at least one year. Sometimes the company decides these eligibility requirements, and sometimes the company works with the plan administrator to decide the requirements.
Regardless of how benefit eligibility requirements are determined, these criteria must be applied indiscriminately to the workforce to avoid top-heaviness and discrimination in the plan. The term top-heaviness refers to a plan (generally a pension plan) in which more than 60 percent of the assets are contributed by or on behalf of key employees, such as owners or executives, or those who earn more than a specified amount of compensation. Plans that are top-heavy are subject to financial remedies that redistribute plan assets more proportionately.
Another eligibility-related term that generally applies to pension plans is vesting. The term vesting refers to the point when employees take ownership of the contributions that the company makes to the pension plan on their behalf. This table illustrates three types of vesting:
| Type of Vesting | Description |
|---|---|
| Graded vesting | With this type of vesting, for each year that employees remain with the company, they gain a larger percentage of ownership of the employer-contributed account balance. The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) provides minimum requirements for graded vesting that are based on at least 20 percent vesting not later than the third year of employment. An additional 20 percent vests each year thereafter. Full vesting is required by the seventh year of employment. |
| Cliff vesting | With this type of vesting, full vesting occurs no later than the fifth year of employment. However, no vesting is required prior to year five. |
| Other vesting schedules | A vesting schedule can be more generous than cliff or graded vesting but, in order to comply with ERISA standards, it cannot be more restrictive. |
By instituting a vesting schedule, a company creates an incentive for employees to remain with the company. If employees leave the company before they are fully-vested in the plan, they forfeit a portion of the contributions made by the employer on their behalf and any earnings associated with those contributions. These forfeited funds must be redistributed within the plan.
Some benefit plans contain open enrollment or re-enrollment periods. Open enrollment refers to a time during which employees can change their benefit coverage or begin enrollment in a plan in which they were not previously enrolled. If an employee makes such changes outside the open enrollment period, waiting periods might be required before the changes take effect, or the employee might be prohibited entirely from making changes outside the open enrollment period. Re-enrollment occurs when a plan is based on a specific time period—generally, one year. Employees must re-enroll in the plan annually. During the re-enrollment period, employees can sign up for different coverage than they had previously.
Frequently, annual re-enrollment periods are associated with cafeteria plans or flexible spending account plans. Cafeteria plans—often referred to as flexible benefit plans—are an effective way of enabling employees to select benefits that are useful to them. Employees pick from a group of benefit options and pay for only those options that they choose. This method of selecting benefits represents a cost savings to both employee and employer because they both pay only for benefits that the employee uses. Generally, employers grant employees a specified number of flex credits that they employees use to pay for the benefits that they choose. Each benefit option has a flex cost, and that cost is deducted from the total number of flex credits granted to the employee.
When an employee does not have enough flex credits to pay for the benefits that the employee chooses, the excess amount can be deducted from the employee's payment through payroll deductions.
When an employee has more than enough flex credits to pay for the benefits that the employee chooses, some employers allow the employee to use the excess credits in one of these ways:
-
Receive the excess amount in the form of a taxable addition to the employee's pay.
-
Use the excess amount for other life needs, such as tuition expenses, weight-loss programs, smoking cessation programs, or financial planning expenses.
Some employers do not permit employees to use excess flex credits.
Flexible spending accounts (FSAs) are offered to employees under section 125 of the Internal Revenue Code. These benefits enable employees to elect a specified amount to be deducted from their payments on a pretax basis for future use in paying medical-related or dependent-care expenses. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) strictly regulates the expenses that are eligible for reimbursement and the amount of money that employees can contribute annually to these FSAs. Additionally, as required by the IRS, the employee must forfeit any amount that remains in the employee's account after the end of the plan year and reimbursement period.
7.2 Enrolling Employees
This section provides an overview of employee enrollment, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for the Enrollment with Eligibility program (P08334).
-
Enroll employees using eligibility.
-
Set processing options for the Enrollment Overrides program (P08330).
-
Enroll employees using overrides.
-
Run the Batch Enrollment program (R083800).
-
Set processing options for the Batch Enrollment program (R083800).
-
Unenroll employees using batch enrollment.
-
Run the Confirmation Statement program (R083440).
-
Set processing options for Confirmation Statement program (R083440).
7.2.1 Understanding Employee Enrollment
You enroll employees in benefits plans so that they can participate in the benefit that the organization offers. You also enroll employees so that they can pay premiums or make contributions to the benefit plans through payroll deductions. You can select from these methods for enrolling employees in benefits:
-
Enrollment with eligibility
-
Enrollment overrides
-
Batch enrollment
-
Self service enrollment
For benefit plans that have eligibility requirements, you can enroll employees using enrollment with eligibility or batch enrollment. You also use these methods when that company requires a specified group of employees to participate in particular plans. For example, you can use batch enrollment to enroll every employee assigned to the management benefit group in a mandatory management medical plan.
When you use enrollment with eligibility or batch enrollment, the system verifies that the employee's eligibility meets the standards for the plans and plan options that are available to the benefit group.
