Setup for Health and Welfare Management
Setup for Health and Welfare Management Overview
You use the implementation features of Standard and Advanced Benefits to design the benefit programs that you offer to your employees and other eligible participants. You can define eligibility and enrollment requirements for programs and plans, set up activity rate calculations, and define reporting groups and system extracts.
Advanced Benefits includes all the components of Standard Benefits plus features for managing life events and setting up flexible benefit programs.
See: Advanced Benefits Setup: Overview
Use the administration features of Standard and Advanced Benefits to manage benefits enrollments and to maintain your benefit programs.
See: Standard and Advanced Benefits Administration: Overview
See: Advanced Benefits Administration: Overview
The application provides a Total Compensation Setup Wizard to guide you through the setup process.
See: Total Compensation Setup Wizard
Features Common to Standard and Advanced Benefits
Standard and Advanced Benefits share a number of common setup features:
-
Plan Design: You can design the program structure of the benefits you offer to your employees and other qualified participants and dependents. Use the Total Compensation Setup Wizard to help automate the setup process.
-
Eligibility Profiles: You set up participant eligibility profiles and dependent coverage eligibility profiles to restrict who is able to participate in a benefit plan.
-
Enrollment Requirements: You define enrollment requirements to determine when an eligible person can enroll in a benefit plan.
-
Activity Rates: You define an activity rate calculation to determine the standard or variable contribution or distribution for a benefit. Activity rates also control the calculation of coverage amounts, monthly premiums, and imputed income taxation.
-
-
Communications: Oracle HRMS helps you manage employee communications. You set up communication type definitions to control the data the application generates for inclusion in a communication. For example, you can extract a participant's available benefit choices and price tags into a flat file that you then merge into the body of a pre-enrollment letter.
Note: The application restricts Standard Benefits users to setting up communications for COBRA and HIPAA administration.
-
System Extract: The system extract feature lets you manage the extract and format of person benefits data for delivery to organizations such as third party benefits administrators.
-
Plan Design Copy: Use this feature to save time during your implementation. You can set up your plan design in a test database, for example, then use Plan Design Copy to transfer the finalized design into your production database without repeating data entry. For plans that share components, you can define a plan once, then modify copies of the base plan as necessary.
Managing Benefits Using SSHR
You can set up Standard and Advanced Benefits so that individuals can manage their elections through a web browser, thus saving the back office from the task of election processing.
For information on setting up Self-Service Benefits enrollments, refer to My Oracle Support Note 215159.1, Self-Service Benefits Enrollments with Standard and Advanced Benefits.
Key Concepts
To broaden your understanding of Standard Benefits, and features common to both Standard and Advanced Benefits, see:
Eligibility Requirements for Total Compensation
System Extract, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Self-Service Benefits Enrollments
Advanced Benefits Setup: Overview
Advanced Benefits enables administration based on life events that occur to participants. You can generate enrollment actions, activity rate changes, and communications based on seeded life events or events you define.
You also use Advanced Benefits to design benefit programs that are based on flex credit accrual.
Advanced Benefits Features
In addition to the core features available with Standard Benefits, Advanced Benefits comprises several distinct features:
-
Life Events: The system lets you trigger enrollments, activity rate changes, and communications based on the occurrence of a life event to a primary participant or dependent.
-
Life Event Reasons: These are the changes to a person's HR record that you define as valid reasons for an enrollment action. Life events can be external, such as the birth of a dependent, or internal, such as a work location change or the start of an open enrollment period.
-
-
Online Benefits Administration: This feature is useful for HR call centers. Using the Benefits Service Center, you can record a change to a person's HR record, evaluate the change for enrollment impact, and process an election online all from a centralized form. You control the application windows, reports, and processes available to your benefits administrators.
-
Flex Credit Calculation: For those programs where you offer a choice of benefits and coverage levels, you can define flex credit calculations that determine the amount of flex credits a person must spend to purchase a benefit. You also define restrictions as to how a participant can distribute unused flex credits.
Key Concepts
To learn more about Advanced Benefits, see:
Online Benefits Administration
Total Compensation Setup Wizard
Use Total Compensation Setup Wizard for a fast and easy way to enter your plan design into Oracle HRMS. Total Compensation Setup Wizard uses the Oracle Applications Framework to provide a task-oriented process for creating Health and Welfare programs and the business processing rules associated with them.
Advanced Benefits customers can use Total Compensation Setup Wizard to set up:
-
General program details for flex credit and non-flex credit programs
-
Health and Welfare plans, options, coverage amounts, coverage restrictions, interim coverages, standard and variable rate calculations, dependent and beneficiary eligibility, and designation requirements
-
Annual open enrollment periods
-
Explicit life events from a set of pre-determined data triggers that generate a corresponding enrollment period
-
Enrollment requirements for unrestricted programs
-
Enrollment requirements for specific life event processing (along with available dependent changes)
-
General or life event specific default enrollment requirements
-
Final plan design review page and submit process to load data into the business group
For Standard Benefits, the Total Compensation Setup Wizard automatically determines your configuration options. Use the Wizard to:
-
Configure your plan design
-
Set up unrestricted programs
-
Define participant eligibility requirements
-
Set up activity rates, including variable rates and coverage calculations
After you complete your plan design, you can use the Wizard to:
-
Update FastFormula in plan design objects
-
Update multiple standard and variable activity rates simultaneously (Mass Update of Rates)
You can then use the professional user interface to:
-
Define flex credit calculations and benefit pools (OAB)
-
Set up actual premium calculations
-
Define colliding life event logic (OAB)
-
Set up distribution rules if you offer reimbursement plans
-
Define communication types
-
Set up the Benefits Service Center for centralized administration (OAB)
Advantages of Advanced Benefits Life Event Processing
As an Advanced Benefits customer, you can take advantage of a range of features, including:
-
Automated Life Event Management
-
What-If Eligibility Determination
-
Mass Enrollment Processing
Oracle strongly recommends that you implement the Life Event processing model to automate benefits administration. This model enables you to configure enrollment restrictions based on specific life events that you define. Life event processing manages complex situations; for example, when a participant reports a life event that occurred in the past and other elections are already in place, or when the elections and rates for a life event must become effective in the past.
Consider the following questions that illustrate the advantages of the Life Event processing model:
-
Do you want to process mid-year election changes automatically for a single participant? Would you like to perform mass enrollment updates or corrections?
-
Do you need to automatically assign certain benefits to employees or family members?
-
Do you anticipate automating your administration practices in the future? Do you need to enforce business rules, such as requiring or reminding a participant to designate dependents or requiring a participant to provide "Evidence of Insurability?"
-
Do you restrict an employee's benefit choices based on life events, such as a marriage or the addition of a child?
-
Would you like to operate in a Self-Service environment where employees record their own elections through a web browser? Would you like to allow employees to use Self-Service for mid-year election changes and to restrict the allowable updates based on the reason for the change?
Answering Yes to any of the above questions--in conjunction with planning the components of your benefits program--should justify implementing the life event model. The Total Compensation Setup Wizard assists you with this configuration.
Standard and Advanced Benefits Implementation
Oracle HRMS provides a complete solution for Total Compensation management. Your Oracle Human Resources license includes the Standard Benefits feature set that enables you to manage your enterprise's benefits offerings.
The Oracle Advanced Benefits license provides the Standard Benefits feature set plus additional functionality enabling you to design flexible benefit programs and to administer benefits based on life events.
See: Advanced Benefits Implementation
Standard Benefits Implementation
Standard Benefits provides the functionality you need to administer benefit programs that do not offer flex credit based benefits. The Standard product is also useful if you outsource a significant portion of your benefits administration.
What kinds of benefit plans are supported by Oracle HRMS?
You can use the product to manage the most typical plan types, including:
-
Medical plans
-
Dental Plans
-
Vision Plans
-
Prescription drug plans
-
Short term and long term disability plans
-
Group term life insurance
-
Dependent life insurance
-
Group legal services
-
Savings plans (such as 401(k) and money purchase)
-
Vacation Buy/Sell plans
-
Continuing benefits (such as COBRA and HIPAA)
In addition, you can accommodate other forms of benefits such as company cars, reduced rates on loans, subsidized dependent care, or other goods or services for which your enterprise offers employee reimbursement.
Can you restrict who is eligible to receive a benefit?
You use eligibility profiles to restrict which participants may enroll in a given benefit. You create an eligibility profile by grouping together your eligibility criteria, such as work and personal factors.
You create a dependent coverage eligibility profile when you want to restrict the criteria that must be met for a dependent to be covered by a benefit.
How do I schedule an enrollment period?
In Standard Benefits, you use the unrestricted enrollment method to process your enrollments. Unrestricted enrollments are not limited to a period of time. You can record the dates of your open enrollment in the system, but these dates do not restrict your enrollment processing.
How do I define payroll deductions and payments for benefits?
You define activity rate calculations for a benefit plan that determine the contribution amount required to purchase the benefit. Activity rates can also be used to calculate employer contributions to a plan and distribution payments from a plan.
Can you vary the rate that different participants pay to purchase a benefit?
If your plan rules stipulate that the amount a participant must pay to purchase a benefit varies based on certain factors, you can define a variable rate profile to define these variable criteria. Then, when eligible participants meet these criteria, they will receive the variable rate.
You can vary an activity rate based on employment factors, such as an employee's work location, or length of service with your organization.
Advanced Benefits Implementation
By licensing Advanced Benefits, you can also fulfill the following business requirements.
How do I define qualifying life events?
You define a life event reason as a database change to a person's HR record. This change may require or enable an enrollment action. An enrollment action is an enrollment, de-enrollment, change in election, or change in contribution rate that is implemented either automatically, by default, or at the explicit request of the participant.
You link life events to scheduled enrollment periods, benefit plans, and communications. When a life event occurs to a participant, the system evaluates the life event to determine benefits eligibility and electable enrollment choices.
For example, if an employee's work location changes, you might want to evaluate this change to see if there is a corresponding change in benefits eligibility or contribution rates. If an employee's status changes from active to terminated, you may need to generate a continuing benefits action (such as for COBRA in the US).
How do I implement a flex credit program?
You can use Advanced Benefits to create flex credit based programs that offer a range of benefit choices to your employees and other eligible participants.
You create activity rate calculations that determine the number of flex credits required to purchase a particular benefit. You can select from a variety of calculation methods, from a flat amount to a multiple of compensation. You can associate a variable rate profile with your flex credit calculation if contribution rates vary for an individual based on factors that you define.
Using benefit pools, you specify how credits may be rolled over between plans and how excess flex credits can be distributed.
Does the application support automatic and default enrollments?
Yes, Advanced Benefits customers can define automatic enrollments to enroll participants in benefits without their explicit request. For example, you could trigger an automatic enrollment based on a life event so that when a person is hired, they automatically receive certain coverages.
Advanced Benefits customers can also define default elections for participants who fail to explicitly make benefit elections.
How do I enroll employees in BASIC BENEFIT plans?
You simply enter the benefit plan for the employee, recording his or her coverage level, contribution amounts from the employee and employer, and any other information you want to record. You can enter this information, using defaults, for a whole batch of employees together.
If you need program-based enrollment or self-service enrollment on the web, you should implement the richer feature set Standard Benefits, instead of Basic Benefits.
How do I control eligibility for BASIC BENEFIT plans?
As for other forms of compensation in Oracle HRMS, you link each benefit plan to employment conditions, such as grades, organizations, full-time or part-time, jobs, salary bases, or any other employee grouping you need to define. Only employees that meet the link conditions can enroll in the plan.
If you need more complex rules-based plan eligibility or you need to control dependents' eligibility, consider using the Standard Benefits feature set in Oracle HRMS.
Can I export BASIC BENEFITS data to a third-party benefits administrator?
Basic Benefits does not provide any special tools to help you do this. Instead of using Basic Benefits, consider implementing Standard Benefits, which provides system extract features that are useful for exporting data to third parties.
I need to manage flexible benefits programs with flex credits.
In that case, look at the features offered by Advanced Benefits, which allows you to design flex credit based programs. You can also process flexible spending account claims, manage online life event processing, create life event triggered enrollments and communications, and model benefits eligibility based on potential life events.
Self-Service Benefits Enrollments
Self-Service Benefits Enrollments
Self-Service Benefits supports a variety of enrollment types, including open, unrestricted, and life event enrollments for one or more flex or non-flex programs.
The enrollment choices, price tags, and other information in Self-Service Benefits web pages are derived from Oracle Applications database tables using the rules of your plan design. Updated information is stored in the Oracle Applications database tables using standard Application Programmable Interfaces (APIs).
Self-Service Benefits supports enrollment for plans and options in a program.
The benefits administrator can control the display format for plans and options in a program. Depending on the display format chosen for a program, employees can:
-
Expand a program to view details of plans and options available in the program. Additional details on certification, coverage, coverage start date help in the enrollment process. Links to the plan and option details provide further information.
-
Use vertical plan types, which can have multiple rates, to enable plan level enrollments and horizontal plans types to enable enrollments in options inside a plan level with single rate. You can click links on options and plans to view further details.
Use Oracle's professional forms interface or the self-service Individual Compensation Distribution web pages to enroll participants in all plans not in a program such as savings plans, Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPP), or 401(k) plans.
Self-Service Benefits Enrollment Functionality
Self-Service Benefits offers an employee the opportunity to:
-
Review current, and future program benefits enrollments, and up to ten past enrollments, within the last two years
-
Select benefits
-
Distribute excess flex credits (Advanced Benefits)
-
Add, update, or review family member information
Note: Family member information entered through the self-service interface and personal contact data entered through the professional forms interface share the same table. Any data entered or updated in Self-Service HRMS or the professional forms interface is reflected in both interfaces.
-
Add, update, or remove dependents
Note: Self-Service requires dependents and beneficiaries to have the personal relationship check box checked on the Contacts window.
-
Add, update, or remove beneficiaries
Employees can select organizational beneficiaries provided that the administrator has entered the Beneficiary Organization using the professional forms interface, and selected the May Designate Organization as Beneficiary check box in the plan enrollment requirements.
-
Add attachments to provide documentation as part of the self service benefit enrollment process
Note: The benefits administrator can control the availability of the Attachments page.
-
View the certification requirements for the enrollment based on the life event, enrollment selections and dependent designations. This includes the certification name, associated compensation object or dependent name and the action item due date.
-
Attach documents to the enrollment. Benefits administrators have access to open and/or save the uploaded documents.
-
Search for and select primary care providers
-
Print a temporary participant identification card
-
Save or print an enrollment confirmation statement as a PDF document
Legal Disclaimer Page
During implementation, you can choose to display a predefined Legal Disclaimer page in Self-Service Benefits. Before self-service users can enroll in a benefit, they must read and accept the terms provided in the Legal Disclaimer page. If they do not accept these terms, the application will not enable the users to enroll.
You can enter the instruction text for the Legal Disclaimer page in the Self Service Instructor Text field in the Communication Types Usages window. This is a one-time process that you can complete when you set up Self-Service Benefits. You can also include HTML tags in the Disclaimer text for formatting effects, such as bold and indented text.
Enrollment Change Workflow Notifications
You can configure the Workflow Builder to send a notification to an HR professional whenever a participant updates a Self-Service Benefits Enrollment web page, excluding the Primary Care Provider page. The notification contains the following information and provides direct access to the Confirmation page for the participant, but is not linked to any Workflow approval process:
-
Name of Employee
-
Social Security Number or National Identifier
-
Life Event Name
-
Enrollment Period
-
Selected Benefit Plans and Options
-
List of Covered Dependents
Oracle Workflow sends a notification to a worklist or group that you maintain after the participant completes the enrollment update. If the participant closes the browser window prior to reaching the Confirmation page, Oracle Workflow sends a notification within one hour of the first enrollment change.
You can manually override the enrollment or contact the participant to correct and resubmit the election if necessary.
See: Self-Service Workflows, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Hidden Fields in Self-Service Benefits
There are a number of fields that are delivered hidden by default on the self-service pages. You can choose to display them. They include:
-
Coverage start and end dates for specific enrollments
-
Cost 2 (after tax), 3 (taxable), and 4 (miscellaneous) columns for displaying multiple rates for a vertical display plan type
-
Physician group and hospital, on the Primary Care Provider Search page
-
Full name
See: Benefits Enrollments for further details of these hidden fields and the regions where you can display them.
Displaying Descriptive Flexfields
The following descriptive flexfields can be entered in self-service Benefits:
-
Additional Ben Prtt Enrt Rslt F Details (BEN_PRTT_ENRT_RSLT_F)
You enter this flexfield data on the Benefits Information page, which appears after the Benefits Selection page if the flexfield has been set up and there are global segments, or segments defined for the selected plan type.
-
Add'l Contact R'ship Det's (PER_CONTACTS)
You enter this flexfield data in the Miscellaneous region of the Family Member Add page. You can also view or enter the flexfield data in the Personal Information module of SSHR.
-
Further Person Information (Person Developer DF)
You enter this flexfield data in the Name and Relationship region of the Family Member Add page.
If you have set up the Further Person Information or Additional Contact Relationship Details flexfields, you can choose to display some or all of the segments in self-service using the Personalization Framework. See: Configuring Flexfields, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
The Additional Ben Prtt Enrt Rslt F Details flexfield appears automatically if you define and freeze this flexfield. You must bounce the Apache server after freezing or unfreezing the flexfield to ensure that your changes are displayed.
Plan Type Context
You may want to display the Additional Ben Prtt Enrt Rslt F Details flexfield only for enrollment in specific compensation objects. For example, you may want to display prior years commission information to participants for a supplemental life insurance plan, while hiding commission information used to calculate group life insurance rates.
To display the flexfield differentially by compensation object, you must define a context for the flexfield based on BG_ID_PL_TYP_ID. On the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window, uncheck the Displayed check box for the context if you do not want to show the context poplist to the user. Notice that if you display this list, it will contain all the contexts for the flexfield (even those for other business groups) unless you restrict them by a value set defined for the context.
If there are frozen segments for the descriptive flexfield but no global segments defined and no segments defined for the selected plan type, the Benefits Information page appears in the enrollment chain but the region pertaining to this plan type does not display. Existing data set up in the flexfield is not affected by any new contexts you define for self-service.
Plan Design Considerations for Self-Service Benefits
Before eligible participants can enroll in self-service benefits using the self-service interface, you must design your benefit plan using Oracle's professional forms interface. The following topics look at the points you should consider when designing your plan for the self-service environment.
Legislative Configurations
Self-Service Benefits is delivered with US-style formatting for the following fields:
-
Address
-
Social Security Number
-
Pre Tax Cost
-
After Tax Cost
For non-US self-service implementations, you can edit field labels to fit your legislative requirements and you can also hide and unhide fields. For example, you may want to hide the list of States from the address fields.
Note: The address style and country used by Self-Service Benefits is inherited from the primary benefits participant.
If your legislation or benefit plan design does not allow for after tax contributions, consider hiding the after tax columns on the tables contained in the following web pages:
-
Benefits Enrollment Overview
-
Current Benefits Overview
-
Benefits Selection
-
Confirmation
See: Setting Up Self-Service Benefits Web Pages
See: Benefits Enrollments for a list of the configurable user interface elements in each delivered web page.
Integration with Authoria HR (US and UK)
The third party product Authoria HR provides a common knowledge repository to manage and communicate HR and benefits information.
After a self-service implementer defines a total compensation plan in the Oracle HRMS professional user interface, licensees of Authoria HR can configure links between Oracle HRMS and Authoria HR.
End users can click on links in the applicable self-service web pages to display context-sensitive Authoria HR documentation.
You can configure the following self-service enrollment windows for use with Authoria HR:
-
Benefits Enrollment Overview page
-
Current Benefits page
-
Confirmation page
-
Benefits Selection page
See Configuring Links Between Oracle Standard and Advanced Benefits and Authoria HR, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Multiple Rates
You can display up to four standard rates for each compensation object to enable employees to see employee and employer paid premiums, and related costs such as fringe benefit taxes and administrative fees. Multiple rates are displayed on the Overview, Benefits Selection, Current Benefits, and Confirmation pages.
Only vertical display Plan Types are able to be custom formatted in self-service to display multiple rates for a single compensation object. Due to display and sizing constraints, horizontal display Plan Types cannot display multiple rates. You can only display one standard rate per column.
When you define standard rates for self-service, you can select any activity type and tax type. However, you must check the Display on Enrollment check box (Processing Information tab) and you must specify the Self Service Display Order number (1 to 4).
When you display multiple rates, the column headings in self-service are Cost 1, Cost 2, Cost 3, and Cost 4. Otherwise, a single rate displays as either Pretax or Aftertax. You can change the column headings using the Personalization Framework.
When defining your standard rate, consider the following:
-
For Costs 2, 3, and 4 you can select the Display on Enrollment check box (Processing Information tab of Standard Rates window) or the Enter Value at Enrollment check box (Calculation Method tab). However, do not select the Enter Annual Value check box on the Calculation Method tab. Annual Value can only be entered in Cost 1, if applicable.
-
Costs 2, 3, and 4 can be used to calculate additional amounts, either based on the coverage or the amount in Cost 1. For example, if you charge a 2% administration fee for a spending account, you would set up the rates as follows:
Coverage-Check the Enter Value at Enrollment box
Cost 1 = Contribution - Select Same as Coverage as the Calculation Method
Cost 2 = Administration Fee - Select Multiple of Coverage as the Calculation Method (0.02 * coverage, in this example)
Cost 3 = Total Cost - Select Multiple of Coverage as the Calculation Method (1.02 * coverage, in this example)
Benefits Pools (Advanced Benefits)
If you are displaying multiple rates, you may not want them all deducted from flex credits. Use the Application tab on the Benefits Pool window to determine which standard rate to deduct. All rates selected on this tab are included in the Flex Credit Used Total. Unused Flex Credits (rollovers) displayed are not impacted by the use of multiple rates.
Flexible Spending Accounts (US)
To ensure that your qualifying participants can enroll in Flexible Spending Account (FSA) plans using Self-Service Benefits, you must set up your plans using one of the following two methods:
The preferred method is to use the Plan Types window to define one plan type for each FSA plan. For example, you define one plan type for Dependent Care FSA plans and a second plan type for Health Care FSA plans. For each plan type, you define the coverage plan or plans into which participants and their dependents can enroll. You also define a decline coverage plan which is linked to each plan type.
Alternatively, you can set up one FSA plan type that covers both dependent care and health care plans. Within this plan type, you define plans for both dependent care and health care. Then, within these plans, you link options for both selecting and declining coverage.
Other items for consideration:
-
When you define the activity rate for the FSA plan, check the Enter Value at Enrollment field in the Calculation Method region of the Standard Rates window.
-
Select Set Annual Rate Equal to Coverage as the calculation method.
-
In the Coverages window, define the minimum and maximum contribution amounts for the FSA plan. Indicate that values for this plan are entered at enrollment.
Flexible Benefits Programs (Advanced Benefits)
With Flexible Benefits Programs, you can offer flex credits to eligible participants to offset the cost of benefits. When you defining a benefit program in the Programs window, select the same periodicity for the activity reference period (the time period in which the system expresses activity rates) and the enrollment rate frequency (the activity rate that is communicated to participants). This ensures that the price tags for selecting benefits and the flex credits available to participants are expressed for the same time period.
Other items for consideration:
-
Unless your flex credits are determined using the result of a calculation, you indicate the number of flex credits associated with a compensation object by entering the value in the Flat Amount field in the Calculation Method region of the Flex Credits window.
-
You must set up a flex credits placeholder plan and link this plan to the flex program. This plan records the total flex credits for the program. Define a rate for this plan by entering zero in the Flat Amount field of the Calculation Method region of the Standard Rates window.
-
Set the processing type of the corresponding element to Recurring.
Temporary Participant Identification Cards
A temporary identification card allows a participant to obtain medical, dental, or other benefit treatment before the participant receives the official membership card from the provider. Using Self-Service Benefits, a participant can print one card for each elected plan that allows for temporary identification cards. The participant can also print a card for each covered dependent.
The application generates a temporary ID card upon:
-
Enrollment
-
Re-enrollment
-
Change in Enrollment
-
Participant Request (due to loss)
The identification card includes information such as:
-
Employee Name and Social Security Number
-
Member Name and Social Security Number (for dependents)
-
Employer Name
-
Plan Name
You indicate that a plan allows for the printing of temporary ID cards by checking the Allow Temporary Identification field on the Plans window.
Declining Coverage
Depending on your plan design, you must set up either a decline coverage plan or option that allows a participant to waive an enrollment opportunity for which they are otherwise eligible.
If a plan type contains multiple plans, you create a decline coverage plan in the Plans window (in addition to the regular plans) and indicate that the plan is of the specified plan type. If a plan type has only one plan, you define a decline coverage option and link it to the plan. This ensures that participants can either select or decline benefit coverage.
Note: If your plan design requires that a participant select at least one option from a group of options or at least one plan from a group of plans, do not define a decline coverage plan or option.
Self-Service Benefits What-if
Self-Service Benefits What-if enables you to model electability for benefits based on proposed changes to a person's HR record, before you make the actual change. When you model electability, the database does not save changes, so you can view different electability scenarios without having to manually save data.
The Self-Service Benefits What-if page is available from Manager and Employee Self-Service Responsibilities. To ensure that certain data is not visible to all users, as an administrator, you can define roles for Self-Service Benefits What-if. Managers can review changes to benefits for employees in their security group that would result from proposed changes to the employee's HR record. Employees can view changes to their benefits based on proposed data changes to their HR records. The comparison is in terms of their electable choices, plan or option enrollment rate.
As a manager or an employee, you can compare current benefits with the proposed benefits based on the electable choices, and a plan or option enrollment rate. For example, you can view the benefits impact of relocation or a change in weekly hours worked.
See: Modeling a Person's Benefits Eligibility (Advanced Benefits)
The system does not allow you to model electability if current life events are in progress. What-if electability depends only on the data changes you elect to model. Using the HRMS System Administrator responsibility, you need to enable the Benefits Compensation Objects Extra Information Type (EIT). This EIT enables you to add information about the type of compensation object such as program, plan type, compensation object name, and a flag indicating whether the compensation object is visible to the user.
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types Against a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
You also define the What-if Label that displays to users who perform the what-if modeling, and the life events for compensation objects and link one or more person changes to each life event.
See: Setting Up What-if Modeling
You can use the HRMS System Administrator responsibility to configure Self-Service Benefits What-if so that managers only view changes to benefits for employees in their security profile.
By default, the Self-Service Benefits pages do not display some fields. However, you can choose to display them using the Personalization Framework.
See: Benefits Enrollments
Benefits Enrollments
This topic provides reference information you need to configure your Self-Service Benefits web pages using the Personalization Framework.
For instruction text, the tables below list--by web page region--the communication short name and the valid communication usages that are required when you define a communication type to display instruction text for a particular program, plan type, plan, or life event.
See: Defining Self-Service Instruction Text
Hidden Fields: This topic also lists--by web page region--all fields the application delivers as hidden which you can display using the Personalization Framework.
For example, by default all person name fields in Self-Service Benefits display names in the format 'First Last Suffix' (without commas between the parts of the name.) You can add the Full Name field to a web page and remove the delivered Name field. In the US, the Full Name field uses the format 'Prefix Last, First Middle Suffix'.
Menu and Function Names
This module can be accessed from the following menus and functions:
| User Menu Name | Function Name |
|---|---|
| Employee Self-Service | Self-Service Benefits Enrollment - Employee |
| Employee Self-Service | Self-Service Benefits Enrollment - Federal |
Configurable Pages and Shared Regions
The following definitions can be configured using the Personalization Framework:
Family Members and Others, and Family Members and Others Detail Page
The Family Members and Others page enables a participant to view a record of their family members and other persons enrolled as dependents or beneficiaries of their benefits. Benefits participants can add another person to the Family Members and Others table by choosing the Add Another Person button, which opens the Family Members and Others Details page.
This page only displays when a person has either:
-
An enrollment opportunity
-
Eligibility for an unrestricted program
-
A detected or unprocessed potential life event as of the system date
If one of these conditions does not exist, the application opens the Current Benefits page.
The seeded life event reason of Added During Enrollment prevents a life event from occurring when you create a family member or update a family member's details. If you define a life event reason of the type Personal, that you make Selectable for Self Service, you can trigger a life event when a person enters or deletes a contact on the Self-Service Human Resources Contacts page and selects a relationship start or end reason.
Note: It is recommended that you provide instruction text indicating that eligibility for benefits may be based on family members. However, you cannot use communication usages to restrict the display of instruction text to a compensation object or a life event for the Family Members page.
Hidden Field: Use the BEN_FAMILY_MBRS_TABLE region to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
Family Members and Others
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Members Content | Instruction | FML.FAMILY_MBRS_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Family Members Content | Help Tip |
Family Members and Others Detail Page
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add or Update Family Members | Instruction | FML.FAM_ADD_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Name and Relationship | Instruction | FML.FAM_ADD_NAME | Program, Life Event | |
| Address | Instruction | FML.FAM_ADD_ADDRESS | Program, Life Event | |
| Miscellaneous Information | Instruction | FML.FAM_ADD_OTHER | Program, Life Event | |
| Second Medical Coverage | Instruction | FML.FAM_ADD_SECOND_MEDICAL | Program, Life Event | |
| Address | Help Tip | |||
| Name and Relationship | Hint (Suffix) | 92638 | __ | __ |
| Address | Hint (Postal Code) | 92639 | __ | __ |
| Miscellaneous Information | Hint (National Identifier) | 92640 | __ | __ |
| Miscellaneous Information | Hint (Date of Birth) | 92637 | __ | __ |
| Message (Required Field Missing) | 92601 | __ | __ | |
| Message (Invalid Birth Date) | 92598 | __ | __ |
Configurable FlexFields
Family Members and Others Page
| Region | Flex Name | Flex Code |
|---|---|---|
| Add or Update Family Members | Further Person Information | hrpersondevdfflex |
| Miscellaneous Information | Additional Contact Relationship Details | Add Cont Details D Flexfield |
See: Configuring Flexfields, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Benefits Enrollment Overview Page
The Benefits Enrollment Overview web page enables a participant to view a record of their current benefits and to enroll into a new set of benefits.
Hidden Fields: You can use the following regions to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
-
BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_CVRD_DEPS_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_BENEF_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_PCP_TABLE
You can use the BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE region to display a column for the taxable cost of a benefit. This column corresponds to a standard rate with an activity type of Self-Service Display, or--if you are displaying multiple rates for the compensation object--to the rate you have defined with 3 in the Self Service Display Order field. If you are displaying multiple rates, you can also display the Cost 2 (After Tax Cost) and Cost 4 (Miscellaneous) columns to show the rates you have defined with 2 and 4 in the Self Service Display Order field.
You can also use the BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE region to display Coverage Start and End Date columns. These columns show the coverage start and end dates for each election.
Benefits Enrollment Overview Page
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrollment Overview Content | Instruction | BEO.ENRL_OVERVIEW_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credits | Instruction | BEO.FLEX_CREDITS | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credit Summary | Instruction | BEO.OVERVIEW_FC_SUMMARY | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credit Rollovers | Instruction | BEO.FLEX_CREDIT_ROLLOVERS | Program, Life Event | |
| Benefit Selections | Instruction | BEO.OVERVIEW_SELECTIONS | Program, Life Event | |
| Covered Dependents | Instruction | BEO.OVERVIEW_CVRD_DEPS | Program, Life Event | |
| Beneficiary Enrollment Overview | Instruction | BEO.ENRL_OVERVIEW_BENEF | Program, Life Event | |
| Primary Care Providers Enrollment Overview | Instruction | BEO.ENRL_OVERVIEW_PCP | Program, Life Event | |
| Enrollment Overview Content | Message (No Enrollment Opportunity, Brief Message) | 92570 | -- | -- |
| Enrollment Overview Content | Message (No Enrollment Opportunity, Detail Message) | 92571 | -- | -- |
Current Benefits Overview Page
The Current Benefits Overview web page enables a participant to see a record of their current benefits.
Hidden Fields: You can use the following regions to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
-
BEN_OVW_CVRD_DEPS_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_BENEF_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_PCP_TABLE
You can also use the BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE region to display Coverage Start and End Date columns. These columns show the coverage start and end dates for each election.
Current Benefits Overview Page
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Benefits Overview Content | Instruction | CBO.CURRENT_OVERVIEW_CONTENT | Program | |
| Flex Credits | Instruction | CBO.FLEX_CREDITS | Program | |
| Flex Credit Summary | Instruction | CBO.OVERVIEW_FC_SUMMARY | Program | |
| Flex Credit Rollovers | Instruction | CBO.FLEX_CREDIT_ROLLOVERS | Program | |
| Benefit Selections | Instruction | CBO.OVERVIEW_SELECTIONS | Program | |
| Covered Dependents | Instruction | CBO.OVERVIEW_CVRD_DEPS | Program | |
| Beneficiary Overview | Instruction | CBO.OVERVIEW_BENEF | Program | |
| Primary Care Providers Overview | Instruction | CBO.OVERVIEW_PCP | Program | |
| Current Benefits Overview Content | Message (No Current Enrollment, Brief Message) | 92572 | __ | __ |
| Current Benefits Overview Content | Message (No Current Enrollment, Detail Message) | 92573 | __ | __ |
Benefits Selection Page
The Benefits Selection page enables a participant to select one or more plans in which to enroll.
You can control the user interface display format for plans and options in a program in the Benefits Selection page.
Use the New Enrollment Page field in the Benefit Self Service Display EIT to present the following features of plans and options within a program on the Benefits Selection page:
-
Columns:
-
Certifications: A pop-up window appears when the user scrolls the mouse over the certification icon for a compensation object.
-
Details: Users can click the Details icon to view further information for plans.
-
Coverage Start Date
-
Coverage
-
-
Expand and collapse view: Instead of the horizontal/vertical display of plans and options, users can expand and collapse compensation objects details.
To enable the New Enrollment page field, complete the following steps:
-
Assign the Benefit Self Service Display extra information type (EIT) to a responsibility. Use the Information Type Security window to link EITs to a responsibility. See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
-
Enable the user interface format for the required program.
-
Navigate to the Programs window.
-
Search for the required program.
-
Click Extra Information.
-
Select Benefit Self Service Display.
-
Click in the Details row. In the Extra Program Info DDF window, select Yes in the New Enrollment Page field.
-
Save your work.
Note: If you want to use this display format for programs, then you must enable the New Enrollment page field for each of your programs.
-
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrollment Selection Content | Instruction | BNS.ENRT_SELECTION_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Top Flex Credit Region | Instruction | BNS.ENRT_SELECTION_CR_TOP | Program, Life Event | |
| Bottom Flex Credit Region | Instruction | BNS.ENRT_SELECTION_CR_BOTTOM | Program, Life Event | |
| Selection Area | Instruction | BNS.ENRT_SELECTION_SELECT_AREA | Program, Plan Type, Life Event | |
| Selection Area | Help Tip (Certification Legend) | |||
| Selection Area | Help Tip (Enter Annual Rate Input Box, Long Tip) | |||
| Selection Area | Help Tip (Enter Rate Input Box, Long Tip) | |||
| Selection Area | Help Tip (Enter Benefit Amount Input Box, Long Tip) | |||
| Selection Area | Message (Enter Annual Rate, Long Tip) | BEN_ENRT_ANN_RTVAL_TIP | ||
| Selection Area | Message (Enter Rate, Long Tip) | BEN_ENRT_BNFTAMT_TIP | ||
| Selection Area | Message (Enter Benefit Amount Tip) | BEN_ENRT_RTVAL_TIP | ||
| Selection Area | Message (Tokens for above messages) | BEN_ENRT_SLECT_TIP_ANY_AMOUNT | ||
| Selection Area | Message (Tokens for above messages) | BEN_ENRT_SLECT_TIP_ANY_VALUE |
Dependents Selection Page
The Dependents Selection page enables a participant to add their dependents to a plan.
Note: For Advanced Benefits customers: if participant dependents are not displaying in this page, verify that you have linked the appropriate life events to the program or plan enrollment requirements in the Dependent Change of Life Event window.
Hidden Field: Use the BEN_ENRL_DEPEN_SELECTION_TABLE region to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
Dependents Selection Page
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependents Selection | Instruction | -- | -- | |
| Dependents Selection | Instruction | DPS.ENRL_DEPENDENTS_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Dependents Selection | Hint (Dependent Table) | DPS.ENRL_DEPENDENTS_CONTENT_PL | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Dependents Selection | Message (Can't Designate) | 92588 | __ | __ |
Beneficiary Selection Page
The Beneficiary Selection page enables a participant to add their beneficiaries to a plan.
Hidden Field: Use the BEN_BENEF_SELECTION_TABLE region to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beneficiary Selection | Instruction (Page) | BFS.BENEFICIARY_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Beneficiary Selection | Instruction (Plan Level Table) | BFS.BENEFICIARY_CONTENT_PLAN | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Family Members and Others | Instruction | BFS.BENEFICIARY_CONTENT_FAMILY | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Organizations | Instruction | BFS.BENEFICIARY_CONTENT_ORGS | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Beneficiary Totals Table | Hint | |||
| Beneficiary Selection | Message (Can't Designate) | 92587 | __ | __ |
Primary Care Provider Page
The Primary Care Provider page enables a participant to select a care provider. If your enterprise partners with a third party supplier of primary care provider information, you can configure this page to allow web-based searches of a database of provider information.
See: Configuring the Primary Care Provider Search Facility
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Care Provider Selection Content | Instruction | Instruction | PCP.PcpSelectContentPageLevel | Program, Life Event |
| Primary Care Provider Selection Content | Instruction | Instruction | PCP.PcpSelectContentPlanLevel | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event |
| Primary Care Provider Selection Content | Hint | __ | __ | |
| Primary Care Provider Selection Content | Message (Can't Designate) | 92567 | __ | __ |
Primary Care Provider Summary and Search Pages
Hidden Fields: You can use the following regions to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
-
BEN_PCP_SEARCH_TABLE
-
BEN_PCP_SELECT_TABLE
On the Primary Care Provider Search page, you can use the BEN_PCP_SEARCH_CRITERIA region to add the hidden fields of Physician Group and Hospital. The hidden fields of Location, School, and Degree are reserved for future use.
For the Physician Group, Hospital, Language, and Specialty fields, you must load the available data as provided by your third party provider into the corresponding Lookup Codes--in the following order--using the Application Utilities Lookups window in the Professional User Interface.
-
BEN_PCP_MED_GRP
-
BEN_PCP_HOSPITAL
-
BEN_PCP_LANGUAGE
-
BEN_PCP_SPCLTY
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Care Provider Search | Instruction | PCS.PCP_SEARCH | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Search | Instruction | PCS.PCP_SEARCH_CRITERIA | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| PCP Result Table | Instruction | PCS.PCP_SEARCH_RESULT | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Ben PCP XML Request Params | Tip | |||
| Ben PCP XML Request Params | Message (No PCPs found) |
Attachments Page
The Attachments page enables participants to upload documentation as part of the self-service benefits enrollment process.
Control the Display of the Attachments Page
The BEN: Attachments in Self-Service profile option controls the rendering of the Attachments page in the self-service benefits enrollment train. Set the profile option to Yes to make the Attachments page available to participants during the self-service benefits enrollment process. If the profile option is set to No, then this page is not displayed during the enrollment process.
Add Self-Service Instruction Messages to the Attachments Page and Page Regions
If you are using the Attachments page, then you can configure the self-service instruction messages in the Attachments page and the page regions using the Communication Types window. Navigate to the Communication Types window and use the following details to identify the page and regions to add the instruction messages:
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attachments Page | Instruction (Page) | - | BPA.ATTACHMENT_CONTENT |
| Person Attachment | Instruction | - | BPA.PERSON_ATTACHMENT_CONTENT |
| Dependents Attachment | Instruction | - | BPA.DEPENDENTS_ATTACHMENT_CONTENT |
| Beneficiary Attachment | Instruction | - | BPA.BENEFICIARY_ATTACHMENT_CONTENT |
See: Defining Self-Service Instruction Text
Confirmation Page
The Confirmation page enables a participant to see a summary of their choices and a warning of any oversights or miscalculations they may have made.
Note: You can also use the Confirmation page to display a signature region for participants to print from their web browser. Use this region if you require a participant's signature as part of a benefits enrollment. Use the Personalization Framework to display the signature region for this page.
Benefits users can print a summary statement of their enrollment, along with their signature, to keep as a proof of their records or to submit to an HR Representative if required. They can also view, print, or save the summary as a PDF document instead. The statement page displays a summary of the participant's benefits enrollment along with any warning messages, oversights, or miscalculations the participant may have made during the enrollment. Depending on the participant's enrollment data and personalization on the page, the Confirmation Page displays the following:
-
Flex credits summary
-
Benefits selection
-
Covered dependents
-
Beneficiaries
-
Primary care providers
-
Signature region
To print a benefits confirmation statement, click Printable Page. The printable page prints only the relevant information, excluding navigation buttons, tip messages, instruction text, tabs, and other user interface components.
To open or save the statement as a PDF document, click Publish PDF. Choose Open or Save in the File Download dialog box. You can print the document once you open it.
If you want to change the layout of the PDF Confirmation page, you can configure a copy of the default RTF template that XML Publisher uses for this page, which is Benefits Enrollment Confirmation.
Hidden Fields: You can use the following regions to add the hidden Full Name field to the page and to remove the Name field if necessary.
-
BEN_OVW_BENEF_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_CVR_DEPS_TABLE
-
BEN_OVW_PCP_TABLE
You can use the BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE region to display a column for the taxable cost of a benefit. This column corresponds to a standard rate with an activity type of Self-Service Display, or--if you are displaying multiple rates for the compensation object--to the rate you have defined with 3 in the Self Service Display Order field. If you are displaying multiple rates, you can also display the Cost 2 (After Tax Cost) and Cost 4 (Miscellaneous) columns to show the rates you have defined with 2 and 4 in the Self Service Display Order field.
