| Oracle® Auto Service Request Release 3.5 for Oracle Linux and Solaris |
|
Welcome to the Auto Service Request (ASR) software from Oracle. ASR is a secure, scalable, customer-installable software feature of Oracle Premier Support for Systems and Oracle/Sun Limited Warranty support that provides auto-case generation when specific hardware faults occur. ASR is designed to enable faster problem resolution by eliminating the need to initiate contact with Oracle for hardware failures, reducing both the number of phone calls needed and overall phone time required. ASR also simplifies support operations by utilizing electronic diagnostic data. If your qualified system is under warranty or covered by a service plan, you are entitled to ASR at no charge. Visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr) for information to see which server, storage, and Oracle Exadata products are qualified for ASR.
|
Note: ASR is not a monitoring solution and is not a substitute for the normal monitoring processes/services that customers have. |
This document provides complete instructions to install the ASR software. Before beginning the installation, review the following topics in this section:
ASR provides the following features:
Telemetry Collection and Forwarding: ASR collects specific hardware telemetry data from all ASR-enabled systems, called ASR Assets. ASR filters this telemetry data and forwards what it determines to be potential hardware faults directly to Oracle. Hardware faults cover faults coming from fans, to power supplies, disks, memory, CPUs, and other internal hardware components. The fault telemetry sent to Oracle includes specific hardware faults, but also includes the conditions that may later result in a component failure. The ASR fault coverage is different for each qualified system type.
Automatic Creation of Service Requests: Once fault telemetry is sent to Oracle's ASR infrastructure, systems filter the data again to confirm the reality of the fault and then automatically generates a Service Request. Once created, Service Requests are sent to Oracle Support and also communicated, via e-mail, to the technical support contact on record for the qualified system reporting the fault.
Support Response: Service Requests are actively reviewed by Oracle Support Services and service response is provided in accordance with your Service or Warranty contract.
Whether this is a new installation of ASR, or if you already have some familiarity with the ASR software, it is highly recommended that you review the ASR architecture discussed below. Understanding the architecture and the nomenclature of ASR is key to a successful installation. The following diagram shows the end-state environment once ASR is installed. Use the numbered indicators in the diagram to review it in sequential order and for corresponding explanations in the text that follows.
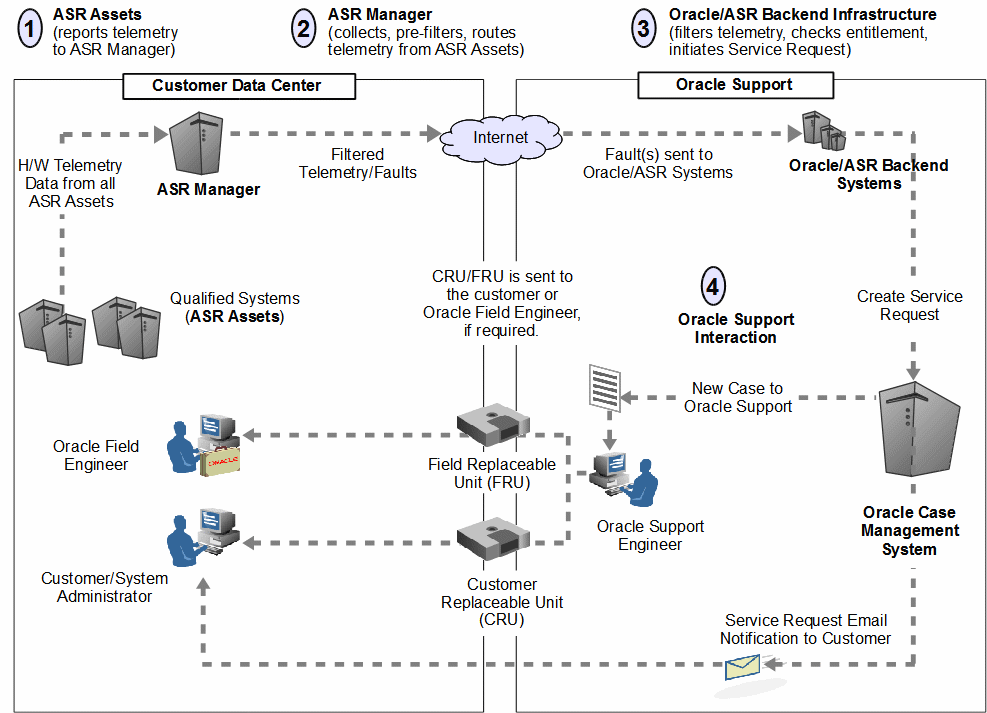
ASR Assets: ASR Assets are qualified systems that are configured to report its hardware telemetry to an ASR Manager.
