Talent Management
Talent Management Overview
Talent Management is essentially the management of worker competencies to meet enterprise objectives. Oracle HRMS, Oracle SSHR, and Oracle Learning Management (OLM) each supply key components of the Talent Management functionality. For many talent-management tasks, you can use either the Oracle HRMS forms-based interface or the SSHR interface.
Oracle HRMS and Talent Management
The Oracle HRMS Talent Management functionality encompasses competency management, career paths, education and qualifications, events, and reviews.
Competency Management
Competencies are measurable skills a workforce either has or must develop to meet enterprise objectives. The Oracle HRMS competency management functions enable you to:
-
Define a library of competencies or upload competency definitions from third-parties. You can use such definitions throughout the enterprise to ensure consistency of approach.
-
Identify each worker's competencies in a competency profile.
-
Measure competencies using either general rating scales or proficiency scales that are specific to the competency.
-
Define the competency requirements of a business group, organization, job, or position.
-
Define core competencies for a business group or organization. All workers in the business group or organization must have its core competencies.
-
Link competencies to qualifications.
Career Paths
You can define career paths based on either job progression or position progression. You define job-based career paths using the Oracle HRMS Map Career Path function. For position-based career paths, you use new or existing position hierarchies.
Education and Qualifications
The Education and Qualifications functions enable you to:
-
Identify the educational and professional qualifications your enterprise recognizes.
-
Identify the educational establishments that deliver recognized qualifications.
-
Record qualifications obtained by each worker.
Events and Reviews
You can set up an event, such as a training course or departmental meeting, and identify employees who are to attend the event. You use this functionality for scheduling training courses only if you are not using Oracle Learning Management.
You can record information about any employee review meeting, such as a performance review, disciplinary hearing, or medical test, using the Employee Review function.
Work Preferences
You can enter work preferences (such as preferred work locations and work hours) for an individual in the Oracle HRMS Work Preferences window.
Oracle SSHR and Talent Management
Managers, HR professionals, and employees can access talent-management functions using SSHR.
Competency Profile
Managers can use the self-service Competency Profile function to update the competency profiles of their subordinates. Employees can use this function to update their own competency profiles.
Suitability Matching
Managers and HR Professionals can use the self-service Suitability Matching function to find a person for a work opportunity or a work opportunity for a person. The process uses factors such as a person's current role, a person's competency levels (as defined in their competency profile), and succession plans in identifying candidates and opportunities. Employees can use this function to find opportunities suited to their competency levels.
Succession Planning
The Succession Planning functionality enables managers to plan for future vacant positions by identifying possible successors for employees, jobs, and positions.
Education and Qualifications
Managers can use the self-service Education and Qualifications function to update records of educational qualifications obtained by their subordinates. Employees can use this function to update their own records.
Other Professional Qualifications
Managers can use the self-service Other Professional Qualifications function to update records of professional qualifications obtained by their subordinates. Employees can use this function to update their own records.
Events and Bookings
Managers can use the self-service Event and Bookings function to create events and event bookings for their subordinates. Employees can use this function to create events and event bookings for themselves.
Employee Reviews
Both managers and employees can use the self-service Employee Review function to set up review meetings and invite reviewers to attend.
Work Preferences
Managers can use the self-service Work Preferences function to enter work preferences (such as preferred work locations and work hours) for a subordinate. Employees can use this function to enter their own work preferences.
Note: The purchase of a Self-Service HR license on or after June 18th, 2007 does not permit the use of Oracle Performance Management. You must purchase a separate Oracle Performance Management license in addition to an Oracle Self-Service HR license to use the Appraisals, Questionnaire Administration, and Objectives Management self-service functions.
See: Oracle Performance Management Overview, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Oracle Learning Management (OLM) and Talent Management
Oracle Learning Management (OLM), formerly Oracle Training Administration, is a complete system for the definition and delivery of training. OLM is tightly integrated with the talent-management functionality of HRMS. For example:
-
When a learner completes a class, OLM can automatically update the learner's competency profile with the competencies and competency levels delivered by the class.
-
An appraisal can include a learning path, which identifies classes to be taken by the appraisee.
Oracle Learning Management requires a separate license.
See: Introduction to Oracle Learning Management, Oracle Learning Management User Guide
Reporting in Talent Management
The Talent Management functions together provide over 50 standard and HRMSi reports. These reports extract and present talent-management-related information about the individual and the enterprise.
See Reports and Processes in Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Window Navigation and Reports Guide
Talent Management Key Concepts
For more information about the Talent Management functions, see:
-
Succession Planning, Oracle Self-Service Human Resources Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Oracle Performance Management is a separately licensed product. You must purchase a separate Oracle Performance Management license in addition to an Oracle Self-Service HR license to use the Appraisals, Questionnaire Administration, and Objectives Management functions.
See: Oracle Performance Management Overview, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Talent Management Requirements
Oracle HRMS enables you to define all the components of a talent management system to meet the needs of your enterprise.
Oracle Performance Management is a separately licensed product. You must purchase a separate Oracle Performance Management license in addition to an Oracle Self-Service HR license to use the Appraisals, Questionnaire Administration, and Objectives Management functions.
See: Oracle Performance Management Overview, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
What are the advantages of the competency functions?
The Oracle HRMS competency functions enable you to:
-
Identify and measure consistently the knowledge, skills, and behavior displayed by your workers across the enterprise.
-
Speed the deployment process within your enterprise and reduce recruitment costs. You can identify and select workers and applicants on a common basis and match them with opportunities that arise across the whole enterprise. This ensures that an able candidate is not rejected because of a mismatch for one vacancy when other suitable vacancies exist.
-
Ensure your enterprise meets its business goals. You do this by linking the competencies held by your workers into the competencies required to meet the business goals of your enterprise.
Can I perform competency evaluation during appraisals?
Yes. Oracle HRMS's highly configurable web interface enables you to perform competency-based evaluation as part of the appraisal process. You create appraisal templates, which can include competency assessment templates, to define the structure of the appraisal.
Can I define my enterprise's career paths in Oracle HRMS?
Yes. Oracle HRMS enables you to define career paths based on either job progression or position progression. You use the model that best reflects the structure of your enterprise.
Can I link competencies to qualifications?
Yes. You can link a person's acquisition of competencies to their achievement of formal qualifications, typically awarded by external, nationally recognized bodies. Such competencies have well defined performance standards that an assessor uses to determine whether a person has achieved a competency. Thus, you can measure workforce competencies against both enterprise and industry or national standards. You can encourage your workforce to acquire such qualifications by developing related competencies, thereby improving the enterprise skill base.
How can I use the suitability function in my enterprise?
Managers and HR Professionals can use the self-service Suitability Matching function to find a person for a work opportunity or a work opportunity for a person. The process uses factors such as a person's current role, a person's competency levels (as defined in their competency profile), and succession plans in identifying candidates and opportunities. Employees can use this function to find opportunities suited to their competency levels.
Can I create succession plans?
You can use the Succession Planning functionality to plan for future vacant positions by identifying possible successors for employees, jobs, and positions.
How can I use Oracle Learning Management (OLM) to help with talent management?
OLM enables you to record the competencies that a course is expected to deliver. You can then use this information to update the competency profiles of the learners who have attended a class.
Important: This software should not be used as the sole method of assessment for making judgements about hiring, performance, or deployment. Your company may be held liable if you rely on incorrect computer data or computerized rules to make such judgements.
It is the customer's responsibility to take all appropriate measures to comply with the Data Protection and Privacy laws of the countries in which they operate.
All personal information that you store or use with this software must be up to date, accurate and relevant. You should confirm the details of the restrictions that apply to the computerized storage and use of personal information with your own legal department or representative.
Can I use HRMS Intelligence to investigate and monitor career management?
Yes. HRMS Intelligence Reports, Discoverer Workbooks, and Performance Measures enable you to investigate competencies, proficiencies, appraisal activity, and training in your enterprise. You can use HRMS Intelligence to answer business questions such as:
-
Who has the required competencies for the job?
-
How quickly can I improve the skills of a group of people, and at what cost?
-
How do a worker's competencies compare with those required by a particular job?
-
Do my employees need more training?
I need to enter competency information from a third-party skills vendor. How can I do this efficiently?
You can quickly and efficiently load competency details from a third-party skills vendor directly into Oracle HRMS using Web Applications Desktop Integrator (Web ADI). Web ADI enables you to manipulate and upload competency information, such as rating scales, rating levels, and competencies, from a text file or spreadsheet into the application. This means you can automatically load data into the application without having to enter the details individually.