You can also use the BEN_OVW_SELECTIONS_TABLE region to display Coverage Start and End Date columns. These columns show the coverage start and end dates for each election.
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ben Enrollment Confirmation Content | Instruction | BEC.ENRL_CONF_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credits | Instruction | BEC.FLEX_CREDITS | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credit Summary | Instruction | BEC.OVERVIEW_FC_SUMMARY | Program, Life Event | |
| Flex Credit Rollovers | Instruction | BEC.FLEX_CREDIT_ROLLOVERS | Program, Life Event | |
| Benefit Selections | Instruction | BEC.OVERVIEW_SELECTIONS | Program, Life Event | |
| Covered Dependents | Instruction | BEC.OVERVIEW_CVRD_DEPS | Program, Life Event | |
| Beneficiaries Enrollment Confirmation | Instruction | BEC.ENRL_CONF_BENEFICIARIES | Program, Life Event | |
| Primary Care Providers Enrollment Confirmation | Instruction | BEC.ENRL_CONF_PCP | Program, Life Event | |
| BEN_ENRL_CONF_WARNINGS | Message (Confirmation Success) | 92605 | __ | __ |
| BEN_ENRL_CONF_WARNINGS | Message (Action Item Warning) | 92606 | __ | __ |
Configurable FlexFields
Confirmation Page
| Region | Flex Name | Flex Code |
|---|---|---|
| Benefit Selections | Additional Ben Prtt Enrt Rslt F Details | N/A |
Unused Flex Credits Page
The Unused Flex Credits page provides a summary of the flex credits left unspent by a participant.
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unused Flex Credits Content | Instruction | FLX.UNUSED_FLEX_CREDIT_CONTENT | Program, Life Event | |
| Unused Flex Credits Content | Instruction | FLX.UNUSED_FLEX_CREDIT_NONE | Program, Life Event | |
| Unused Flex Credits Content | Message (No Unused Flex Credits) | 92633 | __ | __ |
| Unused Flex Credits Content | Message | 92632 | __ | __ |
Change Session Date Page
The Change Session Date page lets you test future-dated elections. For example, you may want to perform system testing before the start of an open enrollment period. This page should be removed in your production environment so that benefits participants do not alter their enrollment date.
See: Setting the Effective Date of a Scheduled Enrollment in Self-Service Benefits
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name |
|---|---|---|
| Session Date Content | Instruction | 92604 |
| Session Date Content | Tip (Effective Date) | 92637 |
Temporary ID Card Page
The Temporary ID Card page lets a participant print an ID card which the participant can use to obtain medical, dental, or other benefit treatment before the participant receives the official membership card from the provider.
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name | Required Communication Short Name | Valid Communication Usages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle Self-Service Human Resources Identification Card | Instruction | TMP.ENRL_TEMP_ID_PAGE | Program, Life Event | |
| Ben Temporary ID Card Content | Instruction | TMP.ENRL_TEMP_ID_PLAN | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event | |
| Temporary ID Card | Instruction | TMP.ENRL_TEMP_ID_CARD | Program, Plan Type, Plan, Life Event |
See: Configuring Web Pages, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Self-Service Benefits What-if Pages
You can access Self-Service Benefits What-if from the following menus and functions:
| User Menu Name | Function Name |
|---|---|
| Manager Self-Service | Self-Service Benefits What-if Manager |
| Employee Self-Service | Self-Service Benefits What-if Employee |
You can configure the following definitions using the Personalization Framework.
| Region | Tip Type | Message Name |
|---|---|---|
| Impact on Benefits Region | Header Text | BEN_93423_SS_WATIF_HDR_LABEL |
| Choose Winning Life Event Region | Message (Error) | BEN_93393_WATIF_CONFLICT_LER |
| Choose Winning Life Event Region | Instruction | BEN_93392_WATIF_CNFLT_LER_INS |
| Effective Date Region | Instruction | BEN_93389_WATIF_EFF_DATE_INS |
| Associated Data Changes Region | Instruction | BEN_93391_WATIF_DATA_CHG_INS |
| Impact on Benefits Region | Instruction | BEN_93394_WATIF_PG_INS_TEXT |
You can personalize the following columns to display them:
| Column Name | Displayed Detail |
|---|---|
| Reference Period | Activity Reference Period |
| Current Electable | Compensation objects currently electable |
| Current Coverage | Coverage information about currently electable compensation objects |
| Current Defined Amount | Defined Amount |
| What-If Electable | Compensation objects based on the what-if modeling |
| What-If Coverage | Coverage information about compensation object based on the what-if modeling |
| What-If Defined Amount | Defined Amount based on what-if modeling |
Setting Up Self-Service Benefits Enrollments
You must complete your plan design in the professional forms interface before you can view a Self-Service Benefits enrollment web page. If you license Advanced Benefits, you can run the Participation Batch Process from the Concurrent Manager to create electable choices for eligible participants.
If you use Standard Benefits, or if you are an Advanced Benefits customers using the unrestricted enrollment method, you can begin to allow participant enrollments after you create your plan design. The application creates the self-service enrollment page when the person logs into Self-Service Benefits.
To set up self-service benefits enrollments
-
Review the sample benefits web pages. You can configure the following elements using the Personalization Framework:
-
Section titles
-
Table Layout
-
Hints
-
Tips
-
Fields (you can choose to display fields that are hidden by default)
-
Field labels
See: Configuring Web Pages, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
-
-
Choose whether to display a predefined Legal Disclaimer page that the user must accept before processing an election.
Oracle Self-Service Benefits delivers the Legal Disclaimer page as hidden by default.
-
Define instruction text for each web page region. You do this by defining a communication type and associating the instruction text with a web page Region.
See: Defining Communication Types
You can include a link in your instruction text to another web site using HTML syntax. You could create a link to reference information contained in a summary plan description. For example:
See the <a href="http://www.visionmedical.com" target=_newWindow">Vision Medical web site </a> for more information.
In this example, the application opens the web page in a new browser window.
-
Define when you want the instruction text displayed. You can vary the instruction displayed according to:
-
Program
-
Plan Type
-
Plan
-
Life Event (Advanced Benefits)
-
-
Create a hypertext link from a compensation object to a web page which describes that program, plan type in program, plan in program, plan, or option in plan. To create a hypertext link, use one or more of the following windows:
-
Programs (for a program)
-
Plan and Plan Type window (for a plan or a plan type in program)
-
Plans window (for a plan)
-
Maintain Plan Options window (for an option in a plan)
The link appears in the Benefits Selection web page, or--for Programs--the Overview page.
-
-
Review Messages and change any that do not meet your requirements.
-
Configure Action Item messages (Advanced Benefits) to meet your requirements.
The application displays Action Item messages at the end of the enrollment process on the Confirmation page.
See: Enrollment Action Types in Enrollment Requirements
-
Set up any life event reasons that you want to trigger when a user adds, updates, or deletes a family member contact in Self-Service Benefits.
-
Configure whether benefits participants have the option to select a Primary Care Provider (PCP) for a benefits plan.
-
Configure whether you want benefits participants to have access to the Primary Care Provider Search facility.
-
Configure the RTF template if you want to modify the default Confirmation page. Perform the following steps to configure your own Confirmation page:
-
Copy the default template, Benefits Enrollment Confirmation, and ensure that your copy has a template code beginning with BENSSCNF.
-
Make the default template inactive.
-
-
Control the availability of the Attachments page during the self-service benefits enrollment process.
See: Attachments Page
-
Test your implementation. A system administrator can debug Self-Service Benefits by generating a PYUPIP trace file for an individual user.
Setting Up Flexible Spending Accounts
To set up a Flexible Spending Account (FSA), create two elements, a plan with no options, and two standard rates.
-
In the Element window, create two elements, one for employee contributions and the other for employer contributions.
-
In the Plan window (or the Plan Design Wizard) create an FSA plan with no options.
-
In the Plan Enrollment Requirements window (under the General and Plan tabs, select Coverage), click Coverage Restrictions and set up a Max value equal to the FSA limit for the year.
-
In the Coverages window, select your plan in the Compensation Object field. Under the Calculation Method tab, create a Flat Amount calculation method with your Min, Max, Increment, and Default parameters. Check Enter Value at Enrollment.
-
In the Standard Rates window, create two standard rates, one for employers (FSA ER) and one for employees (FSA EE). For both, specify a calculation method of Post Enrollment Calculation Rule and attach a formula type of Rate Value Calculation. Also for both rules, create Rate Periodization rules using a formula of type Rate Periodization.
For standard rates, see: Defining Activity Rates for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
For formula creation, see: Writing or Editing a Formula, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Enabling Self-Service Benefits Enrollment Notifications
You can configure Self-Service Benefits Enrollments so that an enrollment update generates a notification to an HR professional.
To enable enrollment notifications, you update one of the seeded functions in the Form Functions window using the system administrator responsibility.
See: Enrollment Change Workflow Notifications
To enable Self-Service Benefits Enrollment Notifications
-
Query the function that you want to update. Choose one of the following:
-
Employee Self-Service (BEN_SS_BNFT_ENRT)
-
Manager Self-Service (BEN_SS_MGR_ENRT)
-
-
Choose the Form tab.
-
In the Parameters field, verify that the following parameter appears:
displayDate=N&allowEnrt=Y&sessionDate=&sendFYINotification=N&wfProcessName=FYI_NOTIFICATION_PRC.
Note: If you do not see this string, you must manually enter the parameter.
-
To enable workflow notifications, replace sendFYINotification=N with sendFYINotification=Y.
-
Replace the wfProcessName=FYI_NOTIFICATION_PRC portion of the parameter with your custom process name.
-
Save your work.
Setting Up User Access to Self-Service Benefits
Self-Service Benefits functions are attached to the Benefits Self-Service menu. You can change menu names and function names, or remove menus and functions if required.
As a standard practice, you should copy and edit all delivered menus you want to update. Otherwise, your changes will be overwritten the next time you apply a patch to the application.
If you create a new submenu, you must update the AK regions which point to the submenou.
See: Configuring Tabbed Regions, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
To set up user access to self-service benefits
-
Log on to Oracle HRMS with the System Administrator responsibility.
-
Open the Menus window.
-
Query the Self-Service Menu in the Menu field: HR_EMPLOYEE_DIRECT_ACCESS_WEB. The following Self-Service User Menu Name displays to users:
-
Employee Self-Service
You can change the menu name if required.
-
-
Query the Benefits Submenu in the Menu field: BEN_SELF_SERVICE_BENEFITS. The following Benefits Submenu User Name displays:
-
Benefits Self Service
Because the Benefits Self Service submenu is not linked to a top level menu (it has no prompt) the submenu is hidden. The Benefits Self Service submenu has the following prompts.
-
Benefits Enrollment
-
Current Benefits
These prompts function as the labels on the tabs of the self-service web page.
-
-
Save your work and close the Menus window.
-
If you create a new submenu, you must update the AK regions which point to the submenu.
Complete steps 7 to 14 to update the region items, or proceed to step 15 if you do not intend to create any new submenus.
See:Configuring Tabbed Regions, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Using an AK Developer responsibility, log on to the application.
-
Open the Regions window.
Query one of the following regions in the Region ID field:
-
BEN_BENEFICIARY_PAGE
-
BEN_CURR_OVW_PAGE
-
BEN_ENRL_CONF_PAGE
-
BEN_ENRL_DEPENDENTS_PAGE
-
BEN_ENRL_OVERVIEW_PAGE
-
BEN_ENRT_SELECTION_PAGE
-
BEN_FAMILY_MBRS_PAGE
-
BEN_FAM_ADD_PAGE
-
BEN_PCP_SEARCH_PAGE
-
BEN_PCP_SELECT_PAGE
-
BEN_UNUSED_FLEX_CREDIT_PAGE
-
-
Choose the Region Items button to open the Region Items window.
-
In the Attribute Name column, select the Application Menu entry.
-
Scroll to the Menu Name column and update the field with the new menu as entered in the Menu field of the Menus window.
-
Repeat for each region listed in step 9.
-
Save your work and close the Region Items window.
-
You can use the Form Functions window to customize the seeded functions--BEN_SS_BNFT_ENRT and BEN_SS_MNGR_ENRT.
-
Use the Form Functions window to create your own Self-Service Benefit functions from the sample functions supplied. The sample User Function Names are:
-
Self Service View Current Benefits
-
Self Service Benefits Enrollment
The Function Names are:
-
BEN_SS_CURR_BNFT
-
BEN_SS_BNFT_ENRT
If you update the seeded functions, you must update your custom function to use the seeded parameters and HTML Calls.
Note: It is a good practice to check the Readme for each Self-Service Benefits patch you apply to see if the parameters and HTML Calls for the seeded functions have changed.
-
-
Update the displayAgreement parameter value to Y to display a Legal Disclaimer page that the user must accept before continuing with an enrollment.
-
Set Security Profiles. Use the System Profile Values window to link the responsibility you have created to a Security Profile and your Business Group. The Security Profile is:
-
HR: Security Profile
Note: If you fail to link your Responsibility to your Business group with the HR: Security Profile, any benefits participants who attempt to enroll will receive an error message indicating they cannot enroll.
-
-
Set the HR: Business Group Profile. Use the System Profile Values window to link the responsibility you have created to your Business Group. The Business Group Profile is:
-
HR: Business Group
-
-
Define the people you would like to access Self-Service Benefits.
There are two ways to do this. You can follow the typical steps for defining a new user and assign each user a responsibility that enables access to Self-Service Benefits, one at a time.
Or, you can set up concurrent programs to automate this manual process.
See Batch Creation of User Accounts, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Setting the Effective Date of a Scheduled Enrollment in Self-Service Benefits
Self-Service Benefits provides different ways of controlling the date on which the application records a participant election:
-
The Change Session Date web page (for testing environments in both Standard and Advanced Benefits)
-
The Change Session Date menu parameter (Standard Benefits)
-
Normal date processing based on the session date (Advanced Benefits)
The Change Session Date web page lets you test future-dated elections, such as for an upcoming open enrollment period.
Use the Change Session Date menu parameter if you use standard benefits and you want to record the life event occurred date of an enrollment for a date that is not equal to the system date.
For example, if you schedule your open enrollment period for the first two weeks in November, you can set the session date to record all enrollments as of January 1st of the following year.
Note: You can use both features simultaneously, but the date the user enters in the Change Session Date web page overrides the session date parameter for the current session.
To set the session date in Self-Service Benefits
-
Log in to Oracle HRMS using a System Administrator responsibility and open the Form Functions window.
-
Choose the Description tab.
-
Query the Function Name for which you want to set the session date. Choose from:
-
BEN_SS_BNFT_ENRT (Employee Self-Service Benefits)
-
BEN_SS_MGR_ENRT (Manager Self-Service Benefits)
-
-
Choose the Form tab.
-
Update the seeded parameter to display the Change Session Date page or to set the effective date to a date you choose.
Note: If you do not set the session date, Self-Service Benefits processes dates based on the date codes you select in your plan design.
In the following example, setting displayDate=Y displays the Change Session Date web page. Setting &sessionDate=12/31 sets the session date to December 31st for the BEN_SS_MGR_ENRT function.
displayDate=Y&sessionDate=12/31&pFromPersonSearch=Y&pFormFunction=BEN_SS_MGR_SRCH
You enter the session date in mm/dd format. Do not include the year.
Note: You should remove this web page from your production environment by setting displayDate=N so that benefits participants cannot alter their enrollment date.
Deriving the Year of the Session Date
The application derives the year to use for the session date, so you should not include a year in the session date parameter.
If you enter a session day and month that is prior to or equal to the system day and month, the application uses the following year. If you enter a session date that is later than the system day and month, the application sets the session date to the current year.
Configuring Unrestricted Program Enrollment Processing
Whenever a participant accesses the Benefits function in Self-Service Benefits, the Participation Process evaluates the participant's eligibility for unrestricted program enrollments. During an annual open enrollment period, with many participants accessing the application at once, this can impede system performance.
To reduce system load, you can restrict when the application re-evaluates unrestricted programs for a participant.
Also, you can remove access to the Benefits Enrollments web page during those periods when you do not want participants to enter or update benefits elections for any event. In these instances, participants can still view their past, current, and future elections using the Current Benefits Overview web page.
To configure unrestricted program enrollment processing
-
Log in to Oracle HRMS using a System Administrator responsibility and open the Form Functions window.
-
Choose the Description tab.
-
Query the Function Name for which you want to configure unrestricted enrollment processing. Select one of the following:
-
BEN_SS_BNFT_ENRT (Self-Service Benefits Enrollment - Employee)
-
BEN_SS_MGR_ENRT (Self-Service Benefits Enrollment - Internal Use)
-
-
Choose the Form tab to display the following parameter:
displayDate=Y&allowEnrt=Y&sessionDate=&sendFYINotification=Y&wfProcessName=FYI_NOTIFICATION_PRC&ssProcessUnrestricted=Y
-
If you do not see the parameter, enter the parameter string as listed above.
-
To force the Participation Process to re-evaluate a participant for each access of the Benefits function, leave the seeded parameter ssProcessUnrestricted=Y. Use this setting during open enrollment.
-
To disallow unrestricted enrollments in Self-Service Benefits, update the seeded parameter by setting ssProcessUnrestricted=N. Use this setting outside of your Open Enrollment period to prevent Self-Service enrollments.
-
Set ssProcessUnrestricted=P to restrict Unrestricted enrollment evaluation during your Open Enrollment period to the following scenarios:
-
This is the first time the application has evaluated the unrestricted event for the person, and no unrestricted events exist for the person.
-
The Participation Process has not processed the unrestricted event for the current annual enrollment period, and the current session date is later than the existing unrestricted life event occurred on date.
-
The Life Event Occurred On Date for the unrestricted event equals the session date, and there is a person change made after the last unrestricted process run to one of the following tables.
-
Per_addresses
-
Per_all_assignments_f
-
Per_all_people_f
-
Per_contact_relationships
-
Per_pay_proposals
-
Per_periods_of_service
-
Per_qualifications
-
Ben_per_bnfts_bal_f
-
Per_absence_attendances
-
Per_person_type_usages_f
-
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Self-Service Instruction Text
Use the Communication Types window in the Professional User Interface to define regional instruction text for Self-Service Benefits Enrollments and Individual Compensation Distributions.
You can vary the instruction text that displays in a region based on different criteria, such as the presence of a life event or enrollment in a particular compensation object.
To define a communication type
-
Enter a Name for the communication type you are defining.
-
Enter a Short Name for this communication type.
Note: Self-Service uses the short name to link the instruction text you write to a specific region in a Self-Service Benefits web page. You must enter the short name in the following format: BEN.REGIONNAME. Exclude the BEN prefix from the regionname portion of the short name.
See: Benefits Enrollments for a list of the required short names for each web page region.
-
Select a To Be Sent code of Not Applicable.
-
Select a Usage type of Self Service Instruction Text to indicate you are configuring a self-service web page.
-
Save your work.
-
Choose the Usages button.
-
Select a value for one or more of the following parameters to limit the conditions under which instruction text is displayed.
-
Life Event
-
Program
-
Plan
-
Plan Type
-
Enrollment Period
-
Action
-
-
Select a Usage Rule if your criteria for determining the conditions under which instruction text is generated cannot be fully accommodated by the usage criteria on this window.
-
Enter instruction text in the Self Service Instruction Text field that corresponds to the region of the self-service web page that you are configuring.
-
Click in the next Or Combination of field and enter the next set of instruction text in the Self Service Instructor Text box if you enable the Legal Disclaimer page.
You cannot specify limitation parameters, such as life event or plan, when defining instruction text for the Legal Disclaimer page.
Note: The application displays the disclaimer text entered in each field as a separate paragraph on the Legal Disclaimer web page. You can enter a maximum of 2000 characters for each disclaimer text paragraph. Advanced Benefits users can check whether a person has accepted the legal disclaimer in the Person Communication window. When you query the name of the person in the window, the Type field displays Legal Disclaimer, indicting that the user has accepted the legal disclaimer with details of the life event name and date. Both Standard and Advanced Benefits users can create a system extract to report on this information.
-
Save your work.
Configuring the Primary Care Provider Search Facility
As part of a self-service enrollment, a benefits participant can select a primary care provider (PCP) for a benefit plan. As a system administrator, you can configure Self-Service Benefits so that a participant can select a primary care provider through a web-based search of a PCP database.
Self-Service Benefits also supports free form text entry of primary care providers without validation when a repository of PCP data is not used.
Follow the instructions below based on the search type configured by your enterprise.
Setting up an XML-Enabled Primary Care Provider Search
If the search criteria entered by a benefits participant is formatted as an XML search request for use with a database of primary care providers (maintained by your enterprise or a third party), you use the Personalization Framework to configure information such as the URL of the information provider and the Document Type Definition (DTD) used by the search.
Note: If you change your PCP Search Configuration, you must delete any Personalization changes and re-enter the PCP configuration data.
To set up an XML-enabled primary care provider search:
-
Navigate to the Primary Care Provider Search page from the Self-Service Benefits Enrollments menu.
-
Choose the Personalize Ben PCP XML Request Params link.
-
Select a Personalization Level.
-
Choose the Advanced Settings button.
-
Select the Ben PCP Provider Information item and enter the URL of the information provider in the New Column Name field.
Note: Enter the URL as you would in the Address or Location field of your web browser. Do not enclose the URL in quotations.
-
Select the Ben PCP XML DTD item and enter the URL of the XML Document Type Definition in the New Column Name field.
-
Select the Ben PCP Info Provider Client ID item and enter the Client ID given by the information provider in the New Column Name field.
-
If you use a proxy server to access an external web site, select the Ben PCP Server Proxy Set item and enter true in the New Column Name field.
-
If you do not use a proxy server, enter false.
-
-
If you use a proxy server, select the Ben PCP Server Proxy Port item and enter the port number (typically 80) in the New Column Name field.
-
If you use a proxy server, select the Ben PCP Proxy Host item and enter the URL of the proxy server in the New Column Name field.
-
Select the Ben PCP XML Version item and enter the version of XML you are using in the New Column Name field, such as 1.0
-
Select the Ben PCP Max Records item and enter the maximum number of records to be returned by the query in the New Column Name field.
Note: For best performance, it is recommended that the maximum number of records be set to 100 or less.
-
Select the Ben PCP Request Method item and enter the HTTP request method expected by the information provider (such as GET or POST) in the New Column Name field.
-
Select the Ben PCP Show Label item and enter a message to display in the Result Table if the search returns no provider.
-
Select the Ben PCP Direction item and enter the text to display in the Map Column of the Result Table.
-
Select the Ben PCP Table Bar Text item and enter the text to display in the Result Table Bar.
Setting Up a Primary Care Provider Search without XML
Customers who create a search page which does not format the PCP query in XML can follow these guidelines for a creating a PCP search that is compatible with Self-Service Benefits.
To set up a primary care provider search without XML
-
Navigate to the Primary Care Providers page from the Self-Service Benefits Enrollments menu.
-
Choose the Personalize Primary Care Provider Selection Table link.
-
Select a Personalization Level.
-
Choose the Advanced Settings button.
-
Select the Search item and enter the URL in the URL field that is accessed when a participant clicks the Search button on your custom Search web page.
-
A system administrator or application developer creates a search page that performs the query and accepts the following page-context variables:
-
PcpPersonId = (Person ID of the person for whom you are searching for a primary care provider )
-
PcpPlId = (Plan ID defined for the plan in the database)
-
PcpPlTypId = (Plan Type ID defined in the database)
Note: You do not need to use these variables if they are not required for your search or validations.
-
-
If the search is canceled without a selection of a PCP, the following URL must be used to return to the search page:
-
/OA_HTML/OA.jsp?akRegionCode=BEN_PCP_SELECT_PAGE&akRegionApplicationId=805&pcpSearchCancel=1.
Note: Replace the directory OA_HTML with the base HTML directory of your installation.
-
-
If the search is successful, the URL accessed by the query must return the following information (properly formatted) with the following parameter names and data types:
Parameter Name Data Value Example ExtIdent ID of the primary care provider per the plan. Number 10154244 (id) PcpName Name of the primary care provider String Sue Jones, MD (doctorsName) PcpSpecialty Specialties of the primary care provider String Internal Medicine, Pediatrics (specialty) PcpPlId The plan ID that corresponds to the plan name Number 905 (planId) PcpPersonId The person ID passed to the database as part of the query Number 928374655 (personId) PcpTypCd The code of the first primary care provider specialty that is returned by the query Number 23 (pcpTypCd) The URL returned by the search should look like this:
-
/OA_HTML/OA.jsp?akRegionCode=BEN_PCP_SELECT_PAGE&akRegionApplicationId=805&ExtIdent=id&PcpName=doctorsName&PcpSpecialty=specialty&PcpPlId=planId&PcpPersonId=personId&PcpTypCd=pcpTypCd
Note: Replace the directory OA_HTML with the base HTML directory of your installation and replace the variables in the URL with the actual values.
-
Generating Self-Service Benefits Trace Files
If you experience enrollment problems during system testing, or while in production, you can generate a trace file of a PL/SQL procedure to track the source of the problem for an individual user. The hr_utility.set_location function generates output that lets you examine the flow of code execution for key APIs and business processes.
Set the profile option OAB: Enable Self-Service Benefits Trace to select the module that you want to trace.
Note: You should set the profile option for only one user at a time.
Using a system administrator responsibility, open the Find System Profiles Value window to set the profile option for a user.
To generate a Self-Service Benefits trace file
-
Deselect the Site check box.
-
Select the User check box.
-
Select the person for whom you are running the trace from the User list.
-
Select the OAB: Enable Self-Service Benefits profile option in the Profile field.
-
Click Find.
-
In the System Profile Values window, select a User value for the profile option.
-
BENACTBR (Activity Base Rate): This user value traces the rates computation process.
-
BENDISRT (Distribute Rates): This user value traces a user-entered rate change that calculates other dependent rates, such as parent/child rates or annual-to-communicated rates.
-
BENELINF (Election Information): This user value traces the enrollment process when the user changes elections on the Benefits Selections Page and clicks Next.
-
BENOLLET (On-Line Life Event): This user value traces the Participation Process for a single user. For example, when the user clicks Next on the Dependents and Beneficiaries page.
-
-
Save your work.
-
Close the System Profile Values window.
-
Run your test case in Self-Service Benefits based on the profile option you selected.
Note: The browser window stops responding while the page waits for the trace pipe to open for the user.
-
To view the results of the trace, enter the following command on a server where you can access the application database. The example below shows the command for the BENELINF value of the profile option.
$PAY_TOP/bin/PYUPIP <apps userid>/<apps pwd>@<dbname> BENELINF > PYUPIP.txt
-
Read the PYUPIP.txt file to analyze the results of the trace.
Additional Information: You can upload the trace file to Oracle Support for analysis as part of a Technical Assistance Request.
-
Close your test browser session.
-
After you complete the trace, navigate to the System Profile Values window and clear any value from the OAB: Enable Self-Service Benefits profile option.
Warning: If you do not return the profile option value to null, the Self-Service application stops responding while the page waits for the trace pipe to open for the user the next time they access Self-Service Benefits.
COBRA Benefits and HIPAA
COBRA Administration
Oracle HRMS provides an approach to COBRA administration that allows you to design COBRA programs in accordance with US regulatory requirements while giving you administrative flexibility.
As a prerequisite to creating COBRA programs and plans, you should have a familiarity with the application's features for benefit plan design, eligibility profiles, and activity rate definition.
COBRA administration can be thought of in the following phases:
-
Designing the COBRA program
-
Defining COBRA life events (Advanced Benefits)
-
Establishing enrollment requirements for programs (Advanced Benefits)
-
Creating COBRA eligibility profiles
-
Defining contribution rates for COBRA plans
-
Defining COBRA communication types
-
Setting up communication extracts
Once you have defined your COBRA program, the following COBRA administration tasks apply:
-
Determining first-time and on-going eligibility for COBRA
-
Running pre-enrollment literature extracts
-
Enrolling participants, covered dependents, and beneficiaries in COBRA programs
-
Recording participant COBRA payments
-
Tracking temporally-based COBRA eligibility
-
De-enrolling ineligible COBRA participants
COBRA Program Design
You administer COBRA benefits in Oracle HRMS by defining a COBRA program that contains those medical, dental, vision, and flexible spending account plans that are subject to COBRA regulations.
Because you can link a plan to more than one program, there is no need to define one plan for your regular program and a second plan for a COBRA program. You can apply activity rates at the plan in program level so that the COBRA plan has a different contribution rate than the regular plan.
You define a COBRA program by selecting a program type of COBRA or COBRA with Credits on the Programs window. Select COBRA if you enroll COBRA participants using the Non-Flex Enrollment window, or select COBRA with Credits if you are an Advanced Benefits customer and you use the Flex Enrollment window to enroll COBRA participants. or each plan that is subject to COBRA, you link the plan to the COBRA program and enter a COBRA Payment Day for the plan in the Plans window.
Note: You can define a single COBRA program to contain all your COBRA plans, or you can define multiple COBRA programs.
Maximum Enrollment Periods
You can define the maximum enrollment period for a COBRA program. This period can vary based on a life event. You must define a maximum enrollment period in order to cover qualified beneficiaries.
For example, the standard maximum enrollment period for COBRA is 18 months. However, subsequent qualifying life events that occur while a person is covered under COBRA can extend the maximum enrollment period. For example, the divorce or death of the participant can extend the coverage period for the participant's spouse and covered dependents.
Limitations to Changing Coverage (Advanced Benefits)
COBRA participants can change their elections during an open enrollment period. You can define enrollment restrictions that limit a participant's election options based on the coverage they had before the COBRA qualifying life event.
COBRA Life Events (Advanced Benefits)
Advanced Benefits customers can define the life events that trigger a first time COBRA enrollment, or a subsequent life event (such as a divorce) that extends COBRA coverage.
When you define a life event that impacts COBRA eligibility, select the COBRA Qualifying Event field in the Life Event Reasons window.
The product is delivered with the following predefined COBRA life events:
-
Loss of Eligibility - This life event is triggered when a participant waives COBRA coverage or does not enroll during the initial enrollment period.
-
Non or Late Payment - This life event is triggered when a participant fails to make a payment or makes a late payment.
-
Maximum Enrollment Period Reached - This life event is triggered when the maximum enrollment period is reached.
-
Voluntary End of Coverage - This life event is triggered when the participant voluntarily terminates coverage.
Participation Eligibility Profiles for COBRA
You define COBRA eligibility profiles to control eligibility for a COBRA plan. Oracle HRMS provides all the eligibility criteria you need to create eligibility profiles that allow you to administer COBRA plans according to regulations.
When you define a COBRA eligibility profile, you include one criteria type in each profile. The compensation object to which you link the profile depends on the criteria in the profile. Eligibility profiles can be defined such that participants who meet the specified criteria are either included or excluded from eligibility.
See: COBRA Eligibility Profiles for an overview of each eligibility profile that you can create to determine COBRA eligibility.
Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles for COBRA
COBRA regulations allow dependents to make elections independent from the elections of a primary participant. The system supports the definition of two optional dependent eligibility profiles for COBRA.
Covered in Other Plan
This dependent eligibility profile excludes dependents from COBRA plan eligibility who were not enrolled in a plan subject to COBRA one day before the COBRA qualifying event.
-
Select the plans in a program that are subject to COBRA that you want to include in the profile.
-
Select a Date Determination code of Date of Determination Minus 1.
Designator Currently Enrolled
This dependent eligibility profile determines if a dependent designator is enrolled in a COBRA plan. During an open enrollment period, COBRA participants can add or remove dependents from COBRA coverage. You can use this eligibility profile to exclude dependents from open enrollment who were not enrolled in COBRA coverage after the qualifying life event.
COBRA Eligibility Determination
You run the Participation batch process in Life Event or Scheduled mode to determine eligibility and electability for COBRA benefits if you are an Advanced Benefits customer. If you use Standard Benefits, the system determines COBRA eligibility when you query a person's record in an enrollment window, such as the Non-Flex Program window.
Note: The Participation process determines eligibility and electability for COBRA plans after all other plans have been processed. A participant must no longer be eligible for any plans subject to COBRA before becoming eligible for a plan in a COBRA program.
COBRA Eligibility Profiles
You can use the following eligibility profiles to determine COBRA participation.
Eligibility: Leaving Reason
| Description | Identifies the leave reason critiera that exclude a participant from COBRA eligibility. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | Yes |
| Comments | Use this criteria to exclude participants terminated for reasons of Gross Misconduct. |
Eligibility: Other Coverage
| Description | This criteria excludes participants from COBRA eligibility who are ineligible for all plans subject to COBRA but who have coverage from another plan sponsor. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | No |
| Comments | Select a value of Yes in the Other Coverage field when defining this profile. The participant will be found eligible if they do not have other coverage. Use the People window to record if a person has other coverage. |
Eligibility: Opted for Medicare
| Description | This criteria excludes a participant from COBRA eligibility who becomes entitled to Medicare benefits. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | No |
| Comments | Check the Opted for Medicare field and the Exclude field when defining this profile. Use the People window to record if a person is covered under Medicare. A participant who becomes entitled to Medicare as an active employee may become ineligible for both regular benefits and COBRA benefits. The dependents of an active employee who opts for Medicare become eligible for COBRA. If the participant who opts for Medicare is currently covered by COBRA, the participant's dependents can extend their COBRA coverage for 36 months if the initial COBRA qualifying event is Termination or Reduction in Hours. |
Eligibility: COBRA Qualified Beneficiary
| Description | Use this criteria to find qualified beneficiaries eligible for coverage extensions based on qualifying events that occur during COBRA coverage, such as the death or divorce of the primary participant. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | No |
| Comments | Select a value of Yes in the Qualified Beneficiary field when defining this profile. This profile also prevents a qualified beneficiary from being found eligible once the maximum enrollment period is reached. |
Eligibility: Participant in Other Plan Type
| Description | You define this profile to exclude a participant from COBRA eligibility who is currently eligible for any plan subject to COBRA in a plan type that you include in the profile. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan Type in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | Yes |
| Comments | Check the Subject to COBRA field when defining this eligibility profile so that the system only checks for plans in the plan type that are subject to COBRA. |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Plan Type in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in the plan type in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan Type in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | Yes |
| Comments | Check the Subject to COBRA field when defining this eligibility profile so that the system only checks for plans in this plan type that are subject to COBRA. Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in any plans in the plan type one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Covered in Other Plan Type in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant's dependents were covered by the plan type in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan Type in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | Yes |
| Comments | Check the Subject to COBRA field when defining this eligibility profile so that the system only checks for plans in this plan type that are subject to COBRA. Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the dependent was covered in any plans in the plan type one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Plan in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in the plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in this plan one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Covered in Other Plan in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant's dependents were covered by the plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the dependent was covered by this plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Eligible for Another Plan
| Description | This criteria determines if a participant is currently eligible for any plans subject to COBRA. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | No |
| Comments | Check the Exclude field when defining this profile to determine that a participant who is eligible for this plan is ineligible for COBRA. |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Plan
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in the plan one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in this plan one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Covered in Other Plan
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant's dependents were covered by the plan one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the dependent was covered by this plan one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in a COBRA program on the day of open enrollment. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | COBRA Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Use this profile to limit eligibility for COBRA open enrollment periods to those participants currently enrolled in the COBRA program. Select a Date Adjustment value of Day of Determination to determine if the participant was enrolled in the program during the open enrollment period |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Plan in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in the plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in this plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. Select a Date Adjustment value of Day of Determination to determine if the participant was enrolled in the program during the open enrollment period |
Eligibility: Covered in Other Plan in Program
| Description | This criteria determines if the participant was enrolled in the plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Include |
| Required? | |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in this plan in program one day before the COBRA qualifying life event Select a Date Adjustment value of Day of Determination to determine if the participant was enrolled in the program during the open enrollment period. |
Eligibility: Enrolled in Another Option in Plan
| Description | Use this criteria to exclude a participant from COBRA eligibility who was enrolled in the waive option of a plan one day prior to the COBRA qualifying life event. |
| Associated COBRA Compensation Object | Option in Plan in Program |
| Include or Exclude? | Exclude |
| Required? | This profile is only required if you define a plan subject to COBRA that contains a waive option. |
| Comments | Select a Date Adjustment value of Date of Determination Minus 1 to determine if the participant was enrolled in the waive option one day before the COBRA qualifying life event. |
Setting up a COBRA Program
Follow this process to set up a COBRA program.
Define COBRA Programs and Plans
To define COBRA programs and plans
Define the plans that are subject to COBRA and link these plans to the COBRA program.
-
Define the benefit plans for which you provide continuing eligibility based on COBRA regulations.
-
Indicate that the plan is subject to COBRA regulations by selecting a value of COBRA in the Regulations field of the Maintain Plan Related Details window.
-
Enter the day of the month (as a number) by which COBRA payments must be received for this plan in the COBRA Payment Date field of the Plans window.
-
Define the COBRA program.
-
Select a Program Type of COBRA or COBRA with Credits (if you use flex credits to offset COBRA costs) in the Programs window.
-
Select the level at which you are administering COBRA programs in the Determine Enrollment Period Level field.
-
Select Program if your COBRA administration rules are set at the program level and apply to all plan types and plans in the COBRA program.
-
Select Plan Type in Program if your COBRA administration rules vary between the plan types in the COBRA program.
-
-
Use the Plan and Plan Type window to link the plans you include in the COBRA program.
Note: You also link the plans subject to COBRA to the regular program.
-
Define a maximum enrollment period of 18 months for the COBRA program. You must define a maximum enrollment period in order to cover qualified beneficiaries.
Note: Advanced Benefits customers can use the Life Event window to vary the maximum enrollment period based on a defined qualifying life event such as a divorce or the death of the employee. You can indicate if the life event extends coverage for the spouse or a dependent.
Set up the Administrator Contact
You enter an administrator's information to provide the COBRA participant with the name of a contact and the address where they should return the COBRA election page.
You can set up contacts by plan, or establish one contact for all plans in a program. Contacts you set up at the program level override contacts you enter for any plans in the program.
See: Associating an Organization with a Benefits Program
See: Associating Options with a Plan
To set up an administrator contact
-
To enter an administrator for a program, open the Programs window and select the Organizations tab.
-
Select the administrator's Organization.
You must first enter your administrator's organization using the Organization window. The address you define for the organization appears as the administrator's mailing address in a COBRA letter.
-
Enter the administrator's name in the Organization Roles field.
-
In the Organization Role Types field, select Administrator.
-
Save your work.
-
To enter an administrator for a plan, open the Plans window. Choose the Details button and select the Organizations tab.
-
Complete the fields as you would for a program, following steps 2-5.
Define COBRA Qualifying Life Events (Advanced Benefits)
Define the life events that qualify a participant for COBRA coverage or that extend the coverage period of a participant, spouse, or dependent.
To define COBRA qualifying life events
-
Define the Life Event, indicating that it qualifies an eligible person for COBRA, by checking the COBRA Qualifying Life Event field in the Life Event Reasons window.
Define COBRA Eligibility Profiles
Define participation eligibility profiles and link the profiles to your compensation objects.
To define COBRA eligibility profiles
-
Define the eligibility profiles which participants and dependents must meet in order to qualify for COBRA coverage.
See: COBRA Eligibility Profiles for an overview of each eligibility profile that is applicable to COBRA.
-
Link the eligibility profile to the appropriate compensation object depending on the kind of profile you have defined.
Define Open Enrollment Requirements for COBRA
COBRA participants can change elections during an open enrollment period. The elections that a COBRA participant can make are limited based on COBRA regulations.
-
Define the enrollment requirements for each COBRA plan.
Define COBRA Contribution Rates
Define the contribution activity rate for your compensation objects that are subject to COBRA. The contribution rate may be up to 102% of the actual premium.
You can define one activity rate for the regular compensation object--either a plan in program or an option in plan in program--and a second rate for the same compensation object in the COBRA program.
To define COBRA contribution rates
-
Define the activity rate for the compensation object subject to COBRA that is in the regular program.
-
Define the activity rate for the compensation object subject to COBRA that is in the COBRA program.
See: Defining Activity Rates for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
Define COBRA Communication Types
Define the COBRA communication types that you send to participants, such as the notification of eligibility, a grace period expiration letter, and a COBRA expiration letter.
Use the Communication Types window to define the features of each COBRA communication type.
See: Defining Communication Types
To define COBRA communication types
-
Query one of the seeded COBRA communication types in the Communication Types window. Choose either:
-
COBRA Initial Information
-
COBRA Notification Letter
-
-
Choose the Triggers button to open the Communication Type Triggers window.
-
Select a COBRA communication trigger.
-
For the COBRA Benefit Initial Information letter, a typical example is Post Enrollment Confirmation Literature -Form- Enrollment Results Created/Modified/Deleted
-
For the COBRA Notification Letter, a typical example is Eligibility -BENMNGLE- Determines First Time Eligible
-
-
Close the Communication Type Triggers window.
-
Choose the Usages button.
-
Select the applicable COBRA program.
For the COBRA Notification Letter, the application detects the communication type when a person becomes newly eligible for the COBRA program.
Create PDF versions of COBRA letters
You can create XML-driven PDF versions of the COBRA letters. To do so, you must use the System Administrator responsibility.
Generate COBRA Letters
You can generate and print COBRA letters directly from Oracle HRMS. Choose from the following reports:
-
The COBRA Benefit Initial Information report provides employees with information about their rights under COBRA
-
The COBRA Benefits Notification Letter report extracts electable choice information for selected persons
You cannot modify the seeded templates generated by the COBRA reports, but you can copy them and change the copies. See "To modify the seeded letter format" below.
You run reports from the Submit Requests window.
To generate a COBRA letter
-
Select the appropriate COBRA letter in the Name field.
-
Enter the Parameters field to open the Parameters window.
-
Select an individual in the Person Name field to generate a letter for a single person.
-
To generate a letter for multiple persons, select one or more of the following criteria:
-
Organization
-
Benefit Group
-
Location
-
Program (COBRA Benefits Notification Letter only)
The report generates a letter for each person who has the COBRA communication type detected.
