Release 11g (11.1.1)
Part Number E13881-01
Contents
Previous
Next
| Oracle Fusion Middleware Report Designer's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher Release 11g (11.1.1) Part Number E13881-01 | Contents | Previous | Next |
This chapter covers the following topics:
Bursting is a process of splitting data into blocks, generating documents for each block, and delivering the documents to one or more destinations. The data for the report is generated by executing a query once and then splitting the data based on a "Key" value. For each block of the data, a separate document is generated and delivered.
Using BI Publisher's bursting feature you can split a single report based on an element in the data model and deliver the report based on a second element in the data model. Driven by the delivery element, you can apply a different template, output format, delivery method, and locale to each split segment of your report. Example implementations include:
Invoice generation and delivery based on customer-specific layouts and delivery preference
Financial reporting to generate a master report of all cost centers, splitting out individual cost center reports to the appropriate manager
Generation of pay slips to all employees based on one extract and delivered via e-mail
A bursting definition is a component of the data model. After you have defined the data sets for the data model, you can set up one or more bursting definitions. When you set up a bursting definition, you define the following:
The Split By element is an element from the data that will govern how the data is split. For example, to split a batch of invoices by each invoice, you may use an element called CUSTOMER_ID. The data set must be sorted or grouped by this element.
The Deliver By element is the element from the data that will govern how formatting and delivery options are applied. In the invoice example, it is likely that each invoice will have delivery criteria determined by customer, therefore the Deliver By element may also be CUSTOMER_ID.
The Delivery Query is a SQL query that you define for BI Publisher to construct the delivery XML data file. The query must return the formatting and delivery details.
Prerequisites:
You have defined your data set for your data model
The data set is sorted or grouped by the element by which you want to split the data in your bursting definition
The delivery and formatting information is either:
stored in a database table available to BI Publisher (for a dynamic delivery definition)
or can be hard coded in the delivery SQL (for a static delivery definition)
On the component pane of the data model editor, click Bursting.
On the Bursting definition table, click the Create new Bursting button.
Enter the following for this bursting definition:
Name - for example, "Burst to File"
Type- SQL Query is currently the only supported type
Data Source - select the data source that contains your delivery information
The following figure shows a Bursting definition:
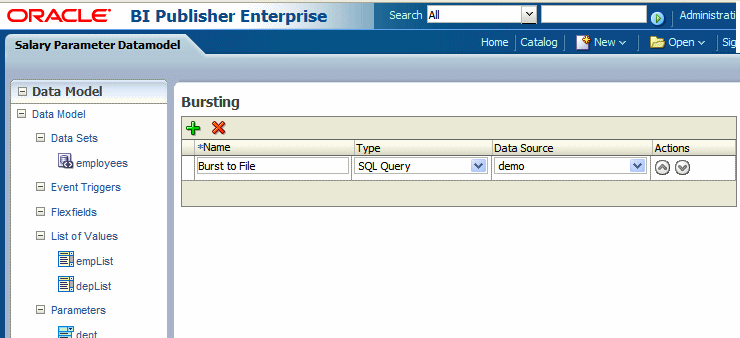
In the lower region, enter the following for this bursting definition:
Split By - select the element from the data set by which to split the data
Deliver By - select the element from the data set by which to format and deliver the data
SQL Query - enter the query to construct the delivery data set. For more information, see Defining the Query for the Delivery Data Set.
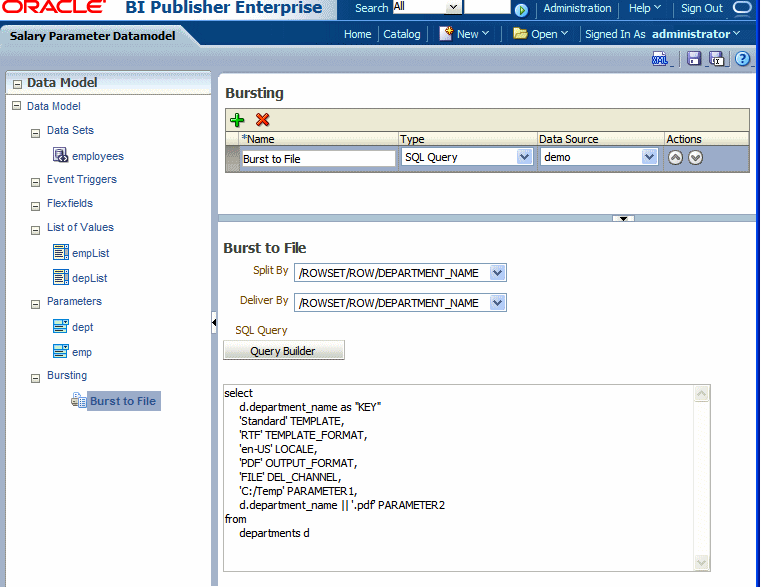
The bursting query is a SQL query that you define to provide BI Publisher with the required information to format and deliver the report. BI Publisher uses the results from the bursting query to create the delivery XML data set.