ASR Manager: The ASR Manager is a system that centrally accepts hardware telemetry data sent from a group of ASR Assets. The ASR Manager filters the incoming data and forwards potential fault telemetry to Oracle/ASR Backend systems. Additional features of the ASR Manager include the following:
The ASR Manager is always installed first, followed by ASR Assets.
You have the option to install more than one instance of an ASR Manager. The reasons to do this may be to support a large amount of ASR Assets and/or for organizational reasons, such as grouping ASR Assets by data center, support group, subnet, or other grouping scheme as desired by the customer. An ASR Asset communicates its telemetry to one ASR Manager only.
The ASR Manager system can be installed as an ASR Asset. This way, the ASR Manager system can report its hardware telemetry, as does an ASR Asset.
The telemetry data that is sent from the ASR Manager to the Oracle /ASR Backend Systems is encrypted. For more information on this topic, refer to the ASR White Paper at: http://www.oracle.com/asr.
Refer to "Close-Up of the ASR Manager" for more information on the ASR Manager system.
Oracle/ASR Backend Systems: The ASR backend infrastructure at Oracle collects all telemetry data forwarded to it from the ASR Manager, or ASR Managers if multiple instances are installed. The fault rule technology on these backend systems ascertain the reality of the fault telemetry, and forwards recognized faults to Oracle's Service Request system. From there, the following actions occur:
A Service Request, also called a case, is created and assigned to an Oracle Support Engineer. At the same time, an email notification of the Service Request is sent to your support contact on record associated with the system reporting a fault.
The Service Request is handled in accordance with the asset's Support or Warranty contract.
Oracle Support Interaction: Once an Oracle Support Engineer begins working on the Service Request, the engineer may collect additional information from you to better determine resolution to the hardware issue. Resolution to the issue may involve system configuration or the following possibilities:
Order and ship a replacement part with installation instructions to you. These are called Customer Replaceable Units (CRUs).
Order and ship a replacement part to the customer site to be installed by an Oracle Field Engineer. These are called Field Replaceable Units (FRUs).
The ASR Manager software runs as a plug-in application to the Oracle Automated Service Manager (OASM) software. OASM is an applications environment that manages various plug-in applications used mainly for system-level management. OASM simplifies different Oracle Network Service deployments and provides a secure transport mechanism for telemetry data. In addition to ASR, an example of another OASM plug-in application is Secure File Transport (SFT). The diagram below shows the relationship between ASR, OASM, and SFT.

This section summarizes the ASR installation process so that customers are better prepared to install ASR.
Prerequisites overview
Valid Oracle Support Contract
Access to My Oracle Support
Customer Support Identifier
Identify ASR Manager and Assets
Download and install the ASR package
Download ASR and Services Tools Bundle (STB) packages
Identify Telemetry sources
Configure ASR Manager and Assets
Register ASR Manager and Assets
Using ASR
ASR e-mails
Updating traps
Troubleshooting and support
Keep the following guidelines in mind when installing ASR:
Installing ASR consists of installing an ASR Manager followed by ASR Assets. The ASR Manager system is always installed first. Once the ASR Manager is installed and activated, ASR Assets can be added or removed as needed. For more on the roles of these ASR components, refer to "ASR Architectural Summary".
Installers of ASR should have systems administration experience and some measure of support responsibility for the systems where ASR is to be installed.
The ASR installation process may vary given the differences across computing environments. This document makes every attempt to accommodate these differences, but it is helpful to be aware of the following considerations that may alter the process:
Hardware Platform: Some hardware may not support the installation of ASR. This document provides the platform criteria for ASR installation. Visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr) to see which server, storage, and Oracle Exadata products are qualified for ASR.
Operating System Version: The operating system version – either Oracle Linux or Solaris – may impact the ASR installation. Some platforms may require an operating system update and/or a patch upgrade.
Existing Hardware Telemetry Sources: The existing telemetry sources on systems may impact the installation of ASR. In some cases, telemetry software may need to be upgraded.