-
-
Choose the OK button.
-
Choose the Options button to select a printer if you want to send the letter directly to a printer.
-
Complete the batch process request and choose Submit.
Note: THIS EXAMPLE LETTER/MATERIAL HAS BEEN PRODUCED BY OR FOR THE INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE. ORACLE PROVIDES THIS LETTER/MATERIAL ON AN "AS IS" BASIS. ORACLE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL ORACLE BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, OR DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, REVENUE, DATA, INCURRED BY YOU OR ANY THIRD PARTY IN CONNECTION WITH THE LETTER/MATERIAL, WHETHER IN AN ACTION IN CONTRACT OR TORT, EVEN IF ORACLE HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. ORACLE'S ENTIRE LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES IN RESPECT OF THE LETTER/MATERIAL AND ANY RELATED MATERIAL SHALL IN NO EVENT EXCEED TEN THOUSAND DOLLARS (U.S. $10,000).
To modify the seeded letter format
-
Attach the XML Publisher responsibility to your User.
-
Log in to the XML Publisher responsibility.
-
Query "COBRA Initial Letter" or "COBRA Notification Letter" in the template of the XML Publisher Administrator.
-
Download the seeded RTF file and make your changes.
-
End Date the seeded template (but do not make any changes to the data source).
-
Create a new template including the new RTF file. Ensure that:
-
the application is Oracle Advanced Benefits or Advanced Benefits
-
the data source is either "COBRA Initial Letter" or "COBRA Notification Letter"
-
the template Type is RTF
-
HIPAA Certification
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) contains provisions intended to guarantee that employees and their dependents who leave an employer's group health plan have ready access to a subsequent employer's health plan, regardless of their health or claims experience.
HIPAA regulations require that employers keep records of the health care coverage of plan participants and that documentation certifying prior coverage be issued for a participant or their dependents after the loss of coverage from an employer group health plan.
Former plan participants and their dependents can request HIPAA certification any time within 24 months after termination of coverage.
Oracle HRMS provides the ability to generate HIPAA certifications through the use of two HIPAA communication triggers that are seeded with the product, one for participant loss of coverage and one for dependent loss of coverage. You can generate and print HIPAA letters for participants and dependents directly from the application.
Setting Up HIPAA Certification
Follow this process to set up the application so that you can generate HIPAA certificates for qualifying individuals. As a prerequisite, you should already have defined the compensation objects that comprise your benefits package.
Define Plans Subject to HIPAA Regulations
The application triggers a HIPAA certificate when a loss of coverage occurs for a participant or a dependent covered by a plan subject to HIPAA and the person no longer has any electable choices for any other plans subject to HIPAA in the plan type.
You define a plan as subject to HIPAA by linking the HIPAA regulation to the plan.
Note: Regulation types are seeded with the product.
To define a plan subject to HIPAA regulations
-
Define a plan subject to HIPAA regulations in the Plans window.
-
Choose the Details button.
-
Choose the Regulations tabbed region.
-
Select the HIPAA regulation type.
Define a HIPAA Communication Type
You define a HIPAA communication type so that a HIPAA certification is triggered for all qualified participants and dependents when coverage in a plan is terminated and the person no longer has any electable choices for any other plans subject to HIPAA in the plan type.
See: Defining Communication Types
To define a HIPAA communication type
-
Query one of the seeded HIPAA communication types in the Communication Types window. Choose either:
-
HIPAA Letter
-
HIPAA Dependent Letter
-
-
Choose the Triggers button.
-
Select a HIPAA communication trigger in the Communication Type Triggers window. Choose either:
-
HIPAA Participant Deenrollment
-
HIPAA Dependent Loss of Coverage
Note: When a participant loses coverage, one HIPAA letter is generated if the participant and his or her dependents all reside together. Dependents who do not reside with the participant receive a separate letter.
-
-
Close the Communication Type Triggers window.
-
Choose the Usages button.
-
Select the plan types to which this HIPAA communication type applies in the Communication Type Usages window.
Set up the Administrator Contact
You enter an administrator's contact information to provide the name and return address on the HIPAA certificate. You can set up contacts by plan, or establish one contact for all plans in a program. Contacts you set up at the program level override contacts you enter for any plans in the program.
See: Associating an Organization with a Benefits Program
See: Associating Options with a Plan
To set up an administrator contact
-
To enter an administrator for a program, open the Programs window and select the Organizations tab.
-
Select the administrator's Organization.
You must first enter your organizations using the Organization window.
-
Enter the administrator's name in the Organization Roles field.
-
In the Organization Role Types field, select Administrator.
-
Save your work.
-
To enter an administrator for a plan, open the Plans window. Choose the Details button and select the Organizations tab.
-
Complete the fields as you would for a program, following steps 2-5.
Note: The address you define for the organization in the Organization window also appears in the letters.
Generate HIPAA Certificates
Run the HIPAA Letter report to generate HIPAA certificates for participants. For dependents who reside with the participant, the report generates a single letter. Dependents who do not live with the participant each receive a letter.
Use the HIPAA Dependent Letter report to generate HIPAA certificates for dependents only. For example, dependents who age out of a plan receive a HIPAA certificate, even though the participant may still be enrolled in the plan.
The participant or dependent must have the communication type detected in the Person Communication window for either report to generate a letter. The reports update the Person Communication window with the Sent Date once the process is complete.
The reports extract participant and plan data from Oracle HRMS and merge the data into the body of the seeded HIPAA letters. The extracted information includes:
-
Administrator's name and mailing address
-
Participant's name, address, and Social Security Number
-
Date the certificate was issued (equal to the process run date)
-
Business group
-
Plan name
-
Waiting period start and end date (if the person's enrollment was less than 12 months)
-
Coverage start and end date
-
Covered dependents under each plan
You run reports from the Submit Requests window.
Note: You cannot modify the seeded templates generated by the HIPAA reports.
Note: THIS EXAMPLE LETTER/MATERIAL HAS BEEN PRODUCED BY OR FOR THE INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE. ORACLE PROVIDES THIS LETTER/MATERIAL ON AN "AS IS" BASIS. ORACLE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL ORACLE BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, OR DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, REVENUE, DATA, INCURRED BY YOU OR ANY THIRD PARTY IN CONNECTION WITH THE LETTER/MATERIAL, WHETHER IN AN ACTION IN CONTRACT OR TORT, EVEN IF ORACLE HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. ORACLE'S ENTIRE LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES IN RESPECT OF THE LETTER/MATERIAL AND ANY RELATED MATERIAL SHALL IN NO EVENT EXCEED TEN THOUSAND DOLLARS (U.S. $10,000).
To generate a HIPAA certificate for a participant
-
Select the HIPAA Letter report in the Name field.
-
Enter the Parameters field to open the Parameters window.
-
Select an individual in the Person Name field to generate a certificate for a single person.
-
To generate a HIPAA certificate for multiple persons, select one or more of the following criteria:
-
Organization
-
Benefit Group
-
Location
-
Program
The report generates a certificate for each participant and dependent who has a detected HIPAA Participant Deenrollment communication type.
-
-
Choose the OK button.
-
Choose the Options button to select a printer if you want to send the certificate directly to a printer.
-
Complete the batch process request and choose Submit.
To run the HIPAA Dependent Letter report
-
Select the HIPAA Dependent Letter report in the Name field.
-
Enter the Parameters field to open the Parameters window.
-
Select an individual in the Person Name field to generate a certificate for a single person.
-
To generate a HIPAA certificate for multiple dependents, select one or more of the following criteria:
-
Benefit Group
-
Program
The report generates a certificate for each dependent who has a detected HIPAA Dependent Loss of Coverage communication type.
-
-
Choose the OK button.
-
Choose the Options button to select a printer if you want to send the certificate directly to a printer.
-
Complete the batch process request and choose Submit.
Define a System Extract for HIPAA
If you do not want to use the seeded HIPAA letters, you can define a system extract profile to extract the data you want to include in a HIPAA certificate that you maintain.
See: Defining an Extract Criteria Profile, Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
To define a system extract for HIPAA
-
Define an extract criteria profile using the Criteria Definition window.
-
Choose the Communications tab.
-
Select a Criteria Type of Person Communication - Type.
-
Select a HIPAA Communication Type that you have defined.
-
-
Select a Criteria Type of Person Communication Provided - To Be Sent Date and check the Exclude field.
-
Select Beginning of Time as the From value and Today as the To value so that communications which have already been sent are not re-sent.
-
-
Select a Criteria Type of Person Communication Provided - Sent Date to exclude
-
Select Beginning of Time as the From value and End of Time as the To value.
-
-
Choose the Benefits tab.
-
Select a Criteria Type of Enrollment Coverage During Period.
-
Select 18 Months Ago as the From value and Today as the To value.
-
-
Select a Criteria Type of Enrollment Status and check the Exclude field.
-
Select the Values of Backed Out and Voided to prevent these types of canceled enrollment records from appearing in the extract.
-
-
Select a Criteria Type of Enrollment Data Links.
-
Select a value of Extract Enrollments Linked to Communications via Usages so that the enrollment records in this HIPAA extract are restricted to the compensation objects associated with this HIPAA communication type.
-
-
Select a Criteria Type of Benefits DateTrack Override Date.
-
Enter the effective start date of the HIPAA communication extract.
-
-
Select other extract criteria as necessary to limit the data to include in the HIPAA Certification letter.
-
Define the extract layout using the Layout Definition window.
-
Complete the extract definition using the Define Extract window.
-
Choose the Options tab and check the Special Handling for Dependents (ANSI 834, HIPAA) field.
Note: If you check this field, you should consider selecting the data element of Person Participation Type (ANSI) when defining the layout for this extract to distinguish participant and dependent enrollment records in the extract results.
-
-
Run the Extract Process from the Concurrent Manager for the HIPAA extract you have defined.
The Extract Process creates a flat file with the results of the extract. You can use these results in a mail merge program to create individual HIPAA Certification letters.
Maintaining COBRA Qualified Beneficiaries
A dependent who is covered by a primary participant's health plan one day before the participant experiences a COBRA qualifying life event is considered a qualified beneficiary under COBRA legislation. Qualified beneficiaries are entitled to coverage extensions if certain secondary life events occur during the period of COBRA coverage.
You can use the COBRA Qualified Beneficiaries window to assign a person who is not a qualified beneficiary the status of qualified beneficiary.
To maintain COBRA qualified beneficiaries
-
Query the Name, Social Security number, or other standard identifying information for the person you are creating as a qualified beneficiary.
-
Check the Qualified Beneficiary field to indicate that the person is a qualified beneficiary.
-
Select the Covered Employee who is the originally covered participant.
-
Save your work.
Creating Medicare Part D Notices
As mandated by the Medicare Modernization Act (2005), you can notify prescription plan participants of their eligibility for the Medicare prescription plan and whether their current plan is creditable.
To create and send these notices, use the overall process outlined in System Extract, Human Resources Information Systems Guide, adding these specific steps.
To create Medicare Part D notices
-
In the Extract Definition window, Copy the Medicare_Part_D extract.
See: Defining a System Extract, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration
-
In the Criteria Definition window, under the Benefits tab, add a plan name to the Extract Criteria Type Enrollment Plan Name.
See: Defining an Extract Criteria Profile, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration
-
Optionally, change the value of the Extract Criteria Type Enrollment Coverage During Period.
-
To restrict the notices to a category of people, add the criterion Person Type Usage and set it to Employee or another value.
-
Open the Layout Definition window. To change the plan name used in the notice, select the Data Elements tab, then change the value of the decoded field data element Medicare_Plan_Name.
See: Defining an Extract Layout, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration
-
Specify string values for the data elements
-
Medicare_Plan_Contact_Name
-
Medicare_Plan_Contact_Position
-
Medicare_Plan_Contact_Phone
-
-
If you change any XML tag names or the Extract Record setup, ensure that you make the corresponding changes to the template.
-
To print the person's title in Initial Caps rather than ALL CAPS, add the Initial Capital format mask to the data element Medicare_Person_Title.
Basic Benefits Setup
Overview
Using Basic Benefits, you can set up benefit plans in just the same way you handle all other components of your compensation and benefits packages. You use elements to represent the various benefits available to your employees. When you give these elements a benefits classification, Oracle HRMS automatically:
-
Defines whether coverage is available to dependents and beneficiaries
-
Defines whether the plan is COBRA-eligible
Elements can represent benefits ranging from tangible items such as lunch vouchers and company cars, to perquisites such as company stock purchase or life insurance, to health care coverage plans for employees and their dependents.
To enroll employees in benefits, you make entries to benefits elements, either manually or in a batch using BEE.
Benefit Programs and Core-Plus-Options Arrangements
You may need to group benefit offerings together as a hierarchy (program, plan type, plan, option) so that administrative rules set at the program level cascade to the plans in that program. You may also need program-based enrollment for fixed and core-plus-options arrangements. These features are not supported in Basic Benefits. You need to use the Standard Benefits feature set.
Flexible Benefit Programs
If you administer your own benefits, including flexible benefit plans, consider implementing Advanced Benefits, which provides the full solution for benefits management, including self-service enrollments, management of life events, and eligibility modeling.
What To Read Next
If you decide that Basic Benefits meets your limited requirements for benefits administration, you can read more in the following topics:
-
Benefits Classifications - describes the classifications available for benefits elements; you select one classification for each benefit.
-
Benefits Enrollment - summarizes the procedure for enrolling employees in benefit plans, recording their beneficiaries, and setting up cover for their dependents.
-
Basic Benefits Setup - summarizes the procedures for defining elements and other aspects of implementation.
-
Management of COBRA-Eligible Benefits - summarizes employer responsibilities under COBRA and describes the standard letters and reports supplied for COBRA administration.
Basic Benefits Setup
The process for setting up benefit plans in the Basic Model is similar to the process for setting up any other form of compensation and benefit.
If you use Oracle Payroll, you initiate deductions for payments toward the cost of benefits. The system then generates elements representing the benefit plan, along with the formulas, balances, and formula rules you need to process the benefit deduction in the payroll run. You can customize the generated elements, formulas, and balances if you need to. See: Initiating Non-tax Deductions.
At Oracle HRMS sites that do not include Oracle Payroll, you define elements to represent benefits and benefit plans using the Element window. Use the primary classification Information and the appropriate benefits classification. See: Defining an Element to Hold Information.
Elements for Health Care Plans
Elements for health care plans--in the benefits classifications: Medical, Dental or Vision--typically require the following input values:
-
Coverage, to hold plan coverage levels such as Employee Only, Employee and Spouse, Employee and Family
-
EE Contr and ER Contr (Employee and Employer Contribution), to hold either default dollar amounts or percentages, as you choose, for employee deductions and/or employer payments at a given coverage level taken to pay for the plan.
If you create these input values for your benefit plan element, you can use the Benefit Contributions window to enter a list of values for the Coverage input value and default contributions for EE Contr and ER Contr. Oracle Payroll users must then edit the formula generated from the Deductions window to make use of these inputs.
Benefits Carriers
Using the Organization window, you enter benefits carriers into the database as external organizations with the classification Benefits Carrier. You can then associate the appropriate carrier with an element representing a benefit or benefit plan, by selecting the carrier from a list when you create the benefit element.
Eligibility for Benefits
You establish employee eligibility for benefits in the same way that you set eligibility rules for any element, that is, by building element links. Links define the components that must be present in employees' assignments for the employees to be eligible for entries to the element. For example, if group life insurance is available only to employees who work full time, you can build a link for the element for this benefit to the employment category Full Time.
Setting Up Basic Benefits
You set up Basic Benefit plans in much the same way that you set up other components of your compensation and benefits packages. Before you start, review the features offered by Oracle's other benefits administration solutions (Standard Benefits and Advanced Benefits) to ensure that you implement the model that most closely matches your needs.
Create Benefit Carriers
-
Use the Organization window to enter benefits carriers as external organizations with the classification Benefits Carrier. See: Creating an Organization, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Define Validation
Define validation for entries made to enroll employees in benefit plans.
-
To restrict entries to a list of valid values, define a new Lookup Type and add values for this new lookup. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
To validate entries using formulas, write a formula of type Element Input Validation. See: Writing Formulas for Validation, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Define Categories
-
If you need a new category for your benefit plan elements, add it in the Application Utilities Lookups window. Benefit plan elements are in the Information classification (Lookup type US_INFORMATION) if you don't use Oracle Payroll and in the Voluntary Deductions classification if you do use Oracle Payroll. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Define Coverage Levels
-
Basic Benefits includes four coverage levels for benefit plans: Employee Only, Employee and Spouse, Employee and Children, Employee and Family. If you need additional coverage levels, add them in the Application Utilities Lookups window for the Lookup type US_BENEFIT_COVERAGE. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Define Elements for Information
-
If you are not using Oracle Payroll, create elements to represent benefit plans. See: Defining an Element to Hold Information
Define Benefit Deductions
If you are using Oracle Payroll to process earnings and deductions:
-
Initiate deductions to generate benefit plan elements, formulas, and balances.
-
See: Customize Generated Elements, Balances, and Formulas
Identify Carrier and Contribution Frequency
-
In the Further Element Information window, select the benefits carrier and a period type to identify the frequency of employee contributions to the plan.
Define Links
-
If employer charges for the benefit should be distributed over other elements, define the distribution set.
-
Define element linksfor each benefit to define one or more groups of employees who are eligible to receive it.
See also: Element Link Details Report
Enter Coverage Levels and Default Contributions
-
For health care benefit plans, you can enter coverage levels and default employee and employer contribution amounts in the Benefit Contributions window.
To enable this, you must first create specific input values for your element, and configure the formula and formula result rules generated by the Deductions window.
See: Configuring Components for Health Care Benefit Plans
See: Establishing Health Care Plan Coverage and Default Contributions
Set Up COBRA
-
Basic Benefits includes two reasons for terminating continued coverage under COBRA: End of Coverage and Non-payment. If you need additional reasons, add them in the Application Utilities Lookups window for the Lookup type US_COBRA_TERM_REASON. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
If necessary, modify the standard letters supplied for COBRA notification and termination. See: Standard Letters for COBRA Notification and Termination
Configuring Components for Health Care Benefit Plans (Basic Benefits)
If you want to enter coverage levels and default employee and employer contribution amounts in the Benefit Contributions window for health care benefit plans, you must complete a number of additional setup steps.
These steps apply to elements in the benefits classifications Medical, Dental, and Vision.
To configure generated components for health care benefit plans
-
Query the element in the Element window and set your effective date to the element's start date (that is, the date you used to define or initiate the element).
-
In the Input Values window, create the following input values, being careful to enter the names exactly as shown:
-
Coverage (Character)
Select US_BENEFIT_COVERAGE as the Lookup and select the appropriate value (such as Employee only) as the Default.
-
ER Contr (Money)
-
EE Contr (Money)
-
-
In the Benefit Contributions window, select the appropriate coverage levels and default contribution amounts.
See: Establishing Health Care Plan Coverage and Default Contributions
In the Element window, create a nonrecurring ER Liability shadow element for indirect results.
-
In the Formula window, modify the generated Oracle Payroll formula for the pre-tax deduction as shown in the following table:
In the section . . . Replace this text . . . With this text . . . INPUT VALUES DEFAULTs Default for Amount is 0 Default for EE_Contr is 0 Default for ER_Contr is 0 INPUTS SECTION INPUTS are Amount, Period_Type(text) INPUTS are EE_Contr, ER_Contr, Period_Type (text) Main formula body THEN (IF Amount WAS DEFAULTED AND /* NOT Flat Amount */ Percentage WAS DEFAULTED THEN /* NOT Percent either! */ THEN (IF EE_Contr WAS DEFAULTED AND /* NOT Flat Amount */ Percentage WAS DEFAULTED THEN /* NOT Percent either! */ dedn_amt = Amount * deduction_freq_factor IF Period_Type = UPPER('Calendar Month') AND (dedn_amt + AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH - Amount ) <= .02 AND (AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH + dedn_amt) > Amount THEN dedn_amt = Amount - AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH)ELSE /* Percentage calculation */( dedn_amt = EE_Contr * deduction_freq_factor IF Period_Type = UPPER('Calendar Month') AND (dedn_amt + AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH - EE_Contr ) <= .02 AND (AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH + dedn_amt) > EE_Contr THEN dedn_amt = EE_Contr - AMY_MED_PRETAX_ASG_GRE_MONTH) ELSE /* Percentage calculation */( ,to_within/*========================= End Program =============================*/ ,to_within, ER_Contr /*============= ============ End Program =============================*/ See: Writing or Editing a Formula, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
-
In the Formula Result Rules window, select the benefit plan element and choose the Find button. Click on the processing rule that was generated from the Deductions window.
-
In the Formula Results region, select the new formula result (ER_Contr) and create the following result rule:
-
Type: Indirect Result
-
Element: the ER Liability element you created in step 4
-
Input Value: Pay Value
See: Defining Formula Processing and Result Rules, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
-
-
Link the benefit plan element. Also link the ER Liability element if you want to establish costing.
Establishing Plan Coverage and Default Contributions (Basic Benefits)
To enter coverage levels and default employee and employer contribution amounts for a health care benefit plan, use the Benefit Contributions window.
Note: The plan element must be in the benefits classifications, Medical, Dental, or Vision. You must configure the plan element, formula, and formula results rules as described in Configuring Components for Health Care Benefit Plans.
To enter plan coverage levels and contribution amounts
-
Query the benefit plan in the Benefit Contributions window.
-
Enter the coverage levels available for the plan in the Coverage field.
-
For each coverage level, enter an employee and an employer contribution amount. Enter an amount of zero when a plan has no contribution from the employer or from the employee.
-
Save your work. You are now ready to enroll employees in this plan.
COBRA-Eligible Basic Benefits
Management of COBRA-Eligible Benefits (Basic Benefits)
COBRA is the term commonly used to reference the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985. Under this federal legislation, most employers who provide health insurance plans to employees must offer continued access to this insurance when certain changes (qualifying events) occur to the status of employees or their dependents.
Under COBRA, employers must offer continued access to group health insurance in accordance with these rules:
-
Employees and their dependents must be offered continued access for 18 months after:
-
the employees' hours are reduced, or
-
they become unemployed for any reason other than gross misconduct.
-
-
Continued access for 36 months must be offered to
-
the dependents of deceased employees
-
an employee's former spouse following divorce or legal separation
-
dependent children after they cease to be dependent
-
active employees who become entitled to Medicare.
If one of these qualifying events occurs, each qualified beneficiary must be offered an opportunity to elect to continue to receive the group health plan coverage that he or she received immediately before the qualifying event. If the plan has a core/noncore feature, the beneficiary may elect core coverage only. At the end of the 18- or 36-month period, employers must offer conversion to an individual policy if the group plan permits conversion.
-
To cover their administrative costs, employers can require employees and dependents electing continued coverage to pay up to 102% of the insurance premiums. In addition, employers can require disabled employees to pay up to 150% of the insurance premiums after the first 18 months of COBRA coverage.
COBRA does not affect employers with fewer than 20 employees or those with church plans. Nor does it apply to plans maintained by US federal, state or local governments.
Employer Responsibilities under COBRA
To administer continued health plan coverage under COBRA, you do the following:
-
identify which of your benefit plans are COBRA-eligible
-
enter and maintain information about employees' dependents
-
record the events that qualify employees or dependents for continued coverage as they occur, and the qualifying dates
-
notify employees, former employees and dependents of their eligibility for continued insurance coverage, and record their acceptance or rejection of such coverage. Oracle HR includes a standard COBRA notification letter you can use.
Employees and dependents have 60 days from their qualifying date or the date they receive their notification letter, whichever is later, in which to elect continued coverage. For those who make this choice, you must:
-
determine and schedule the premium payments to be made for continued coverage, and record the receipt of these payments.
-
record the eventual termination of their continued coverage.
Standard Letters for COBRA Notification and Termination
Oracle HR provides standard letters for informing employees or dependents of their eligibility for continued coverage, or of pending termination of this coverage. You can modify these letters as you wish using SQL*ReportWriter 2.0. The standard letters are:
-
The COBRA Notification Letter, informing people of their eligibility for continued coverage under COBRA.
-
The COBRA Grace Period Expiration Letter, informing people electing continued coverage that a premium payment is overdue, and that nonpayment will result in termination of the continued coverage.
-
The COBRA Expiration Letter, informing people electing continued coverage that this coverage will terminate soon, because the time period over which it was available (18 or 36 months) is ending.
Standard COBRA Reports
The COBRA Coverage Report
This report shows information about the employees and dependents eligible for continued coverage under COBRA whom you have entered into the system. This report shows employees' names and assignment numbers, or dependents' names and relationships, as well as their qualifying events and dates, their notification date and their COBRA status.
For those who elect continued coverage, it shows the start and end dates of the coverage period, the benefit plan names, and the premium amounts charged.
The COBRA Payments Report
This report shows information about COBRA payments due and payments received, after you have entered this information into the system. As well as the name and assignment number or relationship of covered employees and dependents, it displays their qualifying events and dates, their amounts due and due dates, and dates of payment receipts, amounts received and amounts outstanding.
Setting Up Continued Coverage under COBRA (Basic Benefits)
To set up continued coverage under COBRA
-
For an employee or dependent who elects continued coverage, enter in the COBRA Coverage window the Period Start Date from which the coverage will continue. The system automatically supplies the end date of the continued coverage period (either 18 or 36 months after the period start date).
-
In the COBRA Coverage window, choose the Benefits button to go to the COBRA Benefits window, which displays all the benefit plans eligible for continued coverage in which the employee was enrolled before the COBRA qualifying date.
The Basic column of the Costs region displays each plan's basic cost, that is, the total of employee and employer contributions toward the plan.
-
Check the Accepted box for each plan for which the employee or dependent is electing continued coverage. Under Coverage, select the level of the continued coverage, which must be equal to or lower than the employee's original coverage.
-
Under COBRA in the Costs region, enter the premium for continued coverage of this plan. If the amount entered exceeds 102% of the basic cost of the plan, you receive a warning message, which you can override. Save your work.
-
When you finish setting up continued coverage, establish a payment schedule for the coverage. Then use this schedule to record payments as you receive them.
Obtaining COBRA Reports and Standard Letters (Basic Benefits)
To obtain these reports and letters, use the Submit Requests window.
To run the COBRA Coverage or Payments report
-
In the Name field of the Submit Requests window, choose the report name. If the Parameters window does not automatically open, click in the Parameters field.
-
Control the list of employees and dependents the report covers by the report parameters. For example, if Termination is the parameter for Qualifying Event, the report lists only those employees and dependents eligible for continued coverage under COBRA whose qualifying event is employee termination.
To obtain a COBRA standard letter
-
In the Name field of the Submit Requests window, choose the letter type. The available types are:
-
COBRA Notification Letter
-
COBRA Grace Period Expiration Letter
-
COBRA Expiration Letter
If the Parameters window does not automatically open, click in the Parameters field.
-
-
Enter the appropriate parameters for the letter and choose Submit. The letter prints out just as a report does. These letters do not include address information for employees or dependents.
Recording COBRA Qualifying Events (Basic Benefits)
To administer COBRA-eligible benefit plans, you use the COBRA Coverage window.
To record a qualifying event and its date
-
For all qualifying events except termination, set your effective date to the qualifying date. This is the day after the date of the qualifying event, that is, the day on which current benefit coverage would cease.
-
In the COBRA Coverage window, select the qualifying event from the list. The following events require you to offer continued coverage of COBRA-eligible benefit plans to employees, together with any dependents previously included in their coverage:
-
Medicare entitlement
-
Reduced work hours which result in the loss of coverage
-
Termination
When selecting one of these events, do not enter a dependent's name or relationship.
Note: For the events Reduced Hours and Termination, the system checks for a reduction in the employee's standard working hours or for a termination. If it finds no hours reduction or termination, it issues an error message.
The following events require you to offer continued coverage to dependents:
-
Death of Employee
-
Divorce or Legal Separation
-
No Longer Dependent
For one of these events, select also the name and relationship of the dependent responsible for electing and paying for any continued coverage, for example, the spouse of a deceased employee. If it is unclear which dependent to select, for example if all the dependents of a deceased employee are minor children, consult your Benefits Administrator.
-
-
The status of COBRA coverage resulting from entry of the qualifying event defaults to Awaiting Notification, as of the effective date. Save your work at this status. After sending out notification of eligibility for continued coverage, and when this coverage is rejected or accepted, enter status changes.
Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
As a requirement of Employer Shared Responsibility (ESR) reporting under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), all Application Large Employers (ALEs) including self-insured companies that provide health insurance to their employees must submit information returns to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These returns report on employees' health insurance coverage. The returns include information reported on Form 1094-C, Transmittal of Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage Information Returns, and Form 1095-C, Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage. Any employer required to file 250 or more information returns must file them electronically.
ACA information returns and transmittals are electronically filed through the IRS' ACA Information Return (AIR) system. Oracle Standard Benefits and Oracle Advanced Benefits support electronic filing using the AIR UI Channel.
Note: IRS A2A Channel filing and paper filing are not supported.
For more information about the Affordable Care Act (ACA), see https://www.irs.gov/Affordable-Care-Act.
For information about filing electronically with the IRS, see the IRS page https://www.irs.gov/for-tax-pros/software-developers/information-returns/affordable-care-act-information-return-air-program.
ACA Reporting for States
You can generate files compatible with the ACA filing requirements for the following states. For guidance about a state's ACA filing requirements, refer to the relevant government website.
-
New Jersey -https://nj.gov/treasury/njhealthinsurancemandate/employers.shtml
-
District of Columbia - https://otr.cfo.dc.gov/sites/default/files/dc/sites/otr/publication/attachments/FAQ%20reporting%20SRP%20Update.3.31.20.pdf
-
Rhode Island - http://www.tax.ri.gov/healthcoveragemandate/index.php
Reporting Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
The employer shared responsibility provisions in Section 4980H require employers to report offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) to the IRS. You can generate 1095-C and 1094-C forms that report HRA codes and information for individuals who receive an HRA offer.
Key Concepts
The following topics explain how you can use the application to generate reports for electronic filing.
Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Processes and Reports
This topic lists the processes and reports for Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This topic also discusses any prerequisites that you must complete before you can run any of the processes.
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Processes:
-
Concurrent programs for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs):
-
Benefits ACA HRA Details Process: Gathers information needed for individuals who have been offered an HRA.
-
Benefits ACA HRA Details Report: Reports on individuals identified by the Benefits ACA HRA Details process.
Important: If you have offered Individual Coverage HRA plans, then you must run these concurrent programs, before you run the Benefits ACA Archive Process.
See Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) for more information.
-
-
Benefits ACA Archive Process
-
Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process: Generates the necessary output files to submit Form 1094/1095-C data to the ACA Information Return (AIR) system.
See: Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process
Recommendation: Before you run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process to generate files for states, ensure that the transmission status of XML files is a status other than “Rejected.”
-
Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process: Generates reports to comply with the ACA filing requirements of states.
See: Running the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process
-
Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML: Marks the applicable records as failed or incorrect for those IRS error data XML files that you upload to the Update Transmission Details page.
See: Running the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program
-
Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML: Marks the applicable records with errors at the state level.
-
Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process: Archives the corrected data. Run this process after records are marked failed or incorrect by the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program and all applicable errors are corrected.
-
Benefits ACA Purge Process
Important: If there is a requirement to purge the archive data from the system, then the state data must be removed first, and only then you can purge the IRS data.
Reports:
-
Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report
-
Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread
See: Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread Process
-
Benefits ACA Errors Report: Generates an output report in PDF format with error details extracted from the error XML data files that are returned by the IRS.
These concurrent programs are added to the Request Group of the seeded US Super HRMS Manager responsibility. If you use any custom equivalent responsibility, then you must add these processes to the custom responsibility.
Prerequisite Steps for the Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Processes:
Complete the following steps for the Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) processes:
Prior to running the reporting processes, define Batch Process Parameters to ensure optimal performance.
To define Batch Process parameters:
-
Log in to the US HRMS Manager (or equivalent) responsibility.
-
Navigate to the Batch Process Parameters window.
-
Select Benefits ACA Archive Process and set the applicable number of threads, chunk size and/or max errors. This batch process is applicable to the following processes:
-
Benefits ACA Archive Process
-
Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread process: Note that while the Benefits ACA Print Process is selected as the process to set the batch process parameters, only the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread process will run as multi-threaded.
-
For further information on Benefits batch process parameters, refer to the My Oracle Support Document 226987.1 - Oracle 11i & R12 Human Resources (HRMS) & Benefits (BEN) Tuning & System Health Checks.
Setting Up Information for the Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The following steps outline the processes that you must complete to produce the employee 1095-C forms as well as the employer information electronic report that you will file with the US Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
To set up information for the Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
-
Create a GRE or legal entity.
Create a GRE or Legal Entity if one does not already exist or update your business group and add the GRE / Legal Entity classification. See: Government Reporting Entities (GREs), Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
Enable and populate the following flexfields.
-
ACA Reporting Requirement
-
ACA Monthly ALE Information
-
ACA Certs of Eligibility
-
ACA TCC Information
-
ACA External 1095C Count
-
ACA Self Service Requirement
The following sections explain how to enable and populate these flexfields.
-
ACA Reporting Requirement
-
Enable the ACA Reporting Requirement flexfield and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Reporting Requirement
-
Multiple Rows: No
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Reporting Requirement window at the GRE/Legal Entity Level. See: Entering the ACA Reporting Requirement Data for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
ACA Monthly ALE Information
-
Review the flexfield segments to assess whether you must set up the flexfield.
If the flexfield is required, then enable it and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Monthly ALE Information
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Monthly ALE Information window at the GRE/Legal Entity Level. See: Entering the ACA Monthly ALE Information for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
ACA Certs of Eligibility
-
Review the flexfield segments to assess whether you must set up the flexfield.
If the flexfield is required, then enable it and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Certs of Eligibility
-
Multiple Rows: No
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Certs of Eligibility window at the GRE/Legal Entity level. See: Entering the ACA Certs of Eligibility Options for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
ACA TCC Information
-
Review the flexfield segments to assess whether you must set up the flexfield.
If the flexfield is required, then enable it and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA TCC Information
-
Multiple Rows: No
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Certs of Eligibility window at the GRE/Legal Entity level. See: Entering the ACA TCC Information for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
ACA External 1095C Count
-
Review the flexfield segments to assess whether you must set up the flexfield.
If the flexfield is required, then enable it and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA External 1095C Count
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Certs of Eligibility window at the GRE/Legal Entity level. See: Entering the ACA External 1095C Count for GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
ACA Self Service Requirement
-
Review the flexfield segments to assess whether you must set up the flexfield.
If the flexfield is required, then enable it and its associated fields. Run the Register Extra Information Types(EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: HR_ORG_INFORMATION_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Self Service Requirement
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
-
Organization Classification: GRE/Legal Entity
-
Application: PER
See: Running the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Populate the values in the ACA Certs of Eligibility window at the GRE/Legal Entity level. See: Entering the ACA External 1095C Count for GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
-
-
-
Configure your plan setup.
-
Identify all applicable healthcare benefit plans that are subject to the Affordable Care Act. For all such plans, date track to January 1, 2015, and configure the plan regulation "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" in the Regulations tab of the Plan window. Note that configuring this Regulation in the plan setup will also require creating a Reporting Group. See: Defining a Reporting Group.
Note also that the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" regulation is for Medical/Healthcare plans, so the correct Regulatory Plan Type to select is "Welfare". See: Defining Regulations for a Plan
-
Define the following plan extra information types (EITs) for plans configured with the ACA regulation:
-
ACA Report Requirements
-
ACA Minimum Rate Requirement
-
ACA Multiple Option Min
-
ACA Requirements
Important: ACA Minimum Rate Requirement, ACA Multiple Option Min and ACA Requirements are optional, only to be configured if needed. Configure the ACA Minimum Rate Requirement EIT if you are using Oracle Standard Benefits. Configure the ACA Multiple Option Min EIT if plans have multiple self-only options.
To set up and define the EITs:
-
Navigate to the Plans window.
-
Search for a plan configured with the ACA regulation.
-
Click Extra Information.
-
Select the appropriate EIT.
The following sections explain how to define the plan EITs.
-
ACA Report Requirements Extra Information Type (EIT)
Complete the following steps to set up and use the ACA Report Requirements EIT.
-
Register the ACA Report Requirements Plan EIT.
-
Run the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: BEN_PL_INFO_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Reporting Requirements
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Assign the ACA Report Requirements EIT to the applicable responsibilities that are authorized to maintain the benefits setup. Use the Information Type Security window to link the EIT to a responsibility. See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide. Select ACA Report Requirements as the Information Type and save.
-
After the plan EIT is registered, specify the following fields:
-
Reporting Year (mandatory): Select the reporting year.
-
Provides Minimum Essential Coverage and Provides Minimum Values: For healthcare benefit plans that have been designated with the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act plan regulation, set the fields to 'Yes' if the plans meet both the requirements.
-
Spouse Offer Conditional: Select a value that is appropriate for Form 1095-C. If the offer to the spouse is conditional, then select Yes in the plan EIT for each applicable benefit plan. This field must be set to Yes for all ACA eligible plans. Otherwise the evaluation may not result in 1J or 1K codes being returned on Form 1095-C.
-
Individual HRA Plan: Set to Yes if the plan represents an Individual Coverage HRA plan.
-
HRA Affordability Address: Select the address type as the plan level default. This is the address type used to search for individual Healthcare Marketplace plan costs.
The options are:
-
Work: Represents the work address on the primary assignment.
-
Residence: Represents the person's address marked as Primary for the person.
Important: If there are multiple HRA plans being offered, then the address type must be the same for all plans.
See Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)for more information.
-
-
-
-
ACA Minimum Rate Requirement Extra Information Type (EIT)
Use the ACA Minimum Rate Requirement Extra Information Type (EIT) at the plan level to store the minimum self-only rate for a plan configured with the ACA regulation effective for the applicable reporting year.
Important:
-
Oracle Standard Benefits customers must provide the minimum self-only rate for all benefit plans that are configured with the ACA regulation. The Benefits ACA Archive Process will then evaluate which plan has the lowest self-only rate based on the person's eligibility.
-
The minimum self-only rate value entered in the plan-level ACA Minimum Rate Requirement EIT must be the monthly rate value.
-
This plan EIT is currently applicable to Oracle Standard Benefits customers only.
Complete the following steps to set up and use the ACA Minimum Rate Requirement EIT.
-
Register the ACA Minimum Rate Requirement EIT.
-
Run the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: BEN_PL_INFO_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Minimum Rate Requirement
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Assign the ACA Minimum Rate Requirement EIT to the applicable responsibilities that are authorized to maintain the benefits setup. Use the Information Type Security window to link the EIT to a responsibility. See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide. Select ACA Minimum Rate Requirement as the Information Type and save.
-
After the plan EIT is registered, specify the following fields:
-
Reporting Year: Enter the applicable reporting year.
-
Minimum Self Only Rate: Enter the monthly minimum rate value for the self-only option for the ACA plan.
-
Save your work.
-
If there is more than one plan configured with the ACA regulation, then repeat steps for each plan.
-
-
-
ACA Multiple Option Min Extra Information Type (EIT)
Configure the ACA Multiple Option Min EIT if plans have multiple self-only options. This EIT helps you to record a single rate for the entire year, or rates on a monthly basis if the rate changes during the reporting year.
Complete the following steps to set up and use the ACA Multiple Option Min Plan EIT.
-
Register the ACA Multiple Option Min Plan EIT.
-
Run the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: BEN_PL_INFO_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Multiple Option Min
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Assign the ACA Multiple Option Min Plan EIT to the applicable responsibilities that are authorized to maintain the benefits setup. Use the Information Type Security window to link the EIT to a responsibility. See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide. Select ACA Multiple Option Min Plan as the Information Type and save.
-
After the plan EIT is registered, specify the following fields:
-
Reporting Year: Enter the reporting year for which the rates are in effect.
-
All Months: Enter the lowest monthly self-only rate for the plan if it is the same value for the entire reporting year.
-
January... December: Enter the lowest monthly self-only rate for the plan offered to employees in the applicable month if the lowest rate changes during the reporting year.
-
-
-
ACA Requirements Extra Information Type (EIT)
Complete the following steps to set up and use the ACA Report Requirements EIT.
-
Register the ACA Requirements EIT.
-
Run the Register Extra Information Types (EITs) concurrent program using the Submit Request window with the following parameters:
-
Table Name: BEN_PGM_INFO_TYPES
-
Information Type: ACA Requirements
-
Multiple Rows: Yes
-
Legislation Code: United States
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
-
Assign the ACA Requirements EIT to the applicable responsibilities that are authorized to maintain the benefits setup. Use the Information Type Security window to link the EIT to a responsibility. See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide. Select ACA Report Requirements as the Information Type and save.
-
After the plan EIT is registered, specify the following fields:
-
Reporting Year: Select the reporting year.
-
Flex Credit Offset: Enter the monthly dollar value provided by the employer to reduce the cost of self only coverage for the employee.
-
Plan Start Month: Enter the month in which the ACA plan years start for the reporting year.
-
-
-
-
If your healthcare plan coverage is self insured, then set 'Primary Funding Method' to 'Self Insured" in the General plan setup for the applicable plans if it is not set already. Ensure that you are date tracked to January 1, 2015 when performing the update (if not previously set). See: Defining a Benefits Plan
-
Review dependent designation requirements to ensure that the proper designation has been configured (i.e. designation may need to differentiate between spouse and children designation if such coverage is offered to your employees) for all applicable plans or options.
Navigate to the Options window. For the applicable option, click the Designation Requirements button. Configure the designation requirements according to your requirements. If the designation requirements are already configured, verify they are set up correctly.
-
-
Enable the ACA Reporting Special Information Type.
Enable the ACA Reporting special information type (SIT) using the Special Information Types window. . Information provided in the Person Special Information Type (SIT) ACA Reporting is used in determining details in Form 1095-C.