To use either enrollment with eligibility or batch enrollment, you must create benefit groups when you set up the system. A benefit group identifies the type of employee who is eligible for a particular set of benefits. Examples of benefit groups include executives, hourly employees, and part-time employees. You can create benefit categories (sets of related types of benefit plans) for each benefit group, and you can link multiple benefit plans to each category. For example, you can create a benefit category called Medical and link two medical plans—a traditional-style plan and a health maintenance organization—to that category.
Additionally, you can set up default plans for some benefit categories. When a category has more than one plan, you can define one of the plans as the default plan. If an employee does not select a plan or plan option, when you run the Enrollment with Eligibility program or the Batch Enrollment program, the system automatically enrolls the employee in the default plan.
You can use enrollment overrides when you need to waive eligibility requirements for specified employees.
As an alternative to staff members entering each employee's enrollment information, you can allow employees to enroll themselves online using self service benefits.
SeeJD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Foundation Guide.
See Understanding Enrolling in Flex Benefit Plans.
7.2.1.1 Enrolling Employees Using Eligibility
To enroll an employee in benefit plans that have eligibility requirements, you can use the Enrollment with Eligibility program. Before you can use this feature, the employee must be assigned to a benefit group. When you enroll an employee, the system tests for eligibility and assigns the applicable enrollment status and date to the employee's record, based on which eligibility requirements are met.
The system displays the selected employee's benefit group, benefit group rule, pay frequency, benefit status, and date started. If the employee's benefit group does not offer flex plans, the system also displays the total payroll deduction for the plans in which the employee is enrolled. The system updates this total as you change the employee's enrollment.
If the selected employee's benefit group offers flex plans, the system displays the Flex Elections tab, which lists the employee's available, spent, and remaining flex credits. The system also displays the employee's non-flex payroll deductions, any flex payroll deduction that results from overspending flex credits, and total payroll deductions.
The system displays a color-coded indicator in the upper-right corner of the enrollment form to indicate the current payroll status of an employee. This table describes the color-coding for the statuses:
| Color | Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Active employee not included in the current payroll cycle. |
| Fuchsia | Active employee included in the current payroll cycle. |
| Red | Terminated employee. |
| Yellow | Employee on leave of absence. |
For some benefit plans, you can enter variable amounts or rates. For example, when you enroll an employee in a retirement plan, you can enter the percentage of salary that the employee contributes to the plan. When you enroll an employee in a plan that requires you to enter an amount or rate that is unique to the employee, an additional form appears on which you can enter the information.
You can set up a default plan for a benefit category in which employees are required to elect a plan. For example, you can set up a medical benefit category that includes three plans, with a default plan for no coverage. Employees can select a medical plan in which they participate. If an employee does not select a medical plan in the category, the system automatically enrolls the employee in the default plan for no coverage.
When you enroll an employee in benefit plans, you can use the options on the Row menu to access detailed information about individual benefit plans.
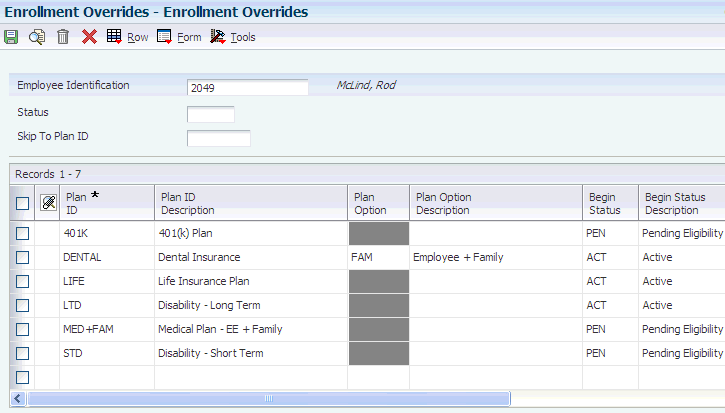
7.2.1.2 Enrolling Employees Using Overrides
Use enrollment overrides when you need to waive eligibility requirements for particular employees. For example, if an organization acquires another company, the acquisition plan might stipulate that you waive the benefits eligibility requirements for the employees in the acquired company. You can use enrollment overrides to enroll these employees in plans for which they would not typically meet the eligibility requirements.
The Enrollment Overrides form includes these date fields, which enable you to review and record the dates that are associated with employee enrollment:
-
Begin Date
-
Ending Date
-
Eligible Date
-
Participation Date
-
DBA Begin Date (deduction, benefit, accrual begin date)
-
DBA End Date
-
User Def Date (user-defined date)
Because the reasons for overriding existing eligibility requirements differ by organization, you can use the User Def Date field to record date information that is specific to the organization's business needs. For example, the organization might track the date on which the employee was hired when overriding eligibility. Or, it might track the date on which an employee would have been eligible for the benefit if the eligibility requirement had not been overridden.
You can use vocabulary overrides to rename this field with a name that fits the organization's needs. For example, you might change the name of the User Def Date field to the Hire Date field or the True Eligibility Date field. You can use this field to track any date that you want to associate with an employee's benefit enrollment.
