Specifications
This chapter explains how to define and use specifications.
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Specifications
- Specification Types
- Specification Collection Elements
- Defining Specifications
- Defining Specification Collection Elements
Overview of Specifications
Specifications define the requirements to which the product must conform. You can define specifications for the key characteristics of the products that you produce or for the materials that you receive from suppliers.
You can attach illustrative or explanatory files to specifications, such as text, images, word processing documents, spreadsheets, video, and so on. Attachments can be used to document processing instructions as well as inspection and disposition procedures.
You can use specifications to ensure that:
-
Items produced internally conform to internal requirements
-
Items shipped to customers conform to customer requirements
-
Items received from suppliers conform to supplier requirements
-
The same item used in multiple organizations has the same specifications in all organizations
For each specification that you define, Quality allows you to specify:
-
A specification type - in this example, an item specification
-
An item, item category, or item category set
-
A specification subtype
-
A reference specification
-
A group of specification elements describing the item
-
Specification limits for each specification element, with up to three different specification ranges
-
Attachments for electronic documents, multimedia instructions, or images
Uses of Specifications
Specifications and their specification elements make it possible to do the following:
-
Prohibit the collection of data that lies outside the reasonable range of a specification element. Input that falls outside the reasonable limit range is rejected.
-
Assist operators as they enter data. You can optionally display specification element specification limits as quality results are directly entered. You can choose to hide specification limits by setting the QA: Blind Results Entry profile option to Blind Entry On. Also, you can specify that the target value be automatically defaulted in when quality results are entered by setting the QA:Default Specification Target profile option to Yes. See: Profile Options.
-
Use specification limit values to define action rules and the actions they invoke. Action rules control when and how to react to the entry of off-specification quality results. For example, you can define an action rule that invokes an action, such as sending an electronic mail message, when a quality results value is outside the upper and lower range limits of a specification element.
Note: If you change the profile set, re-login to the application to ensure that correct data is collected for different number type collection elements.
Related Topics
Defining Specification Elements
Specification Types
Quality supports three types of specifications: item, supplier, or customer. The specification type that you can select is determined by your business application. For example, Item specifications can be used to define requirements for items without regard to the customer or supplier that may purchase or sell them. Conversely, customer and supplier specifications can be used to define the requirements for items sold to or purchased from specific customers or vendors respectively.
The following table presents the three supported specification types.
Specification Subtypes
Quality also supports specification subtypes. Specification subtypes are used to create more detailed specifications. For example, if a similar, yet different supplier specification is required when a supplier ships from one location to another, you can use a specification subtype to ensure that the correct specification is applied.
Specification Collection Elements
Specification elements are the basic components of a specification. They can be any data type, but typically, they are numeric.
You create specification elements by first defining them as collection elements in the Collection elements window, and then adding the collection elements to your specifications. Adding the collection elements to your specification causes them to become specification elements. You also can create specification elements by copying them from an existing specification into a new specification. This is useful when similar items, suppliers, or customers require the same specification elements.
Specification Collection Element Limits
As you create specification elements, any limits that have been assigned to them are defaulted from the source. Limits to specifications can include an acceptable target value as well as user-defined, reasonable, and range limits. The specification limits for a specification element can be updated as required.
Examples of specification elements and their associated limits are presented in the following table.
| Specification Element | Specification Limit Target Value or Range |
|---|---|
| Thickness | User Defined Range: 0.55 +/- 0.002 |
| Torque | Reasonable Range: 45 and <52 |
| Burn-in time | Target Value: 48 hours |
Related Topics
Defining Collection Element Specification Limits
Defining Specification Elements
Defining Specifications
Specifications describe the requirements to which a product should conform. There are three specification types: item, supplier, and customer. Specifications can be further defined using subtypes. By carefully defining your specification you can ensure that the correct specification is applied as you collect data.
Each type of specification can be based on either an Item, Item Category or Item Category Set. If your specification is based on an Item, you must assign an item and, depending on the item, an item revision. If your specification is based on an Item Category, you must assign an item category from a list of values based on either the default item category set specified in the QA:Quality Category Set profile option or on any other category set available in the list of values. If your specification is based on an Item Category Set, you must assign a category set from the list of values based on category sets defined in the Oracle Inventory Category Sets window.