To populate this SIT:
-
Navigate to the People window.
-
Query the relevant employee.
-
Click the Special Info button.
Populate the applicable fields as follows:
-
Assessment Period End Date: If the employee was in an initial assessment period before their full-time eligibility could be established, this is the date that period ended during the reporting year.
-
Stability Period End Date: This is an optional field with no functionality for Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting. Customers have the option to record the date when a stability period ends on the employee and reassessment of ACA Full Time status is needed..
-
Eligible for Section 4980H: Indicate whether an affordability or multiemployer safe harbor applies to the employee.
-
Safe Harbor Override: Select an affordability safe harbor code, if a code other than the Safe Harbor assigned to the ACA Reporting Requirements flexfield for the GRE is applicable for this employee.
-
-
Review or update employees or participants.
Review your employee population:
For each month during the reporting year, assess whether the person was subject to a safe harbor: Were they enrolled? If not, was it because the person:
-
Was not employed that month?
-
Was not ACA Fulltime that month?
-
Was still in an initial assessment period?
-
Was eligible for a Section 4980H safe harbor?
-
-
Define Employee Information for the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
-
For all employees that are considered full time under the auspices of the ACA, designate them as Full Time ACA Eligible employees by checking the "ACA Full Time" flag on the Benefit tab in the People window, either on January 1, 2015 or the applicable effective date.
-
Identify employees that were under an assessment period during the reporting year and capture the Assessment Period End date in the Special Information Type "ACA Reporting". Note that the Assessment Period End Date is used to determine if an employee is eligible as per the Affordable Care Act rules.
-
Identify employees that are covered under a Section 4980H Safe Harbor or Relief and set field "Eligible for Section 4980H" to Yes in the Special Information Type "ACA Reporting".
-
For any employees that are still eligible for safe harbor relief, optionally set an alternate code in the field "Safe Harbor Override" if different than the default code set at the GRE / Legal Entity level under "ACA Reporting Requirement". Note: Take special care when setting a value in the Person SIT as the IRS has special rules around how these codes can be applied to employees.
See: Defining Information for the Employer Shared Responsibility Provision of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (US)
-
-
When you run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process, the concurrent program saves files to an output directory. Ensure that the output directory that you specify in the concurrent process parameter is available and has the write privileges. Otherwise, the concurrent process will fail.
Setting Up Information for the Employee COBRA Offer Details Page
The Employee COBRA Offer Details page allows benefit administrators to enter COBRA offers and enrollment that must be included on the 1095C form when Oracle Advanced Benefits is not the source of COBRA Administration (i.e. it is administered instead by a third party) and there is a need to generate a Form 1095-C for these employees from the Oracle application. See Using the Employee COBRA Offer Details Page for more information.
Before a benefits administrator starts using this page, complete the following setup step:
Set the COBRA Outside EBS field to Yes in the ACA Reporting Requirement window. This step is required for the Benefits ACA Archive process to evaluate any data entered in the Employee COBRA Offer Details page. See: Entering the ACA Reporting Requirement Data for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US)
See Processing for ACA Employer Information Reporting
Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration.
This topic covers the setting up and processing steps to report offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs).
Setup Steps
Complete the following setting up steps:
-
Define the Individual Coverage HRA fields in the ACA Reporting Requirement window for a GRE. See: Entering the ACA Reporting Requirement Data for a GRE, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (US) for more information.
-
Complete the HRA setup for a plan.
-
In the ACA Report Requirements EIT for a plan, define the following fields:
-
Individual Requirements
-
HRA Affordability Address
-
-
In addition, configure the following details for the HRA plan.
-
Set to Yes the Minimum Essential Coverage field on the plan ACA Reporting Requirements EIT.
-
Set to Yes the Minimum Value on the plan ACA Reporting Requirements EIT.
-
Patient Protection and Affordability Act Regulation.
-
Dependent Designations on the Options.
-
Annual Coverage Calculation for Individual coverage.
-
Ensure that the Primary Funding Method is “Self Insured.”
-
-
Processing Steps
Prerequisite: Before you run the Benefits ACA Archive concurrent program, you must complete the following steps if you have offered Individual Coverage HRA plans.
Following are the processing steps:
-
Run the Benefits ACA HRA Details process to collect details of individuals who have been offered an HRA. See: Running the Benefits ACA HRA Details Process.
-
Run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report to obtain a report of individuals identified by the Benefits ACA HRA Details process. The report includes information need to search for the Marketplace Silver Plan costs such as Age as of First Eligible for HRA offer, and Primary Work and Residence zip codes. See: Running the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report.
-
Find the lowest self-only Silver plan premium for individuals offered an HRA. Refer to the IRS website to search for the Silver Plan costs for the states participating in the Federal Healthcare Market.
-
Enter Silver plan costs by navigating to and searching on the ACA Person HRA Details page. See: Entering the ACA Person HRA Details.
After you complete the Person HRA Details and save, proceed with running the Benefits ACA Archive Process and continue as normal with generation and distribution of the 1095Cs. See Processing for ACA Employer Information Reporting.
Processing for ACA Employer Information Reporting
This topic lists the processing steps to generate the individual 1095-C forms and transmit the employer electronic filings to the IRS, including corrections.
The steps to transmit files to the IRS are as follows:
-
Run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread or Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report concurrent program. See: Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread Process.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation process for Transmitter and Issuer GREs. See: Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process.
-
Transmit files to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Affordable Care Act Information Returns (AIR) system.
-
Enter the Receipt ID, submission status, acknowledgement, and the file of any errors returned by the AIR system into EBS using the Transmission Details page. See: Using the ACA Transmission Details Page.
-
For a submission status returned other than “Accepted”:
-
Run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program. This is run in order to mark the GREs and persons that need to be retransmitted to IRS.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Errors Report concurrent program to obtain a report of the records in error. See: Running the Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML.
-
Correct identified improper data.
-
-
If the GRE identifies information previously transmitted is incorrect, although accepted by the IRS:
-
Mark the individual needing correction on the View Employee Archive Details Page.
-
Correct the data. This can be done separately or at the same time as step 6.
-
-
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process for the GREs with corrected errors. This will create a new archive including only those records marked as in error.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation process again for the Transmitter/Issuer GRE to generate the correction XML files from the new archive generated in step 8.
-
Transmit the new files to the IRS AIR system.
-
Enter the Receipt ID, submission status, acknowledgement and the file of any errors returned by the AIR system into EBS using the Transmission Details page.
-
If the returned status is not “Accepted”, repeat from Step 6.
Using the Employee COBRA Offer Details Page
The Employee COBRA Offer Details page helps benefits administrators to:
-
Enter details about the US Affordable Care Act healthcare offers made to their active employees under COBRA when Oracle Advanced Benefits is not the source of COBRA administration COBRA is administered instead by a third-party, and there is a need to generate a Form 1095-C for these employees from the Oracle application.
-
Enter data for employees who have enrolled in self-insured coverage and are terminated during the reporting year. The Benefits ACA Archive process considers all persons who were employed at least one day during the reporting year. Terminated employees will have code 1H reported on Line 14 of their Form 1095-C for the months after termination, but they will be shown as covered in Part III of their Form 1095-C.
For an overview, see Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Important: If you already use Oracle Advanced Benefits to administer COBRA offers, then there is no need to enter any offer details using this page. Any data that is entered in this page for such employees will be ignored when the Benefits ACA Archive Process is run.
Prerequisite: Set the COBRA Outside EBS field to Yes in the ACA Reporting Requirement window at the GRE level to indicate that COBRA is administered outside of Oracle Advanced Benefits. For more information, see Setting Up Information for the Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
Use the Employee COBRA Offer Details page to perform the following tasks:
Searching and Selecting an Employee
Select an applicable value in the Year ACA Fulltime field, and then either the Employee Number or Employee Name, and then click Go. The results table displays the employee's details. Click the Action icon.
Entering the Person COBRA Details
In the Person COBRA Details region, click to add a row.
-
Select the Year along with Start and End Months of the COBRA offer, even if the employee did not elect COBRA coverage.
-
Indicate which compensation object represents the 'best offer' made to the employee through the COBRA program by selecting from the available options. Note that this may not necessarily match what the employee actually enrolled in. This would be the plan and option that meets the most of the following criteria:
Plan provides Minimum Essential Coverage
Plan provides Minimum Value
Option provides coverage for the most dependent types
-
Enter the lowest COBRA rate for Self Only coverage offered to the employee.
-
Select the applicable check box:
-
Person Covered: Indicates whether the employee or the person is enrolled in the coverage.
-
Self Insured: Indicates whether the coverage is in a self-insured plan.
-
Entering Dependent Self Insured Enrollment and Insured Covered Dependent Details
If the employee is enrolled in a self-insured plan through COBRA, then add all the dependents also covered by this plan along with the start and end months of their coverage. Click Add Another Row to get started, and then search for and select the dependent by name. Repeat this step as needed to add all the applicable dependents.
Completing the Details
Once complete, click Save to save your work. Click Apply to return to the Search page to search for and select another COBRA employee to update. You can also click Delete to remove any changes already entered. You can also click Cancel without saving any changes and you will be returned back to the Search page.
Archiving Data Entered in the COBRA Page
Run the Benefits ACA Archive Process at the end of the year to generate the archive data required for reporting on the Employee or Recipient Form 1095-C. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Archive Process
Running the Benefits ACA HRA Details Process
See Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) for more information.
Run the Benefits ACA HRA Details process to collect details of individuals who have been offered an HRA.
Run this process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Process:
-
In the Name field, select Benefits ACA HRA Details Process.
-
Click in the Parameters window.
-
Enter the following parameters.
-
Year: Select the reporting year. This is a mandatory parameter.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which you are submitting data. This is a mandatory parameter.
-
Validate: Select Commit or Rollback. Like other processes in the Benefits application, this process can be run in rollback mode (data is not saved) or commit mode (data is committed in the database).
-
Person: Important: Use the Person field only if you want to debug information for a person and in this case, the recommended validation method is Rollback.
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report concurrent program. See Running the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report for more information.
Running the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report
See Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) for more information.
Run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report concurrent program to obtain a report of individuals identified by the Benefits ACA HRA Details process. The report includes information that is required to search for the Marketplace Silver Plan costs such as Age as of First Eligible for an HRA offer, and Primary Work and Residence zip codes.
Run this process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Report:
-
In the Name field, select Benefits ACA HRA Details Report.
-
Click in the Parameters window.
-
Enter the following parameters.
Year: Select the reporting year.
GRE: Select the GRE for which you are submitting data.
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Entering the ACA Person HRA Details
See Setting Up and Processing Reporting Offers for Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) for more information.
Prerequisites
- You must run the Benefits ACA HRA Details Process to use the ACA Person HRA Details page.
- Search for individuals and then use the Maintain HRA page to enter Silver plan costs for individuals who are offered an HRA.
Searching HRA Details
To search for a person, select the mandatory criteria Year and GRE, and then the person name or the employee number. The search displays individuals who are identified by the Benefits ACA HRA Details process as having received an HRA offer for the year from that employer. Click Update to access the HRA offer details for the individual.
Using the Maintain HRA Page
On this page, you can:
-
Override the address type that is used to find the Marketplace Silver Plan, which defaults from the plan. You can override the address and the zip code. Note that this action does not update the Assignment or the Person record.
-
Enter the monthly Silver Plan cost for each month, the individual received an HRA offer. The Employee Required Contribution is calculated automatically by subtracting the monthly individual coverage amount from the Silver plan premium cost.
-
Verify the affordability of the resulting Employee Required Contribution. The default is that the offer is affordable. If the result does not meet the affordability method that an employer uses, then deselect the Affordability check box.
-
Save the record.
You can delete a person's information and then reprocess using the Benefits ACA HRA Details concurrent program.
Running the Benefits ACA Archive Process
Run the Benefits ACA Archive Process at the end of the year to generate the archive data required for reporting on the Employee or Recipient Form 1095-C.
The Benefits ACA Archive process evaluates:
-
The data that is entered in the Employee COBRA Offer Details page for Part II (Employee Offer and Coverage) and Part III (Covered Individuals) of Form 1095-C. This process also evaluates the data entered in the Employee COBRA Offer Details page for persons who were enrolled in self-insured coverage and were terminated during the reporting year. The archive process considers all persons who were employed at least one day during the reporting year. Note that these terminated employees will still have code 1H reported on Line 14 of their Form 1095-C for the months after termination, but they will be shown as covered in Part III of their Form 1095-C.
-
Employees designated as Full Time ACA Eligible employees by checking the ACA Full Time flag in the Benefit tab of the People window.
-
Any person (non-ACA employee or non-employee) enrolled in a self insured ACA Plan and their covered dependents.
Run the Benefits ACA Archive Process using the Submit Request window.
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Prerequisites
- Set the batch process parameter for the Benefits ACA Archive Process before running the program. See: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Processes and Reports
To run the Benefits ACA Archive Process
-
Select Benefits ACA Archive Process in the Name field.
-
Select the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the year for which the report must be submitted
-
GRE: Select the appropriate GRE for which the data needs to be archived. Note that if this process has already been run for a GRE for the selected year, then this GRE will not appear in the list of values.
-
Validate: Select Rollback or Commit. Like other processes in the Benefits application, this process can be run in rollback mode (data is not saved) or commit mode (data is committed in the database).
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Debugging Assistance: In the event errors are received or you experience issues running the Benefits ACA Archive Process, consult My Oracle Support Document 2090308.1 - Oracle E-Business Suite Standard and Advanced Benefits: Customer Debugging Tips for Benefits ACA Archive Process. This document provides tips on how to generate further debugging details that will likely be requested by Oracle Support in the event you need to open a Service Request (SR) for assistance.
Viewing Log Files
The data that is being archived must conform to the IRS specifications. The Benefits ACA Archive Process will end in an error status if the log file reports errors. The log file informs the user that validation errors are found during the archival process. For example, zip codes must be of five digits and must not have any characters other than numbers. Therefore, when a zip code has greater than or fewer than five digits, the Benefits ACA Archive Process ends in an error status. Before running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process, manually fix the errors reported in the log file and then rerun the Benefits ACA Archive Process until all errors are resolved. Note that you cannot run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generate Process because the Benefits ACA Archive process will not complete until all the invalid data items have been correct. The Benefits ACA Archive Process does not validate whether person names are greater than 20 characters in length. Instead, the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process truncates names where necessary when creating the XML output file. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process
Viewing the Employee Archive Data
After the Benefits ACA Archive Process has completed successfully for a GRE, you can search for and verify the data for a person using the View Employee Archive Data page. See: Running the Benefits ACA Archive Process
Searching for an Employee to View the Archived Data
You can search for an employee using the following search criteria:
-
Year: This is a mandatory field. Select a year from the list of values for which the person's archived data needs to be verified. This list of values displays only the years for which the archive process was completed.
-
GRE: This is a mandatory field. Select the applicable GRE to which the person belongs. This list of values displays only the GREs for which the archive process has been run for the selected year.
-
Person Name: Select the Person whose archive data needs to be verified. You may search based on employee name or employee number.
After you select all the mandatory fields, click Search to view the archived data for the person. The data is displayed in a layout similar to the actual Form 1095-C. For individuals who are offered Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs), the View Employee Archive Data page shows the age as of the first of the year and the Line 17 zip codes for individuals.
Rearchiving and Printing Form 1095-C for a Single Employee
In addition to the ability to search for and verify the data for an employee, the following buttons are available in the View Employee Archive Data page:
-
Rearchive: This button enables you to rearchive the selected employee's data.
-
Print: This button enables to print or reprint the selected employee's Form 1095-C. Select the format of the Form 1095-C by selecting the desired template in the Template field.
Performing Self-Corrections
The View Employee Archive Data page enables you to perform self-corrections to correct those issues discovered outside of the IRS' ACA Information Return (AIR) system.
The following requirements must be met prior to marking a person record for self-correction:
-
The person record must have already been included in a previous Employer Information Return transmission to the IRS.
-
The status for the most recent transmission which included this person record must be one of the following:
-
Accepted
-
Accepted with Errors
-
Partially Accepted
-
Rejected
-
-
If there is an Error Acknowledgement file provided by the IRS along with the transmission status, then you must run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program.
To perform a self-correction
-
Search for the person using the Year, the GRE, and the Person Name criteria. If a person record meets the requirements, then the Mark Error button will be displayed for that person.
-
Click the Mark Error button to add self-correction comments.
-
Add the error text in the Self Correction Error Details popup.
-
Click Apply. This action saves the changes and marks the person record for self-correction. You can view an Error Information region, which contains a list of error messages reported by the IRS, if any, and any errors added through self-correction. Check boxes indicate whether the person record is marked for retransmission by the IRS through the Error Acknowledgement XML or by the Transmitter or the Issuer themselves through self-correction.
-
Use the Edit Error button to update the self-correction comments.
-
Use the Delete button to remove the self-correction comments.
Archiving the Corrected Person Records
After a person record is marked for retransmission through self-correction, complete the following steps to archive the corrected person records.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process to archive the corrected person details. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process
-
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process to generate the output file for transmitting the corrected Employer Information Return. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process
Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process to generate the necessary output files when submitting your Form 1094/1095-C data to the IRS' ACA AIR system. Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process generates the necessary manifest header and form detail output files using the IRS required file-naming conventions. If the form data output is greater than 100MB, which is the IRS AIR system limit, then multiple form detail files are generated along with the manifest header files. Each form file has an associated manifest file. All the generated manifest files and form files must be uploaded to the IRS AIR system in manifest or form file pairs.
Note: You can also run this program after the corrected data archive has been successfully generated by running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process. You use the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process to generate both the original and the corrected or replacement transmission output files for transmitting to the IRS.
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- The Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process can be submitted for a GRE only if that GRE is marked as either an Issuer or a Transmitter in the ACA TCC Information EIT for a GRE.
The Transmitter Control Code (TCC) must be populated when selecting the Issuer or the Transmitter as the TCC role for the GRE.
To run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation process
-
In the Name field, select Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process.
-
Click in the Parameters window.
-
Enter the following mandatory parameters.
-
Year: Select the reporting year.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which you are submitting data. Note that a GRE can be selected only if the TCC information is populated in the ACA TCC Information EIT for the GRE.
-
Filing Indicator: Select from the available values: T (for AATS) or P (for Production). The value selected here will be used by the IRS to determine whether the transmission needs to be validated or stored against their test or production system. If you are submitting your production 1094/5-C data, then select P.
-
Validate: Select Rollback or Commit. Rollback is used to check for any errors during the XML generation process. The transmission process can be run as many times as required when Rollback is selected. Select Commit only when you are ready to generate the output files for transmitting to the IRS.
-
Output Directory: Enter the name of the output directory to which you want to save the concurrent program files. If no value is provided, then the process picks a value from the “v$parameter” table for “user_dump_dest.”
-
Viewing the Report Output
To know where the output files are stored and view the names of the output files:
-
Navigate to the Find Requests window.
-
Search for the request that you had submitted.
-
In the Requests window, click View Output. The application displays a text file with the following information about the generated file set:
-
Directory where the files are stored
-
Transmission files
-
Transmission manifests
-
After the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process has run successfully, view the Authoritative 1094-C (Transmittal) details in the View Authoritative 1094C page. For more information, see Using the View Authoritative 1094C Page.
Transmitting to the IRS ACA Information Returns System
To transmit to the IRS ACA AIR system:
-
After the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process generates output files, submit the files to the IRS using the appropriate IRS AIR portal. Once the transmission is complete, you will receive a Transmission Confirmation message from the IRS. The message contains the Receipt ID along with a date-and-time stamp indicating when the files were transmitted. The Receipt ID is critical as it is required to check transmission status.
-
Use the IRS AIR portal to verify the transmission status. If the IRS AIR Transmission Status Details page shows a status other than Accepted, then further corrective action is required.
-
Save the error file (XML) returned by the IRS. This XML data file contains the transmission error details.
-
Use the View Authoritative 1094C page to view the Authoritative 1094-C (Transmittal) details. For more information, see Using the View Authoritative 1094C Page.
-
Use the ACA Transmission Details page to search for and select the transmission that requires updating. For more information, see Using the ACA Transmission Details Page.
Running the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Recommendation: Before you run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process to generate files for states, ensure that the transmission status of XML files is a status other than “Rejected.”
To generate files compatible with the state filing requirements, run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process. See ACA Reporting for States for more information. Based on the number of threads set for this process, the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process (multithread) will be spawned automatically for those GREs with higher volumes of individuals included in the file.
Run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process
-
Select Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process in the Name field.
-
Select the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the reporting year for which the process must be run.
-
Authoritative GRE: Select the GRE responsible for transmitting the 1094/5-C files.
-
Filing Indicator: Select P for Production or T for Test.
-
Validate: Select "Commit" to generate the actual file to submit to the state; when testing select Rollback.
-
Output Directory: Enter the output directory to where you would like the output file to be generated.
-
State: Select the applicable state. See ACA Reporting for States for more information.
-
-
Click OK and then submit.
Using the View Authoritative 1094 C Page
After the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process runs successfully, you can view the Authoritative 1094-C (Transmittal) details in the View Authoritative 1094C page. This page enables you to download employee 1095-C data to meet audit requirements. Access the View Authoritative 1094C page by clicking the menu option in the Affordable Care Act submenu. This page shows you all the details (Parts 1 through 4) of the Form 1094-C information in a page similar to the actual paper transmittal form. In the Search Criteria region, select the year and the GRE for which you want to view the Authoritative 1094-C (Transmittal) details.
Download to Spreadsheet
You can download employee 1095-C data to a spreadsheet based on the GRE and the reporting year that you selected. Select a version, if any and then select Part II or Part III to download the data to a spreadsheet. When Part II is selected, the employee data includes the values reported in Line 14 (Offer of Coverage code)), Line 15 (lowest self-only cost of coverage) and Line 16 (Safe Harbor code) of Form 1095-C for each month of the reporting year (including the All 12 month value). It also reports on the individual's ACA Full Time status. For individuals who are offered Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs), Part II includes the contents of the Line 17 Zip Code. The Part III download includes participants and their dependents enrolled in a self-insured plan subject to the ACA regulation. It will indicate what months the individuals were enrolled (including the an 12 month indicator).
The employee data that you download focuses on the values reported in Line 14 (Offer of Coverage code), Line 15 (lowest employee-only cost of coverage), and Line 16 (Safe Harbor code) of Form 1095-C for each month of the reporting year (including the All 12 months value). The spreadsheet reports the employee's ACA Full Time status value Yes or No.
The drop-down list on the Version field enables you to filter the employee data based on the selected version. If a transmission has been submitted to the IRS, but no corrections have been submitted for the reporting year or GRE selected, then Original will be the only value available in the drop-down list. After you submit corrections to the IRS, the list will also contain values such as Corrected [version]1, Corrected [version]2 and so on. The values are listed in reverse chronological order, with the most recent submission appearing first in the list. When a version is selected from the drop-down list, the page is refreshed with the information for the selected version.
Using the ACA Transmission Details Page
Use the ACA Transmission Details page to search for and to select the transmission that requires updating. For more information, see Transmitting to the IRS ACA Information Returns (AIR) System. Access the ACA Transmission Details page by clicking the Affordable Care Act submenu.
Search for Transmissions
To find the transmission that you need to update, search using one or more of the following criteria:
-
Year (reporting year)
-
GRE
-
State: Select the applicable state. See ACA Reporting for States for more information.
-
Transmission Status
-
Receipt ID
The search results display a list of transmissions along with their transmission statuses and other details based on the selected criteria. If you have completed only one original transmission (you have run the Benefits ACA Transmission Generation Process only once), then the ACA Transmission Details page shows one row with the GRE name, the reporting year, a transmission type of Original, and a transmission status of Submission Pending. The Receipt ID and the Error Data XML columns will be blank.
Update Transmissions
After you receive the Transmission Status from the IRS, you can update the transmission in the ACA Transmission Details page by clicking the Update icon.
You can perform the following tasks for a transmission:
-
Change the transmission status from Submission Pending to the appropriate status according to the transmission status returned by the IRS.
-
Enter the receipt ID and set the transmission status.
-
Upload the error file returned by the IRS.
-
Enter the Transmission Error Code and the Transmission Error Message returned by the IRS.
You can update the transmission status multiple times before the next archive process is run to generate corrections for any of the GREs present in the transmission file. If there are error XML data files, then you must run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program to process the XML output and to mark the submissions and records as failed or incorrect. After this concurrent program is run successfully, the transmission status cannot be updated further for this transmission. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program.
Transmission Statuses
To set a transmission status other than Pending Transmission, you must provide the receipt ID associated with the transmission.
The possible transmission statuses are:
-
Processing: The transmission file is currently being processed by the IRS.
-
Accepted: The transmission file has been accepted by the IRS.
-
Accepted with Errors: The transmission file has been accepted by the IRS, but with some errors that require correcting by benefits administrators. The IRS will provide the Error Data XML output file or error message with this status. You must either upload the Error Data XML output file or enter the Transmission Error Code and Message when you this status while updating your transmission.
-
Partially Accepted: The transmission file has been partially accepted by the IRS. Some of the submissions within the transmission file have been rejected. The IRS will provide the Error Data XML output file or error message with this status. You must either upload the Error Data XML output file or enter the Transmission Error Code and Message when you select this status while updating your transmission.
-
Rejected: The transmission file has been rejected by the IRS. The IRS will provide the Error Data XML output file or error message with this status. You must either upload the Error Data XML output file or enter the Transmission Error Code and Message when you select this status while updating your transmission.
-
Not Found: The IRS has not found the Receipt ID that you provided for retrieving the status.
-
Submission Pending: This is the default status for transmissions that are pending submission. This is the only status that does not have a Receipt ID, which has not yet been provided by the IRS because submission is still pending.
Running the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program
Run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program to mark the applicable records with an error status. You run this program after you upload the Error Data XML file that was return by the IRS to the Oracle database using the Update Transmission Details page. For more information, see Using the ACA Transmission Details Page.
Run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program
-
In the Name field, select Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML.
-
Click in the Parameters window.
-
Enter the following mandatory parameters:
-
Year: Select the reporting year for which the correction transmission needs to be generated.
-
Transmitting GRE: Select the applicable GRE for which you are submitting corrected data. This is the GRE with the Transmitter Control Code (TCC) role set to T (Transmitter) in the ACA TCC Information additional organization window for which error data xml files need to be processed. You can select a GRE only if all files that were originally generated for this GRE using the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process are transmitted either successfully or with a rejected or an error status.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Errors Report concurrent program to view the error details of the employee records. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Errors Report .
Running the Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML Program
Run the Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML program to identify errors at the state level. Run this program from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML Program:
-
In the Name field, select Benefits ACA State Process Error Data XML.
-
Enter the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the reporting year.
-
State: Select the applicable state.
-
GRE: Select the applicable GRE for which you are submitting corrected data. This is the GRE with the Transmitter Control Code (TCC) role set to T (Transmitter) in the ACA TCC Information additional organization window for which error data XML files need to be processed. You can select a GRE only if all files that were originally generated for this GRE using the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process are transmitted either successfully or with a rejected or an error status.
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Steps to Consider
Following are the points that you must consider when processing errors at the state level and for the IRS:
-
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process and transmit files to the IRS.
-
Record the status of the files transmitted to the IRS on the View Transmission Details page.
-
If the status is Rejected, then:
-
Run the Benefits ACA process Error Data XML concurrent program.
-
Perform the necessary corrections.
-
Run Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process.
-
Run Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process concurrent program.
-
Return to step 1.
-
-
If the status is Accepted, then run the Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process and transmit the files to the state.
-
Record the status of the state transmissions on the View Transmission Details page.
-
If the status from the transmission to the IRS is other than “Accepted” or “Rejected” (that is, “Partially Accepted” or “Accepted with Errors”), the recommended practice is to follow Step 3, until the transmission is “Accepted” by the IRS to minimize the correction process and submit the final records to the states. However, you can optionally proceed to file with the states by running the “Benefits ACA State Transmission Generation Process” and recording the transmission status.
For Corrections to the IRS and the States:
-
For transmitted files to the IRS with a status other than Rejected (see above steps) or Accepted (that is “Partially Accepted” or “Accepted with Errors”), run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program to mark the records with errors. For transmitted files to the states with a status other than Accepted, then the Benefits ACA State process Error Data XML program must be run.
-
Perform the necessary corrections.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process. Note: The GRE will be available for selection in the "Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process" only if steps 7 and 8 are completely satisfied. The output of this process includes all records identified by the IRS and the states into a new single archive.
Important: If there is a requirement to purge the archive data from the system, then the state data must be removed first, and only then you can purge the IRS data.
Running the Benefits ACA Errors Report
The Benefits ACA Errors Report program generates an output report in PDF format with error details extracted from the error XML data files returned by the IRS.
The report has the following sections:
-
GRE Errors: This section lists the error code and the error text for the GRE.
-
Person Errors: This section lists the person last name in alphabetical order, the error code, and the error text for each employee.
Run the Benefits ACA Errors Report concurrent program if the error XML files returned by IRS have any of the following statuses:
-
Accepted with errors
-
Partially Accepted
-
Rejected
Run the Benefits ACA Errors Report concurrent program from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- Run the Benefits ACA Errors Report program after you have:
-
Updated the applicable transmission in the ACA Transmission Details page and uploaded the Error Data XML file from the IRS to the Oracle database.
-
Run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML program to mark the applicable records with an error status. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program.
To run the Benefits ACA Errors Report
-
Select Benefits ACA Errors Report in the Name field.
-
Click in the Parameters field.
-
Enter the following mandatory parameters.
-
Year: Select the applicable reporting year from the list of values.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which the error report is to be generated.
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Report Output
The report output is provided in PDF format. The errors that are included in the report output are generated only for the most recently transmitted GRE, whether the latest correction, if a correction has been made, or the original for the selected year.
Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process
To archive the corrected data, run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process. You run this program after the transmission records are marked with an error status by the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML concurrent program and all applicable errors have been corrected. Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process is a mandatory step to transmit your corrected or replacement file (if your original or corrected transmission was rejected) to the IRS.
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process concurrent program for the following transmissions:
-
Transmissions that received a status of Accepted with Error
These transmissions will generally have an error file generated by the IRS, which contains error details related to person or GRE records. In this case, when you run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML concurrent program, the applicable records are marked with an error status. Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process concurrent program after the errors are corrected re-archives the relevant data from the Oracle E-Business Suite Benefits tables.
-
Transmissions that received a Rejected or Partially Accepted status
Transmissions usually receive this status due to errors in the manifest file. For example, if the XML transmission process was run with the Filing Indicator parameter set to Test instead of to Production, or if you attempted to submit an already submitted file, or if there are formatting or naming convention issues.
In such cases, complete these steps in the following order:
-
Make the necessary corrections or apply a corrective patch (to correct invalid characters, for example).
-
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process concurrent program. The concurrent program records the corrections for the manifest file and copies the data from the previous archive. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process .
-
Run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process to generate new output files. The corrected or replacement manifest and the form files to be transmitted to the IRS will be generated. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process.
Run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process
-
Select Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process in the Name field.
-
Click in the Parameters field and enter the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the relevant year from the list of values.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which correction records need to be re-archived.
-
Validate: Select Rollback for data that is not committed to the database or Commit for data that is committed and the archive data created.
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
After the corrected data archive has been successfully generated, you can run the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Transmission XML Generation Process.
Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
The Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report concurrent process generates and prints Employee 1095-C forms for the GRE and year selected. Note that these forms can be generated in the PDF or XML formatted output. This process generates the forms based on the data archived by running the Benefits ACA Archive Process.
Run the ACA 1095C Print Report from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- Before you run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report, you must have run the Benefits ACA Archive Process successfully run for a GRE and verified the data. See: Running the Benefits ACA Archive Process.
To run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report
-
Select Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report in the Name field.
-
Select the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the year for which the 1095-C PDF forms /XML data must be generated or printed. This list of values displays only the years for which the Benefits ACA Archive Process has been successfully completed.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which the 1095-C PDF forms /XML must be generated or printed. This list of values displays only the GREs for which the Benefits ACA Archive Process has been successfully completed.
-
Output Type: Select XML or PDF.
-
XML: Selecting XML will produce an output file with the applicable employee 1095-C data in an XML format. This option is useful for those customers who are using a third-party to print and distribute Employee or Recipient 1095-C forms.
-
PDF: Selecting PDF will generate the Employee or Recipient 1095-C forms in a PDF format. If you select PDF, then select the applicable Template Code.
-
-
Template Code: This parameter will be enabled only if PDF is selected as the Output Type. Select the desired template.
-
Additional Information
-
You can run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report multiple times for the same GRE and reporting year.
-
If it is determined that corrections are required either to the employer or employee data after running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report, then run the Benefits ACA Purge Process. Running the Benefits ACA Purge Process will remove all archived data for the GRE and Year selected, so special care must be taken when running this process. Important: The purge process must be run only if data requires correcting.
-
f the Benefits ACA Purge Process is run, then the Benefits ACA Archive Process must be run after any necessary corrections have been made. If the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report is run before the Benefits ACA Archive Process is rerun, then no person will be selected for printing and therefore no output will be produced.
Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread Process
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
The Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread process provides customers with large employee populations improved performance for printing Form 1095-C for recipients.
Run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread process from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- Set the batch process parameter for the Benefits ACA Print Process before running this process. See: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Processes and Reports
To run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread process
-
Select Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread in the Name field.
-
Select the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the year for which the 1095-C PDF forms must be generated or printed. This list of values displays only the years for which the Benefits ACA Archive Process has been successfully completed.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which the 1095-C PDF forms must be generated or printed. This list of values displays only the GREs for which the Benefits ACA Archive Process has been successfully completed (for the year selected).
-
Sort Order 1 and Sort Order 2: Use these fields to sort the output of this report and to print high volumes of forms 1095-C to employees or other individuals. The ability to optionally sort is available at two levels: Sort Order 1 and Sort Order 2. You can optionally order by Sort Order 1 and Sort Order 2, if desired. The sorting can be done based on Location, Employee Name, Organization, or Payroll.
-
Select the desired template.
-
Process Output
The main parent thread of the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread concurrent process does not process any employees. Click View Output of the main parent thread for Request IDs of the child processes. These child processes process the employee records and generate the Forms 1095-C in a PDF format based on the selected layout.
Printing Corrected 1095-C Forms for Participants
Complete the following steps in this order to print corrected 1095-C forms:
To print corrected 1095-C forms for participants
-
Run the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML concurrent program, which processes the error data XML file from the IRS and marks problem records with an error status. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Process Error Data XML Program.
-
Make corrections and then run the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process concurrent program after corrections are performed. This program archives the corrected data. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA Correction Archive Process .
-
Run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread concurrent program to generate corrected 1095-C forms for employees or recipients. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report Multi Thread Process.
This program prints the 1095-C forms with the Corrected box checked. If you need to produce an XML output file instead, then you must run the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report and select XML as the output type. For more information, see Running the Benefits ACA 1095C Print Report.
Running the Benefits ACA Purge Process
For an overview, see: Employer Shared Responsibility Reporting Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Administration
Important: If there is a requirement to purge the archive data from the system, then the state data must be removed first, and only then you can purge the IRS data.
Run the Benefits ACA Purge Process to purge the archive data generated by running the Benefits ACA Archive Process. See: Running the Benefits ACA Archive Process. Run this Benefits ACA Purge Process if any data discrepancies are found and corrections are required before printing the Employee 1095-C forms. After purging, make the necessary changes and rerun the Benefits ACA Archive Process.
Run the Benefits ACA Purge Process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Benefits ACA Purge Process
-
Select Benefits ACA Purge Process in the Name field.
-
Select the following parameters:
-
Year: Select the year for which the purge process must be run. The list of values displays only those years for which the archive process was completed.
-
Purge Mode: Only Archive can be selected currently. This option will purge the data archived by running the Benefits ACA Archive Process.
-
GRE: Select the GRE for which the purge process must be generated. The list of values displays only those GREs for which the Benefits ACA Archive Process was successfully completed. Note that this parameter will be enabled only when Purge Mode is set to Archive.
-
State: Select the applicable state. See ACA Reporting for States for more information.
-
If the State parameter value is left null, then the purge process applies to the process that was run to produce the output files for the IRS.
-
If the XML generation processes have been run for both the IRS and the applicable state, then the purge the data for the state first and then purge the data for the IRS.
-
-
Authoritative GRE: Select the GRE for which you want to purge the Authoritative 1094-C (Transmittal) data.
-
Validate: Select Rollback or Commit. Like other processes in the Benefits application, this process can be run in rollback mode (data is not saved) or commit mode (data is committed in the database).
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Life Events
Life Event Reasons
You define a life event reason as any change to a person that impacts benefits participation. The system creates a life event when it detects a change in a person's HR record that you have defined as a life event reason.
You can define these types of life event reason:
-
Compensation--Use this type to set up one life event reason for each Compensation Workbench plan
-
Absence--Use this type to set up three life event reasons (Absence Started, Absence Ended, and Absence Deleted) to detect creation of, and changes to, absence records.
-
Checklist--Use this type to assign an HR administrator a series of tasks based on a common event, such as a new hire or termination.
If you use iRecruitment, use the iRecruitment type to set up one life event reason to process compensation plans for applicants.
In Advanced Benefits, assignment changes, an anniversary of employment, a marriage, or the occurrence of an open enrollment, are all examples of life events (in addition to the Compensation and Absence life event reasons). You can define life event reasons to determine key benefits processes, including:
-
Enrollment eligibility and electability
-
Rates and coverage amounts
-
Available flex credits
-
Coverage start and end dates
-
Required communications
-
Automatic and default enrollments
Life events can be explicit, temporal, or scheduled.
-
Explicit life events are changes to a person's HR record, such as a job change.
-
Temporal life events occur with the passage of time, such as the six month anniversary of employment.
-
Scheduled life events are assigned life events, such as an open enrollment period.
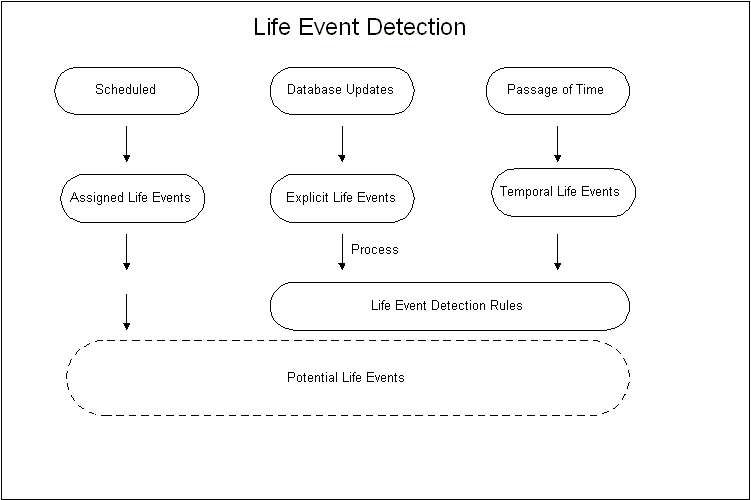
Because life event detection can be complex, and because the accurate determination of qualifying life events is important to benefits administration, detected life events are initially given a status of potential so that they do not generate enrollment actions.
You can review potential life events for a person and then process the life event using the Participation batch process. Potential life events become active life events if they meet your plan design requirements. Active life events can trigger enrollment opportunities.
Life Event Terminology
Life events are a cornerstone of benefits processing; understanding some basic terminology before you define any qualifying life event reason is important. The table below outlines the basic life event terminology:
Life Event Terminology
| Terminology | Description |
| Life Event Reason | A life event reason is an approved explanation for enrollment, de-enrollment, or change in enrollment resulting from a life event. Participation eligibility is determined based on the life event reasons and eligibility profiles you associate with programs, plans, and options. |
| Related Person Life Event Reason | A related person life event reason occurs when a life event experienced by the primary participant generates a life event for a person related to the participant. |
| Person Change | A person change is a change in system data that you define to indicate that a person has experienced a given life event. |
| Related Person Change | A related person change is a change in system data that you define to indicate that a person has experienced a given related life event. |
Life Event Definition
You define a life event by specifying the processing characteristics of the life event and the database change that triggers the life event. You can trigger life events with criteria similar to those you use to define your eligibility profiles and variable rate profiles. Not all criteria are available to trigger life events, but you can always write a formula (using the Person Change Causes Life Event formula type) to trigger an event using criteria that are not available in the list of tables and columns.
You can also trigger life events based on changes to segments in special information types.
See: Setting Up Special Information, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Life events are defined separately from any compensation object or activity rate so that a single life event can have multiple uses.
Life Event Notification
Because life events are not always reported and recorded in a timely manner, you can specify whether a life event is processed as of the date the life event occurred, as of the notification date (the date the life event is recorded in the system) or the later of the actual date or notification date.
Temporal life events, such as age changes, are always processed as of the actual occurred date.
Person Changes
You define the changes to a person's record that trigger a life event by specifying the value of the database field that indicates this person change has occurred.
Note: Do not define person changes for Compensation life event reasons.
You select the database table and column for which you want to define a change that the system detects and processes as a life event. You specify the new value for this combination of database table and column that, when detected, indicates that a life event has occurred.
For example, you can define that a person change is detected when the database value of a person's marital status changes from Single to Married.
A person change can be defined based on the detection of:
-
A new value
-
A change from a specific old value to a specific new value
-
Any change to a value
-
A change from any value to no value
-
A change from no value to any value
You can also select a rule that defines more complex conditions for triggering a life event.
You link the person change that you define to a life event. You can link multiple person changes to a single life event and you can link a single person change to more than one life event.
You can define a life event to trigger based on changes to more than one table, or based on multiple changes to the same table.
For changes based on multiple tables, the APIs detect the life event when there is a data change in one of the tables that meet your Person Change criteria (an Or condition).
For multiple changes in the same table, the person must satisfy all Person Change criteria associated with the table for the API to detect the life event (the And condition).