7.2.1.3 Enrolling Employees Using Batch Enrollment
To enroll multiple employees at the same time, use the Batch Enrollment program (R083800). The Batch Enrollment program is an especially efficient tool for enrolling employees in mandatory plans. For example, you can enroll all employees who are assigned to the management benefit group in a mandatory management medical plan.
You can also use the Batch Enrollment program to enroll employees in default plans. That is, if a category has more than one plan, you can set up one plan as the default. If an employee does not make a selection from the category, the system enrolls the employee in the default plan.
In addition, if you have enrolled employees who did not immediately pass the eligibility requirement, you can run the Batch Enrollment program to retest their eligibility. The program also tests continuing eligibility. For example, an employee who experiences a reduction in hours can become ineligible for the benefit plan. The system uses the defined effective date to retest the employees and enrolls the employees who meet the test criteria. To test for eligibility, the system uses the eligibility rules and date codes that are assigned to the plan in conjunction with the enrollment parameters.
For example, an employee might have a three-month waiting period for active enrollment. Suppose that you receive the election forms one month after the hire date and enter the elections. The employee does not pass the initial eligibility test, so the system gives the employee an ineligible status. When you run the Batch Enrollment program with an effective date that is three months after the hire date, the program retests the employee using the initial eligibility test. This time, the employee passes the eligibility test, and the system updates the records. You can review both the before and after enrollment records to review the changes that the system made.
If you use data selection criteria for the version of the Batch Enrollment program that you run, you must include benefit status in the data selection criteria.
Depending on how you set the processing options, the Batch Enrollment program generates one or more of the reports described in this table:
| Report | Usage |
|---|---|
| Detail By Employee | Review all employees and their corresponding enrollment status for each benefit plan. |
| Invalid Enrollment | Identify any employees enrolled in a benefit plan that is not available for the benefit group. |
| One Election Required | Identify employees who have not elected at least one plan within a category that requires election of a plan. |
| Manual Review | Identify any employees enrolled in a benefit plan that is not available for the benefit group. |
| No Action Taken | Review the records that the system did not change during the batch enrollment. The report includes remarks indicating why the enrollment was not made and the action that must occur before the system enrolls the employee. Additionally, the report lists invalid date errors and indicates that incorrect dates were included in the plan setup. |
To preview the changes that will take place during batch enrollment, you can run the Batch Enrollment program in proof mode. After you review the reports to verify that the enrollments are correct, you can run the Batch Enrollment program in final mode. To verify enrollment for the employees that you selected, select
Daily Processing menu (G08BB1), Enrollment with Eligibility or Enrollment Overrides.
|
Note: The system recalculates the plan costs every time that you run the Batch Enrollment program. |
7.2.1.4 Unenrolling Employees Using Batch Enrollment
To simultaneously unenroll multiple employees from a benefit plan, use the Batch Enrollment program (R083800). If you add data selection criteria for the version that you create, you must include benefit status.
To preview the changes that will take place when you run the version that you have created, you can run the Batch Enrollment program in proof mode. After you review the reports to verify that the information is correct, you can run the Batch Enrollment program in final mode. To verify that the employees you selected are unenrolled, select
Daily Processing menu (G08BB1), Enrollment with Eligibility or Enrollment Overrides.
When you have successfully unenrolled the selected employees, you no longer need the enrollment parameters that you created for each plan from which employees were unenrolled. We recommend that you delete them from the Enrollment Parameters program (P08392).
Before you can unenroll employees using batch enrollment you must:
-
Determine the plans or categories from which you need to unenroll employees.
-
Enter this information in the Enrollment Parameters program (P08392) to create enrollment parameters for each plan from which you are unenrolling employees:
-
Benefit status equals *.
-
Enrollment status equals ACT.
-
Valid plan equals Y.
-
Date code equals F.
-
New status equals TRT.
-
7.2.1.5 Printing a Confirmation Statement
After you enroll employees using batch enrollment, you can print a confirmation statement. The Confirmation Statement report (R083440) contains the benefit plans and benefit plan options in which an employee is enrolled. It also lists all applicable deductions, benefits, and accruals. Employees use this statement to confirm that they have been correctly enrolled according to their choices.
7.2.2 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section, you must:
-
Set up benefit plans and related information.
-
Create an employee record for each employee whom you need to enroll in benefits.
-
If necessary, enter or change the benefit group selection for a group of employees before you enroll them in benefit plans:
-
Assign a benefit status to all employees whose records will be processed in batch.
If necessary, enter or change the benefit group selection for a group of employees before you enroll them in benefit plans:
-
Review the setup for the Batch Enrollment Parameters table (F08392).
7.2.3 Forms Used to Enroll Employees
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Enrollment With Eligibility | W08334A | Daily Processing menu (G08BB1), Enrollment with Eligibility
On the Work With Enrollment With Eligibility form, select each record in the detail area for a benefit plan or plan option in which you want to enroll the employee, and then select Elect from the Row menu. If any of the plans that you select requires an amount or rate, the Change Amount or Rate form appears. |
Enroll employees using eligibility. |
| Enrollment Overrides | W08330B | Daily Processing (G08BB1), Enrollment Overrides | Enroll employees using overrides. |
7.2.4 Setting Processing Options for the Enrollment with Eligibility Program (P08334)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
7.2.4.1 Dates
These processing options specify the dates that the system uses when it processes enrollments with eligibility.