Access to My Oracle Support: You must have a login and access to My Oracle Support (http://support.oracle.com) before installing ASR.
Accuracy of Data in the My Oracle Support Database: A key task to installing ASR involves validating hardware serial numbers, contract levels, and support contacts in the My Oracle Support database. If this data is inaccurate, you will have to correct it. ASR relies on the accuracy of this data to verify service entitlement, to ensure the proper routing of Service Requests, and to ensure the correct support personnel are contacted when specific systems send fault telemetry.
Refer to the following sections for a summary of the major milestone steps with installing Oracle Auto Service Request.
This milestone determines which host system will have the ASR Manager installed. It includes sizing the system and ensuring it is qualified for ASR. This milestone also consists of determining which systems will be installed as ASR Assets and ensures that they too are qualified for ASR.
This milestone also involves accessing My Oracle Support and validating/updating key information in its database. This information includes hardware serial numbers, contract levels, and support contacts.
Select systems for ASR implementation (ASR Manager, ASR Assets)
Qualify systems for ASR support.
Register/access My Oracle Support.
Validate system information (active contract, serial number, technical contacts, etc.).
This milestone involves assessing the state of the systems designated for ASR installation. Items reviewed include an operating system version check, Java (JRE/JDK) version check, a check of proper network connectivity, and to confirm the specific hardware telemetry sources installed on the systems.
Depending on the results of the systems assessment, this milestone may involve installing appropriate OS patches, Java updates, and network configurations.
Verify Oracle Linux or Solaris version and patch level.
Confirm network setup and connectivity.
Confirm Java version (for the ASR Manager system only).
Confirm telemetry sources on all ASR systems.
Set up telemetry sources (e.g., ILOM).
This milestone includes installing supporting software that may be required for ASR, depending upon your qualified platform. This may include the Service Tools Bundle (STB), for example.
Once the above milestones are complete, the ASR Manager can be installed. This milestone, along with installing ASR Assets, is the quickest part to the overall installation.
Download the latest Oracle Automated Service Manager (OASM) and ASR packages.
Install the OASM and ASR packages.
Register and validate the ASR Manager.
The last milestone to installing the ASR environment is to configure ASR Assets and validate the installation. Configuring ASR Assets may involve installing supporting software, such as Service Tools Bundle (STB) or Service Tags.
|
Note: Service Tags andasrassetbundle are not required for Solaris 11. |
Install Service Tools Bundle (STB) or Service Tags.
|
Note: STB is required for Solaris 10 ASR Assets and optional for Solaris 11 ASR Assets. |
Obtain the ASR Asset Bundle (via shell script).
Configure ASR telemetry sources to send events to the ASR Manager.
Activate ASR Asset(s).
Login to My Oracle Support (http://support.oracle.com) to complete activation of the asset.
Review all ASR Asset status in My Oracle Support.
Generate a test alert to validate data transmitted to Oracle (results are emailed to the ASR administrator).
Repeat steps for each ASR Asset.
This section explains how to initially designate which system will have the ASR Manager installed and which systems will be installed as ASR Assets. This process involves sizing the systems and making sure all the systems are qualified for ASR.
Use the following procedure to designate an ASR Manager system. To use these instructions, it is important to understand the difference between an ASR Manager and an ASR Asset system.
Choose a system that you intend to install as the ASR Manager. This system does not need to be a dedicated server and can co-reside with other applications and services. See "Oracle Auto Service Request Configuration Requirements" for information about operating system and Java requirements.
|
Note: The ASR Manager can be installed on a database server in Oracle Database Machine. However, Oracle recommends that it is installed on a standalone server. |
Size the system:
Establish roughly how many ASR Assets will report their hardware telemetry to the ASR Manager system now and in the future
Refer to the Hardware and Network Configuration page (see http://www.oracle.com/asr for more information) to confirm system requirements, depending on how many ASR Asset(s) will report their telemetry to the ASR Manager.
If the system you selected to be an ASR Manager is under-sized, consider the following options:
Select another system that is better sized, or upgrade the current system.
Reduce the number of ASR Assets that you will associate to this ASR Manager system. If you choose this option, you will have to consider installing an additional instance(s) of the ASR Manager to accommodate the remaining ASR Assets. Focus on the first ASR Manager and its associated ASR Assets before installing additional ASR Manager instances.