The BI Publisher bursting engine uses the delivery data set as a mapping table for each Deliver By element. The structure of the delivery XML data set is as follows:
<ROWSET>
<ROW>
<KEY></KEY>
<TEMPLATE></TEMPLATE>
<LOCALE></LOCALE>
<OUTPUT_FORMAT></OUTPUT_FORMAT>
<DEL_CHANNEL></DEL_CHANNEL>
<TIMEZONE></TIMEZONE>
<CALENDAR></CALENDAR>
<OUTPUT_NAME></OUTPUT_NAME>
<SAVE_OUTPUT></SAVE_OUTPUT>
<PARAMETER1></PARAMETER1>
<PARAMETER2></PARAMETER2>
<PARAMETER3></PARAMETER3>
<PARAMETER4></PARAMETER4>
<PARAMETER5></PARAMETER5>
<PARAMETER6></PARAMETER6>
<PARAMETER7></PARAMETER7>
<PARAMETER8></PARAMETER8>
<PARAMETER9></PARAMETER9>
<PARAMETER10></PARAMETER10>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>where
KEY is the Delivery key and must match the Deliver By element. The bursting engine uses the key to link delivery criteria to a specific section of the burst data.
TEMPLATE - is the name of the Layout to apply. Note that the value is the Layout name (for example, 'Customer Invoice'), not the template file name (for example, invoice.rtf).
LOCALE - is the template locale, for example, "en-US".
OUTPUT_FORMAT - is the output format. Valid values are:
HTML
PDFZ
RTF
EXCEL
EXCEL2000
MHTML
PPT
PPTX
XSLFO
XML
CSV
ETEXT
SAVE_OUTPUT - indicates whether to save the output documents to BI Publisher history tables that the output can be viewed and downloaded from the Report Job History page.
Valid values are 'true' (default) and 'false'. If this property is not set, the output will be saved.
DEL_CHANNEL - is the delivery method. Valid values are:
FAX
FILE
FTP
WEBDAV
TIMEZONE - is the time zone to use for the report. Values must be in the Java format, for example: "America/Los_Angeles". If time zone is not provided, the system default time zone will be used to generate the report.
CALENDAR - is the calendar to use for the report. Valid values are:
GREGORIAN
ARABIC_HIJRAH
ENGLISH_HIJRAH
JAPANESE_IMPERIAL
THAI_BUDDHA
ROC_OFFICIAL (Taiwan)
If not provided, the value “GREGORIAN” will be used.
OUTPUT_NAME - is the name that will be assigned to the output file in the report job history.
Delivery parameters by channel. The values required for the parameters depend on the delivery method chosen. The parameter values mappings for each method are shown in the following table. Not all delivery channels use all the parameters.