- 1. Effective Date
-
Specify the effective date. To use the system date as the effective date, leave this processing option blank. The effective date is used in conjunction with the plan's initial and continuing eligibility tests to determine the employee's enrollment status and date. When you enter an effective date on the Enrollment with Eligibility form, that date overrides the date that you enter in this processing option.
- 2. Eligible Date
-
Specify whether to automatically calculate and display eligibility dates for unelected plans and plan options. Values are:
0: Do not calculate for unelected plans.
1: Calculate eligibility dates for unelected plans and plan options.
Calculating eligibility for unelected plans and plan options significantly increases the time required to display the employee's plan information.
- 3. Qualifying Life Event Date
-
Specify a date when a qualifying life event, such as marriage, occurs.
7.2.4.2 Defaults
These processing options specify the default information for processing enrollments.
- 1. Future Enrollment Status
-
Specify the value that you are using to indicate that a future enrollment record exists for the plan. The values that you enter in this processing option are not associated with a user-defined code (UDC) table.
For this processing option, future means that the actual plan enrollment date is greater, or later in the future, than the entered effective date. Values can be any three-digit alphanumeric status.
- 2. Mistaken Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES for the enrollment status assigned to mistaken enrollments. If you leave this processing option blank, the system displays an error message when you select the Mistaken Enrollment option on the Enrollment with Eligibility form.
- 3. Ending Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES for the enrollment status that you want to assign to enrollments that have ended. If you leave this processing option blank, the system displays an error message when you select the Stop - Auto Dt/Sts (stop - automatic date and status) option on the Enrollment with Eligibility form.
- 4. Ending Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES that affects enrollments in only those plans for which you enter an ending date in either the Plan Master form (P08320) or the Plans within Categories form (P08351). For example, a flexible spending account plan might have an ending date because employees must re-enroll in the plan each year. Specify the UDC 08/ES for the ending enrollment status assigned to enrollments in these plans. The system assigns the ending enrollment status when you enroll the employee in the plan.
- 5. Ending Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES assigned to enrollments that have ended because of a rate change to a plan or option.
The system checks for plan and option rate change as of the effective date entered. If there is a rate change, the system verifies the existence of DBA history for the plan or option. If DBA history exists, the processing option ends the enrollment. A new enrollment and new Employee DBA Instruction records with the new rates are created. If no DBA history exists, the existing Employee DBA Instruction records are replaced with the new rates.
- 6. Enrollment Event Code
-
Specify the three-character code that represents a qualifying life event, such as marriage.
- 7. Call Enrollment Event Form
-
Specify whether to call the form that is used to enter the enrollment event code and event date. Values are:
0: Do not call the form.
1: Call the form.
- 8. Plan/Option Description
-
Specify the field from which to retrieve the description. Values are:
0: Retrieve the description from the Plan/Option Description field in the F08320 table or the F083202 table.
1: Retrieve the description from the Self Service Description field in the F08320B table.
7.2.5 Enrolling Employees Using Eligibility
Access the Work With Enrollment With Eligibility form.
Figure 7-1 Work With Enrollment With Eligibility form
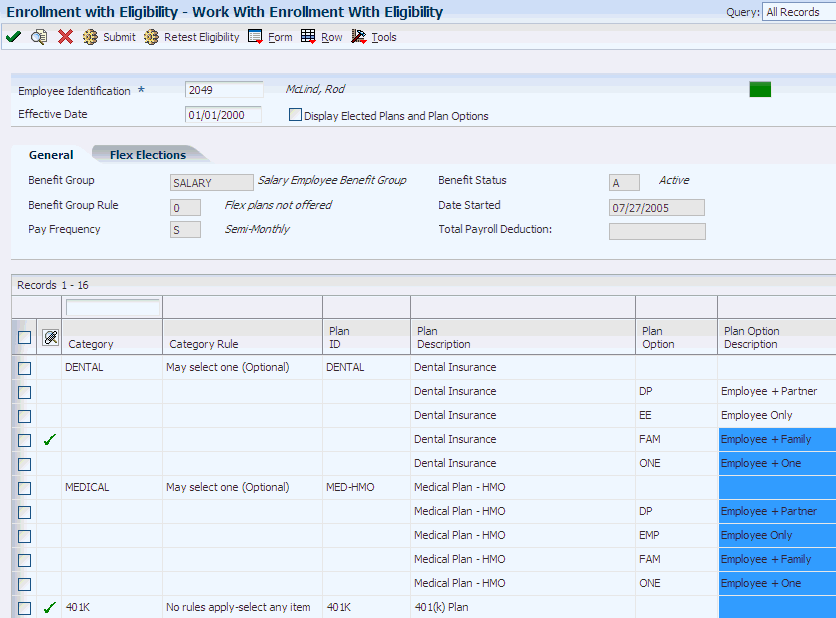
Description of "Figure 7-1 Work With Enrollment With Eligibility form"
To enroll an employee using eligibility:
-
Complete these fields and click Find:
-
Employee Identification
-
Effective Date
-
-
Review the information in these fields:
-
Benefit Group
-
Benefit Status
-
Benefit Group Rule
-
Date Started
-
Pay Frequency
-
-
If the selected employee's benefit group offers flex plans, click the Flex Elections tab and review the information in these fields as you change the employee's enrollment:
-
Flex Credits Available
-
Non Flex Payroll Deduction
-
Flex Credits Spent
-
Flex Payroll Deduction
-
Flex Credits Remaining
-
Total Payroll Deductions
-
-
In the detail area, select each record for a benefit plan or plan option in which you want to enroll the employee, and then select Elect from the Row menu.