See: Uploading Third-Party Competency Information
Competencies
Competencies Overview
In Oracle HRMS, a competency is any measurable behavior or ability that is required by the enterprise and that a worker demonstrates in the work context. For example, a competency can be:
-
Knowledge (such as knowledge of consumer-protection or taxation laws)
-
A skill (such as negotiation or critical thinking)
-
An attitude (such as tenacity or commitment)
-
An attribute (such as absence of color blindness or perfect pitch)
Competency definitions are the basis of many talent-management activities. In particular, you can define:
-
A competency profile for each worker showing the worker's level of proficiency in various competencies
See: Competency Profiles
-
The competency requirements of a business group, organization, job, or position to enable you to identify suitable candidates for vacancies and assess workers against these requirements.
Global and Local Competencies
You can define competencies that are available to a particular business group. Alternatively, you can create global competencies, which are available throughout the enterprise, provided that your system administrator has identified a global competence key flexfield structure on the HR:Global Competence Flex Structure profile option.
Global competencies are most useful if your enterprise operates in multiple countries but you want to use the same competency definitions in all legislations.
Competency Measurement
The HRMS competency functions enable you to set performance expectations for your workers that are consistent and objective.
During appraisal activities, HRMS enables you to assess the degree to which a worker possesses a competency. For example, for the negotiation skills competency, a worker's proficiency level could be 3 on a scale of 1 through 5, where 5 indicates the greatest expertise.
Defining Competencies
You can define competencies individually in the Competencies window. Alternatively, you can upload multiple global competencies from third-party suppliers using the Oracle HRMS Web ADI interface. This approach may be useful to enterprises implementing competency support for the first time.
See: Defining Competencies and Uploading Third-Party Competency Information
Unit Standard Competencies
Some legislations identify a special type of competency known as a unit standard competency. (A Unit Standard is typically a nationally registered document that describes performance standards for a competency. Industry representatives define and maintain the Unit Standard.)
A formal qualification results from the achievement of one or more unit standard competencies. Such qualifications are registered with a national Qualifications Framework, which identifies, for example, the number of credits attached to the qualification and to its constituent competencies, the awarding body, and the field of learning to which the qualification belongs.
Competency Types
If your enterprise defines many competencies, you may find it helpful to classify them by type. For example, you can define a competency type of Language Skills to include any language competency that your enterprise values (such as written Spanish, spoken Spanish, written Japanese, spoken Japanese, and so on). You can then retrieve competency definitions by type.
See: Competency Types
Rating Scales
Rating scales describe competencies and objectives in a general way.
Rating scales are of three types:
-
Proficiency scales measure a person's mastery of a skill or technique. For example, a person's management skills could be:
-
Basic
-
Good
-
Excellent
-
Expert
You apply proficiency rating scales to competencies only. You can apply a single proficiency scale to multiple competencies. (Alternatively, you can define proficiency levels that are unique to a competency. See: Competency Measurement)
You can measure unit standard competencies using proficiency rating scales. You may want to measure all enterprise competencies using the same scale, for example. However, you must also define outcomes and assessment criteria for unit standard competencies if they are to lead to formal qualifications.
-
-
Performance scales measure a worker's delivery of a competency or objective. A worker's competency can rank high on a proficiency scale but less high on a performance scale, or low on a proficiency scale but much higher on a performance scale. You can select a performance rating scale when defining competency assessment templates, objective assessment templates, and appraisal templates.
-
Weighting scales measure the importance of a competency to the enterprise. For example, a competency's importance could be one of:
-
Low
-
Medium
-
High
A skill that is extremely important to the enterprise would attract a higher weighting than one that is occasionally relevant or of minor importance. You can select a weighting scale when defining a competency assessment template.
-
Note: You can also apply weighting values to objectives. However, you do not use weighting scales. Instead, the lookup HR_WPM_WEIGHTING defines a single scale for use throughout the enterprise.
You can create rating scales that are available to a particular business group only or you can create global rating scales that are available to all organizations within your enterprise, irrespective of the setting of the HR: Cross Business Group profile option. If you use more than one rating scale of a particular type (for example, if you use multiple proficiency rating scales), ensure they are comparable by giving high numbers to high ratings and low numbers to low ratings.
Default Rating Scales
When you define a proficiency, performance, or weighting scale, you can make it the default scale of that type either within the current business group or globally. A default rating scale applies only when you define competencies.
Rating Scale Attachments
You can add attachments to rating scales. For example, you can attach a competency or objective description or a video of a person demonstrating a skill.
Competency Measurement
To measure competencies, you can define:
-
Proficiency levels, which are specific to a single competency
-
Proficiency rating scales, which you can apply to multiple competencies
Proficiency Levels
Each proficiency level that you define for a particular competency has a brief description and a detailed behavioral indicator that enables an assessor accurately to identify a worker's proficiency level.
The following table shows proficiency levels and behavioral indicators for the competency Merchandise Display.
| Level | Description | Behavioral Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Novice | Has no or minimal merchandise-display experience. Has completed no recommended training. |
| 2 | Beginner | Has completed five or fewer merchandise-display activities. Has completed training level 1. |
| 3 | Intermediate | Has completed 20 or fewer merchandise-display activities. Has completed training level 2. |
| 4 | Advanced | Has significant merchandise-display experience. Has completed training level 4 and trains junior staff. The worker's merchandise displays are known to improve sales of displayed items. |
| 5 | Expert | Is an acknowledged expert by his or her peers inside and outside the enterprise. Has significant merchandise-display experience. Has completed training level 6 and trains both junior and senior staff. |
The behavioral indicator for each proficiency level is detailed and specific: you could not apply these behavioral indicators unaltered to a different competency.
Proficiency levels are part of the competency definition.
Proficiency Rating Scales
Each level in a proficiency rating scale comprises a brief description and can include a behavioral indicator. However, the behavioral indicators are general enough to enable you to apply the scale to multiple competencies. For example:
| Level | Description | Behavioral Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Novice | Cannot work unsupervised. |
| 2 | Beginner | Can perform simple tasks unsupervised, but generally requires guidance. |
| 3 | Intermediate | Can perform basic tasks unsupervised, but requires guidance for more complex tasks. |
| 4 | Advanced | Can perform most tasks unsupervised, but requires occasional guidance. |
| 5 | Expert | Can perform all tasks unsupervised, and supervises others. |
As this rating scale lacks detail relevant to a specific competency, you could apply it to various competencies, such as Negotiating with Suppliers, Planning Store Layouts, and Inventory Control.
See: Rating Scales
Which Method of Measurement?
Proficiency levels are suitable if your enterprise competencies are varied and you want to define accurately what is expected of your workforce. The result is multiple, equivalent measurement systems. Proficiency rating scales are suitable if generic proficiency levels provide enough detail for your purposes and if consistency of measurement is important.
You can use both methods. For example, you could use a proficiency rating scale for your core competencies and proficiency levels for specific job or position competencies. Whichever approach you adopt, give high numbers to high ratings and low numbers to low ratings, so that analysis of the ratings gives consistent and sensible results.
Measuring Unit Standard Competencies
For unit standard competencies, which can lead to formal qualifications, you must define outcomes and specify assessment criteria. Outcomes are nationally defined behaviors or performance standards specific to the unit standard competency. Each outcome has a set of assessment criteria. A registered assessor (from the awarding body, for example) determines whether a worker has achieved the unit standard competency by measuring the outcomes using the assessment criteria.
You can also measure unit standard competencies using proficiency levels or proficiency rating scales. For example, you may want to measure all enterprise competencies using a general rating scale, regardless of whether they lead to formal qualifications. However, the proficiency rating scale or proficiency levels must be in addition to the outcomes and assessment criteria you define for unit standard competencies.
Assessing Competencies
During an appraisal, you assess a worker's competency levels using the measurement scheme defined for each competency.
See: Assessing Competencies and Objectives, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Competency Types
Enterprises that make full use of the Oracle HRMS competency functions may create or import many competency definitions. For example, you can define the competencies required by each grade of every job or position in your enterprise. For ease of management and retrieval, you can group competency definitions into competency types. The types themselves are for you to define. For example, you can define competency types to differentiate various skill sets, such as management skills, language skills, neonatal nursing skills, retail management skills, and so on. Alternatively, you can define a competency type for each job or position, such as sales manager, department manager, sales assistant, area manager, and so on. A competency can belong to more than one type, and overlap between types is likely to occur.
You can retrieve competencies by competency type when searching for competencies:
-
In the Find Competencies window
-
To include in the Competencies section of an appraisal when defining a competency assessment template
See: Assessment Templates, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
You can update a competency-type definition unless you have included the competencies belonging to a type in a current assessment template. This restriction prevents use of the type in multiple templates giving different results.
Defining Rating Scales
Use the Rating Scales window to define performance, proficiency, and weighting scales.
To define a rating scale
-
Enter a name and description for the rating scale.
-
Select the rating-scale type.
-
Select Default Rating Scale to make this rating scale the default of its type either within the business group or globally.
-
To make this rating scale available to all enterprise business groups, select Global.