| Delivery Channel | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| Parameter1: Email address Parameter2: cc Parameter3: From Parameter4: Subject Parameter5: Message body Parameter6: Attachment value ("true" or "false"). If your output format is PDF, you must set this parameter to "true" to attach the PDF to the e-mail. Parameter7: Reply-To Parameter8: Bcc (Parameters 9-10 are not used) | |
| Printer | Parameter1: Printer group Parameter2: Printer name or for a printer on CUPS, the printer URI, for example: ipp://myserver.com:631/printers/printer1 Parameter3: Number of Copies Parameter4: Sides. Valid values are:
If the parameter is not specified, single-sided will be used. Parameter5: Tray. Valid values are:
If not specified, the printer default will be used. Parameter6: Print range. For example "3" will print page 3 only, "2-5" will print pages 2-5, "1,3-5" will print pages 1 and 3-5 (Parameters 7-10 are not used) |
| Fax | Parameter1: Fax server name Parameter2: Fax number (Parameters 3-10 are not used) |
| WebDAV | Parameter1: Server Name Parameter2: Username Parameter3: Password Parameter4: Remote Directory Parameter5: Remote File Name Parameter6: Authorization type, values are “basic” or “digest” (Parameters 7-10 are not used) |
| File | Parameter1: Directory Parameter2: File Name (Parameters 3-10 are not used) |
| FTP and SFTP | Parameter1: Server name Parameter2: Username Parameter3: Password Parameter4: Remote Directory Parameter5: Remote File Name Parameter6: Secure (set this value to "true" to enable Secure FTP) (Parameters 7-10 are not used) |
Although you can define multiple bursting definitions for a single data model, you can enable only one for a report.
Enable a report to use a bursting definition on the Report Properties dialog of the report editor. For more information see Configuring Report Properties.
After you configure the report to use the bursting definition, when you schedule a job for this report you can choose to use the bursting definition to format and deliver the report. For more information see Creating a Bursting Job.
Note that you can also opt not to use the bursting definition and choose your own output and destination as a regular scheduled report.
The following example is based on an invoice report. This report is to be delivered by CUSTOMER_ID to each customer’s individual e-mail address.
This example assumes that you have created a table in your database named "customers" to hold the delivery and formatting preferences for each customer. The customers table includes the following columns that will be retrieved to create the delivery data set file dynamically at runtime:
CST_TEMPLATE, CST_LOCALE, CST_FORMAT, CST_EMAIL_ADDRESS
The SQL to generate the delivery data set for this example is as follows:
select distinct
CUSTOMER_ID as "KEY",
CST_TEMPLATE TEMPLATE,
CST_LOCALE LOCALE,
CST_FORMAT OUTPUT_FORMAT,
'EMAIL' DEL_CHANNEL,
CST_EMAIL_ADDRESS PARAMETER1,
'accounts.receivable@oracle.com' PARAMETER2,
'bip-collections@oracle.com'PARAMETER3,
'Your Invoices' PARAMETER4,
'Hi'||CUST_FIRST_NAME||chr(13)|| 'Please find attached your
invoices.' PARAMETER5,
'true' PARAMETER6,
'donotreply@mycompany.com' PARAMETER7
from customersIf the delivery information is not easily available in your existing data sources, you may consider creating a table to use for your query to create the delivery XML data set. Following is a sample:
Important: If the JDBC driver you use does not support column alias, when you define the bursting control table, the columns must match exactly the control XML tag name. For example, the KEY column must be named “KEY”, upper case is required. PARAMETER1 must be named “PARAMETER1”, not “parameter1” nor “param1”, and so on.
CREATE TABLE "XXX"."DELIVERY_CONTROL"
( "KEY" NUMBER,
"TEMPLATE" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE),
"LOCALE" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE),
"OUTPUT_FORMAT" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE),
"DEL_CHANNEL" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE),
"PARAMETER1" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER2" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER3" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER4" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER5" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER6" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER7" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER8" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER9" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"PARAMETER10" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"OUTPUT_NAME" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"SAVE_OUTPUT" VARCHAR2(4 BYTE),
"TIMEZONE" VARCHAR2(300 BYTE),
"CALENDAR" VARCHAR2(300 BYTE)
) PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255 NOCOMPRESS LOGGING
STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645
PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT)
TABLESPACE "EXAMPLES";
Tips for creating a creating bursting delivery table:
If your split data set does not contain a DELIVERY_KEY value, then the document will not be generated nor will it be delivered because the system will not know how. For example, using the preceding example, if customer with ID 123 is not defined in the bursting delivery table, this customer will not have a document generated or delivered.
To enable a split data set to generate more than one document or deliver to more than one destination, duplicate the DELIVERY_KEY value and provide different sets of OUTPUT_FORMAT, DEL_CHANNEL, or other parameters. For example, customer with ID 456 wants his document delivered to two e-mail addresses. To achieve this, insert two rows in the table, both with 456 as the DELIVERY_KEY and each with its own e-mail address.
![]()
Copyright © 2004, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.