If any plans that you select require an amount or rate, the Change Amount or Rate form appears.
-
On the Change Amount or Rate form, enter the amount or rate that the employee pays in the unlabeled field to the right of the Employee Payroll Ded DBA (employee payroll deduction DBA) field.
-
If applicable, complete the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field.
If the company has set up the system to calculate the employer-paid DBA based on information from the employee-paid DBA, leave the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field blank. For this type of setup, the system calculates the amount or rate based on the value in the employee-paid field. If the company has not set up the system so that it calculates the employer-paid DBA based on the employee-paid DBA, enter the amount or rate in the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field.
-
When you have entered the amounts or rates, click OK to close the Change Amount or Rate form.
-
On the Work With Enrollment With Eligibility form, review the amount in the Total Payroll Deduction field on either the General tab or the Flex Elections tab.
The system displays the Total Payroll Deduction field on the General tab only if the selected employee's benefit group does not offer flex plans. If the selected employee's benefit group offers flex plans, the system displays the Total Payroll Deduction field on the Flex Elections tab.
Before you click Submit to save the elections, you can undo an incorrect election by clearing the check mark for that election.
-
Click Submit to save the entries.
Note:
Every time that you submit records on the Enrollment with Eligibility form, the system recalculates the DBA amounts.If you discover an incorrect election after you have saved the record, select the Mistaken Enrollment option from the Row menu to remove the election.
See Working with Enrollment with Eligibility.
-
Effective Date
Enter the date that identifies when a date is first valid. The effective date is used generically. It can be a lease effective date, a price or cost effective date, a currency effective date, a tax rate effective date, or whatever is appropriate.
-
Date Started
Displays the date on which the employee actually reported to work for the most recent period of hire. When an employee initially begins working, the default date is the original hire date. If no original hire date exists, the system uses the current date. This field can be updated multiple times if, for example, an employee is a seasonal worker.
For the calculation tables in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Payroll and the eligibility tables and date codes in Human Resources, the system also uses this date as a start date when it calculates deductions, benefits, and accruals.
-
Pay Frequency
Displays a UDC 07/PF that indicates how often an employee is paid. Values are:
B: Biweekly
W: Weekly
S: Semimonthly
M: Monthly
A: Annually
C: European Annualized
The system uses the value in the Description-2 field in the UDC to calculate the amount per pay period for a salaried employee.
-
Flex Credits Available
Displays the total flex benefit credits available to an employee.
-
Non Flex Payroll Deduction
Displays the cost that the system calculates for a plan or plan option.
-
Flex Credits Spent
Displays the total amount of flex benefit credits spent by the employee.
-
Flex Payroll Deduction
Displays the amount of the payroll deduction when the flex benefit deductions for an employee are greater than the flex benefit credits provided by the employer.
-
Flex Credits Remaining
Displays the amount of the remaining flex benefits. The system derives the amount by subtracting the flex benefits spent by an employee from the flex benefits available to that employee.
-
Total Payroll Deductions
Displays an amount that represents the total payroll deductions for an employee for a pay period as a result of enrollment in a benefit plan. This amount is the total of applicable flex and non-flex benefit deductions.
-
Total Payroll Deduction:
Displays the cost that the system calculates for a plan or plan option.
-
7.2.6 Setting Processing Options for the Enrollment Overrides Program (P08330)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
7.2.6.1 Defaults
These processing options specify the default values that the system applies when you enroll employees with overrides.
- 1. DBA Points Multiplier
-
Specify a factor to convert plan DBA points to a monetary amount. The system multiplies the factor by the DBA points.
The factor can be a whole number and up to four decimal places, or up to four decimal places only without a whole number. For example, 1.4321 has the format for a whole number and decimal places, and .9876 has the format for a factor that is less than one.
Blank is a value when the plan DBA points do not need to be converted to a monetary amount.
- 2. Plan/Option Description
-
Specify whether to retrieve the description from the Plan/Option Description field in the Benefits Plan Master table (F08320) and the Plan Additional Options table (F083202), or from the Self Service Description field in the Plan/Plan Option Tag table (F08320B). Values are:
0: Retrieve the description from the Plan/Option Description field in the F08320 table or the F083202 table.