Note: You cannot change this selection after saving the rating scale.
-
Enter the first level and level name. For example, enter 1 in the Level field and Novice in the Name field.
-
In the Behavioral Indicator field, describe the behaviors that define this performance level (for example, the worker cannot work unsupervised). You can enter up to 2000 characters in this field.
-
Save your work.
-
Repeat Steps 5 through 7 for subsequent levels until the rating scale is complete.
-
To add attachments to the rating scale, position the cursor in the rating-scale name field and click the Attachments icon to open the standard Attachments window.
-
Save your work.
Defining Competencies
Use the Competencies window to define competencies.
-
Select New in the Find Competencies window.
-
Select either Local or Global in the Scope region.
-
A local competency is visible only within the current business group, and the competency key flexfield for the business group defines the competency name structure.
-
A global competency is visible to all business groups in your enterprise. You can select Global only if your system administrator has set the HR: Global Competency Flex Structure user profile options to Yes. The global competency key flexfield defines the competency name structure.
Note: After saving a competency, you cannot change its scope.
If you change your scope selection before saving the competency, Oracle HRMS deletes any information that you have entered in the Name, Rating Scale, and Primary Evaluation Method fields.
-
-
Click in the Name field, and complete the fields in the Competence Flexfield window.
-
Enter a description for the competency.
-
If you use Oracle Projects, enter a name or code in the Alias field to identify the competency. Otherwise, leave the field blank.
-
If you are defining a unit standard competency, select Unit Standard in the Cluster field.
Note: After saving a competency, you cannot change its cluster value from Unit Standard to any other value.
Entering Rating or Proficiency Information
-
On the Valid Date and Proficiency tab, enter the dates between which the competency is valid. You must enter a start date, but you can leave the end date blank.
-
You can either select a general rating scale or define proficiency levels specific to this competency.
Note: This step applies primarily to competencies that are not unit standard competencies. Although you can select a rating scale or specify proficiency levels for a unit standard competency, you must also complete the tasks described in Entering Outcomes and Assessment Criteria.
To select a rating scale:
-
If you have defined a default proficiency rating scale for this type of competency (local or global), its name appears automatically in the Rating Scale field. Otherwise, select a rating scale.
-
To view the selected rating scale, click Levels.
To specify proficiency levels:
-
Click Levels to open the Levels window.
-
Define the first proficiency level by assigning a level number (for example, 0), a name (for example, Beginner), and a behavioral indicator (for example, the worker has no experience of inventory management and cannot perform basic tasks without supervision). Repeat this step for other proficiency levels.
Entering Competency Evaluation Details
-
Select the main method of evaluating the competency (for example, Written Examination or Peer Assessment).
-
To specify when the competency must be reassessed, enter a number in the Renewal Period field and select a unit. For example, enter 5 in the Renewal Period field and select Year if you assess the competency every 5 years.
-
Select Certification Required if you need a certificate to confirm possession of the competency. For example, you may need a driver's license to prove competency to drive.
If you select Certification Required, enter the certification method and date whenever you include this competency in a worker's competency profile.
-
Save your work.
The rest of this topic applies only if you are defining a unit standard competency.
Entering Qualifications Framework Details
Note: This section applies only if you are defining a unit standard competency.
-
Click the Unit Standard Qualifications Framework Details tab.
-
In the Unit Standard ID field, enter the Qualifications Framework code for the competency.
-
Select the main and subsidiary fields of learning to which the competency belongs.
The main field of learning identifies the industry or sector to which the competency belongs (for example, Management Studies or Nursing).
The subsidiary field identifies the subject area within the field of learning to which the competency belongs (for example, Marketing or Neonatal Care).
-
Select the level type and level.
Qualifications Framework levels indicate the extent to which knowledge and skills have been advanced by learning. For example, a competency could be at Level 6 on a scale ranging from Level 1 through Level 8.
The level type identifies the category to which the Qualifications Framework level belongs (for example, NQF, NVQ, or HND).
-
Select the credit type and enter the number of credits this competency earns.
The credit type identifies the unit of measure for unit standard credits. For example, the credit type could be notional hours of work or study required to achieve a unit standard competency.
-
Select the codes that identify the provider of the unit standard competency and the provider's Quality Assurance (QA) organization.
Entering Qualifications Information
Note: This section applies only if you are defining a unit standard competency.
-
Click Qualifications to open the Competency Qualifications window.
-
In the Qualification Links region, select the name of a qualification to which this unit standard competency contributes.
The identifier of the selected qualification appears automatically.
-
Select the unit standard type. This value specifies the relevance of the unit standard competency to the qualification (for example, core or optional).
-
Repeat Steps 20 and 21 for additional qualifications. (A single unit standard competency can contribute to more than one qualification.)
-
Save your work.
Entering Outcomes and Assessment Criteria
Note: This section applies only if you are defining a unit standard competency.
-
Click Outcomes to open the Outcomes and Assessment Criteria window.
-
Enter the number and name of a behavior or performance standard (for example, "Audience response above average" for a presentation skills competency).
-
Enter the dates between which the outcome is valid. You must enter a start date, but you can leave the end date blank.
-
In the Assessment Criteria field, define how to assess the outcome (for example, the audience rating for a minimum of three presentations is 60% or higher). This information must help an assessor decide whether an outcome has been achieved.
-
Repeat Steps 25 through 27 for additional outcomes.
-
Save your work.
Querying Competencies
When you open the Competencies window, the Find Competencies window opens automatically.
You can query competencies by specifying any combination of:
-
Full or partial competency name
-
Competency type
-
Qualifications Framework qualification, which limits the search to unit standard competencies that are linked to the qualification
-
Organization, job, or position, which limits the search to the competency requirements of the specified work structure
To query a competency
-
Specify a scope value:
-
Local limits the search to competencies in the current business group.
-
Global limits the search to competencies defined as global.
-
-
Enter your search criteria.
-
Click Find.
The first competency that matches your search criteria appears in the Competencies window. Scroll through additional matching competencies using the Down Arrow key.
The competency name comprises the values you entered in the Competency Flexfield window when you created the competency. For example, if the Competency Flexfield window has one required field and two optional fields, and you enter the competency name Teamwork in the required field and leave the optional fields blank, the competency appears in the Competencies window as "Teamwork ..", where two dots represent the empty optional fields.
Uploading Third-Party Competency Information
The Upload Third Party Skills function enables you to upload global competency definitions and rating scales from a text file or spreadsheet to Oracle HRMS using Oracle HRMS Web Applications Desktop Integrator (Web ADI).
See: Data Upload Using Web ADI, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
If you intend to upload competency information from a text file, then ensure the text is formatted correctly.
See: Format of Text Files, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Otherwise, you can enter competency information directly into the spreadsheet that Web ADI creates.
-
Select Upload Third Party Skills from the Career Management menu, and follow the on-screen instructions to populate the spreadsheet.
Note: Select an appropriate integrator and layout for the competency-information type that you want to upload. For example, select Upload Third Party Rating Scale integrator to upload rating scales.
-
Upload the spreadsheet contents to Oracle HRMS.
See: Uploading Data Using Web ADI, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
If the upload fails, correct any errors in the spreadsheet and retry the upload. Diagnostic messages appear in the Messages column at the end of each spreadsheet row.
Grouping Competencies into Types
Use the Competence Types window to group competencies into types.
Before you can perform this task, your system administrator must have added the enterprise competency types to the lookup COMPETENCE_TYPE.
To group competencies into types
-
Query the competency type.
-
Select competencies to include in this competency type.
-
Save your work.
Competencies that you do not add to a competency type belong to the type Other by default.
Competency Requirements
Competency Requirements
A worker's competency profile identifies competencies that the worker possesses and records the worker's proficiency level in each competency. You can also define the enterprise's competency requirements, which are competencies the workforce must have to deliver business success. You can use this information in various ways. For example:
-
You can search for candidates for vacancies and opportunities for workers, and identify the best match between the requirements of a role and the skills and experience of the worker.
-
When assessing workers during appraisals, you can compare worker competencies with the requirements and proficiency levels for their roles. Having a benchmark statement of requirements that is based on business need brings consistency and objectivity to the appraisal process.
-
You can target training and other development activities to close the gap between a worker's competencies and those required by the enterprise.
You can define your competency requirements for:
-
Business groups
-
Organizations
-
Jobs
-
Positions
In addition:
-
If you use Oracle iRecruitment, you can define competency requirements for vacancies.
See: Creating and Maintaining Vacancies, Oracle iRecruitment Implementation and User Guide
-
When using the Oracle SSHR Suitability Matching function, you can construct one-time lists of competency requirements when searching for:
-
Workers who meet those requirements
-
Work opportunities that require those competencies
-
Business Group (Core) Competencies
Competency requirements that you define for the business group are referred to as core competencies. Typically, core competencies are generic and fundamental to your enterprise strategy. For example, communication skills, negotiation skills, and quality focus may be suitable core competencies in your enterprise. Every member of the business group should demonstrate the core competencies, though the degree of proficiency can vary with seniority and experience. When you define the core competencies, you specify maximum and minimum proficiency levels to encompass the acceptable range.