Once the ASR Manager is sized, record the hostname and hardware type.
Follow the procedure below to designate ASR Asset system(s). To use these instructions, it is important to understand the difference between an ASR Manager and ASR Asset systems. Refer to "ASR Architectural Summary", if needed.
|
Note: The ASR Manager system is always installed first. If you have not completed the installation of the ASR Manager, go to "ASR Installation Overview". |
Choose the qualified systems that you intend to install as ASR Assets and make note of the hardware type of each (for example, Sun Fire V490, E12K, SPARC Enterprise T5120, Sun Blade X6240, etc.).
Verify your system is qualified for ASR. Visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr) to see which server, storage, and Oracle Exadata products are qualified for ASR.
From the Qualified Systems List, confirm that your system is on the list. If not, the system is not yet qualified to run ASR.
Once the ASR Asset system(s) are qualified, record the hostname(s) and hardware type of each. Use your own mechanism for tracking this information or use tracking forms provided in "ASR E-mail Examples".
This section provides the instructions to assess your Oracle system environment for the ASR installation. An assessment of your operating system version, network setup, and available telemetry sources is necessary to determine if any of these items need upgrading or other configuration to support the ASR installation.
|
Note: The instructions in this section apply to both the ASR Manager and ASR Assets. |
For ASR Assets, only the hardware listed on the Systems Qualified for ASR page is supported. Visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr) to see which server, storage, and Oracle Exadata products are qualified for ASR.
Qualified ASR Asset hardware must be associated with a valid support identifier in My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com).
|
Note: Oracle Auto Service Request Release 3.1 no longer requires the designated ASR Manager to be qualified. However, there are still minimal operating system, Java, telemetry, etc., requirements. |
Designated ASR Managers support Oracle Auto Service Request running Oracle Linux or Solaris operating systems.
|
Note: ASR Assets support Oracle Auto Service Request running Solaris. If you choose to include your ASR Manager as an ASR Asset, it must be running the Oracle Solaris operating system. |
Two versions of Oracle Linux are supported:
Oracle Linux 5.3 or later is supported for ASR.
Oracle Linux 5.5 with Oracle Unbreakable Linux Kernel (version 2.6.32-100.0.19.el5)
To check your systems, run /etc/enterprise-release. The output should look like this:
Enterprise Linux Enterprise Linux Server release 5.3 (Carthage)
The following Solaris releases are supported for ASR Manager systems:
Solaris 11
Solaris 10, Update 6 (10u6), or later
To check your Solaris version, run cat /etc/release.
If your qualified ASR Asset indicates a particular patch version, verify your patch level (see http://www.oracle.com/asr for information on Solaris requirements for Server Products Qualified for ASR):
patchadd -p|grep patch number
To download any required patches, visit My Oracle Support (login required) at http://suppport.oracle.com.
ASR Manager (versions 2.5 and higher) systems require at least JDK 1.6.0_04 or later (see JDK 6 on the Java SE Downloads page: http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp). This version of Java is required for Oracle Automated Service Manager (OASM) 1.2. To check your version of Java, run:
java -version
The ASR Manager System must have an internet connection – either a direct connection or through a proxy. If you access the internet through a proxy, check with your network administrator to collect information needed to configure the ASR Manager system. You will need to know:
Proxy server name
Proxy port number
Proxy user name
Proxy password
NTLM Domain Name (if applicable)
NTLM Host Name (if applicable)
SASM Host Information (if applicable)
Check and make note of the ASR Manager IP address:
ifconfig -a
To test the connection to Oracle, in a browser, go to:
https://transport.oracle.com:443
You can also test your connection in a terminal window:
telnet transport.oracle.com 443
/usr/sfw/bin/wget https://transport.oracle.com
If you receive a “connected” message, the connectivity is successful.