1: Retrieve the description from the Self Service Description field in the F08320B table.
- 3. Enrollment Event Codes
-
Specify whether the qualifying event code appears on the form. The enrollment event code identifies a life event such as marriage. An enrollment or change by override cannot be made without an enrollment event, but the code does not need to appear on the form. Values are:
0: Plan and option description.
1: Self service description.
7.2.7 Enrolling Employees Using Overrides
Access the Enrollment Overrides form.
To enroll employees using overrides:
-
On the Enrollment Overrides form, to locate the employee for whom you need to enter plans, complete the Employee Identification field and click Find.
The system displays all of the plans in which the employee is enrolled.
-
To enroll the employee in a plan, complete these fields in a blank record in the detail area:
-
Plan ID
-
Begin Status
-
Begin Date
-
Eligible Date
-
Participation Date
-
-
To track a user-defined date, complete the Use Def Date field.
-
If the plan has associated options, complete the Plan Option field.
If the plan requires an amount or rate, the Change Amount or Rate form appears.
-
On the Change Amount or Rate form, enter the amount or rate that the employee pays in the unlabeled field to the right of the Employee Payroll Ded DBA field.
-
If applicable, complete the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field.
If the company has set up the system so that it calculates the employer-paid DBA based on information in the employee-paid DBA, do not complete the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field. For this type of setup, the system calculates the amount or rate based on the value in the employee-paid field. If the company has not set up the system to calculate the employer-paid DBA based on information in the employee-paid DBA, enter the amount or rate in the unlabeled field to the right of the Employer Paid Benefit DBA field.
-
When you have entered the amounts or rates, click OK to close the Change Amount or Rate form.
-
To enroll the same employee in another plan, repeat the preceding steps.
-
When you are finished entering the plans, click OK.
-
To verify changes to an amount or rate for a plan, review the DBA instructions for the employee.
-
Begin Status
Enter a code from UDC 08/ES that indicates the status of an employee's enrollment in a plan. You must use these guidelines for the definitions:
All statuses indicating active participation in a plan must begin with the letter A.
All statuses indicating an ending status that does not result in a new enrollment (such as a termination) must have the letter X in the first position of the Description 2 field value (data item DL02) on the General User-Defined Codes form.
A status beginning with the letter X, when used as an ending status, represents a mistaken enrollment. No employee DBA instructions are written.
An asterisk (*) indicates all statuses not otherwise specified.
-
Begin Date
Enter the date that the benefit plan goes into effect after the employee's eligibility is verified.
-
Eligible Date
Enter the date on which the employee is eligible to enroll in the benefit plan. This date is not necessarily the date that the employee begins participating in the plan.
For example, the XYZ company requires that employees work for the company for six months before they are eligible to participate in the 401(k) plan. Employees can enroll in 401(k) two times per year, on January 1 and July 1. Therefore, an employee who begins working for the company on March 1, 2008, has an eligibility date of January 1, 2009.
The eligibility date is the date on which the employee becomes eligible, provided that eligibility continues. If the employee changes to an ineligible status, the eligibility date on the new record is blank.
-
Participation Date
Enter the date on which the employee begins participating in the plan for the specified enrollment period.
Here is an example. XYZ company requires that employees work for the company for six months before they are eligible to participate in the 401(k) plan. Employees can enroll in 401(k) two times per year, on January 1 and July 1. An employee who begins working for the company on March 1, 2008, is eligible to participate in the plan on January 1, 2009. However, if the employee does not enroll in the plan until July 1, 2009, the employee's participation date is July 1, 2009.
The participation date is the first date on which the employee begins participating in the plan, provided that the employee continues to participate. When participation stops, the participation date on the new record is blank. If the employee has a break in eligibility, the participation date is the date that participation began for the latest enrollment period.
-
User Def Date (user-defined date)
Enter a user-defined date that you can use in enrollment for any date tracking need.
For example, you can use this field to display the employee's hire date as in this example:
Empl No - 6001, Plan ID 401K
Ineligible Status, Begin 04/13/97, End 12/31/97, User Date 04/13/98
Elig/Not Particp Status, Begin 01/01/98, End 05/31/98, Eligible 01/01/98, User Date 04/13/98
Active Status, Begin 06/01/98, End 08/31/99, Eligible 01/01/98, Particip 06/01/98, User Date 04/13/98
Ineligible Status, Begin 09/01/99, End 05/31/99, User Date 04/13/98
Active Status, Begin 06/01/99, End 06/01/99, Eligible 06/01/99, User Date 04/13/98
For this example, you would change the User Date column heading to Hire Date.
-
7.2.8 Running the Batch Enrollment Program (R083800)
Select Daily Processing (G08BB1), Batch Enrollment.
7.2.9 Setting Processing Options for the Batch Enrollment Program (R083800)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
7.2.9.1 Date
This processing option specifies the dates that the system uses when it processes batch enrollments.