Life Event Detection
Advanced Benefits
When you define a life event, you specify whether or not it is an overriding life event. If two or more life events with the same Occurred On date are detected for a person, the system picks the overriding life event as the winner.
If two or more potential life events are detected with the Override Flag set to On, the Participation batch process records an error in the log file. In these cases, you use the Potential Life Events form to select the winning life event.
You can select a timeliness evaluation code that indicates if a life event that occurs prior to the current calendar year or a given number of days prior to the system date should be voided or processed manually.
You can set a life event treatment code to prevent temporal event detection for a specified life event reason under certain conditions.
See: Defining General Characteristics of Life Events Reasons
Absence Life Events
Absence life events are processed by the Participation Process in Absence mode. In this mode, the process handles multiple potential life events in date order.
Closing, Backing Out, and Voiding Life Events
You can remove the processing of a life event performed by the Participation process, and you can prevent further processing of a life event.
-
Close a life event to prevent further processing.
-
Back out a life event to roll back any updates generated by the Participation Process (such as updates to eligibility, rates, automatic de-enrollments, and so on)
-
Void a life event to roll back any updates and prevent further processing by the Participation process.
Life Event Usage (Advanced Benefits)
Once you create a life event definition, you can use that definition for a variety of purposes. This section describes the ways that you can use life events.
Enrollment Requirements
You can link life event definitions to your enrollment requirements for a compensation object so that a person must experience a particular life event before they can enroll in a plan for which they are eligible. You can also use life events to restrict enrollment changes based on whether or not the participant is currently enrolled in a benefit.
Because scheduled enrollments are also a kind of life event, you must link scheduled life events to a compensation object if you are defining an enrollment period for that benefit.
Enrollment requirements based on life events can be applied to both participants and dependents.
Enrollment Coverage
You can vary the amount of coverage available for a plan based on a life event. You define the standard coverage amount for the plan or option in plan and then the coverage level available for those participants who experience the life event you select.
You can also limit a currently enrolled participant's ability to change coverage levels based on a life event.
Communications
You can generate a reminder letter for a participant with an open life event. Communications can also be triggered based on emerging life events, such as an event that will occur due to a temporal event.
Collapsing Life Events (Advanced Benefits)
You create a collapsing life event definition for those instances when a combination of two or more detected life events results in either a different life event or the voiding of the detected events.
The system uses your collapsing life event definition in conjunction with other life event reasons that you have defined. You must define life event reasons before you define how to collapse life event combinations. Life events with a status of potential or active can be collapsed.
Using And/Or expressions, you define the life event combinations that cause a collapsing life event. You can include up to ten life events as part of your collapsing life event definition. Select a collapsing logic code to indicate if the detected life events should be voided or collapsed into another life event.
Collapsing Life Event Date Determination
You can select the effective date of the new life event as:
-
The effective date of the batch process.
-
The earliest or latest life event occurred date for the set of potential life events being evaluated.
-
The date of the resulting life event if it is included in the set of potential life events being evaluated.
-
The earliest life event, latest life event, or batch process date if the resulting life event is not in the set of potential events being evaluated.
You can specify the number of tolerance days that the system considers when detecting life events that are evaluated by your collapsing life event rule. The tolerance period is based on the earliest life event occurred on date of the set of potential life events under consideration. For example, if the tolerance level is 10 days and the earliest life event occurred on date is 01-JAN, then the system considers all potential life events detected between 01-JAN and 11-JAN.
Collapsing Life Events Process
After you define your life events and collapsing life event rules, you run the Participation batch process to determine the winning life event for each selected participant. Your collapsing life event definitions are considered in conjunction with your other life event definitions, including overriding life event definitions and timeliness evaluations that determine how potential life events are processed.
Seeded Life Event Reasons
Oracle HRMS delivers seeded life event reasons you can use for benefits administration. Seeded life event reasons are pre-defined; you can re-name them but they cannot be otherwise modified or deleted. You do not set up person changes for seeded life event reasons as you do with user defined life event reasons.
You link seeded life event reasons to your plan design just like user defined life event reasons, or you can include a seeded life event reason as a parameter when you run either of the following batch processes to manage life events:
-
Participation Process: Life Event
-
Participation Process: Temporal
For example, you could run the Temporal Participation Process to detect changes in age that might make a person age into a savings plan or age out of a medical plan. In this example, you would select the seeded life event reason Age Changed as a parameter when you run the process from the Concurrent Manager.
See: Life Event Usage
The following is a description of the life event reasons that are seeded with Oracle HRMS:
Administrative and Open Enrollment
-
Administrative: Assign the administrative life event reason to a person or group of persons when the terms and conditions of a benefit plan change significantly and participants must be allowed to re-evaluate their elections. Examples of administrative life events include renegotiation of contract rates or addition of a new benefit
-
Open Enrollment: Use the Open life event reason to determine eligibility for an open enrollment period. Open enrollments typically occur at recurring scheduled periods, such as an annual health and welfare benefits enrollment or a quarterly savings plan enrollment.
-
Unrestricted: The unrestricted life event reason is used for benefit enrollments that are not time-dependent, such as a savings plan.
When you run the Participation Process in Scheduled mode from the Concurrent Manager, and select the enrollment period start date, the system creates a life event with a status of Detected for each person who meets the batch process criteria.
Temporal
When you run the Participation Process in scheduled, life event, or temporal mode, the system creates a life event when the minimum or maximum boundary is crossed as specified in the definition you create for the applicable derived factor. The seeded life event reasons for temporally derived factors are:
-
Age Changed
-
Combined Age and Length of Service Changed
-
Compensation Changed
-
Hours Worked in Period Changed
-
Length of Service Changed
-
Total Percent Full Time Changed
You implement temporally based life events by creating the derived factor, including the derived factor in an eligibility profile or variable rate profile, and linking the profile to a compensation object.
See: Derived Factors
COBRA Administration (US Only)
The seeded life event reasons for COBRA are used to determine ineligibility or enrollment period change for COBRA benefits. COBRA life event reasons should be associated with programs or plans subject to COBRA regulations.
-
Loss of Eligibility: This seeded life event reason detects when a COBRA enrollment period has passed.
-
Maximum Period of Enrollment Reached: This seeded life event reason detects when a COBRA participant is to be de-enrolled due to reaching the maximum period of enrollment, which can vary based on subsequent life events that occur during COBRA coverage, such as a divorce or qualifying disability.
-
Non or Late Payment: This seeded life event reason detects when a COBRA participant's payment is delinquent or late based on the participant's enrollment start date and the COBRA Payment due date. The initial payment is granted a 45 day grace period.
-
Voluntary End of Coverage: This seeded life event reason detects when the participant's COBRA participation has been voluntarily ended. This indicates that the COBRA eligibility end date has been reached as recorded in the COBRA Beneficiaries window with an ineligible reason of Voluntary End of Coverage.
-
Period of Enrollment Changed: This seeded life event is created when a person's COBRA eligibility end date is changed. For example, this could occur for a participant who is initially eligible for 18 months of COBRA coverage who becomes disabled during the first 60 days of coverage. The participant's enrollment period is changed to 29 months and the COBRA eligibility period end date is changed accordingly.
Miscellaneous Seeded Life Event Reasons
-
Enrollment Override: Use this seeded life event reason when you employ the Participation Overrides window or the Enrollment Override window to make a person eligible or ineligible for a benefit, or for enrollment or de-enrollment.
-
Quartile in Grade: This seeded life event is created by the system when a change in a person's grade, salary basis, or salary moves them into a new quartile in grade. These conditions trigger the Quartile in Grade life event if the BEN: Enable Quartile in Grade Life Event user profile option is set to Yes. If you set this profile option to No, the system never creates a Quartile in Grade potential life event.
-
Reduction of Hours: This seeded life event reason is used when a reduction in hours causes a person to experience a change in benefits status, such as becoming eligible or ineligible for a benefit.
-
Satisfied Waiting Period: This seeded life event is created by the system when a person experiences a life event but has not yet satisfied the waiting period for the benefit and is therefore not eligible. The life event is created with the occurred on date equal to the date the person satisfied the waiting period. The life event is given a status of potential until the waiting period completion date is reached.
-
Added During Enrollment: This seeded life event is used by Self- Service Benefits enrollment to prevent a life event from occurring when you create a family member or update a family member's details. You can define a gain dependentlife event reason if you want to trigger a life event based on a family member change in Self-Service.
Life Event Definition (Advanced Benefits)
This example shows you the high level steps necessary to create a marriage life event.
-
Use the Life Event Reasons window to define the Marriage life event reason this person change triggers.
-
Use the Person Changes window to define the person change that triggers this Marriage life event.
-
Use the Person Change Causes Life Event window to associate the person change with the Marriage life event.
-
A FastFormula programmer creates a Marriage rule that specifies how the system detects the Marriage life event when doing so is more complex that steps 2 and 3 can accommodate.
-
Use the Life Event Reasons window to associate this Marriage rule to the Marriage life event.
-
After you define these person changes, every time a database change occurs, a program reads the table you populate using the Person Change Causes Life Event window. If all conditions are met, this program updates the Person in Life Event Reason table.
This step requires no human intervention.
-
On a periodic basis, the benefits administrator runs the Participation batch process which reads the Person in Life Event Reason table and then determines the impact on the person's eligibility for enrollment, change in enrollment, and de-enrollment.
Defining General Characteristics of Life Event Reasons
You use the Life Event Reasons window to date effectively define life events and their associated processing.
To define general characteristics of a life event reason:
-
Set your effective date to the appropriate start date for this life event reason.
-
Enter a Name for this life event reason.
Note: Use a noun for the life event reason name since this life event may appear in communications that you send to participants.
-
Select a life event reason Type. Choose from a variety of types including:
-
Absence: Select this type if you want entry and ending of absences to trigger life events.
-
Checklist: Select this type to trigger HR Checklist events for HR administrators.
-
Compensation : Select this type if you are defining a life event for a Compensation Workbench plan.
-
Personal (Advanced Benefits only): Examples include Marriage, Divorce, and Birth.
-
Scheduled (Advanced Benefits only): Examples include age and length of service changes.
-
Work (Advanced Benefits only): Examples include Change in Job Assignment, New Hire, and Termination.
-
iRecruitment: Select this type if you are defining a life event for compensation plans for iRecruitment applicants.
-
-
If you selected Absence as the Type, select the Life Event Operation Code: Delete Event, Start Event, or End Event. For example, to set up the life event reason that detects entry of an absence end date, select End Event.
-
Select an Evaluation Rule to apply to this life event reason. You can use an evaluation rule to define:
-
How to combine multiple detected life events into one
-
How to fully detect a life event when its detection is complex
-
When to eliminate a previously detected life event.
-
-
Enter a description of the life event in the Description field.
-
Select a Life Event Treatment code if you want to limit the detection of seeded temporal life events. Choose from:
-
Do Not Detect Past Temporal Events: Prevents the detection of past temporal events while the application processes this life event.
-
Do Not Detect Past or Future Temporal Events: Prevents temporal event detection while the application processes this life event. Use this code with the seeded open and administrative events, or any other explicit events, when you do not want to detect temporal events.
-
Never Detect This Temporal Life Event: Prevents the automatic detection of a specific temporal event. Set this code for any seeded temporal event, such as Age Change or Length of Service Change, that you do not want to detect, such as for mid-year changes.
-
-
Select a Timeliness Evaluation code to indicate how the system processes potential life events that fall outside a time period that you define.
By default, the Timeliness Evaluation field is set to Process Potential Life Event Manually.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Enter the number of days after the life event occurred beyond which the system does not process this potential life event in the Timeliness Days field.
By default, Timeliness days is set to 90.
Note: By selecting timeliness evaluation and timeliness days values for user-defined events, you can avoid over writing processed life events during retroactive batch processing.
-
Select a Timeliness Period if the potential life event should be voided or processed manually because it occurred prior to the current calendar year.
-
Select a Rule that controls your timeliness definition.
Note: The Timeliness Days and Timeliness Period fields are mutually exclusive.
-
-
Select an Occurred Date Determination code that controls if the life event is processed according to the date the event occurred or the date the event was recorded in the system.
Note: By setting the profile option BEN: Comp Objects Display Name Basis in the System Profile Values window, you can choose whether compensation object names display in application windows (both in the professional and Self-Service user interfaces) based on the life event occurred on date or the user's session date. The default profile option value is Session.
-
If you want to link a life event reason to a self-service process, select a value in the Selectable for Self Service field to indicate in which processes this life event should be available.
-
All--the life event can be selected in all self-service processes
-
Add/Update/Delete Family Members--the life event can be selected in Self-Service Benefits when the user adds, updates, or end dates a family member contact
-
Add/Update Family Members--the life event can be selected in Self-Service Benefits when the user adds or updates a family member contact
-
Delete Family Members--the life event can be selected in Self-Service Benefits when the user end dates a family member contact
-
Basic Registration--the life event can be selected in the New Employee Registration process
-
COBRA Registration--the life event can be selected in the Non-employee Registration process
-
Basic and COBRA Registration--the life event can be selected in both the New Employee and the Non-Employee Registration processes
Note: In Self-Service Benefits, a user can select life event reasons with a Selectable for Self Service value of All, Add/Update/Delete Family Members, or Delete Family Members as valid reasons for ending a relationship between the primary participant and a dependent or beneficiary.
Note: Do not use the Life Events page in self-service registration if you are the employer of benefits recipients. This page is only for third party benefits providers.
See: Configuring the New Employee and Non-Employee Registration Processes, Oracle HRMS Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
-
-
Select the appropriate value from the Show Primary Care Providers in Self Service to display or hide primary care providers in Self-Service for this life event. By default, the application displays all the primary care providers in Self-Service for this life event.
-
Select the Check Related Persons Eligibility field if the system generates a related person life event when the primary participant experiences this life event.
If you select the Check Related Persons Eligibility field, complete the Causes Related Person Life Events block as described in step 15
-
Select the Override field if this life event is the overriding life event in the case of the collision of two or more life events.
Note: When two or more overriding life events collide, no life event is selected as the winner. You use the Potential Life Events form to select the winning life event.
-
Select the COBRA Qualifying Life Event field if this life event impacts eligibility for US COBRA benefits.
-
Select the name of the related person life event this life event triggers in the Causes Related Person Life Event field.
Repeat this step for each related person life event that is triggered by this life event.
-
Save your work.
Next Step
Defining Person Changes
You define the changes to a person's record that trigger a life event by specifying the value of the database field that indicates this person change has occurred.
To define a person change:
-
Query or enter a life event in the Life Event Reasons window.
-
Choose the Person Changes button if you are defining a life event for a primary participant.
-
Or, choose the Related Person Changes button if the life event experienced by the primary participant causes a life event for a related person.
-
-
Choose the Define Person Change button or the Define Related Person Change button depending if you chose Person Changes or Related Person Changes in step 2.
-
Enter a Name for the person change you are defining.
-
Select the Table Name of the database table containing the column name (field) and new value that indicates a person has experienced this life event.
Note: Refer to the Oracle HRMS Technical Reference Manual for definitions of the database tables and columns.
-
Select the Column Name.
-
Select the Old Value if the life event you are defining is only detected when the column name value change from a specific old value to a specific new value.
-
Select the New Value that triggers a detected life event.
-
If necessary select a Rule of the type Person Changes Causes Life Event to refine the circumstances under which the system determines that this person change has occurred. You can use this rule if changes to different columns on the same table trigger the same life event.
Note: If you select a rule and associate this person change with an absence-type life event, the values you enter in the Old Value and New Value fields are ignored and only the rule is evaluated. If the rule returns the value Yes, the Person Change has occurred, regardless of the value in the selected column.
-
Enter the text in the What-if Label field that represents this person change when you model eligibility using the What-if Eligibility/Ineligibility Participation window.
-
Select the Rule Overrides check box if you attach a Person Changes Causes Life Event rule to this Person Change and you want the results of the formula to determine how to detect the event.
The API executes the rule when a change happens on the table you select for this Person Change.
If you do not select this check box, the application detects a life event when a person meets the criteria of both the rule and the table/column values you selected in steps 5 through 8.
-
Click the Add Record icon on the toolbar if you want to define another person change.
You can add a person change based on another column in the same table you previously selected, or a column in a different table. Changes based on columns in the same table function as an And condition; changes based on columns in different tables function as an Or condition.
-
Save your work.
Associating a Person Change with a Life Event
In order to know when a person has experienced a life event, you associate a person change with each life event you define. A person change is a change to a person's HR record that indicates a life event might have occurred.
You can also associate a related person change with a life event if a change to the primary participant's HR record generates a life event for a person related to the primary participant.
Note: You must define your person changes and related person changes before these can be associated to a life event. See: Defining Person Changes
To associate a person change with a life event:
-
Query or enter a life event in the Life Event Reasons window.
-
Choose the Person Changes button if you are defining a life event for a primary participant.
-
Or, choose the Related Person Changes button if the life event experienced by the primary participant causes a life event for a related person.
-
-
Select the Name of a person change that you have defined.
Repeat this step for each person change you link to this life event reason. If you define the Person Change based on a single table, the application must detect Person Changes in all the columns you select to trigger the life event (the And condition).
For Person Changes based on multiple tables, the application must detect all Person Changes for at least one of the tables to trigger the life event (the Or condition).
-
Save your work.
Defining a Collapsing Life Event (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Collapsing Rules window to build your collapsing life event definition. By selecting life events and expressions (and/or), you create the conditions that the system evaluates when determining the new life event.
To define a collapsing life event:
-
Enter the Seq (sequence) in which this collapsing life event definition is processed relative to any other collapsing life event definitions.
-
Select the life event into which your life event combination collapses in the Results in field.
-
Use the Tolerance field to enter the number of days after the earliest life event occurred date beyond which the system ignores any detected life events when evaluating your life event combinations.
-
Select the primary life event in your life event combination in the first Life Event field.
-
Select the Expression (and/or) used to evaluate the detected life event combination.
-
Select another life event to include in combination with the primary life event in the next Life Event field.
-
Select more life event/expression combinations depending on the complexity of your collapsing life event definition.
-
Select a Collapsing Logic code or rule that indicates if the detected life events are voided or collapsed into a resulting life event.
-
Select a Life Event Occurred Date code or rule to specify the occurred on date of the resulting life event.
-
Save your work.
Benefit Enrollment Requirements
Enrollment Requirements
Enrollment requirements determine when an eligible person can enroll in a benefit. You define enrollment requirements for a program, plan type, or plan to determine scheduled enrollment periods and the qualifying life events that enable an enrollment.
Enrollment requirements that you define at the program level cascade to the plan type and plan levels unless you override these requirements for a given plan type or plan. Although there are many program-level enrollment attributes, participants do not technically enroll in a program. Instead, they enroll in the plans associated with that program.
You can also use the enrollment requirements forms to implement other restrictions, as follows.
-
You can coordinate coverage levels between all plans in a plan type. For example, you can require that a person who elects the "employee only" coverage option in one plan elects this coverage level for all plans in the plan type in which they enroll.
-
For insurance plans, you can limit the coverage level that can be elected by a spouse or a dependent to a percentage of the coverage elected by the primary participant.
-
Advanced Benefits customers can require that an action item be completed before an enrollment is valid.
-
You can also define dependent coverage requirements such as dependent information that is required for an enrollment to be valid (date of birth or social security number) and required certifications.
-
You define beneficiary designation requirements at the plan level.
General Program Enrollment Requirements
For a Program
You can define general enrollment requirements for a program, such as enrollment coverage start and end dates and activity rate start and end dates. These dates are not particular calendar dates, but dates relative to a scheduled enrollment in the program year.
Advanced Benefits customers can define at the program level whether default or automatic enrollments apply to any plans in this program.
For insurance plans, you can limit the coverage level that can be elected by a spouse or a dependent to a percentage of the coverage elected by the primary participant.
For a Plan Type in a Program
You can define enrollment requirements for the plan types in a program if these requirements differ between plan types. For example, you can define a required period of enrollment for the plans in one plan type.
Other requirements you can set at the plan type level relate to life insurance plans. You can:
-
Specify if the plans in a plan type limit the amount of coverage a spouse or a dependent of the primary participant can elect as a percentage of the coverage elected by the primary participant
-
Specify if the system determines imputed income and life insurance maximums for a plan type
You can limit the maximum number of plans in a plan type in which a person can enroll, or require that a participant enroll in a minimum number of plans in a plan type.
For a Plan in a Program
Advanced Benefits customers can define if a plan in a program is the default enrollment for a participant who fails to make an election. You can limit the circumstances under which a plan is the default based on whether or not the participant is currently enrolled in the program.
For example, you can define a default plan for newly enrolled participants, and indicate that currently enrolled participants must remain enrolled in their current plan.
Scheduled Program Enrollments and Life Event Enrollments (Timing)
Scheduled Enrollments for Programs
For scheduled enrollments, you define the enrollment type for the program, either open, administrative, or unrestricted.
Important: Open and administrative enrollment types are only available to Advanced Benefits customers. Because unrestricted enrollments are not date dependent, the system does not recognize an enrollment period for unrestricted enrollments. An unrestricted enrollment is considered closed when the enrollment is saved.
You cannot combine unrestricted and life event processing in the same program. If a plan does not require a life event for electability, attach the plan to a separate, unrestricted program or set up a plan not in program.
You associate a program year period with those programs that contain one or more plans with scheduled enrollments. Within the program year, you can specify the enrollment period for plans in the program, the date on which defaults are assigned, the date after which no further processing is allowed, and the enrollment close date.
For programs that allow an override to the enrollment start and end dates or the activity rate start and end dates, you can specify these enrollment and activity rate periods.
Life Event Enrollments for Programs (Advanced Benefits)
You can define the life events that trigger an enrollment opportunity for the plans in a program. You can also specify the date on which defaults are assigned, the date after which a person experiencing the life event is no longer eligible for enrollment, and the life event enrollment close date.
You can define the enrollment coverage start and end dates for a life event. This is not a particular calendar date, but a date relative to the life event.
As with scheduled enrollments, you can define overrides to enrollment start and end dates or activity rate start and end dates for a program that are caused by a life event that you associate with the program.
Life Event Enrollment Requirements for Plan Types and Plans in Program (Advanced Benefits)
You can associate with a plan type or a plan in program those life events that trigger an enrollment action. Depending on the life event and the participant's current enrollment status, you can define whether or not the life event enables an enrollment action. You select from enrollment codes that limit the participant's enrollment options based on whether they are currently enrolled in the compensation object that you specify.
For example, you can specify that a participant who experiences a particular life event and is currently enrolled in a plan can keep their current elections but cannot change their elections. But, if the participant is not currently enrolled in the plan, then they can enroll. You would select an enrollment code of Current, Keep Only; New, Can Choose.
You can also define for a plan in program the enrollment method associated with a life event, either automatic or explicit.
Dependent Coverage Enrollment Requirements for Programs
The information required to enroll a dependent in a benefit can be different from the information required to enroll a primary participant. For dependents you can define:
-
Dependent coverage start and end dates
-
Required information for enrollment, such as social security number/legislative ID and date of birth
-
Required certifications
-
Dependent coverage eligibility profiles
-
Enrollment actions triggered by a life event
-
Certifications required for enrollment after the occurrence of a specific life event
Plan Enrollment Requirements
You specify enrollment requirements at the program level if the requirements apply to all the plans in the program. You use plan level enrollment requirements to override values set at the program level for individual plans. The enrollment requirements that you can specify for scheduled enrollments and life event enrollments are the same at the program and plan level.
In addition, you set enrollments requirements for not in program plans and options in plans by using plan enrollment requirements.
You can define general enrollment requirements for a plan, such as enrollment coverage start and end dates. You can also set limitations to the minimum and maximum number of options in a plan in which a person can be enrolled.
If an action must be complete before an enrollment is valid, you can associate enrollment action types with a plan if you are an Advanced Benefits customer.
You can also define designation requirements that limit the familial relationship types covered by an option.
Enrollment Requirements for Plans Not in Program
You define enrollment requirements for plans not in program just as you do for plans in program. However, plans not in program also have additional enrollment requirements that you can set.
For each plan not in program, you can select a default enrollment code that determines how the system processes an enrollment when a participant fails to make an election.
For a plan not in program with a required enrollment period, you need to specify whether the required enrollment period applies to the plan, the options in the plan, or the plan type that contains the plan.
You can also specify the time period in which activity rates for a plan not in program are expressed in the user interface, for example by month or annually.
Enrollment Requirements for Options
You can define enrollment requirements that apply to the options in a plan, such as:
-
The default option for participants who do not make an election (Advanced Benefits)
-
The options that are required for enrollment in the plan
-
The enrollment method, either automatic or based explicitly on the participant's election (Advanced Benefits)
You can also set designation requirements for an option. See: Defining Options
Rate Start and End Dates
The Total Compensation processing model uses the rate start and end date codes on the Plan and Program Enrollment requirements windows to derive when the standard rate begins and ends for an enrollment. These codes also determine when the corresponding element entry begins and ends.
Depending on the code you select, the application determines the rate dates based on the life event occurred on date, enrollment coverage date, or effective date of the election.
Enrollment Action Types (Advanced Benefits)
An enrollment action is any action that is required of a participant to complete an enrollment or de-enrollment. In addition to the enrollment action types delivered with the product, you can use the Enrollment Action types window to define additional enrollment action types.
You associate an enrollment action with the enrollment requirements for a program or plan.
Enrollment Types
Most benefit plans define when an enrollment can be initiated or altered during the plan year. Often, restrictions are placed on when an eligible participant can enroll in a plan or change a current election.
Oracle HRMS controls enrollments using enrollment types:
-
Unrestricted Enrollment
-
Open Enrollment (Advanced Benefits)
-
Administrative Enrollment (Advanced Benefits)
-
Life Event Enrollment (Advanced Benefits)
-
Automatic and default enrollment (Advanced Benefits)
-
Explicit enrollment
Unrestricted Enrollment
Unrestricted enrollments are enrollments you define that are not time-dependent and often do not require a special reason for enrollment. A savings plan is a typical example of a benefit for which you might elect to use the unrestricted enrollment type.
Oracle customers who do not license Advanced Benefits must use unrestricted enrollments to process participants into a benefits plan. This is the only enrollment type available to you.
Important: Advanced Benefits users cannot combine unrestricted and life event processing in the same program. If a plan does not require a life event for electability, attach the plan to a separate, unrestricted program or set up a plan not in program.
During the plan design phase, you choose the unrestricted enrollment type for all your programs and plans. Then, when a benefits representative (or in the case of self-service enrollments, a participant) processes an enrollment, the system determines the person's electable choices based on the eligibility requirements for the benefit.
Unrestricted enrollments do not restrict an enrollment to a certain period or require that an action item or certification be completed for an enrollment to be valid.
Open Enrollment (Advanced Benefits)
You define an open enrollment for a benefit as a predefined time period during the plan year when a participant can alter elections in a plan. This is the most common type of scheduled enrollment.
Administrative Enrollments (Advanced Benefits)
Administrative enrollments are rare, but you might use this enrollment type when a significant change occurs to the coverage offered under a plan and it is necessary to allow participants to re-evaluate their continued participation in the plan.
Life Event Enrollments (Advanced Benefits)
Life event enrollments are caused by a significant change to the participant which requires or enables an enrollment action.
Automatic and Default Enrollments (Advanced Benefits)
You can automatically enroll an eligible participant into a benefit. To do so, you set up the enrollment method of automatic when defining the enrollment requirements for the benefit. Automatic enrollments are typically used to provide interim coverage before participants can make their own elections.
You define default enrollments as those elections an eligible participant receives if they do not specify an election within a pre-defined enrollment period. Default enrollments are processed when you run the Default Enrollment batch process from the concurrent manager.
Explicit Enrollments
All elections that are neither automatic or default are considered explicit elections. The participant must explicitly elect the benefit into which they enroll either through a self-service form or through their benefits department.
Enrollment Codes
When you define enrollment requirements for a compensation object, you select from enrollment codes that limit the participant's enrollment options based on whether they are currently enrolled in the compensation object. You can select enrollment codes for a program, plan in program, plan not in program, and option in plan. You can also select enrollment codes for specific life events for each compensation object.
For each plan not in program, you can select a default enrollment code that determines how the system processes an enrollment when a participant fails to make an election. Similarly, you can specify default enrollment codes for programs, plans in programs, and plan types in programs to determine default enrollment after specific life events. You can also select a default enrollment code for options in plans to specify when the option is the default based on a new or existing enrollment.
Note: In Standard Benefits, the default enrollment is displayed on the enrollment window but you need to save the election to enroll the participant. In Advanced Benefits, default enrollments are made automatically when you run the Default Enrollments process.
You can select from the enrollment codes and default enrollment codes listed below, or you can create a formula-based rule to define your own requirements.
List of Enrollment Codes
Current, Can Keep or Choose; New, Nothing: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person can keep their current elections or make new elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person cannot make an election.
Current, Can Keep or Choose; New, Can Choose: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person can keep their current elections or make new elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person can make new elections.
Current, Can Keep or Choose But Starts New; New, Can Choose: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person can keep their current elections or make new elections. The coverage ends at the end of the plan year and restarts the next day so that the participant must explicitly re-elect each year, even though the coverage amount may stay the same. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person can make new elections.
Note: You can only select this code from the Program or Plan Enrollment Requirements windows at either the plan type in program, plan in program, or plan level based on a life event. It is recommended that you select this code only for the Open enrollment life event.
Current, Choose Only; New, Can Choose: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must make an explicit election to stay enrolled. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person can make new elections.
Current, Choose Only; New, Nothing: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must make an explicit election to stay enrolled. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person cannot make an election.
Current, Keep Only; New, Can Choose: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must keep their current elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person can make new elections.
Current, Keep Only; New, Nothing: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must keep their current elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person cannot make an election.
Current, Lose Only; New, Can Choose: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must de-enroll from their current elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person can make new elections.
Current, Lose Only; New, Nothing: If a person is currently enrolled in this compensation object, the person must de-enroll from their current elections. If a person is not yet enrolled, the person cannot make new elections.
Current, Assign; New, Assign (Automatic): If the enrollment method code is Automatic, both current and new enrollees automatically enroll and cannot de-enroll.
Current, Nothing; New, Assign (Automatic): If the enrollment method code is Automatic, current enrollees automatically de-enroll; new enrollees automatically enroll and cannot de-enroll.
Current, Assign; New, Nothing (Automatic): If the enrollment method code is Automatic, current enrollees automatically enroll and cannot de-enroll; people not already enrolled cannot make an election.
Rule: Select Rule if you define a FastFormula rule to determine a person's electability based on their current enrollment status. The formula must be of the type Enrollment Opportunity.
List of Default Enrollment Codes
New, Defaults; Current, Nothing: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, enroll that person in the default enrollment for that benefit. If the person is already enrolled in that benefit, de-enroll the person from that benefit.
New, Defaults; Current, Defaults: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, enroll that person in the default enrollment for that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, enroll the person in the default enrollment for that benefit.
New, Defaults; Current, Same Enrollment and Rates: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, enroll that person in the default enrollment for that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, do not change that enrollment or the activity rate.
New, Defaults; Current, Same Enrollment but Default Rates: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, enroll that person in the default enrollment for that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, do not change the enrollment but assign the default activity rate.
New, Nothing; Current, Same Enrollment and Rates: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, do not enroll that person in that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, do not change that enrollment or the activity rate.
New, Nothing; Current, Same Enrollment but Default Rates: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, do not enroll that person in that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, do not change that enrollment but assign the default activity rate.
New, Nothing; Current, Defaults: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, do not enroll that person in that benefit. If a person is already enrolled in a benefit, enroll that person in the default enrollment for that benefit.
New, Nothing; Current, Nothing: If a person is not yet enrolled in a given benefit, do not enroll that person in that benefit. If the person is already enrolled in that benefit, de-enroll that person from that benefit.
Rule: Indicates that you will specify a FastFormula rule for this default treatment. The formula must be of the type Default Enrollment.
Enrollment Period Determination for Life Events
For situations where you back-out and reprocess an event - or when an event occurs during the enrollment window of a prior event - you can determine how the application determines the start and end date of the newly calculated enrollment period.
As part of your implementation, you can select a Period Determination code for each life event you attach to a program or a plan not in program.
Note: You can only set this code at the program level for plans in a program; the code applies to all plans in the program.
The application uses this code to adjust the enrollment period start date in the following situations:
-
You back-out and reprocess an event
-
An event occurs within the enrollment window of another event
-
The application detects a colliding life event
Select one of the following enrollment codes to control the calculation of the new enrollment window.
-
Retain Number of Days in Original Enrollment Period: This is the default value if you select no code; this code does not adjust the start date. The application calculates the enrollment window using the enrollment period start and end date codes based on the later of an existing Processing Date for a prior life event or, the life event occurred on date of the current event being processed.
If you back out and reprocess an event, the enrollment window will be the original number of days from the later of the original enrollment period start date, the backed-out date, or the system date. In most cases, the enrollment window will begin on the system date.
-
Later of Enrollment Period Start Date or Future Enrollments Start Date: This code retains the original enrollment period. However, the enrollment period must be one day or more after any future enrollment start date.
This is the most commonly used code; it always tries to retain the exact enrollment window based on the original start and end dates. If there is an enrollment result after the original enrollment period end date, the enrollment start date will be set to one day after the existing enrollment result. The code keeps the original end date if the end date is later than the new start date, otherwise, the end date will be reset to equal the new start date.
If the enrollment window has past, the participant will not be able to make election changes in Self-Service and the HR professional would need to set the effective date back to the enrollment window to make elections for the participant
You should also select this code if you base participant eligibility on family member information.
-
Later of Future Enrollments Start Date or System Date: This code retains the original enrollment period. However, the enrollment period must be one day or more after any future enrollment start date or the system date if the life event has been backed-out and reprocessed.
Selecting this code allows a participant to update elections in Self-Service on the day you reprocess a backed-out event.
-
Later of Future Enrollments Start Date or Backed Out Date: This code retains the original enrollment period. However, the enrollment period must be one day or more after any future enrollment start date or the backed-out date if the life event has been backed-out and reprocessed.
Note: if you set up your life event to close based on the code 'When Enrollment Period Ends', the Close Enrollment Process closes the event.
Reinstatement of Elections for Reprocessed Life Events
As part of implementation, you can configure how Oracle HRMS reinstates elections when a benefits administrator backs out a life event for a person (due to an intervening or colliding life event) and then reprocesses the original life event.
Select a Reinstate Code to control election reinstatement based on the reprocessed life event. You can also determine how the application processes reinstatements for overriden activity rates by selecting an Override Code. Select from the following codes based on your administrative practices.
-
Reinstate all if no electability change for life event
-
Reinstate if no change for backed out enrollment
-
Reinstate if electability exists for backed out result
-
Never Reinstate
-
Always use overridden rates
-
Override the rates if no change
You can select a Reinstate Code and an Override Code for programs and plans not in program based on each life event you define.
Dependent Coverage and Beneficiary Designation Requirements
Dependent coverage enrollment requirements determine when an eligible dependent can enroll in a benefit. The information required to enroll a dependent can be different from the information required to enroll a primary participant. For dependents you can define:
-
Dependent coverage start and end dates
-
Required information for enrollment, such as social security number/legislative ID and date of birth
-
Required certifications
-
Dependent coverage eligibility profiles
-
Enrollment actions triggered by a life event
-
Certifications required for enrollment after the occurrence of a specific life event
Note: For Standard Benefits, you must link the Unrestricted life event to the compensation object at the dependent designation level.
The enrollment requirements you specify at program level are inherited at plan type and plan level. The requirements you specify at plan level are inherited by all options in the plan.
You can define beneficiary designation requirements at the plan level. All options in the plan inherit these beneficiary designation requirements.
Defining Program Enrollment Requirements
Defining Enrollment Methods for a Program
You use the Enrollment Methods alternate region of the Program Enrollment Requirements window to define how a participant enrolls in a program.
If you use Standard Benefits, you can define requirements for unrestricted enrollments using this window.
Advanced Benefits customers can specify whether default or automatic enrollment rules apply for a program.
To define an enrollment method for a program:
-
Query the Program for which you are defining program enrollment requirements.
The current status of the program is displayed. For a definition of the program statuses, see Defining a Benefits Program.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select the enrollment method, either automatic or based on the participant's explicit choice, in the Method field.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select an Automatic Rule to define the circumstances under which automatic enrollments apply for this program.
-
Check the Allows Unrestricted Enrollment field if this program uses the unrestricted enrollment type.
You must also check the Allows Unrestricted Enrollment field for each plan in this program that uses the unrestricted enrollment type.
Important: You must check this field if you have not purchased an Advanced Benefits license. If you license Advanced Benefits, you cannot combine unrestricted and life event processing in the same program. If a plan does not require a life event for electability, attach the plan to a separate, unrestricted program or set up a plan not in program.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, check the No Default Enrollment Applies field if the system takes no enrollment actions when eligible persons fail to specify available elections for plans or options in this program.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, check the No Automatic Enrollment Applies field if the system does not automatically enroll eligible persons in any plans in this program.
-
Select an Enrollment Code or rule that defines a participant's enrollment choices for this program based on whether the participant is currently enrolled in the program.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Save your work.
Defining Coverage Requirements for a Program
You use the Coverage region of the Program Enrollment Requirements window to define when coverage starts and ends for a program, if coverage levels are coordinated between plans in the program, and rules regarding spousal and dependent coverage for insurance plans.
To define coverage requirements for a program:
-
Select an Enrollment Coverage Start Date code or rule to specify when coverage begins for participants who enroll in plans in this program.
-
Select an Enrollment Coverage End Date code or rule to specify when coverage ends for participants who lose eligibility for a plan in this program.
In the Maximum % of Participant Coverage block:
-
Enter a Spouse Insurance Coverage percentage to specify the maximum insurance coverage amount allowed for spouses for all insurance plans in the program, expressed as a percentage of the employee's insurance coverage amount.
Important: If you define spousal or dependent life insurance coverage limits, you must create one plan type for spousal life insurance plans and another plan type for dependent life insurance plans.
-
Enter a Dependent Insurance Coverage percentage to specify the maximum insurance coverage amount allowed for dependents other than spouses for all insurance plans in the program, expressed as a percentage of the employee's insurance coverage amount.
-
Save your work.
Defining an Action Item Due Date (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Action Types window to enter the date by which a person must complete an action item associated with a compensation object.
Action items include enrollment certifications, and dependent and beneficiary designation requirements.
To define an action item due date:
-
Query the compensation object for which you are defining an action item due date in the Program Enrollment Requirements window or the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Choose the Action Types button.
-
Select an action item in the Action Type field.
-
Select an Action Type Due Date code or rule.
-
Save your work.
Defining Activity Rate Enrollment Requirements for a Program
Use the Rates region of the Program Enrollment Requirements window to define when activity rates start and end for the plans in a program.
To define activity rate enrollment requirements for a program
-
Select a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date on which activity rates apply to the plans in this program.
-
Select a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify when activity rates end for participants in the plans in this program.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Requirements for Plan Types in a Program
You can define enrollment requirements that apply to a plan type in a program.
To define enrollment requirements for a plan type in a program:
-
Choose the General tab and then the Plan Type tab in the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Select a Plan Type in this program for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
Check the Coordinate Coverage for All Plans field to specify that participants in this plan type must elect the same coverage options for all plans in this plan type.
-
Choose from the following if you limit insurance coverage for a spouse or a dependent to a percentage of the employee's insurance coverage:
-
Check the Subject to Spouse's Maximum % Insurance Coverage field if for this plan type you are limiting the insurance coverage of the spouse of an employee to a percentage of the employee's insurance coverage.
-
Check the Subject to Dependent's Maximum % Insurance Coverage field if for this plan type you are limiting the insurance coverage of a dependent of an employee to a percentage of the employee's insurance coverage.
Important: If you define spousal or dependent life insurance coverage limits, you must create one plan type for spousal life insurance plans and another plan type for dependent life insurance plans.
-
-
Check the Sum Participant's Life Insurance field if the system determines imputed income and life insurance maximums for this plan type in this program.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, choose from the following if this plan type is part of a flex credit program:
-
Check the Provides Credits field if flex credits are allocated for this plan type.
-
Check the Credits Apply Only To This Plan Type field if flex credits in this plan type cannot be rolled over into other plan types in this program.
-
-
Select a Required Period of Enrollment Value and UOM for this value to describe the period of time in which a participant's elections for all plans in this plan type must be in effect (except in the case of a qualified life event).
To define a required period of enrollment for an option, see: Defining Options.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Limitations for Plan Types in a Program
You can define the minimum and maximum number of plans in which a person can be simultaneously enrolled for a plan type in a program. You can also specify the required enrollment period for the plans in a plan type.
Use the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
To define enrollment limitations for a plan type in a program:
-
Choose the General tab, then the Plan Type tab.
-
In the Limitations region, select a Plan Type in this program for which you are defining enrollment limitations.
-
Check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum number of plans of this plan type in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
Or, enter the Minimum number of plans of this plan type in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
-
Check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum number of plans of this plan type in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
Or, enter the Maximum number of plans of this plan type in which a participant must be enrolled.
In the Required Period of Enrollment block:
-
-
Enter a Value that represents the length of time for which a person must be enrolled in the plans in this plan type.
-
Select the unit of measure of this value in the UOM field.
-
Select a rule if you use a formula to determine the required period of enrollment for the plans in this plan type.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Requirements for a Plan in a Program
If you are an Advanced Benefits customer, you can specify the circumstances under which a plan is the default for a program. A life event reason can override this information.
To define enrollment requirements for a plan in a program:
-
In the Program Enrollment Requirements window, choose the General tab and then the Plan tab.
-
Select the plan in this program for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select the enrollment method, either automatic or based on the participant's explicit choice, in the Method field.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select an Automatic Rule to define the circumstances under which automatic enrollments apply for this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment Code or rule that defines a participant's enrollment choices for this plan based on whether the participant is currently enrolled in the plan.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Check the Allows Unrestricted Enrollment field if the enrollment type for this plan in program is unrestricted.