Organization, Job, and Position Competency Requirements
Competency requirements that you define for organizations apply to all members of the organization but are not core competencies. Competency requirements that you define for jobs and positions apply to all holders of those roles. You can also define competency requirements for particular grades within job or position. Position competency requirements automatically include the requirements of the associated business group, organization, and job.
Essential Competencies
You can designate any competency requirement as essential. The Suitability Matching function identifies workers who possess essential competencies separately from those who possess desirable (nonessential) competencies.
See: The SSHR Suitability Matching Function
How HRMS Uses Competency Requirements
The SSHR Suitability Matching and Appraisals functions are the primary users of competency requirements.
The SSHR Suitability Matching Function
The Suitability Matching function, which you can access from HR Professional, Employee, and Manager Self-Service menus, enables you to find workers for opportunities and opportunities for workers. The application performs this function by comparing worker competency profiles with the competency requirements of business groups, organizations, jobs, positions, and vacancies. The comparison varies with each suitability-matching action. For example, for the action Find Suitable People by Role, you can search for a worker who matches the requirements of an organization only or of a job, position, or vacancy within that organization. You can also include the core competencies in the list of requirements to match.
When you perform the search for workers who match your competency requirements, HRMS identifies workers who:
-
Meet all essential and desirable competency requirements
-
Meet all essential competency requirements
-
Meet all desirable competency requirements
-
Meet some or no essential or desirable competency requirements
See: Suitability Matching
The Appraisals Function
When you perform an appraisal, you can assess a worker against the competency requirements of their job or position by selecting Include Job Competencies in the competency assessment template. This selection causes the core competencies, any organization competency requirements, and the job or position competency requirements to appear in the Competencies section of the appraisal. You can use the appraisals function View Competency Gaps to identify areas for development and select training to address deficiencies.
Reporting on Competency Requirements
HRMS can generate several reports that analyze competency profiles and competency requirements to provide business intelligence.
Workforce Intelligence Reporting
The Competence Requirement worksheet in the Competence (Skill) Development Detail Workbook lists the competency requirements of all organizations, jobs, positions, and grades in a business group.
See: Competence (Skill) Development Detail Workbook
Workforce Intelligence (HRMSi) Reporting
The Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics Workbook provides various analyses of worker competency profiles compared with the requirements of their roles within an organization hierarchy.
See: Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics Workbook
Defining Core Competencies
Core competencies are those required by every member of a business group, and you define them for the business group.
Use the Competence Requirements window.
To define core competencies
-
In the Business Group field, select a business group.
-
Click Find to display any competency requirements already defined for this business group. If the application displays existing competency requirements, you can:
-
Delete or edit existing competency requirements. To delete an existing core competency, select the competency and click the Delete icon.
-
Define additional competency requirements.
-
-
To define a core competency, click the first empty row of the competency table and select a competency.
-
In the Low and High fields, select the extents of the rating scale that are desirable for this competency in this business group.
-
If all workers in this business group must possess this competency, then select Essential. When performing suitability matches, the application lists workers who possess essential competencies separately from those who do not.
-
Enter the date from which this competency is required in this business group.
-
Repeat Steps 3 through 6 to define additional core competencies for this business group.
-
Save your work.
You can also define competency requirements for organizations, jobs, and positions.
See: Defining Organization, Job, and Position Competency Requirements
Defining Organization, Job, and Position Competency Requirements
You can identify the competencies that workers in an organization or holders of jobs or positions must possess. When you use the Suitability Matching function or advertise a vacancy, the application can compare worker competencies with the competency requirements for an organization, job, or position to find suitable candidates.
Use the Competence Requirements window.
To define competency requirements for an organization, job, or position
-
Select the organization, job, or position.
-
Click Find to display existing competency requirements. Note that positions inherit competency requirements defined for the business group (the core competencies), organization, and job with which they are associated. If the application displays existing competency requirements, then you can:
-
Delete or edit existing competency requirements. To delete an existing competency requirement, select the competency and click the Delete icon.
-
Define additional competency requirements.
-
-
To define a competency requirement, click the first empty row of the competency table and select a competency.
-
In the Low and High fields, select the extents of the rating scale that are desirable for this competency in this organization, job, or position.
-
If all workers in this organization, job, or position must possess this competency, select Essential. When performing suitability matches, the application lists workers who possess this competency separately from those who do not.
-
For jobs and positions only, select a grade, if appropriate.
-
Enter the date from which this competency is required.
-
Repeat Steps 3 through 7 to define additional competency requirements for this organization, job, or position.
-
Save your work.
Related Topics
Copying Competency Requirements
Copying Competency Requirements
You can copy the core competencies (those defined as required for the business group) or competency requirements defined for an organization, job, or position to another organization, job, or position.
Use the Competence Requirements window.
To copy competency requirements
-
Select the organization, job, or position to which you want to copy competency requirements.
-
Click Copy Competencies.
The Copy Competencies window opens.
-
To copy the core competencies, leave Core Competencies selected. Otherwise, deselect core competencies and select the organization, job, or position from which you want to copy the competency requirements.
-
To copy the proficiency levels, leave Copy Levels selected. Otherwise, deselect this value. Note that, if you copy the proficiency levels, then you can edit them after copying.
-
Specify the date from which these competency requirements apply to your organization, job, or position.
-
Click Copy Competencies.
-
Edit or delete any of the copied competency requirements, if required. For example, you may want to enter a grade for competency requirements that you copy to a job, change the validity dates of a requirement, or delete duplicate requirements.
-
Repeat this procedure from Step 2 to copy additional competencies, if appropriate.
-
Save your work.
Viewing Competency Requirements
Use the Competence Requirements window to view competencies required at the business group, organization, job or position level.
To view competency requirements
-
Select the business group, organization, job, or position.
-
Click Find.
The application displays competency requirements defined for the specified work structure.
Competency Profiles
Competency Profiles
A competency profile is a list of a worker's competencies showing the worker's level of proficiency in each competency. For unit standard competencies, which the worker usually acquires in increments, the competency profile shows whether the competency is In Progress or Achieved.
Setting Up the Competency Profile
You can create a worker's competency profile when the worker first joins the enterprise using details from the worker's resume, tests, or interviews. You can also copy competency requirements from a vacancy definition in Oracle iRecruitment to a competency profile.
Copying Core or Primary Assignment Competencies to the Competency Profile
Some competencies are important for all employees throughout your enterprise. Such competencies are referred to in Oracle HRMS as core competencies, and you define them as competency requirements for the business group. Other competencies are required for particular organizations, jobs, positions, or grades within job or position. You can copy both the core competencies and any competency requirements associated with a worker's primary assignment to the worker's competency profile. This feature enables you to set up a worker's competency profile efficiently and ensures that you assess the worker's proficiency in all relevant competencies.
See: Creating a Competency Profile
Maintaining Competency Profiles
You can update a worker's competency profile at any time using:
-
The Manager Self-Service Competency Profile function
-
The Employee Self-Service Competency Profile function
-
The Competence Profile window in the forms-based interface
If you need to recertify a competency at intervals (for example, annually), then you can define a periodic alert (using Oracle Alert) to notify you as the recertification date approaches.
Assessing Competencies in an Appraisal
You can assess a worker's competencies during an appraisal if you include a competency assessment template in the appraisal template. Otherwise, no Competencies section appears in the appraisal. Competency assessment templates can include some competencies (for example, those required by a worker's job) by default. You can update the Competencies section for a worker during the appraisal process. For competencies already included in the worker's competency profile, the worker's current proficiency level appears in the Competencies section of the appraisal.
See: The Appraisal Template, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide and Assessment Templates, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
HRMS can update a worker's competency profile automatically after an appraisal. You can enable this feature at site level by setting the user profile option Apply Assessment Competencies to Person to Yes.
See: Setting Up the Appraisal Process, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Alternatively, you can enable this feature at appraisal level by selecting Update Competency Profile in the appraisal template.
See: The Appraisal Template, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
When you enable this feature, HRMS writes the new proficiency level (allocated to the worker on the Final Ratings page of the appraisal by the main appraiser) to the worker's competency profile.
The Competency Profile and Oracle Learning Management
Training is the primary method of acquiring new skills and developing existing skills. Users of Oracle Learning Management can configure the application to update learners' competency profiles automatically on successful completion of training.
See: Competencies, Oracle Learning Management Implementation Guide and Configuring Competency Update Automation, Oracle Learning Management Implementation Guide
How HRMS Uses Competency Profiles
The Oracle HRMS Self-Service Suitability Matching function enables you to:
-
Find workers for opportunities.