- 1. Effective Date
-
Specify the effective date of the enrollment. To use the system date as the effective date, leave this field blank. The effective date is used in conjunction with the plan's initial and continuing eligibility tests to define the employee's enrollment status and date.
7.2.9.2 Process
These processing options specify the type of information to process during a batch enrollment.
- 1. Mode
-
Specify whether you want to process enrollments in proof mode or final mode. Values are:
0: Proof mode. The system prints the requested reports without updating the employees' DBA instructions. Use the report to verify enrollment information before you process enrollments in final mode.
1: Final mode. The system prints the requested reports and updates the database. Use this mode after you have verified enrollment information and are ready to update the employees' DBA instructions.
- 2. Category
-
Specify the category for which you want to process enrollments. If you leave this processing option blank, the system processes all categories.
- 3. Plan
-
Specify the plan in which to enroll employees. If you leave this processing option blank, the system runs batch enrollment for all plans.
- 4. Plan Additional Option
-
Specify a Plan Additional Option to run batch processing. If you leave this processing option blank, the system runs batch processing for all Plan Additional Options. This processing option must be a valid Plan Additional Option and must be used with the Plan ID processing option.
- 5. Ending Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES that affects enrollments in only those plans for which you entered an ending date in either the Plan Master (P08320) or Plans within Categories (P08351). For example, a flexible spending account plan might have an ending date because employees must re-enroll in the plan each year. Specify the UDC 08/ES for the ending enrollment status assigned to enrollments in these plans. The system assigns the ending enrollment status when you enroll the employee in the plan.
- 6. Benefit Status
-
Specify the change of benefit status of the employees in the report. Values are:
0: Status changed to active.
1: Status is not changed.
- 7. R083805 Version
-
Specify the value in which version of the Update Flex Payroll Deduction UBE (R083805) should be run. If this fields is left blank, then you can not run the R083805.
7.2.9.3 Enrollment
These processing options specify the types of employees to include in the batch enrollment.
- 1. Mandatory and Default Plans for New Hires
-
Specify whether the batch enrollment enrolls newly hired employees in all mandatory and default benefit plans. Newly hired employees are employees who have a benefit status of N. Values are:
0: No, do not enroll new hires in mandatory and default plans.
1: Yes, enroll new hires in mandatory and default plans.
- 2. Mandatory and Default Plans for Rehires
-
Specify whether the batch enrollment enrolls rehired employees in all mandatory and default benefit plans. Rehired employees are employees who have a benefit status of R. Values are:
0: No, do not enroll rehired employees in mandatory and default plans.
1: Yes, enroll rehired employees in mandatory and default plans.
- 3. Mandatory and Default Plans for Transfers
-
Specify whether the batch enrollment enrolls recently transferred employees in all mandatory and default benefit plans. Recently transferred employees are employees who have a benefit status of T. Values are:
0: No, do not enroll transferred employees in mandatory and default plans.
1: Yes, enroll transferred employees in mandatory and default plans.
- 4. Mandatory and Default Plans for Active Employees
-
Specify whether the batch enrollment program enrolls active employees in all mandatory and default benefit plans. Active employees are employees who have a benefit status of A. Values are:
0: No, do not enroll active employees in mandatory and default plans.
1: Yes, enroll active employees in mandatory and plans.
7.2.9.4 Recalculation
This processing option specifies the ending enrollment status for a date-sensitive amount or rate that has changed for an enrolled plan.
- 1. Ending Enrollment Status
-
Specify the UDC 08/ES. Use this processing option when a date-sensitive amount or rate has changed for an enrolled plan. If the DBA within that plan has history attached to it, the system must write the old record with an ending status and create a new record with the new amount or rate.
The code entered in this option can be different from the code defined in the option on the Process tab. This enables you to identify why the plan was ended and started again. If the DBA within that plan has no history attached to it, then the current record is replaced with the new amount or rate.
7.2.9.5 Reports
These processing options specify the reports that the system prints when you process a batch enrollment.
- 1. Detail By Employee
-
Specify whether the system prints the Detail by Employee report when you process a batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Do not print the report.
1: Print the report.
- 2. Invalid Enrollment
-
Specify whether the system prints the Invalid Enrollment report when you process a batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Do not print the report.
1: Print the report.
- 3. One Election Required
-
Specify whether the system prints the One Election Required report when you process a batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Do not print the report.
1: Print the report.
- 4. Manual Review
-
Specify whether the system prints the Manual Review Requested report when you process a batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Do not print the report.
1: Print the report.
- 5. No Action Taken
-
Specify whether the system prints the No Action Taken report when you process a batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Do not print the report.
1: Print the report.
- 6. Changes
-
Specify whether the reports include all records or only the records that changed as a result of the batch enrollment. Values are:
0: Print all records.
1: Print changed records only.
7.2.10 Unenrolling Employees Using Batch Enrollment
Select Daily Processing (G08BB1), Batch Enrollment.
7.2.11 Running the Confirmation Statement Program (R083440)
Select eriodic Processing (G08BB2), Confirmation Statement.
7.2.12 Setting Processing Options for the Confirmation Statement Program (R083440)
Processing options enable you to specify the processing for programs and reports.