You must also check the Allows Unrestricted Enrollment field for the program that contains this plan.
Important: You must check this field if you have not purchased an Advanced Benefits license. If you license Advanced Benefits, you cannot combine unrestricted and life event processing in the same program. If a plan does not require a life event for electability, attach the plan to a separate, unrestricted program or set up a plan not in program.
-
Save your work.
Default Enrollment Requirements
You run the Default Enrollment Process from the concurrent manger to create default enrollments based on your plan design and eligibility requirements. Default enrollment processing is only available for Advanced Benefits customers.
To define default enrollment requirements for a plan in a program
-
Choose General -> Plan -> Default in the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Select a Default Enrollment Method Code or Rule for this plan.
-
Check the Assign on Default field if participants who fail to specify an election are enrolled in this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Coverage Requirements for a Plan in a Program
You can define when coverage starts and ends for participants who enroll in a plan in a program. You can also define restrictions to the amount of available coverage provided by a plan.
Use the Program Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the General tab, then the Plan tab, and then the Coverage region.
To define coverage start and end dates for a plan in a program:
-
Select a plan in this program for which you are defining coverage start and end dates.
-
Select an Enrollment Coverage Start Date code or rule to specify when coverage begins for participants who enroll in this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment Coverage End Date code or rule to specify when coverage ends for participants who lose eligibility for this plan.
Note: You should coordinate your coverage start and end dates with your activity rate start and end dates.
-
Save your work.
Defining Coverage Start and End Dates for a Plan Type in a Program
You can define when coverage starts and ends for participants who enroll in a plan type in a program. These coverage dates apply to all the plans in this plan type unless you override the coverage dates at the plan level.
Choose the General tab, then the Plan Type tab, and then the Coverage region.
To define coverage start and end dates for a plan type in a program:
-
Select a plan type in this program for which you are defining coverage start and end dates.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage Start Date code or rule to specify when coverage begins for participants who enroll in a plans in this plan type.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage End Date code or rule to specify when coverage ends for participants who lose eligibility for a plan in this plan type.
Note: You should coordinate your coverage start and end dates with your activity rate start and end dates.
-
Save your work.
Defining Activity Rate Start and End Dates for a Plan in a Program
You can define when activity rates start and end for the plans in a program.
Use the Program Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the General tab, then the Plan tab, and then the Rates region.
To define activity rate start and end dates for a plan in a program:
-
Select a plan in this program for which you are defining activity rate start and end dates.
-
Select a Rate Start Date code or rule to specify the date on which activity rates apply to this plan.
-
Select a Rate End Date code or rule to specify when activity rates end for participants in this plan.
Note: You should coordinate your coverage start and end dates with your activity rate start and end dates.
-
Save your work.
Defining Activity Rate Start and End Dates for a Plan Type in a Program
You can define when activity rates start and end for the plan types in a program. These activity rate dates apply to all the plans in this plan type unless you override the activity rate dates at the plan level.
Choose the General tab, then the Plan Type tab, and then the Rates region.
To define activity rate start and end dates for a plan type in a program
-
Select a plan type in this program for which you are defining activity rate start and end dates.
-
Choose a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date on which activity rates apply to this plan type.
-
Choose a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify when activity rates end for participants in this plan type.
Note: You should coordinate your coverage start and end dates with your activity rate start and end dates.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Scheduled Enrollment for a Program
You use the Program Enrollment Requirements window to define a scheduled enrollment so that eligible persons can enroll, or alter elections, in one or more plans during a specified time period.
For example, you could schedule an open enrollment period for a benefits program from 1 November to 30 November each year.
Standard Benefits customers can define a scheduled enrollment period for a plan or program, but the information is considered read-only and does not restrict enrollment processing.
To define a scheduled enrollment period for a program:
-
Query a program in the Program Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the Timing tab, and then the Scheduled tab.
-
Select an Enrollment Type for the scheduled enrollment period that you are defining for this program.
-
Select a Year Period that applies to the scheduled enrollments for the plans in this program.
-
Enter the enrollment start date in the Persons May Enroll During the Period From field.
-
Enter the enrollment end date in the To field.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, enter a Defaults Will be Assigned on date to specify the date on which default benefits assignments are made when participants fail to make their choices as part of this scheduled enrollment.
-
Choose a No Further Processing is Allowed After date to specify the latest date on which the plan sponsor can apply elections applicable to this enrollment period.
Important: Typically, a third party administrator's requirements for receiving elections information determines this date.
-
Select a Close Enrollment Date To Use code that defines the enrollment closing date based on one of three factors:
-
Processing End Date
-
When Elections Are Made
-
When Enrollment Period Ends
-
-
Select a Period Determination code to control how the application establishes a start and end date for an enrollment period in the following situations:
-
You back-out and reprocess an event
-
The event occurs within the enrollment window of another event
-
A colliding life event occurs
-
-
Choose the Overrides alternate region to override any enrollment period or activity rate start and end dates for this program.
-
Choose an Enrollment Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an enrollment date applies to this scheduled enrollment for this program.
-
Choose an Enrollment End Date Code or Rule to specify the final date on which an override to an enrollment date applies to this scheduled enrollment for this program.
-
Choose a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an activity rate applies to this scheduled enrollment for this program.
-
Choose a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify the final date on which an override to an activity rate applies to this scheduled enrollment for this program.
-
Choose the Reinstate alternate region.
-
Select a Reinstate Code to control how the application reinstates elections when a benefits administrator reprocesses a backed out life event.
-
Select an Override Code to control how the application reinstates previously overriden activity rates for reinstated elections.
-
Save your work.
Establishing Program Life Event Enrollment Requirements
Defining Requirements for a Life Event Enrollment for a Program (Advanced Benefits)
You define a life event enrollment schedule to establish temporal parameters for enrollment, de-enrollment, or changes to elections following a given life event, regardless of when that life event occurs during the plan year.
To define life event enrollment requirements for a program:
-
Query a program in the Program Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the Timing tab and then the Life Event tab.
-
Select the Enrollment Type of Life Event.
-
Select a Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Enter the number of Days After Enrollment Period to Apply Defaults if you define a default enrollment for this program.
-
Enter the number of days persons can fail to respond in the Days After Enrollment Period for Ineligibility field.
Important: After this number of days, the person is no longer eligible to enroll in benefits for which this life event made them eligible.
-
Enter the number of Additional Processing Days allowed.
-
Select a Close Enrollment Date to use code that defines the enrollment closing date based on one of three factors:
-
Processing End Date
-
When Elections Are Made
-
When Enrollment Period Ends
-
-
Choose the Overrides alternate region to override any life event enrollment period or activity rate start and end dates based on this life event.
-
Select an Enrollment Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an enrollment date applies to this life event enrollment for this program.
-
Select an Enrollment End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an enrollment date applies to this life event enrollment for this program.
-
Select a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an activity rate applies to this life event enrollment for this program.
-
Select a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an activity rate applies to this life event enrollment for this program.
-
Choose the Reinstate alternate region.
-
Select a Reinstate Code to control how the application reinstates elections when a benefits administrator reprocesses a backed out life event.
Note: Select the Reinstate Unless New Explicit Elections Exist code to reinstate elections made for a backed out event unless explicit elections have been made within the plan type for an intervening event.
-
Select an Override Code to control how the application reinstates previously overriden activity rates for reinstated elections.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Periods for Life Event Enrollments for a Program (Advanced Benefits)
You can define an enrollment period for a life event so that a participant experiencing this life event has a defined period in which to take an enrollment action.
When you select an enrollment period start date code, the system calculates the start date as of the effective date of the Participation batch process that detected the life event. The enrollment end date is calculated based on the Life Event Occurred on Date which is displayed on the Maintain Potential Life Events window.
To define an enrollment period for life event enrollment for this program:
-
In the Program Enrollment Requirements window, with the Timing tab and then the Life Event tab chosen, choose the Periods region.
-
Select Life Event in the Enrollment Type field to specify that you are defining a life event enrollment.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining an enrollment period.
-
Select an Enrollment Period Start Date and End Date Code or Rule to specify the enrollment period for this life event.
You can set the enrollment period to a specific number of days from the event by selecting one of the following codes:
-
Number of Days from Event
-
Number of Days from Notified
-
Number of Days from later Event or Notified
Choose Event or Notified based on whether you set the enrollment period from the Date Event Occurred or the Date Event Recorded.
-
-
Select a Period Determination code to control how the application establishes a start and end date for an enrollment period in the following situations:
-
You back-out and reprocess an event
-
The event occurs within the enrollment window of another event
-
A colliding life event occurs
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Coverage and Activity Rate Periods for a Plan in a Program
You use the Enrollment Period for Plan window to define start and end dates for enrollment coverage and activity rates for a plan in a program. You can define enrollment periods for scheduled or life event enrollments.
To define an enrollment period for a plan in a program:
-
Select the plan for which you are defining coverage and activity rate start and end dates.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage Start Date code or rule to specify when coverage begins for participants who enroll in this plan.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage End Date code or rule to specify when coverage ends for participants who lose eligibility for this plan.
-
Select a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date on which activity rates apply to this plan.
-
Select a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify when activity rates end for participants in this plan.
-
Save your work.
Associating an Enrollment Rule with a Program
You can associate an enrollment rule with a program. You can also associate such rules with overrides for enrollment or activity rate start and end dates.
To define an enrollment rule for a program:
-
Navigate to the Enrollment Rules window.
-
Enter a Seq (sequence) number for the enrollment rule you are defining for this enrollment or override for this program.
-
Select this Rule.
-
Save your work.
Defining Life Event Enrollment Requirements
You use the Life Event tabbed region of the Program Enrollment Requirements window to define life event requirements for a program, plan type in program, or a plan in program.
Your life event enrollment requirements restrict a participant's enrollment changes based on their current enrollment status.
To define life event enrollment requirements for a plan type or a plan in program:
-
Query the program for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
Choose the Program, Plan Type, or Plan tabbed region based on whether you are defining life event enrollment requirements for a program, plan type in program, or a plan in program.
-
Select the plan type or plan in program for which are defining life event requirements if you selected the Plan Type or Plan tabbed region.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
Only Life Events of the Personal and Work types are displayed in the list of values.
General Change of Life Requirements
-
Choose the General alternate region to define enrollment restrictions based on whether the participant is currently enrolled in this compensation object.
-
Check the Current Enrollment Precludes Change field if a participant who is currently enrolled in this compensation object cannot change elections based on this life event.
-
Check the Still Eligible, Can't Change field if a participant who is still eligible for this compensation object after this life event cannot change their current elections.
-
Select a factor in the Enrollment Change field that limits the compensation objects a participant can change when this life event occurs.
-
Choose the Enrollment alternate region.
-
Select an Enrollment Method code:
Explicit: An eligible person can choose from available offerings following the occurrence of this life event.
Automatic: The system automatically enrolls an eligible person in a given offering following the occurrence of this life event.
-
Select an Enrollment Code or Rule to indicate if the participant can alter elections based on if they are newly or currently enrolled in this compensation object.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Select a Default Enrollment code to specify the default treatment when a person who experiences this life event fails to make an election.
-
For a plan in program, check the Assign on Default field if this plan in program is the default plan for those persons who do not enroll as a result of this life event.
-
Save your work.
Managing Dependent Coverage Enrollment Requirements (Program)
Defining Dependent Coverage Enrollment Requirements for a Program or a Plan Type in Program
You can define how participants designate dependents for a program. Then, all plan types and plans in this program inherit these dependent coverage enrollment requirements unless you specify otherwise at the plan type or plan in program level.
Important: Unless otherwise noted, the dependent coverage requirements you define for a program apply to all compensation objects in this program's hierarchy, regardless of the dependent designation level (plan type or plan) you define.
To define dependent coverage requirements for a program:
-
Query a program in the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Choose the Dependent Coverage tab then choose the Program or Plan Type tab.
-
Select a Designation Level code to specify at what level of the compensation object hierarchy dependent information is recorded for this program or plan type in program.
-
Select the Plan Type in this program for which you are defining dependent coverage enrollment requirements if you choose the Plan Type tab.
-
Select a Program or Plan Type Dependent Designation code to specify whether you require participants to designate dependents when enrolling at any level in this program or plan type.
-
Select a Dependent Coverage Start Code or Rule to specify how the system determines the date on which coverage for dependents in this program or plan type takes effect.
-
Select a Dependent Coverage End Code or Rule to specify the date on which coverage for dependents in this program or plan type ends.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
By default, Advanced Benefits suspends an election if the participant does not provide required information for a dependent, such as a certification or date of birth. For Standard Benefits, the application does not suspend elections.
-
Check the No Certification Needed field to specify that you do not require the participant to submit certification for a dependent to qualify that person as a dependent.
-
In the following fields, select whether you require the participant to provide dependent information.
-
Social Security Number/Legislative ID
-
Date of Birth
-
Address
Note: Failure of the participant to provide this information results in election suspension if you require the information.
-
-
Check the Derivable Factors Apply field to alert the system to the fact that a derived factor is associated with a dependent coverage eligibility profile for this program or plan type.
The system uses this information to determine whether to calculate derived factors. If you do not check this field, then no dependent coverage in any plan types or plans in this program can have any derived factors associated with them.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Certifications for a Program
You use the Dependent Certifications window to date effectively define the certifications necessary to enroll dependents in a program.
To define a dependent coverage certification for a program:
-
Select the dependent coverage Certification Type for this program.
-
Select a Certification Required by value to specify when you require this certification type in order for a participant to enroll in this program.
-
Select a Relationship Type to indicate the kinds of dependents who must provide this certification.
-
Check the Required field if this dependent coverage certification type is required.
-
Check the Preferred field if this dependent coverage certification type is preferred for this program, but not required.
-
Check the Lack of Certification Suspends Designation field if failure to provide this dependent coverage certification type suspends the dependent's enrollment in this program.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles for a Program
You use the Dependent Eligibility Profiles window to link a dependent coverage eligibility profile to a program.
To define a dependent coverage eligibility profile for a program:
-
Select a dependent coverage eligibility profile or a coverage eligibility rule to associate with this program.
-
Check the Mandatory field if a person must meet criteria in this eligibility profile in order to qualify as a dependent for the plans in this program.
Note: If multiple dependent coverage eligibility profiles are attached to the program, a person must satisfy all profiles marked as Mandatory and at least one profile that is not marked Mandatory.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles for a Plan Type in a Program
You use the Dependent Eligibility Profiles window to date effectively maintain dependent coverage eligibility profiles for a plan type in program.
To define eligibility profiles for dependent coverage for a plan type in a program:
-
Select a Profile.
-
Check the Mandatory checkbox if a person must meet criteria in this dependent coverage eligibility profile in order to qualify as a dependent in this plan type in this program.
Note: If multiple dependent coverage eligibility profiles are attached to the plan type in program, a person must satisfy all profiles marked as Mandatory and at least one profile that is not marked Mandatory.
-
Select a Coverage Eligibility Rule if you are using a rule to define the dependent coverage eligibility for this plan type in program.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Change of Life Event Enrollment Requirements
You use the Dependent Change of Life Event window to maintain enrollment requirements for dependents based on life events for a plan type or a program.
Note: For Standard Benefits, you must link the Unrestricted life event to the compensation object at the dependent designation level.
To define dependent coverage change of life event enrollment requirements
-
Select a Life Event for which you are defining life event enrollment requirements for dependent coverage in this plan type or program.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Select a Change Dependent Coverage Code or Rule that limits how a participant can change their dependent coverage when this life event occurs.
-
If this life event results in adding dependent coverage, select a Coverage Start Date code or Rule to specify how the system determines when that coverage begins following the occurrence of this life event.
-
If this life event results in removing dependent coverage, select a Coverage End Date Code or Rule to specify how the system determines when that coverage ends following the occurrence of this life event.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required certification for this life event does not result in election suspension for the participant.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Certifications for Change of Life Event Enrollment Requirements
You use the Dependent Change of Life Event Certifications window to maintain the certifications that you require to enroll a dependent in a plan type or a program after a given life event.
Select a life event in the Dependent Change of Life Event window and choose the Change of Life Event Certifications button.
To define dependent coverage certifications for a change of life event enrollment requirement:
-
Select a Certification Type for this life event.
-
Select a Certification Required By value to specify the date when you require this certification type in order for a dependent to receive coverage following this life event.
-
Select the Relationship Type for which this certification type is generated based on this life event.
-
Check the Required field to specify that this dependent coverage certification type is required.
-
Check the Lack of Certification Suspends Enrollment field if failure to provide this dependent coverage certification type suspends the dependent's enrollment.
-
Save your work.
Defining Plan Enrollment Requirements
Defining an Enrollment Method for a Plan
You define enrollment requirements for a plan or the options in a plan using the Plan Enrollment Requirements window. Enrollment methods restrict when a participant can enroll in a plan.
To define an enrollment method for a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see: Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
With the General tab and the Plan tab selected, choose the Enrollment tabbed region.
-
For Advanced Benefits customers, select an Enrollment Method to specify the type of enrollment this plan uses.
Explicit: An eligible person can choose from available offerings in this plan.
Automatic: The system automatically enrolls an eligible person in a given offering in this plan (Advanced Benefits customers only).
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select an Automatic Rule to define the circumstances under which automatic enrollments apply for this plan.
-
Select a Post-election Edit Rule if you have defined a special post-election processing rule for this plan.
-
Check the Allows Unrestricted Enrollment field if enrollment in this plan is unrestricted.
Important: You must check this field if you have not purchased an Advanced Benefits license. If you license Advanced Benefits, you cannot combine unrestricted and life event processing in the same program. If a plan does not require a life event for electability, attach the plan to a separate, unrestricted program or set up a plan not in program.
-
Check the Enroll in Plan and Option field if this plan requires or allows simultaneous enrollment in both a plan and one or more options in plan.
Important: You should check this field if you define a savings plan where a participant can elect the plan and one or more investment options in the plan.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
By default, Advanced Benefits suspends an election if the participant does not provide required certification. For Standard Benefits, the application does not suspend elections.
-
Select a Code that controls when you require certification for enrollment in this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment Code that defines whether a participant can keep, lose, or choose elections based on if they are currently enrolled in this plan or newly enrolling.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Coverage Requirements for a Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define enrollment coverage requirements for a plan.
To define enrollment coverage for a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see: Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
With the General tab and the Plan tab selected, select the Coverage tabbed region.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage Start Date Code or Rule to specify when coverage begins for participants in this plan.
-
Choose an Enrollment Coverage End Date Code or Rule to specify when coverage ends for participants in this plan.
-
Check the Dependent Covered by Other Plans field if you do not allow a participant to designate a dependent for this plan if the dependent is already covered under another plan.
-
Save your work.
To define coverage restrictions for a plan
-
Query the plan for which you are defining coverage restrictions.
-
Choose the Coverage Restrictions button.
-
Select a value in the Restrict Change Based On field if you want to limit changes in coverage to a plan or an option.
-
Benefit Restriction Applies limits changes in coverage to a plan.
-
Option Restriction Applies limits changes in coverage to an option in a plan.
-
-
Select a value in the Change Restrictions field that limits a participant's ability to decrease or increase coverage in this plan.
In the Values block:
-
Define the minimum coverage level a participant may elect. Choose one of the following options:
-
enter the minimum coverage amount
-
select a Min Rule that determines the fixed minimum coverage amount
-
check the No Min field if the plan defines no minimum coverage amount
-
-
Define the maximum coverage level a participant may elect. Choose one of the following options:
-
enter the maximum coverage amount
-
select a Max Rule that determines the fixed maximum coverage amount
-
check the No Max field if the plan defines no maximum coverage amount.
-
enter the maximum coverage amount a person may elect if they provide certification in the Max with Certification field.
-
-
Enter the maximum multiple coverage value available with certification in the Max with Certification field.
In the Increases block:
-
Define the maximum flat amount increase for a participant who is already enrolled in this plan. Choose one or both of the following options:
-
enter the maximum coverage increase amount in the Max field
-
enter the maximum coverage increase amount available with certification in the Max with Certification field
In the Multiple Increases block:
-
-
Define the maximum multiple coverage increase level for a participant who is already enrolled in this plan. Choose one or both of the following options:
-
enter the maximum multiple increase amount in the Max field
-
enter the maximum multiple increase amount available with certification in the Max with Certification field
Note: Increase levels are based on the options attached to the plan. For example, to restrict a maximum level increase from 1x salary to 3x salary, enter a maximum increase of 2.
In the Interim to Assign block:
-
-
Select an Assign Code or rule that determines the interim coverage to assign in those cases where a participant's election of this coverage has been suspended pending the completion of an action item.
See: Interim Coverage for an explanation of the codes.
Note: Set the profile BEN: Carry Forward Certification profile option to Yes to carry forward interim and suspended coverage created due to coverage restrictions for a life event when there are no coverage restrictions configured for the plan or subsequent life events.
-
Select an Unsuspend Code that defines the enrollment coverage start date to use when a suspended enrollment becomes unsuspended.
Note: If you do not select an unsuspend code, the coverage start date is the date on which the enrollment is unsuspended.
-
Save your work.
-
For Advanced Benefits customers, choose the Life Event Reason button if the available coverage for a plan varies based on a life event.
-
Select the Life Event that causes the available coverage to vary.
Note: The remainder of the fields on the Life Event Reason window function in the same manner as the fields on the Coverage Restrictions window. Complete these fields as necessary to restrict the available coverage for this plan based on this life event.
-
For Advanced Benefits customers, choose the Certifications button if a certification is required to elect coverage at a particular level.
-
Select an Enrollment Certification Type.
-
Select a Certification Required When rule.
-
Check the Required field if this certification is required to receive this coverage amount for this plan.
Note: If you do not check the Required field, the certification is considered preferred.
-
Save your work.
Defining Activity Rates Requirements for a Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define when activity rates start and end for a plan.
To define activity rate requirements for a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
With the General tab and the Plan tab selected, select the Rates tabbed region.
-
Choose a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify when activity rates start for participants in this plan.
-
Choose a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify when activity rates end for participants in this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Limitations for a Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define the minimum and maximum number of options in which a participant can be enrolled in a plan. You can also define the required period of enrollment for a plan.
To define enrollment limitations for a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
With the General tab and the Plan tab selected, select the Limitations tabbed region.
-
Check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum number of options in this plan in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
Or, enter the Minimum number of options in this plan in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
-
Check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum number of options in this plan in which a participant must be enrolled.
-
Or, enter the Maximum number of options in this plan in which a participant must be enrolled.
In the Required Period of Enrollment block:
-
-
Enter a Value that represents the length of time in which a person must be enrolled in this plan.
To define a required period of enrollment for an option, see: Defining Options.
-
Select the unit of measure of this value in the UOM field.
-
Select a rule if you use a formula to determine the required period of enrollment for this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Designation Enrollment Requirements for a Plan or Option in Plan
You use the Designation Requirements window to date effectively define a group relationship for a plan or an option in plan depending if you navigate to the window from the Plan or Option tab. A group relationship limits the relationship types that can be covered under a plan. You can also limit the number of dependents that a plan covers.
To define designation requirements for a plan or option in plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan Enrollment Requirements field.
-
Choose the Plan or Option tab.
-
Choose the Designation Requirements button.
Select a Group Relationship for which you are defining designation requirements.
-
Select Beneficiaries or Dependents in the Type field to indicate the designee type covered by this designation requirement.
-
Enter the minimum and maximum number of designees that can be covered under this plan.
-
Check the No Minimum or No Maximum field if there is no minimum or maximum number of designees for this plan.
-
Check the Cover All Eligible field if there is no minimum or maximum number of designees for this plan and you want to provide coverage to all designees who meet the eligibility profile.
Note: You enter 0 in the Minimum and Maximum fields if the plan allows no designees.
-
Select one or more Relationship Types to include with this group relationship.
-
Repeat steps 4-7 for each group relationship you are defining for this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Requirements for Not in Program Plans
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define special enrollment requirements for plans that you do not associate with a program.
To define enrollment requirements for a not in program plan
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
With the General tab and the Plan tab selected, select the Not in Program tabbed region.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select a Default Enrollment Code or Rule to define how the system processes enrollments when a participant fails to make an election.
See: Enrollment Codes
Note: If an option in this plan is the default option, you must still select this plan as the default plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Requirements for Options in a Plan
You can specify whether an option is ever a default for a plan, and the circumstances under which that option is the default in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window. A life event reason can override this information.
To define general enrollment requirements for an option in a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
The current status of the plan is displayed. For a definition of the plan statuses, see Defining a Benefits Plan.
-
Select the General tab and then the Option tab.
-
Select an Option in this plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
Select a Post-Election Edit Rule if you have defined a special post-election processing rule for this option.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, check the Automatic Enrollment field if an eligible participant is automatically enrolled in this option.
-
Select a Family Member Code or rule to indicate the kind of family members that must be recorded in a participant's contact record in order for that participant to be eligible for this option.
Note: Family members are recorded in the Contacts window.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select an Automatic Rule to define the circumstances under which automatic enrollments apply for this plan.
To define default enrollment requirements for an option:
You run the Default Enrollment Process from the concurrent manger to create default enrollments based on your plan design and eligibility requirements. Default enrollment processing is only available for Advanced Benefits customers.
-
Choose General -> Option-> Default in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Select a Default Enrollment Code or Rule to specify when this option is the default based on a new or existing enrollment.
-
Or, check the Assign on Default field if a participant who fails to specify an election is enrolled in this option as the default.
See: Enrollment Codes
Note: If this is the default option for the plan, you must also define the plan as the default plan.
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Enrollment Limitations for an Option in a Plan
You can define when a participant is required to enroll in an option and the required period of enrollment for an option.
To define enrollment limitations for an option in a plan:
-
Query the plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements in the Plan field.
-
With the General tab and the Option tab selected, select the Limitations tabbed region.
In the Option is Required block:
-
Check the Required field if enrollment in this option is required.
-
Or, select a Rule to limit the conditions under which enrollment in this option is required.
In the Required Period of Enrollment block:
-
-
Enter a Value that represents the length of time in which a person must be enrolled in this option.
-
Select the unit of measure of this value in the UOM field.
-
Select a rule if you use a formula to determine the required period of enrollment for this option.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Scheduled Enrollment for a Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define a scheduled enrollment so that eligible persons can enroll in a plan or change their elections during a specified time period each year.
For example, you could schedule quarterly enrollment periods for a plan from 1 January to 15 January, 1 April to 15 April, 1 July to 15 July, and 1 October to 15 October of each year.
Standard Benefits customers can define a scheduled enrollment period for a plan or program, but the information is considered read-only and does not restrict enrollment processing.
To define an enrollment period for a plan:
-
Query a plan in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the Timing tab, and then the Scheduled tab.
-
Choose an Enrollment Type code for the scheduled enrollment period you are defining for this plan.
-
Select a Year Period to specify the plan year for which this scheduled enrollment applies to this plan.
-
Enter the date on which participants can begin to enroll in this plan in the Persons May Enroll During the Period from field.
-
Enter the last date on which participants can enroll in this plan in the To field.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, choose a Defaults Will be Assigned on date to specify the date on which default assignments are made when participants fail to make their choices as part of the scheduled enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose a No Further Processing is Allowed After date to specify the latest date on which the plan sponsor can apply elections applicable to this enrollment period for this plan.
Typically, a third party administrator's requirements for receiving elections information determines this date.
-
Select a Close Enrollment Date to use code that defines the enrollment closing date based on one of three factors:
-
Processing End Date
-
When Elections Are Made
-
When Enrollment Period Ends
-
-
Select a Period Determination code to control how the application establishes a start and end date for an enrollment period in the following situations:
-
You back-out and reprocess an event
-
The event occurs within the enrollment window of another event
-
A colliding life event occurs
-
-
Choose the Overrides alternate region to override any enrollment period or activity rate start and end dates.
-
Choose an Enrollment Type code for the override scheduled enrollment period you are defining for this plan.
-
Choose an Enrollment Start Date Code or Rule to specify the start date from which an override to an enrollment date applies to this scheduled enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose an Enrollment End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an enrollment date applies to this scheduled enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an activity rate applies to this scheduled enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an activity rate applies to this scheduled enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose the Reinstate alternate region.
-
Select a Reinstate Code to control how the application reinstates elections when a benefits administrator reprocesses a backed out life event.
-
Select an Override Code to control how the application reinstates previously overriden activity rates for reinstated elections.
-
Save your work.
Associating Enrollment Rules with a Plan
You use the Enrollment Rules window to associate a scheduled or life event enrollment rule with a plan.
Navigate to the Enrollment Rules window from the Scheduled or Life Event tab depending if you are defining an enrollment rule for a scheduled or life event enrollment.
To associate an enrollment rule with a plan:
-
Enter a Seq (sequence) number for the enrollment rule you are defining for this plan.
-
Select an enrollment Rule.
-
Save your work.
Setting Up Life Event Enrollment Requirements - Plan (OAB)
Defining Requirements for a Life Event Enrollment for a Plan (Advanced Benefits)
You define a life event enrollment schedule to establish temporal parameters for enrolling, de-enrolling, or changing elections following a given life event, regardless of when that life event occurs during the plan year.
For example, you could allow newly hired employees 30 days to enroll in a plan before requiring that they wait until the next open enrollment period.
To define requirements for a Life Event Enrollment for a plan:
-
Query a plan in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window. Choose the Timing tab and then the Life Event tab.
-
Select the Enrollment Type of Life Event.
-
Select a Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Enter the number of Days After the Enrollment Period to Apply Defaults if you define a default enrollment for this program.
-
Enter the number of days persons can fail to respond in the Days After Which Becomes Ineligible field.
Important: After this number of days, the person is no longer eligible to enroll in benefits for which this life event made them eligible.
-
Enter the number of Additional Processing Days allowed.
-
Select a Close Enrollment Date to Use code that defines the enrollment closing date based on one of three factors:
-
Processing End Date
-
When Elections Are Made
-
When Enrollment Period Ends
-
-
Choose the Overrides alternate region to override any life event enrollment period or activity rate start and end dates based on this life event.
-
Select a life event for which you are defining enrollment override information.
-
Select an Enrollment Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an enrollment date applies to this life event enrollment for this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an enrollment date applies to this life event enrollment for this plan.
-
Select a Rate Start Date Code or Rule to specify the date from which an override to an activity rate applies to this life event enrollment for this plan.
-
Select a Rate End Date Code or Rule to specify the last date on which an override to an activity rate applies to this life event enrollment for this plan.
-
Choose the Reinstate alternate region.
-
Select a Reinstate Code to control how the application reinstates elections when a benefits administrator reprocesses a backed out life event.
-
Select an Override Code to control how the application reinstates previously overriden activity rates for reinstated elections.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Life Event Enrollment Period for a Plan (Advanced Benefits)
You define an enrollment period for a life event to limit the time when a qualifying participant can make a benefit election based on a life event.
Use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
To define a life event enrollment period for a plan:
-
Choose the Timing tab and the Life Event tab and then choose the Periods region.
-
Select a life event for which you are defining an enrollment period.
-
Select an Enrollment Period Start Date and End Date Code or Rule to specify the enrollment period for this life event.
You can set the enrollment period to a specific number of days from the event by selecting one of the following codes:
-
Number of Days from Event
-
Number of Days from Notified
-
Number of Days from later Event or Notified
Choose Event or Notified based on whether you set the enrollment period from the Date Event Occurred or the Date Event Recorded.
-
-
Select a Period Determination code to control how the application establishes a start and end date for an enrollment period in the following situations:
-
You back-out and reprocess an event
-
The event occurs within the enrollment window of another event
-
A colliding life event occurs
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Life Event Enrollment Certifications for a Plan or Option in Plan (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Life Event Certifications window to maintain the certifications that you require to enroll a participant in a plan or option in plan after a given life event.
To define life event enrollment certifications for a plan or option in plan:
-
Select a life event for which you are defining an enrollment certification.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
By default, Advanced Benefits suspends an election if the participant does not provide required certification. For Standard Benefits, the application does not suspend elections.
-
Select a Determination Code that controls when you require certification for enrollment in this plan or option.
-
Select a Certification Required By Rule to specify when you require certification to support enrollment in this plan or option.
-
Select an Enrollment Certification Type that you require or accept for enrollment in this plan or option in plan after this life event.
-
Select a Certification Required By Rule to specify when you require this certification type.
-
Check the Required field to specify that the receipt of this certification type is required before an enrollment is valid after this life event.
-
Save your work.
Defining Life Event Enrollment Requirements for a Not in Program Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define life event enrollment requirements for a not in program plan and to determine when a participant can enroll or change elections in a not in program plan based on the occurrence of a life event.
Important: You define enrollment requirements for plans in program using the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
To define life event enrollment requirements for a not in program plan:
-
Query a plan and choose the Life Event tab.
-
Choose the Plan tab and then choose the General alternate region.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining general enrollment requirements.
Only Life Events of the Personal and Work types are displayed in the list of values.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Check the Current Enrollment Precludes Change field if a participant who is currently enrolled in this plan cannot change elections based on this life event.
-
Check the Still Eligible, Can't Change field if a person who experiences this life event and is still eligible for this plan cannot change his or her current enrollment elections.
Important: You can set the Still Eligible, Can't Change checkbox at the plan in program, not in program plan, and option in plan levels.
-
Select an Enrollment Change code to specify the degree to which a participant can change enrollment in a plan.
-
Choose the Enrollment alternate region.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
Select an Enrollment Method code for this life event enrollment for this plan.
Explicit: An eligible person may choose from available offerings in this plan following the occurrence of this life event.
Automatic: The system automatically enrolls an eligible person in a given offering in this plan following the occurrence of this life event.
-
For Advanced Benefits users, select an Automatic Rule to define the circumstances under which automatic enrollments apply for this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment Code for a life event enrollment you are defining for this plan.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Choose a Default Enrollment Code to specify for this plan the default treatment when a person experiencing this life event fails to make a choice among available choices.
-
Check the Assign on Default field if this plan is the default plan for those persons who fail to make an election as a result of this life event.
-
Save your work.
Defining Life Event Enrollment Requirements for an Option in a Plan
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define enrollment requirements for a life event for an option in a plan. These enrollment requirements override those you define for the plan associated with the option.
For example, you could define enrollment requirements for an Employee Plus Spouse option in a medical plan when the life event Marriage occurs for the participant.
To define life event enrollment requirements for an option in plan:
-
Query a plan and choose the Life Event tab.
-
Choose the Option tab and then choose the General alternate region.
-
Select the option in this plan for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements.
Only Life Events of the Personal and Work types are displayed in the list of values.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Check the Current Enrollment Precludes Change field if a participant who is currently enrolled in this option cannot change elections based on this life event.
-
Check the Still Eligible, Can't Change field if a person who experiences this life event and is still eligible for this option may not change his or her current enrollment elections.
Important: You can set the Still Eligible, Can't Change checkbox at the program, plan in program, and not in program plan levels.
-
Choose the Enrollment alternate region.
-
Select the Life Event for which you are defining enrollment requirements for this option in this plan.
-
Select an Enrollment Code based on whether the participant is currently enrolled in this option.
See: Enrollment Codes
-
Select a Default Enrollment Code to specify for this option in this plan the default treatment when a person experiencing this life event fails to make a choice among available choices.
-
Check the Assign on Default field if this option in this plan is the default for those persons who fail to make an election as a result of this life event.
-
Check the Automatic Rule field if you use a rule to determine if this life event results in automatic enrollment of this option.
-
Select the Automatic Enrollment rule.
-
Save your work.
Managing Dependent Coverage Enrollment Requirements
Defining Dependent Coverage Requirements for a Plan
You can define how participants designate dependents for a plan. Then, all options in this plan inherit these dependent coverage enrollment requirements.
To define dependent coverage requirements for a plan:
-
Query a plan in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Choose the Designations tab and then the Dependent tab.
-
Select a Dependent Designation Code to specify whether you require participants to designate dependents when enrolling in this plan.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
By default, Advanced Benefits suspends an election if the participant does not provide required information for a dependent, such as a certification or date of birth. For Standard Benefits, the application does not suspend elections.
-
Check the No Certification Needed field to specify that you do not require the participant to submit certification for a dependent to qualify that person as a dependent.
-
In the following fields, select whether you require the participant to provide dependent information.
-
Social Security Number/Legislative ID
-
Date of Birth
-
Address
Note: Failure of the participant to provide this information results in election suspension if you require the information.
-
-
Select a Dependent Coverage Start Code or Rule to specify how the system determines the start date for coverage for dependents in this plan.
-
Select a Dependent Coverage End Code or Rule to specify how the system determines the end date for coverage for dependents in this plan.
-
Check the Derivable Factors Apply field to alert the system that a derived factor is associated with a dependent coverage eligibility profile for this plan. (The system uses this information to determine whether to calculate derived factors or proceed.)
Note: If you do not check this field, then no dependent coverage in this plan may have any derived factors associated with it.
-
Click the Certifications button to open the Dependent Certifications window and to define the certifications necessary to enroll dependents in a plan.
-
Select a dependent coverage Certification Type you require or prefer in order for participants to designate dependents for participation in this plan.
-
Select the Relationship Type for which this certification type is required for this plan.
-
Select a Certification Required by value to specify when you require this Certification Type in order for participants to designate dependents for participation in this plan.
-
Check the Required field to specify that this dependent coverage certification type is required.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles for a Plan
You use the Dependent Eligibility Profiles window to link a dependent coverage eligibility profile to a plan.
To define a dependent coverage eligibility profile for a plan:
-
Select a dependent coverage eligibility profile or a coverage eligibility rule to associate with this plan.
-
Check the Mandatory field if a person must meet criteria in this eligibility profile in order to qualify as a dependent for this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Dependent Coverage Change of Life Event Enrollment Requirements for a Plan
You use the Dependent Change of Life Event window to limit dependent designations for a plan based on a life event.
To define dependent coverage change of life event enrollment requirements for a plan
-
Query a plan in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Choose the Designations tab and then the Dependent tab.
-
Choose the Dependent Change of Life Event button.
-
Select a Life Event for which you are defining dependent coverage enrollment requirements.
Note: For Standard Benefits, you must link the Unrestricted life event to the compensation object at the dependent designation level.
Note: To query a life event, enter a wildcard, a string, or a combination to view those life events that meet the entered criteria.
-
Select whether the system adds or removes coverage for a dependent as a result of this life event in the Change Dependent Coverage Code or Rule field.
-
Select a Coverage Start Date Code or Rule if this life event results in adding dependent coverage.
-
Select a Coverage End Date Code or Rule if this life event results in removing dependent coverage.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
-
Choose the Change of Life Event Certifications button to maintain the certifications that you require to enroll a dependent in a plan after a given life event.
-
Select the Certification Type for this life event.
-
Select a Certification Required By value to specify when you require this certification type in order for a dependent to receive coverage following this life event.
-
Select the Relationship Type for which this certification type is required for this life event.
-
Check the Required field to specify that this dependent coverage certification type is required.
-
Save your work.
Setting Up Beneficiary Designation Requirements (Plan)
Defining Certifications for Enrollment in a Plan
You use the Certifications window to define a certification that is required or preferred for enrollment in a plan.
-
Select the Certification Type you require or prefer in order for a participant to enroll in this plan.
-
Select a Certification Required to specify when you require this Certification Type in order for a participant to enroll in this plan following this life event.
-
Check the Required field if failure to provide this Certification Type suspends enrollment in this plan.
-
Save your work.
Defining Beneficiary Designation Requirements for a Plan
You can define beneficiary designation requirements for a plan. Then, all options in this plan inherit these beneficiary designation requirements.
To define beneficiary designation requirements for a plan
-
Query a plan in the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
-
Choose the Designations tab and then the Beneficiary tab.
-
Select the Beneficiary Designation Code to specify whether beneficiary designations for the plan are optional or required.
-
Select the Default Beneficiary Code to specify the type of person (such as a spouse) who is the beneficiary in those cases when the participant fails to designate a beneficiary for the plan.
Note: This field is information-only and does not effect system processing. You must manually designate a person's beneficiaries.
-
Deselect the Suspend Enrollment check box if failure to provide required information does not result in election suspension for the participant.
By default, Advanced Benefits suspends an election if the participant does not provide required information, such as a certification or date of birth. For Standard Benefits, the application does not suspend elections.
-
Check the No Certification Needed field to specify that you do not require the participant to submit certification for a beneficiary to qualify that person as a beneficiary.
-
In the following fields, select whether you require the participant to provide beneficiary information.
-
Social Security Number/Legislative ID
-
Date of Birth
-
Address
Note: Failure of the participant to provide this information results in election suspension if you require the information.
-
-
Select a Measures Allowed code to define if amounts to be distributed to beneficiaries should be specified by percent only or by percent and amount.
-
Select an Increment Amount and Increment Percent to specify how the system expresses benefit amount increments.
-
Select a Min Designatable Amount and/or Percent to specify the smallest monetary amount that a participant can designate to a beneficiary according to the terms of the plan.
-
Check the appropriate fields in the Restrictions block, as needed.
-
Minor Designee Requires Trustee if you require participants to identify a trustee for any beneficiary the governing regulatory body defines as a minor.
-
May Designate Organization as Beneficiary if this plan allows participants to designate an organization such as a charity as a beneficiary.
-
Qualified Domestic Relations Rule Applies if you require the participant to designate a qualified domestic partner as primary beneficiary, or obtain the consent of a qualified domestic partner to name another individual.
-
Additional Instruction Text Allowed if participants can provide a textual description of how benefits are to be distributed to beneficiaries in those cases when the instructions are complex.
-
Contingent Beneficiaries Allowed if this plan allows participants to identify one or more contingent beneficiaries in addition to any primary beneficiaries.
-
-
Choose the Certification button to open the Beneficiary Certifications window.
-
Select the Certification Type you require or prefer in order for participants to designate beneficiaries for this plan following this life event.
-
Select a Certification Required by value to specify when you require or prefer this Certification Type in order for participants to designate beneficiaries for this plan following this life event.