-
Find opportunities for workers.
The application performs this function by comparing worker competency profiles with the competency requirements of vacancies, jobs, and positions.
See: Suitability Matching
Reporting on Competency Status
HRMS can generate several reports that analyze competency profiles and competency requirements to provide business intelligence.
Workforce Intelligence Reporting
The Competence (Skill) Development Detail Workbook provides two worksheets of interest:
-
The Person Competence Profile Worksheet identifies workers with similar competency profiles and enables you to compare the competency profiles of workers at the same grade.
-
The Competence Delivered by Training Activity worksheet identifies competencies workers acquire by means of formal learning activities.
See: Competence (Skill) Development Detail Workbook
The Competence Updates after Appraisal workbook provides a summary of changes made to competency profiles (either automatically or manually) after appraisal completion.
See: Competence Updates after Appraisal Workbook
Workforce Intelligence (HRMSi) Reporting
The Competence Levels (Organization Hierarchy) Detail Analytics Workbook displays, for an organization hierarchy, each worker's proficiency level in a selected competency.
See: Competence Levels (Organization Hierarchy) Detail Analytics Workbook
The Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics Workbook compares the competency requirements of a job with the competency profiles of workers occupying that role.
See: Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics Workbook
Suitability Matching
The SSHR Suitability Matching function, which is available to HR Professionals, managers, and workers, enables you to compare a worker's competency profile and work preferences with the requirements of a work opportunity.
Depending on the responsibility used, the default Suitability Matching page offers users between four and ten suitability-matching options. For example, workers can use this function to search for work opportunities for themselves, and managers and HR Professionals can use this function to find candidates for work opportunities.
The available suitability-matching options are shown in the following table.
| Category | Option | Access by Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Find a Person for a Work Opportunity | Find Suitable People by Role | Manager, HR Professional |
| Find a Person for a Work Opportunity | Find Suitable People by Competency | Manager, HR Professional |
| Find a Person for a Work Opportunity | Compare People by Current Role | Manager, HR Professional |
| Find a Person for a Work Opportunity | Compare Named Successors for a Position | HR Professional |
| Find a Person for a Work Opportunity | Compare Applicants for a Vacancy | Manager, HR Professional |
| Find a Work Opportunity for a Person | Find Work Opportunities by Role | Manager, Employee, HR Professional |
| Find a Work Opportunity for a Person | Find Work Opportunities by Competency | Manager, Employee, HR Professional |
| Find a Work Opportunity for a Person | Compare Pending Applications | Manager, Employee, HR Professional |
| Find a Work Opportunity for a Person | Compare Succession Options | HR Professional |
| Find a Work Opportunity for a Person | Compare Current Assignments | Manager, Employee, HR Professional |
Creating a Competency Profile
Use the Competence Profile window to create, view, and update a worker's competency profile. Alternatively, you can use the SSHR Competency Profile function, which is available to both employees and managers.
The Competence Profile window displays all competencies, past and present, held by the worker. To see only current competencies and proficiency levels, select Current Competencies. If a worker has a competency profile in more than one business group, then you can see, but not update, any global competencies the worker acquired in other business groups.
To populate a worker's competency profile, you can:
-
Add competencies individually to the profile.
-
Copy competencies to the profile.
The amount of information you enter for a competency depends on the competency type: unit standard competencies require more information than non-unit-standard competencies.
To add individual competencies to a competency profile
-
Select the first competency this worker possesses.
-
Select the worker's proficiency level in this competency.
Note: If you update a proficiency level, enter the date from which the new level applies. When you save the competency profile, HRMS automatically ends the previous proficiency level on the day before the new level starts.
-
Enter the date from which the worker possesses the competency at this level. You can enter an expiry date, if required.
-
In the Source of Proficiency Rating field, you can select the method, such as training course or previous experience, by which the worker gained the competency.
The Status Field
The Status field, which is read only, can contain the value Achieved or In Progress.
-
When the worker has achieved all outcomes for a unit standard competency, its status is Achieved. Otherwise, its status is In Progress.
When you save the competency profile, Oracle HRMS changes the status of a unit standard competency from In Progress to Achieved if the person has achieved all outcomes for the competency.
-
All non-unit-standard competencies have the status Achieved, by default.
When you add a competency to the profile, the Status field is blank. Oracle HRMS populates the field only when you save the competency profile.
-
Entering Certification Details
-
Click the Certification tab.
-
Select the certification method (for example, examination) for the competency, and enter the certification date.
-
In the Next Review field, enter the date on which you must reassess the competency, if appropriate.
Viewing Qualifications Framework Details
-
Note: This step applies to unit standard competencies only.
Click the Unit Standard Qualifications Framework Details tab.
The Qualifications Framework Details for the unit standard competency appear, including the number of credits associated with the competency, the field of learning to which the competency belongs, and the unit standard identifier.
-
Repeat from Step 1 to select additional competencies.
-
Save your work.
To record outcomes achieved
Note: This procedure applies to unit standard competencies only.
You record outcomes achieved towards a unit standard competency in the Outcomes Achieved window.
-
Select a unit standard competency and click the Outcomes Achieved button.
-
Select the name of the outcome achieved towards the selected unit standard competency.
The assessment criteria for this outcome appear in the Assessment Criteria field.
-
In the Date From field, select the date on which the outcome was assessed as achieved.
-
If you must reassess the outcome at a future date, enter that date in the Date To field.
-
Repeat from Step 2 for additional outcomes for this unit standard competency.
-
Save your work.
If the worker has achieved all outcomes for a unit standard competency, Oracle HRMS updates the status of the competency to Achieved when you save the competency profile. Otherwise, the competency status remains In Progress.
To copy competencies to the competency profile
-
Click Copy Competencies to open the Copy Competencies window.
-
In the Copy Competencies window, do one of the following:
-
Select Core Competencies to copy competency requirements defined for the business group.
-
Select Primary Assignment Competencies to copy competency requirements from the organization, job, position, and grade to which the worker is assigned.
-
Select a vacancy to copy the competency requirements from a vacancy definition in Oracle iRecruitment. The application automatically copies the competencies defined for the vacancy.
-
-
Enter the dates between which the copied competencies are valid. You must specify a start date, but the end date is optional.
-
Click Copy.
You can delete or update any of the copied competencies (for example, by specifying proficiency levels and certification details).
-
Save your work.
Entering Work Preferences for a Worker
You can record workers' preferences, such as their willingness to travel or relocate and their preferred working hours. When you use the SSHR Suitability Matching function to match workers to opportunities or find opportunities for workers, the application can take work preferences into account.
To enter work preferences, you can use the Self-Service Work Preferences function, which is available to both managers and employees.
In the forms-based interface, use the Work Preferences window, accessed from the People window.
To enter work preferences for a worker
-
Select any relevant work capabilities. For example, if a worker will accept international travel but is not willing to relocate domestically, select Visit Internationally but leave Relocation Required for Position deselected.
-
Enter the worker's preferred working hours and work schedule.
-
Complete the International Deployment region if the worker is willing to relocate or travel internationally.
-
Save your work.
Related Topics
Entering Work Choices for a Job or Position, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Qualifications
Qualification Types
Oracle HRMS enables you to record the types of qualifications recognized by your enterprise, including:
-
Educational and vocational qualifications
-
Licenses
-
Awards
-
Honors
You can rank qualifications. For example, you could rank a doctorate as 1, a master's degree as 2, a bachelor's degree as 3, and so on. You can rank equivalent qualifications at the same level. For example, you could rank both a bachelor's degree and a vocational qualification as level 3. This feature is useful for identifying all workers qualified at level 3 or above, for example.
Qualifications Framework Qualifications
Qualifications Framework qualifications result from the achievement of unit standard competencies. For this type of qualification, you record national Qualifications Framework details, including the number of credits attached to the qualification, the awarding body, and the field of learning to which the qualification belongs.
Schools and Colleges
You can identify the schools and colleges that deliver the qualifications that your enterprise recognizes so that you can record where a worker gained a qualification. As schools and colleges are available to all business groups, you have to define them once only.
Defining Qualification Types
Use the Qualification Types window to define the qualifications that your enterprise recognizes.
Before you start this task, your system administrator must define generic qualification types (such as Degree, Diploma, and License) in the PER_CATEGORIES lookup.
To define qualification types
-
Enter the name of the qualification.
-
In the Category field, select the qualification type.
-
If required, rank the qualification.
Entering Qualifications Framework Details
Note: This section applies only if you are defining a Qualifications Framework qualification.
-
Enter the Qualifications Framework identifier for the qualification.
-
Select the Qualifications Framework qualification type (for example, Diploma, Bachelor of Arts, or School Certificate).