Contact your network administrator to confirm or enable the following:
Set-up firewall rules to allow bi-directional SNMP/UDP traffic to traverse between ASR Assets and the ASR Manager.
|
Note: If your asset is running Solaris 11, then ensure the designated HTTP(S) port is open to the ASR Manager. |
Ensure that ASR Assets can send SNMP telemetry data out on port 162 to the ASR Manager.
|
Note: If your asset is running Solaris 11, then ensure it can send HTTP(S) telemetry data to the ASR Manager port configured. |
Ensure that the ASR Manager can communicate with ASR Assets, via http, using port 6481.
|
Note: If your ASR Asset system is running Solaris 11, then this step is not required. |
Check and make note of the ASR Asset IP address:
ifconfig -a
If working with a system that has a service processor, such as Blade systems and some T and X-series systems, obtain the service processor and/or the chassis IP address. These will be required for ASR installation
An integral component to ASR functionality is the hardware telemetry sources resident on your ASR Assets. Depending upon your hardware type, you will have one or more hardware telemetry sources resident on your system. Proceed with the installation by continuing to the following sections in order:
"Confirm Existing Telemetry Sources". Use this procedure to determine what telemetry sources exist on your hardware.
"Initially Set-Up and Configure Telemetry Sources". Based on what telemetry sources exist on your system, some configuration or updates may be required.
Use this section to determine the existing telemetry sources on your Oracle Sun system. ASR connects to these telemetry sources, collects potential fault data, and forwards it to Oracle for the automatic creation of Service Requests.
For ASR Assets, visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr) for list of server, storage, and Oracle Exadata products.
Find your hardware platform in the tables.
In the columns titled Telemetry Source on: SERVICE PROCESSOR and Telemetry Source on: HOST, you will see the telemetry sources that are on your system. As indicated, some telemetry sources reside on a service processor (dedicated hardware), and others reside on the host itself. It is also common for some systems to have multiple telemetry sources.
Make a note of the telemetry sources on your system for later use in the installation process (for example, ILOM, FMA, XSCF, etc.).
If the telemetry sources have a Note indicator, review the note at the bottom of the table and make note of the requirements for that telemetry source. Keep the following in mind:
Any Solaris operating system or patch requirements should have been completed. Refer to "Operating System Requirements", if necessary.
In some cases, the telemetry software must be upgraded for ASR. In other cases, the telemetry source requires a dedicated network connection (for example, ILOM-enabled systems).
In some cases, multiple telemetry sources cannot run together on the same system. For example, the SPARC Enterprise T5000 series requires that either ILOM or SunMC be used as the telemetry source, not both.
This section defines all possible telemetry sources that could exist on your system. Your specific telemetry sources should already be known, as explained in "Confirm Existing Telemetry Sources". If you have ILOM telemetry, go to the ILOM section in the list below and follow the specific ILOM instructions. If ILOM is not applicable to you, or you have completed the ILOM instructions, continue to Chapter 3, "Install the ASR Manager."
Fault Management Architecture (FMA): FMA is a capability in Solaris 10 and 11 that automatically diagnoses, isolates, and recovers from many hardware and application faults. As a result, business-critical applications and essential system services can continue uninterrupted in the event of software failures, major hardware component failures, and even software misconfiguration problems.
Solaris 10 can be configured to send SNMP traps to the ASR Manager.
Solaris 11 can be configured to send events to the ASR Manager via http(s) using the Solaris asradm command via the asr-notify service.
Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM): ILOM is embedded into some platforms and comes with dedicated network and serial ports to provide remote management, configuration, and telemetry reporting. ILOM reports power and environmental problems as well as CPU and memory faults on certain servers.
M-Series Extended System Control Facility (XSCF): XSCF incorporates a service processor separate from all other processors. XSCF regularly monitors server components including CPU, memory, disks, fan rotation and device temperatures.
The Oracle Hardware Management Pack (OHMP): OHMP allows ILOM events to be captured by the Host and forwarded through the Host network connection. OHMP is a telemetry source for T5xxx and some x64 servers.
Sun Management Center Agent (SunMC): SunMC provides power and environmental fault information from the host for some servers and from the system controllers of some high-end servers.
If you have determined that the ILOM telemetry source is required for ASR, use the following procedure to set-up and/or confirm your ILOM configuration. The instructions provided here are summarized for your convenience. For complete details on configuring ILOM, refer to your ILOM documentation.
ILOM requires a network connection/route to the ASR Manager system. If you know that ILOM is already set-up and connected to the network, continue to the next step. Otherwise, continue with the tasks below.
A network connection must be made from the Net Management port on the system's service processor (SP) to the network.
An IP address must be assigned to the Net Management port. Obtain and make note of this IP address for later use in the installation.