-
Select a Relationship Type to indicate if this plan limits beneficiary designations to a person who is of a particular relationship to the participant.
-
Select a Beneficiary Type to indicate if this plan limits beneficiary designations to either persons or organizations.
-
Check the Required field if this certification is required from a beneficiary.
-
Save your work.
Activity Rates and Coverage Calculations
Activity Rates
You define an activity rate calculation to determine the contribution that an employee (and, in some cases, an employer) spends to purchase a benefit on a recurring or non-recurring basis. Activity rates also determine the monetary distribution paid from a plan such as a savings plan or a flexible spending account.
The process of defining contribution and distribution activity rates varies depending on the complexity of your calculations. These activities include defining:
-
Standard contributions and distributions
-
Prorated partial month contributions
-
Variable activity rates
-
Employer matching rate contributions
-
Imputed income calculations for plans subject to imputed income regulations in the US
As part of your activity rate definition you can also define deduction schedules and payment schedules for contributions and distributions that do not process each pay period.
You can use the Total Compensation Setup Wizard to update multiple standard and variable activity rates simultaneously. You can:
-
correct existing rates or change rates from an effective date onwards
-
update rates for a combination of rate type, plan type, and plan
-
make updates on the page or by way of Web ADI-enabled spreadsheet loaders
Activity Rates and Element Definitions
When you define an activity rate definition, you select the element to which the activity rate corresponds. That way, when the system calculates an activity rate for a person and a benefit plan or option, the result can be captured in the element and transferred to payroll and other areas of your HR system as necessary.
Note: Set up your elements as a prerequisite to defining your activity rates. If your element definition changes, you must re-attach the element to the rate.
If your plan design allows a participant to enroll in more than one plan at a time in a plan type or more than one option in a plan, you create an element for each plan and each option. If you define activity rates at the plan level that cascade to each option in the plan, you must define an element for each option.
You use eligibility profiles, instead of element links, to determine benefits eligibility. Create an open element link for each benefits-related element. Query the benefits element in the Element Link window and save the record without selecting any assignment criteria to create an open link. If necessary, you can set up several links with assignment criteria for costing purposes. However, you must ensure that these links do not conflict with your eligibility profiles.
Normally, you define one input value per activity rate. However, you can select a formula in the Extra Inputs Rule field and map the formula outputs to input values by choosing the Extra Inputs button.
When a participant enrolls in a benefit, the activity rate result is written to the element. You can view the result in the Element Entries window and the Entry Values window. You cannot manually add or edit an entry for an element associated with an activity rate. These entries are maintained by the system when you make an election change or an enrollment override.
See: Defining and Linking an Element for Standard and Advanced Benefits
See: Elements: Building Blocks of Pay and Benefits
Standard Contributions and Distributions
You define a standard contribution or distribution as a calculation that determines the amount a person must pay to participate in a benefit (a contribution) or the amount that is paid to a participant (a distribution).
You associate a standard calculation with a plan or an option in plan so that when a participant makes an election, the contribution or distribution amount is determined.
Standard calculations are used for a variety of plan types, such as medical plans and savings plans. Other plan types require special activity rate calculations, these include flex credit plans and plans subject to imputed income taxes.
Defining a standard contribution or distribution involves:
-
Defining general characteristics of the activity rate
-
Defining the activity rate calculation method
-
Defining prorated activity rates
-
Defining payroll processing requirements
-
Defining variable rate calculations, if applicable
General Characteristics of Activity Rates
For all activity rates, you indicate if the activity type is a contribution or distribution made by the participant or the employer. Examples of activity types include:
-
Employee Individual Contribution
-
Employer Matching Plan Contribution
-
Employer Distribution
You specify the tax basis on which the contribution or distribution is made, such as pretax or aftertax.
If you are defining a calculation for a non-monetary distribution, you can define the unit of measure in which that distribution is expressed, such as Options for stock options.
Activity Rate Calculation Methods
You define an activity rate calculation method to determine the rate of contribution or distribution for a plan or option. In addition to flat rates, the system supports a range of calculation methods including multiple of actual premium and multiple of compensation.
Calculation methods can also set boundaries for the result of the standard calculation. You can define a minimum and maximum contribution or distribution amount for the result of an activity rate calculation.
You can set the increment by which activity rates are expressed and the default activity rate value.
Prorated Activity Rates
For a participant whose enrollment coverage date falls within the month, you can define if the system prorates the activity rate. For prorated activity rates, you can define the date range within the month that is subject to the prorated rate. For example, you may only want to prorate activity rates for participants who enroll between the 5th and the 25th of the month.
You specify the percentage of the standard activity rate used to calculate the prorated activity rate for participants who enroll mid-month.
Activity Rate Payroll Processing
As part of defining an activity rate calculation for a benefit, you define your payroll processing system, such as Oracle Payroll. Then, you define whether the calculation is recurring or non-recurring. For recurring calculations, you can define a schedule for deductions or payments depending if the calculation is for a contribution or a distribution.
You can also define when the activity rate value should be entered. Typically this is at the time of enrollment, but the system also supports automatic rate entry.
Rate Certification (Advanced Benefits Only)
You can enforce certification requirements for a standard rate attached to a plan or option in plan when the plan is not in a program. The element associated with the standard rate is not entered for the participant until you mark the certification as having been received, on the Person Enrollment Certification window. The element is entered based on the rate start date code specified on the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
When you define the standard rate, you can select a certification type from the lookup type BEN_ENRT_CTFN_TYP.
Variable Rates
You can associate a variable rate profile with a standard calculation if the activity rate may vary by participant.
Employer Matching Rates
Note: This feature is reserved for future use.
If you define a plan where the employer matches a percentage of the employee's contribution, such as for a savings plan, you can define how the system calculates the matching rate.
Because employer matching percentages may vary based on the employee's contribution percentage, you may need to define more than one matching rate for an activity rate.
If the benefit plan sets a maximum employee earnings amount or a maximum contribution percentage beyond which a matching rate should not be calculated, you can define this maximum earnings amount or contribution percentage. That way, if the employee's earnings or contribution percentage exceeds the limit, the system calculates the matching rate based on the maximum amount or percentage that you define.
You define the matching contribution percentage based on the employee's contribution percentage. However, you can also define minimum and maximum employer contribution limits.
Period-to-Date Limits
Note: This feature is reserved for future use.
For those plans with contribution limits, you can associate a period-to-date limit with the activity rate that determines the contribution amount. Period-to-date limits are often used with 401(k) plans in the US.
Variable Rate Profiles
You can define an activity rate for a benefit that varies based on some factor. You group together the factors that cause an activity rate to vary into a variable rate profile. You then associate the variable rate profile with an activity rate which, in turn, you associate with a particular benefit plan or option.
As with participant eligibility profiles, variable rate profiles may consist of employment factors, personal factors, derived factors, and other factors such as participation in a particular benefits plan.
You can use a participant eligibility profile that you have defined as a criteria set in a variable rate profile. This lets you define your criteria once, then reuse the criteria set to control both eligibility and variable rates. Oracle recommends attaching eligibility profiles to variable rates--as opposed to individual criteria--to improve system performance.
Note: You can only attach one participant eligibility profile to a variable rate profile. You cannot attach an eligibility profile to a variable rate profile if you have already attached existing criteria to the profile. However, you can remove any existing criteria, then attach an eligibility profile.
Most variable rate profiles are defined so that participants who meet certain criteria are eligible to receive the variable rate. However, you can also define a variable rate profile so that persons who meet the criteria become excluded from receiving the variable rate. In such cases, the standard activity rate for the benefit applies to these persons.
FastFormula Rules in Variable Rate Profiles
If you use a FastFormula rule as part of your variable rate profile, the participant must meet the criteria of the rule and one value from any other criteria that you include in the profile. If you use more than one FastFormula rule, by default the participant must meet the criteria of all the rules. If you change the user profile option BEN:VAPRO Rule from AND to OR, the participant need only meet the criteria of one rule.
You can associate a variable rate profile with the following kinds of activity rates:
-
Standard contributions and distributions
-
Flex credit calculations
-
Imputed income calculations
-
Actual premiums
-
Reimbursement plan rates (for flexible spending accounts)
Coverage Calculations
A coverage calculation defines the level of benefits coverage a participant receives under plans such as a group term life insurance or accidental death & dismemberment insurance plan.
Typical business requirements allow a participant to choose either a flat coverage amount or an amount that is a multiple of the participant's salary. The system also supports many other coverage calculation methods.
Here are several of the aspects of a coverage calculation that you can define:
-
Minimum and maximum coverage amounts
-
Maximum coverage amount available with certification (Advanced Benefits)
-
Maximum coverage increases for flat amounts and coverage amounts that are a multiple of a given value
-
Prorated coverage for employees who enter flexible spending accounts at any time other than the beginning of the plan year
When you define a coverage calculation method you define if the coverage level amount is entered at the time of enrollment or during the definition of the coverage calculation. You can choose from the following calculation methods depending on the requirements of the plan:
-
Flat fixed amount
-
Flat range
-
Flat amount plus multiple of compensation
-
Flat amount plus multiple of compensation range
-
Multiple of compensation
-
Multiple of compensation plus flat range
-
Multiple of compensation range
-
No standard value
-
Same as annualized elected activity rate
-
Post Enrollment Calculation Rule
If necessary, you can associate a variable rate profile with a coverage calculation when the calculation may vary by participant.
You can define a life insurance plan where spouse or dependent coverage is a percentage of the participant's elected coverage. Write a FastFormula with a rule type of Coverage Amount Calculation and attach the rule to the coverage calculation using the Post Enrollment Calculation Rule.
This formula executes both when you run the Participation Process to determine electable choices and when you save an enrollment or choose the Recalculate button on the Flex Enrollment window, Non-Flex Enrollment window, or the Benefits Selection page in Self-Service.
Note: Since the formula executes when you run the Participation Process, the coverage amount selected by the employee may not be available. Therefore, the formula should contain a default coverage value.
Coverage Across Plan Types
For those benefit programs that restrict the amount of coverage that a participant can elect across plan types in a program, you can group the plan types in the program to which a minimum or maximum coverage amount applies.
Cross plan type coverage limits work in conjunction with coverage limits you define at the plan level. If you define a maximum coverage limit at the plan level, the cross plan type coverage limit must not have a maximum coverage level that is less than the maximum you set for a plan in that plan type.
For example, suppose your organization defines a Group Term Life Insurance plan type. Within that plan type, you offer the Employee Group Term Life Insurance plan that provides coverage equal to two times earnings up to a maximum of $200,000.
You also maintain a corresponding plan type for Non-Group Term Life Insurance plans. In this plan type, you define a plan that has a maximum coverage level of $120,000.
You could define an across plan type coverage limit called "All Life Insurance Maximum" that limits the maximum coverage a participant can elect across these two plan type to $300,000.
Interim Coverage (Advanced Benefits)
As part of your plan design, you can define the interim coverage assigned to a participant when a participant's enrollment in a benefit is suspended pending the completion of an action item.
For example, you might require a certificate of good health from a participant who is currently enrolled in a life insurance plan with a coverage level of 1x compensation if the participant newly elects a coverage of 3x compensation during an open enrollment period. If you suspend the new election pending receipt of the certification, you can provide interim coverage until the certification is provided.
Interim Coverage Determination
You can qualify the conditions under which interim coverage is provided based on the participant's current enrollment and the new suspended election. You can either use an interim to assign code or an interim to assign rule to determine the interim electable choice.
Interim to Assign Code
Each interim to assign code contains two parts.
-
The first part identifies if the suspended election is current or new. Current means that the suspended enrollment is for the Same Option in Plan, Same Plan, or Same Plan Type as the participant's current enrollment.
-
The second part defines the interim coverage that is provided. You have the following options:
-
Same: The system assigns the person's current election as interim coverage.
-
Next Lower: The system assigns as interim coverage the plan in plan type, option in plan, or coverage amount of a range that is the next lower sequence that will not be suspended based on your plan or option definitions. You assign a sequence number when you define a plan or option.
-
Default: The system assigns as interim coverage the default compensation object or coverage amount defined for the plan, based on the default enrollment codes.
-
Min: The system assigns as interim coverage the minimum option in plan, plan in plan type, or coverage amount within a range defined for the plan.
-
Nothing: The system assigns no interim coverage in place of the suspended coverage.
Example: Current Same Plan Type, Default; New, Nothing--This code means that if the participant is currently enrolled in a plan of the same plan type, they are assigned the default coverage; if they are not currently enrolled in a plan of the same plan type, they receive no interim coverage.
-
Interim to Assign Rule
The interim to assign rule provides greater flexibility in interim cover determination. You configure an interim to assign rule to return one of the following parameters that meets your business requirements:
-
An interim to assign code
-
An electable choice ID within the plan type of the suspended enrollment
-
An electable choice ID within the plan type of the suspended enrollment, and a benefit amount, which must be less than the amount for the suspended enrollment.
Note: Return a benefit amount only if the interim coverage calculation method is:
-
Flat range
-
Flat amount, and the Enter Value at Enrollment option is selected
-
For more information about the Default to Assign Pending Action formula type, see Oracle HRMS FastFormula Reference Guide available on My Oracle Support (Note ID 218059.1).
Unsuspended Enrollments (Advanced Benefits)
For those cases where a suspended enrollment is unsuspended, you define the enrollment coverage start and end dates and the activity rate start and end dates for the unsuspended enrollment.
If you assign interim coverage when an enrollment is suspended, the interim enrollment is ended one day before the coverage start date of the unsuspended enrollment.
You select an unsuspend enrollment code that controls the enrollment coverage start date of the unsuspended enrollment if the unsuspended date is equal to or later than the original enrollment coverage start date. Select from the following codes:
-
As of Completed Date This code sets the enrollment coverage start equal to the effective date on which the enrollment is unsuspended.
-
Use Existing Enrollment Start Date This code uses the original enrollment coverage start date, even if this date is before the suspension end-date.
-
Recalculate Using Completed Date and Enrollment Start Date CodeThis code recomputes the enrollment coverage date using the un-suspended date as the life event occurred on date or notification date (depending on your life event definition) if the computed coverage start date is less than the effective date of the un-suspension.
The activity rate start and end dates are re-calculated based on the enrollment coverage start date of the unsuspended enrollment.
Imputed Income Calculations (US only)
Section 79 of the US Internal Revenue Service code defines imputed income as certain forms of indirect compensation termed fringe benefits, and taxes the recipient accordingly. You define imputed income calculations to calculate the amount of a benefit that is taxable as imputed income.
For example, if you offer a group term life insurance plan that provides coverage in excess of $50,000 to a participant or in excess of $2,000 to a spouse or dependent, you can define an imputed income calculation that determines the amount of coverage that is subject to imputed income tax regulations.
You can select the payroll system that processes the imputed income calculation and the manner in which the calculations are processed. If your payroll system calculates imputed income on a basis other than every pay period, you can associate one or more payment schedules with the imputed income calculation.
Note: By default, the imputed income calculation assumes that the employer pays 100% of the benefit, and the benefits system does not subtract employee contributions from the calculation. However, you can set the BEN:Imputed Income Post Tax Deduction profile to Y so that the imputed income process deducts the sum of all standard rates defined as Subject to Imputed Income with a Tax Type of After Tax and an Activity Type of either Employee Payroll Contribution, Employee Individual Contribution, or Employee Plan Contribution.
For employees whose participation in an imputed income plan begins mid-month, you can define partial month treatment rules.
You can also restrict the calculation to a subset of people according to assignment type or types (such as Employee, Benefits, or Employee then Benefits).
You associate a variable rate profile with an imputed income calculation because imputed income taxes vary based on a person's age.
See: Imputed Income Plans (US)
Actual Premium Calculations
Premiums are the amount paid by a benefit plan sponsor to the supplier of a benefit. Typically, premiums are calculated on a per-participant basis, but the system also supports premium calculation based on the total participants enrolled in a plan or the total volume of elected coverage.
You can think of premium determination and processing as divided into the following areas:
-
Premium calculation setup
-
Premium determinations that occur during enrollment
-
Recalculation of premiums based on life events (Advanced Benefits)
-
Premiums and credits are determined by the Premium Calculation batch process at month end
-
Manual adjustment of calculated premiums by participant or by plan and review of monthly premium totals
Premium Calculation Setup
You setup premiums calculations to define how the system calculates, costs, and administers premiums. The system supports the administration of the following premium types:
-
regular premiums that are calculated on a per-participant basis
-
premiums based on the total number of participants covered in a plan or option in plan
-
premiums based on the total coverage volume elected in a plan or option in plan
You can calculate premiums prospectively (in advance of the period of coverage) or retrospectively (as a result of coverage previously received). Premium are calculated on a monthly basis in accordance with the most common business practices of benefit suppliers. The system supports pro-rated premium calculations for benefits participants who gain or lose coverage mid-month. You can also define a standard wash rule so that participants who are covered by a plan for less than a full month have no premium obligation.
You can choose how to cost a participant's premium so that the contribution is distributed to the appropriate general ledger account. A single plan or option can have multiple premiums so that, for example, you could calculate one premium for an employee contribution and a second premium for the employer contribution.
Premium setup also includes defining the calculation method you use to determine the premium, including any variable rates. You link premium calculations to the benefit supplier organization so that premiums can be remitted to the appropriate source.
Premiums Based on Total Participants or Total Coverage Volume
For premiums that are determined based on the total number of participants or the total coverage volume elected by all participants in a plan or option in plan, you use variable rate profiles to calculate the premium.
You select a variable rate criteria of Total Participants or Total Coverage Volume and then define a variable rate calculation that determines the premium based on the number of participants or the coverage volume that you specify.
Note: Variable rates for actual premiums must have a tax type of Not Applicable.
Enrollment Based Premium Determination
Premiums that are calculated on a per-participant basis are determined when a participant elects a plan or option in plan.
At month end, you run the Premium Calculation batch process from the Concurrent Manager to select the participants for whom you want to write a premium result.
You can then view monthly premium results by participant in the Monthly Participant Premium window or by plan and option in the Monthly Plan or Option Premium window.
Note: Premiums that vary based on the total number of participants or the total coverage volume elected by all participants for a plan or option in plan are determined only when you run the Premium Calculation batch process.
Premium Changes Based on Life Events (Advanced Benefits)
You can define premiums that vary based on life events.
You link a life event reason that you have defined to a premium definition so that when a participant experiences this life event the premium is recalculated.
Note: You can define a life event such that its impact only effects a participant's premium, and not their eligibility for benefits.
Calculation of Monthly Premiums and Credits by Batch Process
You run the Premium Calculation batch process from the Concurrent Manager to calculate monthly premiums. By selecting parameters, you can control the plan or option in plan for which premiums are calculated. You can also select the processing month and year and the participant or participant groups for whom a premium is calculated.
The batch process uses your premium definition to determine the per participant premium or the total premium for the compensation object depending on your premium type.
Note: You cannot select parameters that limit the results of the Premium Calculation process by person criteria for calculations that allocate premiums to participants based on the total number of participants in a plan or option.
For premiums that have been paid but which should not have been paid (due to retroactive changes or an error in processing), the Premium Calculation process allocates credits to offset the result of the previously paid premium. Credits are applied against the premium due for the current month.
Your credit lookback processing rules determine how credits are applied to a premium. If you restrict the application of credits to the current plan year or you restrict credit lookbacks to a particular length of time, the system does not apply credits to the current premium if the month from which the credits are due is outside the boundary of the credit lookup period.
Credits can only be applied to premiums that are calculated on a per-participant basis. In all cases, the applied credits cannot exceed the premium due.
Manual Premium Adjustments
The product lets you manually adjust a premium result both for a participant and for the premium total for a plan or option in plan. Use this feature if making a manual adjustment to a premium result is a more efficient means of correcting a premium error than recalcuating the premium.
Period-to-Date Limits
For those plans where there is a regulated maximum contribution amount (such as a 401(k) plan in the US) or where a participant has discretion over the amount contributed into the plan, you can define period-to-date maximum contributions.
These maximums are specified either by the plan itself or, as is true in the US, by regulations. In addition to straightforward limits in which the period-to-date amount, once reached, stops subsequent contributions for the remainder of the period, other, more complex, limits must be enforced.
Benefit Balances
You use the Benefit Balances window to create a benefit balance that you can then associate with a person or a formula.
For example, you might define a benefits balance for use when calculating how many flex credits an employee can be given to spend on benefits as part of a flex program.
Benefit balances are useful in transitioning data from a legacy benefits system to Oracle HR.
Variable Rate Factors
You can define from one to dozens of variable factors for a variable rate profile. A participant must meet all the criteria in your variable rate profile in order to receive the variable rate.
Personal Factors
You select personal factors by choosing the Personal tab in the Variable Rate Profiles window.
Uses the first three enabled segments defined for the Competency Key Flexfield for the business group as criteria.
Disabled Uses an employee's disability category as criteria.
Gender Uses a person's gender as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Leaving Reason Uses an employee's termination reason as criteria. This criteria is often used for continuing benefits eligibility, such as for COBRA in the US.
Opted for Medicare Uses whether an employee is enrolled in the US Medicare program as criteria.
Person Type Uses a person's person type(s) as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Postal Zip Uses individual zip/postal codes or ranges of zip/postal codes as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Qualification Title Uses a person's qualification title, such as an advanced education degree, as criteria.
Service Area Uses a person's service area, such as a city or other geographical area, as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Tobacco Use Uses whether or not a participant uses tobacco as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate. In countries where it is illegal to hold information about a person's tobacco usage, for example, Italy, this personal factor is unavailable.
Employment Factors
You select employment factors by choosing the Employment tab of the Variable Rate Profiles window.
Assignment Set Uses an employee's assignment or a set of assignments as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Assignment Status Uses a person's state of employment (Active, Inactive, or On Leave) as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Bargaining Unit Uses an employee's bargaining unit (local union group) as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Full/ Part-time Uses whether an employee works full-time or part-time as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Grade Uses an employee's grade as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Hourly/Salaried Uses whether an employee is hourly or salaried as criteria.
Job Uses an employee's job classification as criteria.
Labor Union Member Uses whether an employee is a labor union member as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Leave of Absence Uses an employee's leave of absence reason as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Legal Entity Uses an employee's legal entity (GRE) as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate (US only)
Organization Unit Uses an employee's organization as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Pay Basis Uses an employee's pay basis as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Payroll Uses an employee's payroll as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
People Group Uses a participant's people group as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Performance Rating Uses an employee's performance rating as criteria.
Position Uses a person's position as criteria.
Quartile in Grade Uses an employee's pay range for a grade, divided by four, to determine the quarter into which the person's salary amount falls.
Range of Scheduled Hours Uses the number of hours an employee is scheduled to work as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate. This is taken from the Working Hours field on the assignment. For employees with more than one assignment, the hours are totaled across all assignments if you check the 'Use All Assignments for Eligibility' check box on either the Programs or Plans window. If you define multiple scheduled hours ranges, the Participation Process evaluates each range as an 'Or' condition.
Work Location Uses an employee's work location as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Derived Factors
You select derived factors by choosing the Derived Factors tab of the Variable Rate Profiles window.
Age Uses an employee's age as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Combined Age and Length of Service Uses an employee's combination age and length of service factor as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Compensation Level Uses an employee's compensation level as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Full Time Equivalent Uses an employee's percent of full-time employment as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Hours Worked in Period Uses an employee's hours worked in a given period as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Length of Service Uses an employee's length of service as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Other Factors
You select other factors by choosing the Other tab in the Variable Rate Profiles window.
Benefits Group Uses a person's benefits group as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
COBRA Qualified Beneficiary Uses whether a person is considered a qualified beneficiary under COBRA regulations to determine the variable rate (US only).
Continuing Participation Used to set the date on which an ex-employee's payment for a continuing benefit must be received.
Health Coverage Selected Uses the plan and option in plan in which the participant is enrolled as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Participation in Another Plan Uses a person's participation in a particular plan as a variable factor to associate with an activity rate. You can use this factor to define special rates when two plans are elected in conjunction with one another.
Rule Uses a FastFormula rule that you define to determine a variable factor to associate with an activity rate.
Total Coverage Volume Uses the total coverage elected for a plan or option in plan by all participants as a variable factor in determining the actual premium owed by a plan sponsor to the benefits supplier.
Total Participants Uses the total number of participants covered by a plan or option in plan as a variable factor in determining the actual premium owed by a plan sponsor to the benefits supplier.
Related Coverages
The criteria available under the Related Coverages tab are designed primarily for COBRA administration in the US but, you can use them for other purposes.
Calculation Methods: Values, Increments, and Operations
You select a calculation method to help you define the contribution or distribution activity rate for a plan or option. Calculation methods are composed of values that you define, operations that you perform on those values, and, in some case, values from the results of other calculations that you have defined.
The following list describes the components that you can include in an activity base rate calculation.
-
Flat Amount: A standard rate that does not vary or an amount you enter as part of a more complex calculation.
-
Minimum Value: The smallest amount a participant can elect to contribute or receive as a distribution.
-
Maximum Value: The largest amount a participant can elect to contribute or receive as a distribution.
-
Increment: The units participants must use to specify elected amounts during enrollment. For example, if the increment value is 100, participants must specify amounts in whole hundreds of currency.
-
Default Value: The value assigned to the participant during a default enrollment or when a participant fails to specify an explicit value when one is required during enrollment.
-
Operation: A mathematical operator that is applied to a value, such as Multiplied by or Percent of.
-
Actual Premium: The per-participant amount paid by a plan sponsor to the benefits supplier.
-
Coverage: The amount of coverage available under the plan or option for which you are defining the activity rate.
-
Coverage Operation: A mathematical operator that is applied to a coverage amount.
-
Compensation Level: The participant's salary.
-
Rounding Code/Rule: Specifies how the system rounds the result of the calculation when the value is not a fixed amount.
-
No Standard Values Used: The calculation always uses a variable rate.
-
Post Enrollment Calculation: This method calculates a person's standard rate or coverage amount based on election information entered during enrollment. It requires that you write a FastFormula rule type of Rate Value Calculation (for rates) or Coverage Amount Calculation (for coverages) and attach the rule to the activity rate definition.
The Participation Process evaluates this rule when first determining electable choices and rates and again after you choose the Recalculate button on the enrollment window. Therefore, your rule must use default electable choice information or return values that will not cause the formula to error when you run the Participation Process.
-
Rule: Uses a FastFormula rule to structure the calculation.
Activity Rate Calculations
The tables below contain sample activity rate calculations for the various calculation methods that you can use with a standard contribution/distribution or a flex credit calculation.
Flat Amount
| Calculation | Value |
| Example | 5 |
Result = 5
Flat Amount Entered at Enrollment
| Calculation | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Increment | Default Value |
| Example | 1,000 | 10,000 | by 1 | 5,000 |
Result = 5,000 (can be changed at enrollment to value between 1,000 and 10,000)
Multiple of Compensation or Balances
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Compensation |
| Example | 1 | Per 10,000 | 25,000 |
Result = 2.5 (1/10,000) x 25,000
Multiple of Compensation or Balances, Enter Value at Enrollment
| Calc | Min Val | Max Val | Increment | Default | Operation | Comp Lvl |
| Example | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | Per 10,000 | 25,000 |
Result = 2.5 (1/10,000) x 25,000
*5.0 (2/10,000) x 25,000
7.5 (3/10,000) x 25,000
Multiple of Compensation or Balances and Coverage
| Calc | Value | Operation | Compensation | Coverage Operation | Coverage |
| Example | (0.0001 | Multiplied by | 25,000) | Per 10,000 | 100,000 |
Result = 25.0 ((.0001 x 25,000) / 10,000) x 100,000
Multiple of Coverage
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Coverage |
| Example | 5 | Per 100,000 | 200,000 |
Result = 10 (5 / 100,000) x 200,000
Multiple of Coverage, Enter Value at Enrollment
| Calc | Min Val | Max Val | Increment | Default | Operation | Coverage |
| Example | 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 | Per 100,000 | 200,000 |
Result = 4 (2/100,000) x 200,000
*8 (4/100,000) x 200,000
12 (6/100,000) x 200,000
Multiple of Parent Rate
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Activity Base Rate (Parent Rate) |
| Example | 1 | Multiplied by | 2.5 |
Result = 2.5 (1 x 2.5)
Multiple of Parent Rate and Coverage
| Calc | Value | Operation | Parent Activity Rate | Coverage Operation | Coverage |
| Example | (1 | Multiplied by | 8) | Per 100,000 | 100,000 |
Result = 8.0 ((1 x 8) / 100,000) * 100,000
Multiple of Actual Premium
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Actual Premium |
| Example | 50 | Percent | 8 |
Result = 4 (50 / 100) x 8
Multiple of Actual Premium and Coverage
| Calc | Value | Operation | Actual Premium | Coverage Operation | Coverage |
| Example | (10 | Percent of | 8 | Per 10,000 | 100,000 |
Result = 8.0 ((10 / 100 * 8) / 10,000) x 100,000
Coverage Calculations
You use the Coverages form to calculate the coverage amount available for a plan or an option. You can set the contribution rate necessary to purchase this coverage using the Standard Rates window.
The tables below contain sample coverage calculations for the various calculation methods that you can use in defining coverage for a benefit.
Flat Amount
| Calculation | Value |
| Example | 50,000 |
Result = 50,000
Flat Range
| Calculation | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Increment | Default Value |
| Example | 30,000 | 50,000 | by 10,000 | 40,000 |
Result = 30,000
*40,000
50,000
Multiple of Compensation
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Compensation Level |
| Example | 2 | Multiplied by | 25,000 |
Result = 50,000 (2 x 25,000)
Multiple of Compensation Range
| Calc | Min Val | Max Val | Increment | Operation | Comp Lvl | Default |
| Example | 2 | 6 | 2 | Multiplied by | 25,000 | 4 |
Result = 50,000 (2 x 25,000)
*100,000 (4 x 25,000)
150,000 (6 x 25,000)
Flat Amount Plus Multiple of Compensation
| Calc | Value | Min Val | Operation | Comp Lvl | |
| Example | 50,000 | Plus | (2 | Multiplied by | 25,000) |
Result = 100,000 50,000 + (2 x 25,000)
Flat Amount Plus Multiple of Compensation Range
| Calc | Val | Min Val | Max Val | Increment | Operation | Comp Lvl | Default | |
| Example | 50,000 | Plus | (2 | 6 | 2 | Multiplied by | 25,000) | 4 |
Result = 100,000 50,000 + (2 x 25,000)
*150,000 50,000 + (4 x 25,000)
200,000 50,000 + (6 x 25,000)
Multiple of Compensation Plus Flat Range
| Calc | Val | Operation | Comp Lvl | Min Val | Max Val | Increment | Default | |
| Example | (2 | Multiplied by | 25,000) | Plus | 30,000 | 50,000 | 10,000 | 40,000 |
Result = 80,000 (2 x 25,000) + 30,000
*90,000 (4 x 25,000) + 40,000
100,000 (6 x 25,000) + 50,000
Actual Premium Calculations
You use the Calculation Method tabbed region of the Actual Premiums window to define the calculation that determines the actual premium rate per participant for a plan or an option.
The tables below contain sample actual premium calculations for the various calculation methods that you can use with an actual premium calculation.
Flat Amount
| Calculation | Value |
| Example | 5 |
Result = 5
Multiple of Coverage
| Calculation | Value | Coverage Operation | Coverage |
| Example | 5 | Per 100,000 | 200,000 |
Result = 10 (5 / 100,000) x 200,000
Multiple of Total Coverage
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Total Coverage |
| Example | 1 | Per 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
Result = 1000 (1 / 1000) x 1,000,000
Multiple of Total Participants
| Calculation | Value | Operation | Total Participants |
| Example | 5 | Multiply By | 50,000 |
Result = 250,000 5 x 50,000
Defining Standard Contributions and Distributions
Defining Activity Rates for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
You create a separate contribution or distribution activity rate calculation for each plan or option in your benefits offering that requires a contribution or distribution. After you link the calculation to the plan or option, you define the calculation.
You date effectively maintain standard contributions and distributions using the Standard Rates window. You can also use Total Compensation Setup Wizard to update multiple rates simultaneously.
To define an activity rate for a standard contribution/distribution
-
Enter or query the standard contribution or distribution that you are defining in the Name field.
-
Select the Status of this activity rate.
Pending: This plan or option in plan currently does not use this calculation, but could in the future if you change the Status of this calculation to Active. Select the Pending status when setting up a standard contribution/distribution calculation that possibly may not become Active.
Active: The system currently calculates this standard contribution/distribution for this plan or option in plan.
Inactive: The system currently does not calculate this standard contribution/distribution for this plan or option in plan.
Closed: The system currently does not calculate this standard contribution/distribution, nor will it do so in the future.
-
Choose the General tabbed region if it is not already selected.
-
Select the Level in the compensation object hierarchy at which you are defining the activity rate.
-
Select the Compensation Object for which you are defining the activity rate.
-
Select an Activity Type code that identifies the business function this calculation performs, such as an Employee Contribution or an Employer Payroll Distribution.
-
Select the Tax Type indicating the tax impact of this calculation to participants.
You select this Tax Type primarily for classification purposes; the payroll system is primarily responsible for processing taxability.
-
Select a Usage code that limits the use of this activity rate to a particular kind of contribution or distribution.
-
Select a UOM (unit of measure) to express the result of this calculation if this activity rate is for a non-monetary distribution.
-
Select an Element Determination Rule. The application uses this rule to determine an employee's currency for the worksheet amount rate if you choose a Determination Code of Automatic or do not choose a determination code.
See: Defining Processing Information for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
-
Select the Element you defined that corresponds to this activity rate definition.
Note: Set up your elements as a prerequisite to defining your activity rates. If your element definition changes, you must re-attach the element to the rate. For an absence plan, you must also re-select the Extra Input Rule and re-map the input values to formula results.
-
Check the Element and Input Value Required field.
-
Select the Input Value for the activity rate, such as pay value.
-
If you are defining a rate for an absence plan and you need to associate more than one input value with the activity rate, select the Extra Input Rule. This is a formula that calculates the values to be returned to the other input values. When you have finished defining the rate, choose the Extra Inputs button to associate the formula results with the appropriate input values.
-
Check the Uses Variable Rate field if the result of this calculation varies due to some factor or other piece of discreet data about the participant and you associate a variable rate profile with the calculation.
To associate a variable rate profile to this activity rate, see Associating a Variable Rate Profile with a Standard Contribution/Distribution Calculation
-
Select the Parent/Child code to specify whether this calculation is a parent activity rate (the primary activity rate) or a child activity rate (dependent upon the parent activity rate).
-
Check the Subject to Imputed Income field if the activity rate for this compensation object is governed by US imputed income regulations.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Calculation Method for a Standard Contribution or Distribution
You use the Calculation Methods region of the Standard Rates window to define how a standard activity rate is calculated.
See Also
Calculation Methods: Values, Increments, and Operations
Example: Activity Rate Calculations
To define a calculation method for a standard activity rate:
-
Query the activity rate for which you are defining a calculation method in the Name field.
-
Select the method you are using to calculate the activity rate in the Calculation Method field.
Important: The window changes based on the calculation method you select.
-
Complete your calculation definition based on the calculation method you select.
-
Save your work.
Defining Proration for a Standard Contribution or Distribution Calculation
You can specify how the system prorates a calculation (usually a contribution) when a participant's enrollment coverage date falls within a month, and the plan requires that activity rates be prorated based on the date during the month when the participant's coverage starts.
To define proration for a standard contribution/distribution calculation
-
Enter or the query the standard activity rate for which you are defining a prorated value in the Standard Rates window.
-
Select the Partial Month Determination tabbed region.
-
Select a Partial Month Determination Code or Rule to specify how the system calculates this standard contribution/distribution when a participant's enrollment coverage date falls within a month.
All: The system calculates this activity rate as if the participant was enrolled for the entire month.
None: The system calculates this activity rate as if the participant was not enrolled at all for the entire month.
Prorate Value: The system prorates this standard contribution/distribution based on the percentage of the month the participant was enrolled. Use the Proration window to define your proration method for this calculation.
Rule: If special circumstances apply, select a rule that the system uses to calculate this activity rate when a participant's enrollment coverage date falls within a month.
Wash Rule: If special circumstances apply, select a wash rule that the system uses to calculate the day on which to apply the wash rule day for this activity rate.
-
Select an Effective Date Code or Rule to specify how the system calculates the effective date from which the partial month is calculated.
-
Enter a Wash Rule Day if participants whose activity rate start date begins after the wash rule day do not receive a contribution or distribution for that month.
-
Conversely, participants whose activity rate end date is before the wash rule day do not receive a contribution or distribution for that month.
-
-
Choose the Proration button to open the Proration window if you select a partial month determination code of Prorate Value.
-
Select the Prorate on day/month basis check box to base your proration calculation on the day/month ratio, instead of a flat percentage value.
Basing the proration calculation on the day/month basis prevents you from having to set up different proration calculations for months with different numbers of days.
-
Enter the From and To days within the month that represent the starting and ending dates for this proration calculation.
Set the From day equal to the To day to prorate the calculation for a single day.
-
Enter a value specifying the Percent of the total standard contribution or distribution that the system uses to calculate the prorated activity rate for those persons whose enrollment coverage dates fall within these From and To days.
-
Select a Proration Rule if you created a formula of the type Partial Month Proration Rule to calculate prorated activity rates.
See: Oracle FastFormula Reference Guide for Standard and Advanced Benefits, My Oracle Support Note 218059.1.
-
In the Applies to Month with Days field, select the value that represents the months with that number of days (31, 30, 29, 28) to which this calculation applies.
-
Select whether this proration calculation starts or stops on this date range in the When to Use field.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule to specify how the system rounds the result of this calculation.
-
Save your work.
Defining Characteristics of Annual Rates
For those plans where a participant enters an annual contribution rate during enrollment, you can define how the system prorates the minimum and maximum contribution amounts for those participants who enter the plan mid-year.
Note: The annual rate value is calcuated based on a 12-month period regardless if the plan year is for a period of 12 months or less.
If you use Self-Service Benefits, your employees can enter annual rates duing enrollment if you complete the fields on the Annual Rate tab and you check the Enter Value At Enrollment check box on the Calculation Method tab of the Standard Rates window.
To define the characteristics of an annual rate:
-
Enter or the query the standard activity rate for which you are defining a prorated value in the Standard Rates window.
-
Choose the Annual Rates tab.
In the Comparison Balances block:
-
Select whether this annual rate is compared to the claims submitted against the annual amount or the amount contributed to the plan.
-
For those plans where you prorate the annual contribution amount based on the days or pay periods remaining in the plan year, select:
-
A Prorate Minimum Annual Value Code or Rule
-
A Prorate Maximum Annual Value Code or Rule
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Processing Information for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
You use the Processing Information tabbed region of the Standard Rates window to define the system (such as Oracle Payroll) that processes the contribution deduction or distribution payment. You may also select, from a range of choices, the point in the enrollment process when a contribution amount is entered.
To define processing information for a standard contribution/distribution:
-
Complete the Processing Information check boxes by selecting from a range of choices that define when and how a contribution or distribution amount is entered for this plan or option in plan.
Important: These checkboxes are important, because they determine whether an election results in a payroll deduction for a participant.
-
Check the Value Override Allowed field if the participant may override the default rate at the time of enrollment.
-
Check the Assign on Enrollment field to automatically enter the calculated amount during enrollment.
-
Check the Display on Enrollment field to display the activity rate on the enrollment form.
-
Check the Process Each Pay Period Default field if the system calculates this standard contribution/distribution each pay period unless otherwise specified.
Note: Checking this field disables use of the Schedule Information button.
-
-
Select the system that processes this calculation in the Processing Source field.
-
Select a Recurring code. Choose from:
-
Once: the contribution or distribution occurs once for a participant in this plan or option in plan.
-
Recurring: the contribution or distribution occurs on a defined periodic basis for an indefinite period of time.
-
Either: the contribution or distribution can either occur once or on a recurring basis.
-
-
In the Value Passed to Payroll field, select the amount that you want to pass to a participant's element entry on enrollment.
-
Select Estimated Per Pay Period to calculate the element entry based on a fixed number of pay periods, 52 for weekly and 26 for bi-weekly pay periods.
Note: If you select no value, the application passes the per pay period amount. You can only prorate per pay period amounts.
-
-
Select a Compensation Category.
-
Select a Currency Determination Code to indicate how the application processes the source of currency for each employee. Choose from:
-
Automatic - this is the default value. If you select this, then the application first looks at the element determination rule to determine the currency. If you do not define an element determination rule, then the application determines the currency based on the standard rate element. If you do not define a currency at the standard rate element level, then the application determines the currency based on the salary basis element. If you do not define a currency at the salary basis level, then the application uses the currency you define for the plan.
-
Plan - if you select plan, then the application determines the currency you defined for the plan on the not in program tab.
-
Salary Basis Element - if you select this, then the application determines the currency based on the input currency of the element type associated with the salary basis definition linked to the employee's assignment.
-
Standard Element Rate - if you select this, then the application determines the input currency of the element type associated with the CWB worksheet amount standard rate.
-
-
Save your work.
To define rate certification requirements:
-
Choose the Rate Certification button, which is visible for plans that are not in a program.
-
Select a Rate Certification Type.
-
Save your work.
Defining Deduction and Payment Schedules for a Standard Contribution/Distribution
You can define a deduction or payment schedule to specify how frequently the system calculates a contribution (for deductions) or distribution (for payments) if you are using Oracle Payroll and you do not check the Process Each Pay Period Default field in the Processing Information region.
You date effectively define deduction and payment schedules in the Schedule Information window.
To define scheduling for a standard contribution:
-
Select a Deduction Schedule for this standard contribution.
-
For this Deduction Schedule, select a Pay Frequency to specify how frequently the system deducts this standard contribution.
-
Check the Default field if this Pay Frequency is the default pay frequency for this Deduction Schedule.
-
If you associate more than one Pay Frequency with this Deduction Schedule, repeat steps 2 and 3 for each Pay Frequency.