-
Select the main and subsidiary fields of learning to which the qualification belongs.
The main field of learning identifies the industry or sector to which the qualification belongs (for example, Management Studies or Nursing).
The subsidiary field identifies the subject area within the field of learning to which the qualification belongs (for example, Marketing or Neonatal Care).
-
Select the level type and level.
Qualifications Framework levels indicate the extent to which knowledge and skills have been advanced by learning. For example, a qualification could be at Level 3 on a scale ranging from Level 1 through Level 5.
The level type identifies the category to which the Qualifications Framework level belongs (for example, NQF, NVQ, or HND).
-
Select the credit type and enter the total number of credits for this qualification.
The credit type identifies the unit of measure for unit standard credits. For example, the credit type could be notional hours of work or study required to achieve a Qualifications Framework qualification.
-
Select the qualification provider.
-
Select the Quality Assurance (QA) organization that registered the qualification provider.
Entering Qualification Competencies
Note: This section applies only if you are defining a Qualifications Framework qualification.
-
Click Competencies to open the Qualification Competencies window.
-
In the Unit Standard Competency Links region, select the name of a unit standard competency that contributes to this qualification.
The Unit Standard ID appears automatically.
-
Select the unit standard type. This value specifies the relevance of the unit standard competency to the qualification (for example, core or optional).
-
Enter the dates between which the link is valid. You must enter a start date, but you can leave the end date blank.
-
Repeat Steps 12 through 14 for additional unit standard competencies.
-
Save your work.
Entering Qualifications
You can enter your workers' completed and in-progress qualifications when they first join the enterprise. You may need to update a worker's qualifications record after completion of a training course, for example.
Note: If the worker for whom you are entering qualifications has qualifications records in other business groups, then you will be able to see, but not update, qualifications entered for the worker in those other business groups.
Workers and managers can use these SSHR functions to enter and update worker qualification records:
-
Education and Qualifications
-
Other Professional Qualifications
In the forms-based interface, use the Qualifications window, accessed from the People window, to enter and update qualifications.
To enter qualifications
-
Select the qualification type, and enter its title.
For information about defining qualification types, see: Defining Qualification Types
-
Select the qualification status, for example, ongoing or completed.
-
Enter the grade at which the worker holds the qualification, if appropriate.
-
Select the establishment at which the worker gained the qualification. The list comprises establishments you recorded the worker as having attended.
-
Enter the name of the body that awards the qualification. If you record this value in the qualification types record for a Qualifications Framework qualification, it appears here automatically.
-
Enter the dates between which the worker studied for the qualification. Leave the end date blank if the qualification is in progress.
-
Enter the worker's ranking in the study group, if relevant.
-
Save your work.
To enter license details
-
Click the License tab.
-
Enter the license number, for example, a driver's license number.
-
Enter any restrictions on the license. For example, the license may not be valid in certain states.
-
Enter the license expiry date.
To enter tuition fees
-
Click the Tuition tab.
-
Enter the fee amount, and select the currency.
-
Select the tuition method, for example, day release.
-
Specify how the worker's tuition fees will be reimbursed (for example, bank transfer when the qualification is awarded).
To enter training details
-
Click the Training tab.
-
Enter the amount of training completed. For example, enter 30 days completed of a training program that lasts 60 days.
-
Enter the total amount of training required to deliver the qualification (for example, 60 days).
-
Enter the units in which the training is measured, for example, days.
To enter professional membership details
-
Click the Professional Membership tab.
-
Select the professional body to which the person belongs. The list comprises organizations with the classification Professional Body.
-
Enter the worker's membership number and category.
The available membership categories depend on the table used to calculate subscription rates for the professional body. Oracle Payroll uses this table when calculating the amount to deduct from a worker's salary during the payroll run.
-
Select the method by which the subscription is to be paid. This is optional and for information only.
To view Qualifications Framework details
Note: This section applies to Qualifications Framework qualifications only.
-
Click the Qualifications Framework Details tab.
-
Details of the selected qualification appear. For example, you can see its ID, the field of learning to which it belongs, and the number of credits earned. You cannot update this information.
To enter subject details
-
Save your work.
-
Select the first subject the qualification comprises.
-
Select the subject status, for example, passed or ongoing.
-
Enter the dates between which the subject is studied. You must enter a start date, but you can leave the end date blank.
-
If the subject forms a major part of the qualification, select Major.
-
Optionally, enter the grade at which the worker studies the subject.
-
Enter further subjects, as appropriate.
-
Save your work.
Defining Schools and Colleges
Use the Schools and Colleges window to define the establishments that deliver the qualifications that your enterprise recognizes.
To create establishments
-
Enter the establishment name.
-
Enter the location name.
-
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for additional establishments or locations.
-
Save your work.
These establishments appear in the list of schools and colleges in the Schools and Colleges Attended window.
Entering Schools and Colleges Attended
Use the Schools and Colleges Attended window, accessed from the People window, to enter a worker's attendance at educational establishments.
Note: If a worker has person records in other business groups, then you can see, but not update, any establishment information entered for the worker in those other business groups.
To enter schools and colleges attended
-
Select the name of the school or college attended.
If the school or college does not appear in the list of values, then you can enter the information in the name field.
Note: If you enter the name of the school or college, then it is available for this worker only. To update the global list of schools and colleges that is available to all workers, see: Defining Schools and Colleges
-
Enter the attendance dates, and indicate whether the worker's attendance was full time. If the attendance is ongoing, then leave the end date blank.
-
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for additional establishments.
-
Save your work.
In a worker's qualifications record, you select the establishment at which the worker gained a qualification from the list of schools and colleges the worker attended.
Career Paths
Career Paths
A career path defines a route to a job or position from a different job or position that is lower in the hierarchy. You can base career paths on either job progression or position progression, but not both. A job or position can appear in multiple career paths, but once only in any single career path.
You can identify career paths for a worker in various ways. For example, you can include the names of possible career paths:
-
In the Overall Rating and Comments or Advancement Potential sections of the worker's appraisal
-
In appraisal questionnaires
-
In a document or in comments attached to a worker's record
Career Paths Based on Job Progression
The career path is a hierarchy of jobs that you build from the top down. For example, for the job Area Sales Manager, you could define the following career path to show possible routes to that job:
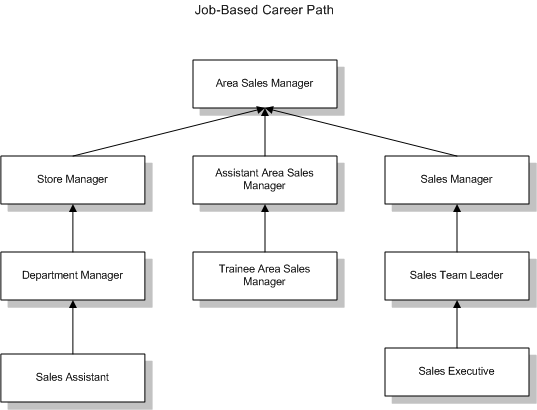
Lines of Progression for Affirmative Action Plan (AAP) Reporting (U.S. Only)
For the AAP-Workforce Analysis report, you use career paths based on job progression to define lines of progression.
Career Paths Based on Position Progression
For career paths based on position progression, you define a standard position hierarchy.
See: Creating a Position Hierarchy, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Defining Career Paths
A career path shows a route to a job or position from a different job or position.
You define career paths for positions using position hierarchies.
See: Position Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
You define career paths for jobs using the Career Path Names window and the Map Career Path window.
To define a career path based on job progression
-
In the Career Path Names window, enter the names of the career paths you want to define.
-
Save your work.
-
Open the Map Career Path window. In the Name field, select the top job in the career path you are mapping.
-
In the Career Path Name field, select the name of a career path you defined in Step 1.
-
In the Job Progression From block, select all jobs that are one level down from the job identified in the Name field.
-
To extend the career path downwards from any one of these jobs, select the relevant Down check box.
The window now shows your selected job in the Name field. The Job Progression To field now shows the job at the top of the career path.
-
Repeat Steps 5 and 6 until the career path is fully defined. To move back up the career path, select the Up check box.
-
Save your work.
Skills Matching
The Special Information Approach to Skills Matching
From Release 11 onwards, the recommended approach to holding and matching skills information is to define a framework of competencies. These provide the common language for a wide range of human resource activities including assessments, appraisals, employee profiling, career development, and recruitment. You can build up a wealth of skills information that can be maintained and used by employees and line managers themselves, using the web Direct Access interface.
However, Oracle HRMS continues to support the earlier approach to handling skills information, using Special Information Types. This is an alternative to the competence approach.
What are Special Information Types (SITs)?
Special Information Types are a flexible way to hold additional information you require about people and, if necessary, to compare this information with the requirements of jobs or positions. For each Special Information Type you can define up to thirty fields to hold details of competencies, professional qualifications, education, and valid experience. For each person, job, or position, you can make multiple entries for each Special Information Type.