For some systems, ILOM can be connected using Sideband Management. (See http://www.oracle.com/asr for information on systems that use ILOM as a telemetry source.) ILOM Sideband Management allows the same ILOM IP address to be used, but it is routed through one of the host Gigabit Ethernet ports, thus eliminating the need for the physical connection to the ILOM Net Management ports. If you want to configure your ILOM system for Sideband Management, go to "ILOM Sideband Management Set-Up". When complete, return and continue with the following instructions.
Confirm the ILOM version. Refer to the list of qualified servers (see http://www.oracle.com/asr) to determine if the version of ILOM running on your platform is supported by ASR.
Use ssh to the IP address of the ILOM network interface and log in as root. ssh IP_Address_of_ILOM_Interface
Run the following command: show /SPor version
If the product version is earlier than 2.x, upgrade it now to the latest ILOM version using your ILOM documentation for instructions.
When you have confirmed that ILOM is enabled and properly networked, continue to "Install the ASR Manager".
ILOM Sideband Management allows ILOM telemetry to be routed through the Host Ethernet port. This shared connection using the Host Ethernet port eliminates the physical connection required for the ILOM Net Management port.
|
Note: Connection to the SP usingssh or the web interface may be lost during configuration of Sideband Management. |
The default ILOM network connection is through the Service Processor's dedicated network port.
|
Note: ILOM Sideband Management is currently available for specific Oracle x64 and Coolthreads servers. Visit the Oracle ASR product page for a complete list of all hardware qualified for ASR:http://www.oracle.com/asr |
Login to the host and confirm the mac address:
# ifconfig -a
Output will looks similar to this:
lo0: flags=2001000849 <UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4,VIRTUAL> mtu 8232 index 1 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask ff000000
e1000g0: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2 inet 10.10.10.235 netmask fffffe00 broadcast 10.10.10.255 ether 0:3:ba:d8:b4:5c <---- This line shows an example of the mac address.
|
Note: Make sure to set the ILOM port to a connected and configured Host Ethernet port. The mac address obtained from the host is the Ethernet port that should be used. |
Login to ILOM using the web interface and configure ILOM trap destination to ASR Manager. See "Enable ILOM: GUI Interface" or "Enable ILOM: Command Line Interface" for details.
Configure the ILOM for Sideband Management; select the Configuration tab and then the Network tab.
Select the ILOM Sideband Management Port by using the drop-down list to activate the desired management port. The SP Network Management Port /SYS/SP/NET0 is the default setting, and the drop-down list allows the user to change to any of the four Host Ethernet ports /SYS/MB/NETx, where x is 0 to 3.
Click Save for the changes to take effect.
The Oracle Hardware Management Pack (OHMP) allows ILOM events to be captured by the Host and forwarded through the Host network connection. This eliminates the need to network the Service Processor. The host must be configured and activated for ASR to properly forward ILOM telemetry. The OHMP is only available on certain systems.
|
Note: The OHMP for ASR is only available for certain systems using Solaris 10. For more information about specific systems visit the Oracle ASR product page (http://www.oracle.com/asr).
The host must be activated for ASR and trap destinations configured. |
Configure the host trap destination to the ASR Manager as described in "Enable FMA Telemetry for Solaris 10 ASR Assets".
Download and install the latest Oracle Service Hardware Management Pack. To download OHMP:
Login to My Oracle Support (https://support.oracle.com).
Click the Patches & Updates tab.
In the Patch Search pane, click Product or Family (Advanced Search).
Enter Oracle Hardware Management Pack in the Product field.
In the Release drop-down menu, select the release of OHMP you want to download and click the Search button.
In the Search Results, click the Patch ID number that corresponds to your operating system (the applicable operating system is shown in the Patch description).
In the patch description, click the Download button to download the patch
Use the Oracle Hardware Management Pack Installation Guide to install OHMP. Please note the reference to CR 6977584 (Unix Installer Issue) in the Installation Issues section of the manual. When using the OHMP installer, if the installation aborts, it is likely to be due to this defect. There are two workarounds for this defect:
Use the command unsetenv DISPLAY to unset the DISPLAY variable before running the installer. The unsetenv command runs in the C shell.
Install the required components of OHMP manually rather than using the OHMP installer. The procedure for manual component installation is included in the Oracle Hardware Management Pack Installation Guide. The packages required to support OHMP telemetry are:
ORCLhmp-libs ORCLhmp-snmp ORCLhmp-hwmgmt
Activate the host for ASR as described in "Activate ASR Assets".