-
Save your work.
To define Payments for a standard distribution:
-
Select a Payment Schedule for this standard distribution.
-
For this Payment Schedule, select a Pay Frequency to specify how frequently the system makes this standard distribution.
-
Check the Default field if this Pay Frequency is the default pay frequency for this Payment Schedule.
-
If you associate more than one Pay Frequency with this Payment Schedule, repeat steps 2 and 3 for each Pay Frequency.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Non-Oracle Payroll System to Process Benefit Earnings and Deductions
You use the Payroll Information tabbed region of the Standard Rates window if a non-Oracle payroll system calculates this contribution or distribution.
To define a non-Oracle payroll system to process earnings and deductions:
-
Enter the Name of the foreign payroll system.
-
Select if this payroll system processes earnings or deductions in the Type field.
-
Save your work.
Associating a Variable Rate Profile with a Standard Contribution/Distribution Calculation
If a standard contribution or distribution can vary based on a derived factor or a discrete piece of data, you can use the Variable Rates window, accessed from a button on the Standard Rates window, to associate a variable rate profile or rule with the activity rate calculation to specify how the result can vary.
To associate multiple conditions that must all be satisfied, you must attach all the conditions to a single variable rate profile. Specifying them in a sequence in the Variable Rates window instructs the application to find only the first satisfying condition and then stop.
Important: You must define a variable rate profile or rule before you define a standard contribution or distribution that uses a variable rate.
To associate a variable rate profile or rule with a standard contribution/distribution calculation:
-
Enter a Seq (Sequence) number to specify the order in which the system processes this variable rate profile relative to any other profiles you associate with this standard contribution/distribution calculation.
-
Select the Name of a variable rate profile you are associating with this standard contribution/distribution calculation.
-
Choose the Rules tab if you are associating a variable rate rule with this calculation. Enter the Seq (sequence) number and select the name of this variable rate rule.
-
Save your work.
Defining Matching Rates for a Standard Contribution Calculation
Note: The matching rates feature is reserved for future use. It is currently not operational.
If you define an employer matching contribution that is a percentage of the employee contribution (in contrast to a fixed employer contribution), you can define how the system performs such matching. Multiple instances of a matching contribution may be necessary if the employer match varies according to the amount the employee contributes.
You define matching rates in the Standard Rates window. Choose the Matching Rates button.
To define matching rates for a standard contribution calculation:
-
If special circumstances apply, select a matching rate calculation rule.
-
Enter a Seq (sequence) number to specify the order in which the system processes this matching rate for this contribution.
-
Enter a From % and To % to specify the lowest and highest employee contribution percentage to which this matching contribution applies.
In the Matching Values block:
-
Enter a Match % to specify the matching percentage for this matching rate.
-
Enter a Minimum and Maximum Amount to specify the boundaries of the employer match, regardless of the value the system calculates.
Check the No Maximum Amount field if the match has no Maximum Amount defined for it.
In the Maximum Pay to Consider block:
-
Enter an Amount to specify the maximum amount of employee earnings against which the system calculates this match.
Check the No Maximum Amount field if the match is not limited by the Maximum Amount of employee earnings.
-
Enter a Percent to specify the maximum percentage of employee earnings against which the system calculates this match.
Check the No Maximum Percent field if the match is not limited by a Maximum Percent of employee earnings.
-
Check the Continue Matching after Maximum field if employer matching contributions continue up to the maximum percentage or amount, even though the worker has met the limit of worker contributions.
Note: This is particularly useful for US 401(k) plans as workers may choose high salary percentages in order to contribute as much as possible as soon as possible. When employer contributions match each pay period, it may occur that the worker is contributing too much each pay period to receive the employer's highest matching amount. For example, a worker could contribute 15% of pay up to the worker maximum contribution limit of $9,000, but the employer matches only 50% up to 6% of what the worker contributes. As Oracle Payroll performs the actual calculation, checking this field only alerts the system to activate the proper calculation process.
-
Save your work.
Associating a Period-to-Date Limit with a Standard Contribution/Distribution Calculation
You can associate period-to-date limits for a calculation or a distribution. You typically define period-to-date limits for savings plans.
Choose the PTD Limits button in the Standard Rates window to select a period-to-date limit.
To define a period-to-date limit for a calculation:
-
Select a Period-to-Date Limit to associate with this calculation.
-
Save your work.
Defining Variable Rates
Defining General Information for a Variable Rate Profile
You use the Variable Rate Profiles window to define a variable rate when an activity rate for a plan can vary for each participant based on one or more factors.
To set up variable rate profiles for use in Grade/Step Progression criteria sets, use the Variable Rate Profiles using the Eligibility Profiles window and set your effective date to 01-JAN-1951
To define general information for a variable rate profile:
-
Enter the Name of the variable rate profile you are defining.
-
Select its current Status.
Pending: This variable rate profile is currently proposed, but not yet associated with an activity rate.
Active: This variable rate profile is currently associated with an activity rate.
Inactive: This variable rate profile is currently not associated with an activity rate.
Closed: This variable rate profile was once Active or Proposed, but is no longer associated with an activity rate.
-
Choose the General tab if it is not already selected.
-
Select an Activity Type code to specify the type of activity rate to which this variable rate applies.
If you are setting up a variable rate profile for use in Grade/Step Progression, the Activity Type code must be Grade Step Progression Salary Amount.
-
Select a Tax Type code to specify the tax status of the activity rate.
Note: The system displays only those tax types that are valid based on the activity type you select.
Note: Variable rates for actual premiums must have a tax type of Not Applicable.
-
Select a Reference Period code to specify the time period applicable to the activity rate.
-
Select a Treatment code to specify the type of calculation the system performs on the activity rate.
-
Select a Usage that limits the kind of activity rate to which this variable rate can apply.
-
Select an Assignment to which this variable rate profile applies. For example, you can define a variable profile of Benefits Assignment Only if you use this profile to determine continuing eligibility.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Calculation Method for a Variable Rate Profile
You use the fields in the Calculation Methods region of the Variable Rate Profiles window to define how a variable activity rate is calculated.
To define a calculation method for a variable rate profile:
-
Query the variable rate for which you are defining a calculation method in the Name field.
-
Click the Calculation Method tab.
-
Select the method you are using to calculate the variable activity rate in the Calculation Method field.
Important: The window changes based on the calculation method you select.
-
Complete your calculation definition based on the calculation method you select.
-
Select Always Sum All Participants or Always Sum All Coverage if you are defining a variable rate profile for an actual premium based on the total coverage volume for all participants or the total number of participants.
-
Conversely, do not select Always Sum All Participants or Always Sum All Coverage if you want the variable rate determined based only on the number of participants who meet the criteria of the variable rate profile.
-
-
Save your work.
Defining the Criteria in a Variable Rate Profile
You define the criteria that compose a variable rate profile so that participants who meet the criteria receive the variable rate you have defined. You can also define a variable rate profile so that participants who meet the criteria are specifically excluded from receiving the variable rate.
Note: You can use a participant eligibility profile that you have defined as a criteria set in a variable rate profile. This lets you define your criteria once, then reuse the criteria set to control both eligibility and variable rates. Oracle recommends attaching eligibility profiles to variable rates--as opposed to individual criteria--to improve system performance.
If you use a FastFormula rule as part of your variable rate profile, the participant must meet the criteria of the rule and one value from any other criteria that you include in the profile. If you use more than one FastFormula rule, by default the participant must meet the criteria of all the rules. If you change the user profile option BEN:VAPRO Rule from AND to OR, the participant need only meet the criteria of one rule.
To define the criteria in a variable rate profile
-
Enter or query the variable rate in the Variable Rate Profiles window.
If you are attaching an Eligibility Profile for a Grade/Step Progression criteria set, use the Variable Rate Profiles using the Eligibility Profiles window and set your effective date to 01-JAN-1951. For a Grade/Step Progression criteria set, you can only attach Eligibility Profiles to your Variable Rate, but not individual criteria.
-
Choose the Eligibility Profiles button to open the Eligibility window if you want to link a participant eligibility profile to the variable rate profile.
-
Select an Eligibility Profile Name.
-
Select the Required check box if the participant must satisfy this eligibility profile to receive the variable rate.
Note: Currently, you can attach only one criteria set to a variable rate profile, so the set is automatically required.
-
Close the Eligibility window.
-
If you want to use variable rate criteria--instead of an eligibility profile--choose the Criteria button to open the Variable Rate Criteria window.
-
Choose a tabbed region that contains a criteria element you want to include in your variable rate profile.
-
Select a criteria element.
For example, in the Other Factors region you could select Participation in Another Plan as a criteria element if you want to define a special rate for when two plans are elected in conjunction with one another.
If you are attaching an Eligibility Profile for a Grade/Step Progression criteria set, you can use the following criteria only:
-
Bargaining Unit
-
Full Time/Part Time
-
Job
-
Location
-
Organization
-
Performance Type
-
Person Type
-
Rating Type
-
Rule
-
Service Area
-
-
Enter a Seq (sequence) number specifying the order the system processes this criteria element relative to any other criteria in the variable rate profile.
Important: You must assign a sequence number of a higher priority to all criteria that are used to exclude eligibility in a variable rate profile.
-
Select a value for the criteria element you have selected.
Check the Exclude field if a person who meets the value of this criteria element is excluded from receiving the variable rate associated with this profile.
-
Repeat steps 7-11 for each criteria element you include in this variable rate profile.
-
Choose the Display All tabbed region to view the criteria elements in this variable rate profile.
-
Save your work.
Defining Matching Rates for a Variable Rate Calculation
Note: The matching rates feature is reserved for future use. It is currently not operational.
The process for defining a matching rate for a variable rate calculation is the same as defining a matching rate for a standard contribution.
From the Variable Rate Profiles window, choose the Matching Rates button.
To define a matching rate for a variable rate calculation:
-
Query the variable rate for which you want to define a matching calculation rate.
-
Choose the Matching Rates button to display the Matching Rates window.
-
Define the matching rate calculation.
See: Defining Matching Rates for a Standard Contribution Calculation
-
Save your work.
Setting Up Coverage Calculations
Defining a Coverage Calculation
You use the Coverages window to define the amount of coverage available for a plan or an option in plan. Coverage calculations are typically used to determine the coverage offered by an insurance plan but may also include other benefit offerings, such as stock options.
To define a coverage calculation for a plan:
-
Enter or query the coverage calculation you are defining in the Name field.
-
Select the Type of benefit provided by this plan or option in plan, such as Coverage or Time Off.
-
Choose the General tabbed region if it is not currently selected.
-
Select the Level at which you are creating a coverage calculation.
-
Select the plan or option in plan for which you are defining a coverage calculation in the Compensation Object field.
-
Select a UOM for non-monetary coverage amounts, such as options or shares.
-
Select a Boundary Period that restricts any lower or upper limit coverage amount that you specify to a specific length of time.
-
Check the Max Overridable field if the user can override the maximum coverage amount.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Coverage Calculation Method
You define a coverage calculation method to define how the coverage amount is calculated for a plan or an option in plan.
See: Calculation Methods: Values, Increments, and Operations
To define a coverage calculation method
-
Enter or query the coverage calculation you are defining in the Name field.
-
Choose the Calculation Method tabbed region.
-
Select the Calculation Method you are using to define this coverage calculation.
-
Check the Enter Value at Enrollment field if you enter the coverage amount at the time of enrollment.
-
Complete the remaining fields based on the calculation method you select.
-
Enter a Lower Limit value or rule to define the minimum amount of coverage available under this plan or option regardless of the result of the coverage calculation.
-
Enter an Upper Limit value or rule to define the maximum amount of coverage available under this plan or option regardless of the result of the coverage calculation.
-
Save your work.
Associating a Variable Rate Profile with a Coverage Calculation Method
You use the Benefit Variable Rates and Rules window to associate a variable rate profile with a coverage calculation if the calculation can vary for each participant.
To associate a variable rate profile with a coverage calculation:
-
Enter the Seq (sequence) number in which the system should process this variable rate profile relative to any other variable rate profiles that you associate with this coverage calculation.
-
Select the variable rate profile in the Profile Name field.
-
Select another profile if you use more than one variable rate for this calculation.
-
Alternatively, choose the Rule tab and select a variable rate rule to associate with this calculation.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Coverage Limit Across Plan Types
You use the Coverage Across Plan Types window to define the minimum and maximum coverage amount that a participant can elect across plan types in a program.
You can place a plan type in only one across plan type group. You can also set coverage limits at the plan level.
To define a coverage limit across plan types:
-
Select the program for which you are defining cross plan type coverage limits.
Note: The system displays the plan types in this program in the Coverage Plan Types block.
-
Enter a name that identifies this cross plan type coverage limit.
-
Enter the minimum amount of coverage that a participant must elect across the plan types in this grouping.
-
Enter the maximum amount of coverage that a participant must elect across the plan types in this grouping.
In the Coverage Plan Types block:
-
Select a plan type for which you are defining a cross plan type coverage limit.
-
Check the Applies To field if you are placing this plan type into this cross plan type grouping.
Note: The Already Used field appears checked if you have already placed this plan type into another cross plan type grouping.
-
-
Repeat step 5 for each plan type that you are placing into this cross plan type grouping.
-
Save your work.
Defining an Imputed Income Calculation
You use the Imputed Income window to date effectively define activity rates that calculate the amount of plan income that is considered a "fringe benefit" and subject to Section 79 of the US Internal Revenue Service code.
To define an imputed income calculation:
-
Enter a Name for the imputed income calculation you are defining.
-
Select the imputed income Plan for which you are defining this calculation.
-
Select an Assignment to Use, enabling you to apply this calculation to a subset or sequence of assignment types.
-
Select a Status code for this imputed income calculation.
Pending: This plan currently does not use this imputed income calculation, but could in the future if you change the Status of this calculation to Active. Select the Pending status when setting up an imputed income calculation that possibly may not become Active.
Active: This imputed income calculation is associated with an imputed income benefit.
Inactive: This imputed income calculation is not associated with an imputed income benefit.
Closed: This imputed income calculation is not associated with an imputed income benefit.
-
Select a processing Source code to identify the system that processes this imputed income calculation.
-
Check the Uses Payment Schedule field if a payroll system uses a payment schedule other than "every pay period" when processing this imputed income calculation.
-
Check the Process Each Pay Period field if a payroll system processes this imputed income calculation every pay period.
-
Enter a Wash Rule Day if participants who start coverage for this plan do not receive imputed income contributions or distributions for the month when their coverage start date is after the wash rule day.
-
Conversely, participants who end coverage for the plan will not receive imputed income for the month when their coverage end date is before the wash rule day.
In the Payroll Information block:
-
-
Select the Element Entry that this calculation creates.
-
Select the Input Value of the element entry.
-
Select a Recurring code to specify whether this imputed income calculation occurs for the participant only Once, Recurs on a periodic basis for an indefinite time period, or Either.
-
Select a Partial Month Determination Code or Rule to specify how the system calculates this imputed income calculation when the employee participates in the imputed income benefit mid-month.
-
Enter a Foreign Earning Deduction ID and Name to identify this payroll system if a non-Oracle payroll system processes this imputed income calculation.
-
Select a Foreign Earning Deduction Type of deduction or earnings to specify how this non-Oracle payroll system processes this calculation.
-
Save your work.
Associating a Variable Rate Profile with an Imputed Income Calculation
You use the Variable Rates window to associate a variable rate profile with an imputed income calculation.
To associate a variable rate profile with an imputed income calculation:
-
Query or enter an imputed income calculation in the Imputed Income window and choose the Variable Rates button.
-
Select a Variable Rate Profile to associate with this imputed income calculation.
Important: Calculation of imputed income does not use the Activity Reference Period from the Variable Rate Profile window; it uses the Activity Reference Period from the Program window. To calculate imputed income at a monthly rate, for example, you must change (or verify) the value in the Program window.
-
If necessary, adjust the From and To dates to specify the dates through which you associate this profile with this calculation.
Associating a Payment Schedule with an Imputed Income Calculation
You use the Payment Schedule window to define a payment schedule for an imputed income calculation if the payroll system uses a schedule other than "every pay period."
To associate a payment frequency schedule with an imputed income calculation:
-
Query or enter an imputed income calculation in the Imputed Income window and choose the Payment Schedule button.
-
Select the Payment Schedule or Rule the payroll system uses to process this imputed income calculation.
Select the Pay Frequency code to specify how frequently the payroll system processes this imputed income calculation.
Check the Default field if the system assigns this payment schedule to this imputed income calculation when the payroll system does not specify which payment schedule to use.
-
Save your work.
Defining an Actual Premium
You use the Actual Premiums window to maintain the criteria used to calculate an actual premium cost.
To define an actual premium:
-
Enter the premium name or a description of the premium in the Name field.
-
Select the premium type in the Type field.
-
Select the premium payer in the Payer field.
-
Select the plan to which you are associating this premium.
-
Select an option in plan if you are associating this premium to an option.
-
Select the organization to which the premium is paid in the Supplier field.
Note: The list of organizations is limited to those organizations that you attach to the plan or to the program containing the plan.
-
Select the Currency in which this premium is paid.
Note: The Activity Reference Period is monthly for all actual premiums. This is a read-only field.
-
Save your work.
General Definitions
Deleting an Actual Premium
You can delete an actual premium that you have created in error if you have not associated the premium with a plan or an option in plan in which a participant is currently enrolled.
Use the end-dating feature of the system to de-activate an actual premium that is no longer valid.
Defining Period-to-Date Limits
You use the Period-to-Date Limits window to date effectively define plan year contribution limits for plans or options in plan. When you define a standard contribution, you can associate a period-to-date limit for those plans or options in plan that require contribution restrictions.
You can base period-to-date limits on a person's accrued activity rate balance, as a percentage of their compensation, or based on a fastformula rule that you define.
To define a period-to-date limit
-
Enter a Name for this period-to-date limit.
-
Select a Determination Code that defines when the limit is reached.
Balance Region
-
Enter the maximum amount that a participant may accrue during a plan year for this balance in the Max Value field.
-
Select the period-to-date balance Type.
Compensation Region
You use the fields in the compensation region if you are limiting a period-to-date contribution as a percentage of a participant's compensation, or based on a derived compensation factor.
-
Enter the maximum percentage of a participant's compensation that can be accrued in this balance in the Max Percent field.
-
Select a compensation factor in the Factor field if you are using a derived compensation factor to determine the period-to-date limit for this balance.
-
Enter the Max Pay to Consider if you define a maximum compensation amount that the system considers when calculating a period-to-date limit based on a percentage of compensation or a derived compensation factor.
Rule Region
-
Select a Rule if you are defining a period-to-date limit based on a FastFormula rule that you have written.
-
Save your work.
You can now use the Standard Contribution/Distribution window to associate your period-to-date limit with the contribution activity rate for a plan or option in plan.
Defining a Benefit Balance
You use the Benefit Balances window to enter and maintain benefit balances that you can link to persons or to formulas.
To define a benefit balance
-
Enter a Name used to identify the benefit balance.
-
Enter a Description of your benefit balance.
-
Select a Usage code.
Your system administrator or benefits administrator defines the benefit balance usage codes as part of the system implementation.
-
Select the unit of measure in which this balance is expressed in the UOM field.
-
Select a Non-Monetary UOM for benefits not expressed in currency, such as stock options or shares.
-
Save your work.
You can now associate this benefit balance with a person benefit balance or a formula.
Flex Credits and Benefit Pools (Advanced Benefits)
Flex Credit Calculations (Advanced Benefits)
Flexible benefit programs offer employees choices among benefits and coverage levels. Participants can receive flex credits for various reasons, such as service credits, health care credits, and credits from vacation sale.
You define flex credits in conjunction with flexible benefit programs so that participants have money to spend on benefits and coverage levels. Flex credits are defined by a special type of activity rate calculation.
You can define flex credits at the following levels in the compensation object hierarchy:
-
Program
-
Plan type in program
-
Plan in program
-
Option in plan
-
Combination plan type in program
-
Combination plans in program
If you are defining a flexible benefits plan, you must create a flex credit program and place the flex credit plan in that program.
Benefit Pools (Advanced Benefits)
Benefit pools define how flex credits are grouped. They restrict the compensation objects that are funded by a flex credit calculation.
You define benefit pools in association with programs that provide flex credits so that when a participant enrolls in a flex program they have flex credits available to spend. You define the amount provided by a benefit pool by creating an activity base rate for the pool object.
Excess treatment codes restrict the distribution of flex credits left unspent by a participant. Excess credits may be rolled over into another compensation object (such as another plan), distributed as cash, or forfeited. You can define minimum and maximum rollover amounts and the order in which excess credits should be distributed.
Benefit pools can be defined at the following levels in the compensation object hierarchy:
-
Program
-
Plan Type in Program
-
Plan in Program
-
Option in Plan in Program
-
Combination of Plan Types in Program
-
Combination of Plans in a Program
Defining Flex Credits
Defining Flex Credits (Advanced Benefits)
Regardless of the level at which you define flex credits, you must associate your flex credit definition with a compensation object that is part of a program. You cannot define flex credits for a benefit plan that is not part of a program.
You define the flex credits in a program in the Flex Credits window.
To define general information for flex credits
-
Enter or query the flex credit calculation you are defining in the Name field.
-
Select the Status of the flex credit calculation.
Pending: This compensation object currently does not use these flex credits, but could in the future if you change the Status of these flex credits to Active. Select the Pending status when setting up flex credits that possibly may not become Active.
Active: The system has applied these flex credits to a compensation object.
Inactive: This compensation object currently does not use these flex credits.
Closed: The system does not apply these flex credits to a compensation object.
On the General Tab
-
Select the Level of the compensation object hierarchy at which you are defining flex credits.
-
Select the Compensation Object for which are defining a flex credit calculation.
-
Select the Activity identifying the business function this activity rate performs.
-
Select a Tax Type to indicate the tax impact of these flex credits to participants, such as pre-tax or after tax.
On the Calculation Method tab
-
Select the Calculation Method the system uses when determining the flex credit rate for the selected compensation object.
The system redisplays the window based on the calculation method you select.
-
Enter or select one or more values based on your flex credit calculation definition. For example, if you select the Multiple of Compensation method, you might enter a multiplier of 10 with the operator Percent Of, and the compensation factor Pensionable Wages.
-
If you did not select the Flat Amount method, you can:
-
Enter a Lower Limit Value or Rule to define the minimum result of this flex credit calculation.
-
Enter an Upper Limit Value or Rule to define the maximum result of this flex credit calculation.
-
-
Save your work.
Defining Regular Processing for a Flex Credit Activity Rate (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Processing tabbed region of the Flex Credits window to define the payroll processing of a flex credit calculation. You must define this information in conjunction with your element definition for this activity rate to be processed.
To define regular processing for a flex credit activity rate:
-
Select a Source code to identify the system that processes this flex credit calculation.
-
Select a Recurring code to indicate if this flex credit calculation is processed once or on a recurring basis.
-
Check the Uses Variable Rate field if these flex credits are calculated using a variable rate profile.
Do one of the following:
-
Check the Process Each Pay Period field if a payroll system processes this flex credit calculation every pay period.
-
Check the Uses Payment Schedule field to specify that one or more payment schedules must be defined if a payroll system processes this flex credits activity rate on a non-pay period basis.
Note: The Process Each Pay Period and the Uses Payment Schedule check boxes are mutually exclusive.
In the Foreign Earning/Deduction block:
-
-
If a non-Oracle payroll system processes these flex credits:
-
Select the ID to identify this activity rate
-
Select a Type code of Earning or Deduction to specify how this system processes this calculation
-
Enter a Name to identify this payroll system
-
Payment Schedule Window
-
Choose the Payment Schedule button to open the Payment Schedule window if you checked the Uses Payment Schedule field.
-
Select the Payment Schedule the payroll system uses to process this activity rate.
-
If no Payment Schedule meets your requirements, select a Rule.
-
-
Select the Pay Frequency code to specify how frequently the payroll system processes this activity rate for this Payment Schedule.
-
Check the Default field if the system assigns this payment schedule to this activity rate when the payroll system does not specify which payment schedule to use.
-
Close the Payment Schedule window.
Activity Variable Rates and Rules Window
-
Choose the Variable Rates button to open the Activity Variable Rates and Rules window if you checked the Uses Variable Rate field.
-
Choose the Variable Rate Profile tab or the Variable Rate Rule tab depending if you are linking a variable rate profile or rule to this flex credit activity rate.
-
Enter a Seq (Sequence) number to specify the order in which the system processes the variable rate profile or rule.
-
Select a Variable Rate Profile or Rule to associate with this flex credit activity rate.
-
Close the Activity Variable Rates and Rules window.
Period to Date Limits Window
-
Choose the Period to Date Limit button if you limit the number of flex credits a participant can receive during a given time period.
-
Select a Period-to-Date Limit to associate with this flex credit activity rate.
-
Save your work.
Defining Partial Month Processing for a Flex Credit Activity Rate (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Partial Month tabbed region of the Flex Credits window to define how the system calculates a flex credit activity rate when a participant enters the plan mid-month.
To define partial month rate processing for a flex credit activity rate:
-
Select a Partial Month Determination Code to specify how the system calculates these flex credits when the employee participates in this compensation object mid-month.
-
If special circumstances apply, select a Partial Month Determination Rule instead of a Partial Month Determination Code.
-
-
Select the Partial Month Effective Date Determination Code to specify how the system determines the effective date it uses to calculate a partial month contribution/distribution proration.
-
If the Partial Month Effective Date Determination Code values do not meet your requirements, select a Partial Month Effective Date Determination Rule.
-
-
Enter the Wash Rule Day if participants who enter this plan do not receive a flex credit allocation for the month when their coverage start date is after the wash rule day.
-
Conversely, participants who end coverage for the plan will not receive a flex credit allocation for the month when their coverage end date is before the wash rule day.
-
-
Choose the Partial Month button.
-
Select if this partial month activity rate starts or stops for this partial month period in the Start or Stop field.
-
Select a From day and a To day within the month that represent the starting and ending dates for the partial date range.
Set the From day equal to the To day to prorate the flex credit calculation for a single day.
-
Select a Percent specifying the percentage of the total activity rate that the system uses to calculate the prorated rate for those persons whose enrollment coverage dates fall within these From and To days.
-
Or, select a Proration Rule that you have defined to calculate the prorated rate.
-
-
Select a Rounding Code to specify how the system rounds the result of this flex credit calculation.
-
If a Rounding Code does not meet your requirements, select a Rounding Rule.
-
Save your work.
Defining Benefit Pools
Defining the General Characteristics of a Benefits Pool (Advanced Benefits)
You define benefit pools to limit how a participant can spend flex credits and how excess flex credits can be rolled over, distributed as cash, or forfeited.
Benefit pools are always associated with a program, but you can also create pools at other levels within a program.
You can specify the percentage or amount of credits that can be distributed as cash based on the number of excess credits.
You use the Benefits Pools window to date effectively maintain benefit pools for your flex credit programs.
To define the general characteristics of a benefits pool:
-
Enter a name for the benefit pool you are defining in the Name field.
-
Select the program to which you are associating this benefit pool.
-
Select the Level at which you are defining flex credits in this program.
-
Select the Compensation Object for which you are defining a benefit pool.
Note: The list of available compensation objects is limited based on the level you select in step 3.
-
Choose the General tab, if it is not already selected.
-
Check the Include Program Flex Credits field if this is a program level pool.
-
Check the Automatically Allocate Excess field if excess credits from this pool are allocated based on your benefit pool definition and without the explicit choice of the participant.
-
Select a code in the Excess Treatment field that defines how a participant may use excess flex credits from this pool.
Receive as Cash or Roll to Another Plan: The participant can choose to receive the excess flex credits as cash or roll the excess credits to another eligible plan.
Roll to Another Plan: The participant can only choose to roll the excess credits to another eligible plan. They cannot receive excess credits as cash.
-
Select a Default Excess Treatment code to define the order in which excess flex credits are either distributed, rolled over, or forfeited.
In the Percent block:
-
Enter the Minimum percentage of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool as cash or check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum percentage.
-
Enter the Maximum percentage of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool as cash or check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum percentage that can be distributed.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule if you are defining a rounding method for the percentage of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool.
In the Amount block:
-
Enter the Minimum amount of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool as cash or check the No Minimum field to indicate that there is no minimum amount.
-
Enter the Maximum amount of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool as cash or check the No Maximum field to indicate that there is no maximum amount.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule if you are defining a rounding method for the amount of excess credits that can be distributed from this benefit pool.
-
Save your work.
Applying a Benefit Pool to a Plan and Option (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Application tabbed region of the Benefit Pools window to apply the benefit pool to a plan and the options in that plan.
To apply a benefit pool to a plan and option:
-
Select the Plan to which you are associating this benefit pool. The system displays:
-
The option or options associated with this plan
-
The activity rate for each option
-
The taxability of the option
-
The effective dates for the association of this plan and option with this benefit pool
-
-
Repeat step 1 for each plan you are associating with this pool.
Note: A credit pool can be applied to more than one plan. Likewise, a plan can be linked to more than one pool.
-
Save your work.
Defining Rollover Rules for a Benefit Pool (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Rollover tabbed region of the Benefit Pools window to set up rollover rules that define how the system processes excess credits for a benefit pool. A credit pool can have different rollover requirements for different plans, and a plan that decrements more than one pool can be subject to multiple rollover requirements.
To define the rollover rules for a benefit pool:
-
Select the Plan and Option to which flex credits from this pool rollover. The system displays:
-
The pretax activity rate for this option
-
The effective dates for the association of this plan and option with this benefit pool
-
-
Enter the Default Order in which the system rolls over credits into the plans and options in this pool.
-
Enter the increment by which flex credits can be rolled over as a percent or an amount in the Increment Percent and Increment Amount fields.
-
Select a Participant Eligibility Rollover Rule if you define a formula that limits the circumstances under which the credits from this pool can be rolled over.
Defining Benefit Pool Rollover Percentages and Amounts (Advanced Benefits)
You use the fields in the Percent and Amount blocks to define minimum and maximum rollover amounts and percentages for this credit pool.
1. Enter the Minimum rollover percentage for this benefit pool or check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum rollover percentage.
2. Enter the Maximum rollover percentage for this benefit pool or check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum rollover percentage.
3. Select a Rounding Code or Rule if you are defining a rounding method for the rollover percentages for this benefit pool.
In the Amount region:
4. Enter the Minimum amount or check the No Minimum field to indicate that there is no minimum amount.
5. Enter the Maximum amount or check the No Maximum field to indicate that there is no maximum amount.
6. Select a Rounding Code or Rule if you are defining a rounding method for the amounts for this benefit pool.
7. Save your work.
Communications
Communications
You send communications to potential, current, and former benefits participants to inform them about available benefits, rates, scheduled enrollment periods, and other information that you need to communicate.
You create a communication type to define:
-
The conditions that trigger a communication
-
The data that is extracted from the database which you can merge into a communication
-
The communication delivery method and medium
You run the Participation batch process (in either of its four modes: Life Event, Scheduled, Selected, or Temporal) from the Concurrent Manager to extract data based on your communication type definition. Using the System Extract feature, this data can be extracted to a text file and then merged into the body of your communication.
Communication Type Definitions
You can create definitions for communications that control different aspects of the communication.
For example, you can:
-
Specify the date a communication is to be sent to a participant relative to a qualifying life event or a point in the enrollment cycle
-
Indicate if the communication is a stand-alone item, or a piece in a kit
-
Select a usage type that categorizes the communication, such as Reminder to Act or Confirmation of Action
-
Limit the kinds of recipients who can receive a communication
Communication Triggers
Communication trigger control the data that is extracted from the database when you run the Participation batch process. For example, the Pre Enrollment Literature trigger extracts a person's electable choices based on your communication usage definition and the parameters you select when you run the Participation process.
Communication triggers are seeded with the product.
Communication Usages
As part of your plan design, you can define the condition or combination of conditions that must be present in order for a communication to be sent to a person. The conditions that you associate with a communication are called usages.
You select from the following criteria to limit when a communication is generated:
-
Life Event
-
Program
-
Plan
-
Plan Type
-
Enrollment Period
-
Action
Selecting more criteria for a communication limits the usage of the communication.
Delivery
You can specify the method by which a communication is delivered, such as home mail delivery or email. You can also specify a delivery medium, such as paper or diskette.
Employees can specify a preferred delivery method and medium. This information is maintained on the People window. You can choose to override this information for a particular program or plan. Or, you can specify a default delivery method or medium for employees who do not specify a preference.
Person Communications
You use the Person Communications window to maintain information about the communications that are requested by a participant or that are sent automatically as events occur in the plan year.
A participant can request to have a communication re-sent which has already been sent. Each time a communication is requested, the system tracks the request by generating a sequence number for that request. You can define the maximum number of requests that a person can make for a particular communication.
You can categorize communications into those that can be requested by a participant and those that can only be requested by a benefits specialist. A benefits specialist can select communications with a trigger type of Online Participant Based Literature Requests and Online Participant Service Representative (PSR) Based Requests. Participants are limited to making selections from communications with a trigger type of Online Participant Based Literature Requests.
When you define a communication type, you select the Always Send checkbox to indicate that the communication is sent whenever it is requested. If the box is unchecked, you must create a communication usage that specifies the program, plan, action type, or enrollment period to which this communication applies.
The participant's address appears on the window as it is entered in the Address window. You can override this address by selecting another address that exists in the database or by using the Address window to enter the address as a secondary address.
You also use the Person Communications window to enter delivery instructions, change the person's default delivery method and media, modify the date on which the communication is sent, and to specify if the communication requires inspection.
See Also
Determine Communications Batch Process
Defining Communication Types
You define, update, and delete communication types in the Communication Types window. You complete your communication type definition by defining communication triggers, usages, and delivery information.
To define a communication type:
-
Enter a Name for the communication type you are defining.
-
Optionally, enter a Short Name for this communication type.
Note: Short names are also used to maintain instruction text for regions of self-service enrollment web pages. You must enter the short name in the following format: PREFIX.REGIONNAME. Exclude the PREFIX prefix from the regionname portion of short name.
See: Benefits Enrollments for a list of the required short names for each web page region.
-
Select a To Be Sent code or rule that defines when the communication should be sent relative to a life event or a given point in the enrollment cycle.
-
Select a kit code in the Part of Kit field to specify whether this communication is a single item (a piece), or one of several communication items in a kit.
-
Select the kit to which this piece belongs in the Kit Name field if this communication is one piece in a kit.
-
View the communication pieces that make up a kit by choosing the View Children button when you have selected a kit.
-
-
Check the Inspection Required field or select an Inspection Required Rule if this communication must be inspected before it is delivered.
-
Check the Always Send field if this communication should always be sent whenever it is requested or triggered.
Alternatively, enter the maximum number of times this communication can be sent in the Max Number Available field.
-
Check the Track Mailing field if the system should track the delivery status of this communication.
-
Enter the maximum number of communication that a person can receive of this communication type in the Max Number Available field.
-
Select a Communication Type Rule that further refines the definition of this communication type.
-
Select a Usage type that categorizes this communication.
Example usage types include Reminder to Act and Confirmation of Action.
Note: Select a usage type of Self Service Instruction Text if you are configuring a self-service web page.
-
Select a Recipient Code that limits the type of benefits participant to whom this communication is being sent, such as a dependent.
-
Enter a Description of this communication.
-
Save your work.
Defining When to Use a Benefits Communication
You use the Communication Type Usages window to define the conditions that generate an extract of communications data.
You also use this window if you are implementing web-based self-service enrollments and you want to write instruction text that appears in a region of a self-service window.
To define a communication usage:
-
Enter or query a communication type in the Communication Types window.
-
Choose the Usages button.
-
Select a value for one or more of the following parameters to limit the conditions under which communications data is generated.
-
Life Event
-
Program
-
Plan
-
Plan Type
US Users Only
Note: : To suppress the communication type HIPAA Letter when the person drops HIPAA coverage but gains electability within a program for another plan type subject to HIPAA, include all Plan Types that are subject to HIPPA for the usages.
-
Enrollment Period
-
Action
-
-
Select a Usage Rule if your criteria for determining the conditions under which communications data is generated cannot be fully accommodated by the usage criteria on this window.
-
Enter instructional text in the Self Service Description field that corresponds to the region of the self-service web page that you are configuring.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Communication Trigger
You use the Communication Type Triggers window to link a trigger to your communication type definition. A trigger controls the kind of data that is extracted from the database when you run the Participation batch process.
For example, the Final Confirmation Literature trigger extracts a participant's benefit elections after the enrollment is closed.
To define a communication trigger:
-
Enter or query a communication type in the Communication Types window.
-
Choose the Triggers button.
-
Select one or more triggers that you are linking to this communication type definition in the Type of Trigger field.
Note: You select a trigger type of Online Participant Based Request or Online PSR Based Request to provide a list of communications that can be requested through the Person Communications form.
-
If special circumstances apply, select a trigger rule instead of a trigger type.
-
Save your work.
Defining a Communication Delivery Method
You use the Communication Type Delivery Methods window to define the method and media by which a communication is delivered. A typical communication delivery uses the postal service as the delivery method and paper as the delivery medium.
-
Enter or query a communication type in the Communication Types window.
-
Choose the Delivery button.
-
Select the Delivery Method for this communication item, such as Email or Postal Service.
-
Check the Default field if this delivery method is the default to use when you do not know a person's preferred way to receive communications.
-
Check the Required field if you must always deliver this communication using this delivery method, regardless of a person's preference.
-
-
Select a Delivery Medium for this communication item, such as Paper or Diskette.
-
Check the Default field if this delivery medium is the default you use when you do not know a person's preferred medium for communications.
-
Check the Required field if you must always use this delivery medium for this communication, regardless of a person's preference.
-
-
Repeat step 4 for each delivery medium you associate with this delivery method.
-
Save your work.
Online Benefit Services (Advanced Benefits)
Online Benefits Administration (Advanced Benefits)
The system is designed with features that enable you to perform a variety of tasks from a central form called the Benefits Service Center.
You use the Benefits Service Center window if the requirements of your organization include the need to perform various benefits and HR-related functions in a real-time environment.
Common requests that you can process include changing a person's address or phone number, adding a dependent or beneficiary, or changing a person's marital status. These and other changes may trigger a life event that enables enrollment, change in enrollment, or de-enrollment in one or more benefits.
Using this window you can:
-
Authenticate a caller's identity
-
Perform a variety of desktop activities, such as viewing current enrollments, sending communications, and entering personnel changes
-
Evaluate changes to a person's record for enrollment impact
-
Enroll eligible participants in benefit plans
You can link the Benefits Service Center to the Oracle TeleService Quick Menu, if you use this customer service application.
See: Setting Up Quick Menu, Oracle TeleService Implementation Guide
Caller Authentication
You can verify the identity of a caller using your organization's authentication criteria. You query the person's record based on the authentication criteria provided by the caller. If the caller's information is authentic, the query displays information about the person such as their address and any life event that is currently active for the person.
If necessary, you can use the results of the query for further caller authentication.
Desktop Activities
The action you take after you authenticate a caller's identity depends on the caller's request, the status of any open life events, and the person's electable benefit choices, if applicable.
You can select an action or form from a list of desktop activities based on the caller's request. For example, you select the People form if the person needs to change their address. You select the Person Communication form if the person is requesting literature about a benefit plan that you offer.
During implementation, a system administrator can configure the desktop activities available to users of the Benefits Service Center. If you configure the People window (PERWSHRG) with custom workflows or taskflows, you can restrict access to the customized form by user responsibility.
A system administrator links the customized Person form function to the menu for the appropriate responsibility. Then, in the Maintain Online Activities window, the administrator selects the version of the Person form available from the Desktop Activities list.
Online Life Event Management
A special feature of online benefits administration is the ability to process a life event in real-time. When you query a person's record, the system indicates if the person has an open life event.
When you process the life event, the system determines if the life event results in the creation of electable benefit choices for the person. You can then enroll a person in one or more benefit plans for which they are eligible based on this life event.
Maintaining Online Activities (Advanced Benefits)
You use the Maintain Online Activities window to select the forms and functions that are available to the user in the Desktop Activities list of the Online Benefits Services form.
Note: You use this form to override the default list of activities. Activities that you select in this form completely replace the default list.
If you configure the People window (PERWSHRG) with custom workflows or taskflows, you can restrict access to the customized form by user responsibility.
To add an activity to the desktop activities list:
-
Query the current list of desktop activity functions.
-
Enter the Seq (sequence) number in which the function displays in the desktop activities list.
-
Select the function in the Function Name field.
-
Enter the name of the function as it should appear in the desktop activities list in the User Function Name field.
-
Select if this item is a form or a function in the Type field.
-
Enter the Start Date on which this form should appear in the desktop activities list.
-
Enter the End Date to indicate the last date on which this form should appear in the desktop activities list.
-
Save your work.
Maintaining Pop Up Messages (Advanced Benefits)
You can use the Maintain Pop Up Messages window to customize the messages that appear on certain forms based on particular events that you select.
Important: As a prerequisite, you must first use the Messages window to write the message that you associate with a form and an event. You must name the message with the BEN prefix and select Oracle Advanced Benefits as the application.
To associate a pop up message with a form and an event:
-
Enter a name for the pop up message in the Name field.
In the Function block:
-
Select the Name of the function with which you are associating this message.
-
Select the Block associated with this message if the message is limited to a particular block in the form.
-
Select the Field associated with this message if the message is limited to a particular field in the form.
-
-
Select the event that triggers the message in the Event field.
In the Formula block:
-
Select the Name of the formula with which you are associating this message if the message is limited to a particular formula in the form.
-
Check the No Formula field to indicate that the system should not process any formula that you have defined for this message.
In the Message block:
-
Select the message in the Name field.
You can view the message text by scrolling to the Description column of the list of values for the field.
-
Select the message display type in the Type field.
For example, you can choose to display the message with a Cancel button or an OK button.
-
Enter the start and end date to limit the time period when the message displays.
-
Save your work.