For example, suppose you want to store details of technical skills. You could set up the following fields:
-
Skills - with a list of valid values to control the vocabulary used to describe the skills
-
Years Experience - to hold the number of years of experience in using the skills
You can display the fields you define in one or more of the following windows:
-
Special Information, to record skills or experience for an employee or applicant
-
Job Requirements, to hold skill requirements for a job
-
Position Requirements, to hold skill requirements for a position
-
Skill Provisions, to record the skills or qualifications provided by training activities in Oracle Training Administration
Using views and reports, you can then match people to posts, according to their skills or other attributes.
Matching Skills Requirements to Special Information
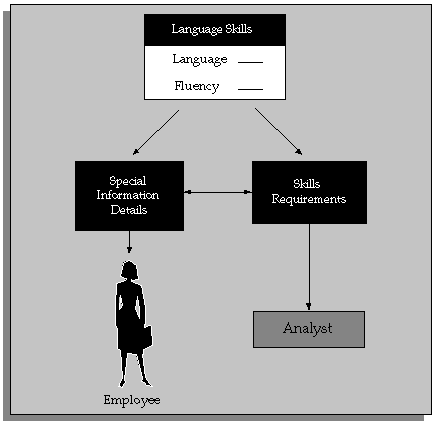
Tips for Defining Special Information Types to Hold Skills Information
-
If you want to give different sets of people access to different categories of skills information, define each category as a separate Special Information Type. You can configure the Special Information window to display just one Special Information Type.
-
If you want to match on a range of skills levels, it is easier to use numeric values. Use a description field to provide the meaning for each level. The description appears automatically when the number is chosen.
-
You can use cross-validation to ensure that users enter correct combinations of segments. For example, you could ensure that when a language skill is entered, a fluency level is also selected.
-
You can speed up data entry and minimize errors by defining an 'Alias' for common combinations of segment values. For example, completion of a course may always result in a specific certificate from a particular licensing body. A user could enter all of these values with a single Alias.
-
If you want users to enter the precise title of a qualification (perhaps read from a resume), you cannot supply a list of values. However, consider providing additional fields with lists of values using broad terms such as 'degree-level' or 'science' to help users searching for information.
Unstructured Information
You may want to hold some skills information, such as resumes, as unstructured, free text information. You can store this information as attachments to the People and Special Information windows.
Skills Matching Report
The standard Skills Matching Report matches people against all the requirements you have entered for one job or position (held in Special Information Types).
The List People By Special Information window displays a list of people who match a particular profile for one Special Information Type.
Running the Skills Matching Report
This report matches employees, applicants, or both against the requirements of one job or position (held in Special Information Types). You can select the closeness of the match you require.
You run reports in the Submit Requests window.
To run the Skills Matching Report:
-
In the Name field, select Job and Position Skills Matching Report.
-
Enter the Parameters field to open the Parameters window.
-
Select the Job or Position to which you want to match people.
-
Select the person type, or types, you require.
-
Select the closeness of match you require from one of the following levels:
-
One or more essential skills
-
All essential skills
-
All essential and one or more desirable skills
-
-
Choose the Submit button.
Event and Attendance Administration
Event and Attendance Administration
You can use the events and attendance administration features in Oracle Human Resources to:
-
Set up events
-
Book employees and applicants onto events
-
Record information about employee interviews, such as disciplinary hearings and performance reviews
Note: The system administrator can create configured versions of the Event Bookings window so that you use one version for employees and another version for applicants.
Event Bookings and Attendance
You can view all the events a person has attended or is scheduled to attend in the Oracle HRMS Book Event window. You can also enter new bookings here. See: Creating a Booking Event
Employee Reviews
You can use the Employee Review window to record information about any employee interview, such as a performance review, disciplinary hearing, or medical test.
To prepare for a performance review, you can view the employee's:
-
Career history, using the Assignment History window
-
Likely career paths
See: Career Paths
If you are using Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR), you can use web-based access to complete assessment and appraisal templates for your employees.
Events, Reviews and Competence Profiles
If you have adopted the competence approach, you can use events or reviews as an opportunity to update your employees' competence profiles. For example, you may decide that employees' attendance at a team-leading seminar provided them with the Team-Leading competence at level 1. Once you have determined the competencies delivered by the event, you can update the appropriate employees' competence profiles.
Entering Performance Ratings
Entering Performance Ratings
You carry forward details from the Employee Review window to the Performance window (which opens from the Salary Administration window). In this window, you can enter performance ratings for an employee at any time. You can also schedule the next performance review, and, optionally, associate a salary change with a performance review.
Note: You cannot use a performance review entered through Oracle Self-Service Human Resources (SSHR).
In order to perform this task, performance rating values for the Lookup Type PERFORMANCE_RATING must have been defined.
To enter a performance rating for an existing review:
-
Select an existing review by one or all of the following:
-
Date
-
Location
-
Type
-
-
Select a performance rating.
-
Enter the next performance review date, if required. (If you entered a time period for regular performance reviews in the Salary Information region of the Assignment window, the date of the next review appears automatically).
To enter a new review and performance rating:
-
Enter the new review date.
-
Select a performance rating, if required.
-
Enter the next performance review date, if required. (If you entered a time period for regular performance reviews in the Salary Information region of the Assignment window, the date of the next review appears automatically)
The Employee Review
Entering an Employee Review
You can record details of a review event using the Employee Review window.
Before you can enter employee reviews, different types of employee interview must have been defined as values for the Lookup Type EMP_INTERVIEW_TYPE. These interview types could include disciplinary hearings and performance reviews.
To enter a review for an employee:
-
Select an interview type, and enter a start date. The other fields are optional.
If you select a location for the employee's review that has a time zone associated with it, the Timezone field displays the time zone with that location, regardless of your location.
-
Save the review.
-
You can select reviewers by name or employee number. Save your work.
If you want to enter a performance rating for the employee associated with this review, navigate to the Assignment or Salary Administration window.
Book Event Window
Creating a Booking Event
You use the Book Event window to create booking events.
Tip: Your system administrator can set up the Additional Event Details descriptive flexfield to record booking statuses (such as Wait Listed, Confirmed, and Attended). This descriptive flexfield displays on the Book Event window, the Employee Review window, and the Applicant Interview window.
You can select relevant values in the Type field, such as departmental meeting or marketing presentation, only if your system administrator defines values for the Lookup Types EMP_EVENT_TYPE and APL_EVENT_TYPE. Before you create booking events, ensure that relevant values are available in the Type field.
U.S. only: All Tenure-specific events must begin with the word Tenure.
To create a booking event
-
Select the type of event in the Type field, and then enter the date, time, supplying organization, location, and contact name.
Note: You can only select locations that are associated with a timezone. You associate a location with a timezone in the Location window.
-
Save the event.
-
You can select attendees by name or number in the Bookings block of this window.
Workforce Intelligence Key Concepts for Competencies, Qualifications and Development
Key Concepts for Competencies, Qualifications, and Development Intelligence
Competencies, Qualifications and Development Intelligence enables you to investigate the competencies and proficiencies of employees and applicants.
The following concepts enable you to accurately interpret the results of the Competencies, Qualifications and Development intelligence reports:
Competencies and Proficiencies
Within Oracle HRMS, you define competencies and proficiencies against a person and job. If a person has multiple assignments for the same job, these reports only count the person once. This ensures that trends remain accurate.
In order to appear in the reports, people must work for the required job and grade for a competence on the report run date.
Note: You must define competencies against jobs, and assign valid grades to jobs, or these reports will not be able to compare individual's proficiencies with their job competence requirements.
Workforce Intelligence for Competencies, Qualifications and Development
Competence (Skill) Development Detail Workbook
This workbook investigates the skills of your workforce, with regard to skills held by workers, skills required, or skills delivered through training, within your organization. The resulting information enables you to:
-
View competencies owned by workers within your organization
-
Analyze competence shortages within your organization
-
Analyze competencies delivered by training
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
Competence Delivered by Training Activity
-
Competence Requirement
-
Person Competence Profile
Competence Delivered by Training Activity Worksheet
This worksheet reports on competencies delivered by training activities and events. The resulting information enables you to:
-
Compare the competencies delivered by training to those required.
-
Analyze training efficiency.
Business Questions
Which competencies do courses provide?
Competence Requirement Worksheet
This worksheet displays competence requirements for all organizations within a business group. The worksheet enables you to analyze competence requirements for business groups, organizations, jobs, positions, and grades. For each requirement you can investigate the:
-
Competencies needed for a particular job.
-
Skills shortages within an organization.
Business Questions
Which jobs require a particular competence, and at what level?
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Required For
Populates the Required For column with the organization and job that require a particular competence.