7.2.12.1 Date
This processing option specifies the date that the system uses when it tests enrollment and selects plans for the report.
- 1. Effective Date
-
Specify the effective date for the selection of plans and for testing enrollment. The confirmation statement cannot be processed without a valid date.
7.2.12.2 Print
These processing options specify whether to print specified information on the report.
- 1. Employee Address
-
Specify whether to print the employee's address. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the employee's address.
1: Print the employee's address.
- 2. Employee Annual Salary
-
Specify whether to print the employee's annual salary. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the employee's annual salary.
1: Print the employee's annual salary.
- 3. Employee Age
-
Specify whether to print the employee's age. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the employee's age.
1: Print the employee's age.
- 4. Employee Life Ins. Annual Salary (employee life insurance annual salary)
-
Specify whether to print the employee's life insurance annual salary. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the employee's life insurance annual salary.
1: Print the employee's life insurance annual salary.
- 5. Benefit Group Description
-
Specify whether to print the benefit group description. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the benefit group description.
1: Print the benefit group description.
- 6. Benefit Group Category Description
-
Specify whether to print the benefit category description. Values are:
Blank or 0: Do not print the benefit category description.
1: Print the benefit category description.
7.3 Working with Fund Allocations
This section provides an overview of fund allocations, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
-
Revise fund allocation percentages.
-
Revise fund allocation start dates.
7.3.1 Understanding Fund Allocations
Many companies offer employees a variety of options for retirement or investment plans, such as 401(k) plans. To set up a retirement or investment plan that includes several investment options, you set up each option as a separate accrual.
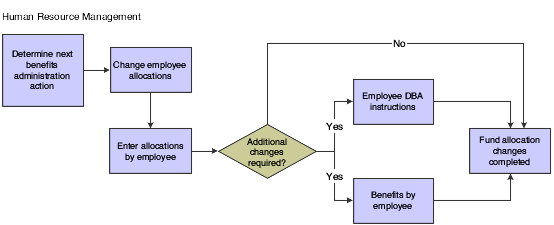
When you enroll an employee in a retirement or investment plan, you identify the percentage or amount of the contribution from the employee's wages and any percentage or amount that the employer contributes. After you enroll an employee in the retirement or investment plan, you create fund allocations to define how the system distributes that total contribution among the available investment options.
To define the way in which an employee distributes funds among investment options, you must add a new allocation. You also specify the percentage of the total contribution that the employee contributes to each investment program.
You change a fund allocation whenever an employee changes an allocation among the investment programs that the company offers. The employee can allocate funds among all available investment programs, but the total must equal 100 percent.
The new allocations begin on the new start date. The previous allocations end one day before the new start date.
An employee might request that you revise fund allocation percentages or start dates. You can revise this information for the upcoming pay period only if the system has not yet made a deduction from the employee's pay. When any pre-payroll processing has occurred, you cannot revise the fund allocation, but must make a new allocation.
This graphic illustrates the process for changing fund allocations:
7.3.2 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section, you must:
-
Link the accrual codes for each investment program to the DBA codes for the retirement or investment plan.
-
Enroll the employee in the retirement or investment plan.
See Enrolling Employees.
7.3.3 Forms Used to Work with Fund Allocations
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Allocations By Employee | W08346D | Daily Processing (G08BB1), Allocations by Employee | Revise fund allocation percentages.
Revise fund allocation start dates. |
7.3.4 Revising Fund Allocation Percentages
Access the Work With Allocations By Employee form.
To revise fund allocation percentages:
-
Complete these fields to locate the employee's allocations:
-
Employee Identification
-
Plan ID
-
-
Select one of these options and then click Find:
-
Current Enrollment
-
Prior Enrollment
-
All
-
-
Select the record that contains the allocations that you want to change, and then select Allocations by EE (employee) from the Row menu.
-
Enter the correct percentage in the New Percent % field and click OK.
7.3.5 Revising Fund Allocation Start Dates
Access the Work With Allocations By Employee form.
To revise fund allocation start dates:
-
On the Work With Allocations By Employee form, locate the employee's allocations by completing these fields:
-
Employee Identification
-
Plan ID
-
-
Select one of these options and then click Find:
-
Current Enrollment
-
Prior Enrollment
-
All
-
-
Select the record that contains the allocation with the incorrect start date and click Delete.
-
On the Delete Confirmation form, click Yes.
-
Select the record that contains the latest allocation for the enrollment, and then select Allocations by EE from the Row menu.
-
Enter the correct percentage in the New Percent % field and click OK.
-
Current Enrollment
If you select this check box, this system displays records without an enrollment end date or an enrollment end date after the system date
-
Prior Enrollment
If you select this check box, the system displays records with an enrollment end date prior to the system date
-
All
If you select this check box, the system does not filter records based on the enrollment dates.
-
New Percent %
Displays the percentage of the total contribution (employee and employer) that the employee allots to the various 401(k) investment funds. The percentages, if not 0, must be greater than 5 percent and they must total 100 percent.
-