Person Competence Profile Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to analyze people's competency profiles by type. It enables you to:
-
View people with similar competencies.
-
Compare people of similar grade.
Business Questions
How proficient is an individual for a particular competence?
Related Topics
Workforce Intelligence for Competencies, Qualifications and Development Key Concepts
Competence Updates after Appraisal Workbook
The Competence Updates after Appraisal Workbook enables administrators and managers to view competence updates, both automatic and manual, made as a result of a completed appraisal. You can view competence updates for all appraisals within your business group, target a specific subset of one supervisor's ongoing appraisals, or specify other combinations.
Worksheets
This workbook contains two worksheets:
-
Competence Updates after Appraisal by Organization Hierarchy
-
Competence Updates after Appraisal by Supervisor Hierarchy
Competence Updates after Appraisal by Organization Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet lists competence updates resulting from completed appraisals performed on workers in a given organization. Data includes appraisee and appraiser names, dates, competence names, and new and previous (if any) proficiency levels for each competence.
Business Questions
What competence updates have appraisees in my department received through appraisals?
Parameters
You must enter values for five parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Rollup Organization
-
Start Date
-
End Date
Competence Updates after Appraisal by Supervisor Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet lists competence updates resulting from completed appraisals performed on workers under a specified supervisor.
Business Questions
What competence updates have my direct and indirect reports received through appraisals?
Parameters
You must enter values for three parameters:
-
Supervisor
-
Start Date
-
End Date
Workforce Intelligence (HRMSi) for Competencies, Qualifications and Development
Competence Levels (Organization Hierarchy) Detail Analytics Workbook
The Competence Levels (Organization Hierarchy) Detail Analytics workbook displays the competence levels attained by individuals in the enterprise for a competence.
Business Questions
Which people are the most proficient and which people are the least proficient in a competence?
Parameters
Before running the worksheets you must enter a value for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Rollup Organizations – Yes/No
-
Person Assignment Type
Use the following parameters to further restrict the values in the workbook:
-
Competence Name
Or you can select a competence from the Competence page item in each worksheet.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
By Person with Rank
-
By Person
By Person with Rank Worksheet
The by Person with Rank worksheet lists each individual who have the selected competence, and shows you both the proficiency level they have achieved, and the proficiency level translated into a proficiency rank. You define proficiency levels against a competence for a job.
Proficiency ranks translate the proficiency levels into a more even spread of values. These values can provide a more consistent method for assessing proficiency ratings across competencies.
Headings and Calculations
The Person with Rank worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Person
The person's name.
-
Proficiency Level
Each person's proficiency level for the selected competence.
-
Proficiency Level Percent
Each person's percentage proficiency level for the selected competence.
-
Proficiency Level Rank
Each person's proficiency rank for the selected competence.
-
Proficiency Rank Percent
Each person's percentage proficiency rank for the selected competence.
By Person Worksheet
The by Person worksheet examines the people who hold the selected competence and their proficiency levels.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Person
The person's name.
-
Proficiency Level
Each person's proficiency level for the selected competence.
Related Topics
Workforce Intelligence for Competencies, Qualifications and Development Key Concepts
Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics Workbook
The Competence Match (Organization Hierarchy) Status Analytics workbook compares the competence requirements of a person's job with the person's competence proficiency levels.
This workbook helps you decide which applicants suit a vacancy, or which contingent worker suits an assignment. The workbook also highlights competence gaps in your enterprise, and so you can use it to gather training requirements.
Business Questions
How do the competencies of people in my enterprise match the competence requirements for jobs in my enterprise?
Parameters
Before running the worksheets you must enter a value for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Rollup Organizations – Yes/No
-
Job
-
Person Assignment Type
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
Compare to Minimum Proficiency
-
Compare to Range
-
By Organization and Location
-
By Person
-
By Person Graph
Compare to Minimum Proficiency Worksheet
The Compare to Minimum Proficiency worksheet compares people's proficiency levels with the minimum proficiency requirement for each competence relevant to their job. The worksheet displays how many people have the required competencies, and compares people's proficiency levels to the required minimum.
Headings and Calculations
The Compare to Minimum Proficiency worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Competence
The competencies you have defined for the job you selected in the Job parameter.
-
Min Required
The minimum level required for the competence.
-
Max Required
The maximum level required for the competence.
-
Without Competence
The number of people in the job who have no competence recorded.
-
Without Level
The number of people who have the competence, but no recorded level.
The worksheet has further columns that list the number of people whose ratings are above or below the minimum competence level required for the job.
The columns are as follows:
| Column Name | Rating |
|---|---|
| <-3 | More than three levels below the competence minimum level |
| -3 | Three levels below the competence minimum level |
| -2 | Two levels below the competence minimum level |
| -1 | One level below the competence minimum level |
| Exact Match (Min Required) | Matches the competence minimum level |
| +1 | One level above the competence minimum level |
| +2 | Two levels above the competence minimum level |
| +3 | Three levels above the competence minimum level |
| <+3 | More than three levels above the competence minimum level |
Compare to Range Worksheet
The Compare to Minimum Proficiency worksheet compares people's proficiency levels to the required proficiency range for each competence relevant to their job. The worksheet displays how many people have the required competencies, and compares people's proficiency levels to the required proficiency level range.
Headings and Calculations
The Compare to Range worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Competence
The competencies you have defined for the job you selected in the Job parameter.
-
Min Required
The minimum level required for the competence.
-
Max Required
The maximum level required for the competence.
-
Without Competence
The number of people in the job who have no competence recorded.
-
Without Level
The number of people who have the competence, but no recorded level.
The worksheet has further columns that list the number of people whose ratings are above or below the minimum competence level required for the job.
The columns are as follows:
| Column Name | Rating |
|---|---|
| <-3 | More than three levels below the competence minimum level |
| -3 | Three levels below the competence minimum level |
| -2 | Two levels below the competence minimum level |
| -1 | One level below the competence minimum level |
| Exact Match (Min Required) | Matches the competence minimum level |
| +1 | One level above the competence minimum level |
| +2 | Two levels above the competence minimum level |
| +3 | Three levels above the competence minimum level |
| <+3 | More than three levels above the competence minimum level |
By Organization and Location Worksheet
The by Organization and Location worksheet enables you to see each person's level of proficiency for the competencies for their job.
Headings and Calculations
The by Organization and Location worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Location Name
-
Organization
The organizations within each location.
-
Competence
The competencies you have defined for the selected job, for each organization.
-
Person
The people in each organization who hold the selected job.
-
Required Proficiency Level
The minimum proficiency level required for the competence for the person's job.
-
Requirement Effective From
The date the proficiency level requirement began.
-
Requirement Essential
Whether the competence is essential for the job.
-
Attained Proficiency Level
The proficiency level attained by the person.
-
Date Attained
The date the person attained the proficiency level.
By Person Worksheet
The by Person worksheet enables you to see individuals' proficiency levels.
You select an individual from the Person page item in the worksheet.
Headings and Calculations
The worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Competence
The competencies you have defined for the selected job.
-
Requirement Effective From
The date the proficiency level requirement began.
-
Requirement Essential
Whether the competence is essential for the job.
-
Attained Proficiency Level
The proficiency level attained by the person.
-
Date Attained
The date the person attained the proficiency level.
By Person Graph Worksheet
The by Person Graph worksheet breaks down each competence relevant to the selected job into percentages below, within, and above the required proficiency ranges for the job. It shows how an individual's competencies map to the requirement range.
You select an individual from the Person page item in the worksheet.
The workbook shows the percentage of the proficiency range that is below the minimum requirement, the percentage that is within the requirement range, and the percentage that is above the maximum requirement range. It reports the individual's proficiency in a competence as a percentage.
The diagram below shows you how proficiency levels for a competence translate into percentages.
Headings and Calculations
The worksheet contains the following columns:
-
Competence
The competencies you have defined for the selected job, for each selected organization.
-
Below Required Range Percent
The percentage of proficiency levels for the competence that are below the required minimum level for the job.
-
Within Required Range Percent
The percentage of proficiency levels for the competence that are within the required proficiency range for the job.
-
Above Required Range Percent
The percentage of proficiency levels for the competence that are above the required maximum level for the job.
-
Attained Level Percent
The percentage achievement level the selected person has attained for that competence.
Graph
A vertical bar chart enables you to see how an individual's proficiency level for a competence compares with the required proficiency standards. The chart displays two bars for each competence. The first bar represents the range of proficiency levels across a competence. The bar has three elements:
-
The minimum achievable proficiency level to minimum required proficiency level.
-
The minimum required proficiency level to maximum required proficiency level.
-
The maximum required proficiency level to maximum achievable proficiency level.
The second bar displays the individual's attained proficiency level for the competence.
Related Topics
Workforce Intelligence for Competencies, Qualifications and Development Key Concepts