You can also attach illustrative or explanatory files - in the form of text, images, word processing documents, spreadsheets, video, and so on - to specifications. Attachments can be used to document processing instructions as well as inspection and disposition procedures. They can be viewed by operations personnel during quality data collection.
Prerequisites
- Define collection elements. See: Defining Collection Elements.
To define specification header information
-
Navigate to the Specifications window.
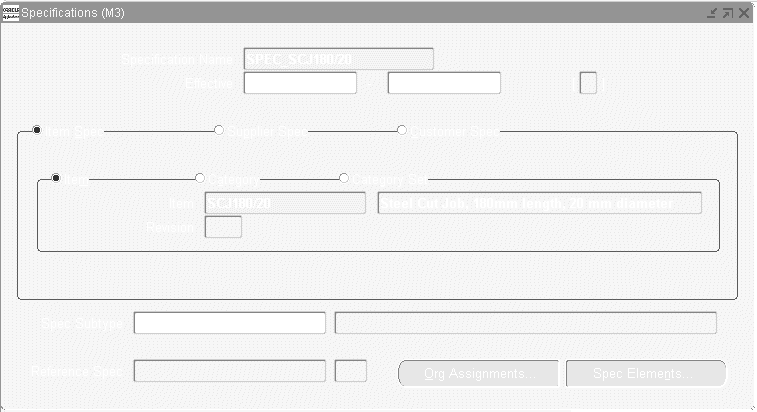
-
Enter the Specification Name.
-
Optionally, enter the From Effective date.
You cannot use the specification before this effective date. If you do not enter a From Effective Date, the specification is effective immediately.
-
Optionally, enter the To Effective date.
You cannot use the specification after this date. Once a specification expires, you cannot select this specification when entering quality result. You can, however, query quality results that were collected using it. If you do not enter a "To" effective date, the specification is valid indefinitely.
-
Choose the Item Spec, Supplier Spec, or Customer Spec radio button.
-
Choose either the Item, Category, or Category Set radio button to base the specification on an Item, Category, or Category Set.
-
If the specification is based on an Item, select the Item and, optionally, the Revision.
-
If the specification is based on the Category, select the Category Set and the Category.
If you are defining an item category specification, the system automatically defaults the category set defined by the QA:Quality Category Set profile option. See: QA:Quality Category Set. You can also select a category set from the list of values. You must assign a category that is a member of the category set selected.
-
If the specification is based on the Category Set, select the Category Set.
If you are defining an item category set specification, the system automatically defaults the category set defined by the QA:Quality Category Set profile option. See: QA:Quality Category Set. You can also select a category set from the list of values.
-
Save your work.
To define specification subtypes
-
Select a collection element.
-
Enter a value for the specification element.
To use the same specification limits as another specification
-
Enter a reference specification in the Reference field.
The child specification uses the same specification limits as the parent specification shown in the Reference field. Any changes to the parent specification limits automatically change the child specification limits, too. The child specification limits are read only and can have a different item, supplier, or customer than the parent specification.
-
Save your work.
To create new specifications linked to an existing specification
-
Choose the Org Assignments button.
The Organization Assignments window shows all of the organizations that the item belongs to.
-
Check the box next to each organization in which you want to create child specifications.
The child specifications use the same specification limits as the parent specification. Any changes to the parent specification limits automatically change the child specification limits, too. The child specification limits are read only.
-
Enter a specification name for each new child specification.
Later, you can inquire on the child specifications. The Reference field shows the parent specification.
-
Choose the Assign button to create the new child specifications.
Important: Define the specification limits for a parent specification before following these instructions to create child specifications. This ensures that the child's specification limits are linked to the parent's limits. See: Defining Specification Elements.
To define specification elements
See: Defining Specification Elements.
To attach files to specifications
See: Attaching Files to Collection Plans, Specifications, and Results Lines.
Related Topics
Finding Specifications While Entering Results Directly.
Attaching Files to Collection plans, Specifications, and Results Lines.
Overview of Item Categories, Oracle Inventory User's Guide
Defining Specification Collection Elements
You can create specification elements by:
-
Adding individual collection elements to your specification
-
Copying specification elements from one or more "source" specifications
-
Copying specification elements from a source specification and adding individual collection elements
Important: Copying specification elements from a source specification is useful when similar items, suppliers, or customers require the same specification elements.
Specification collection elements that are copied from a source specification are added to the destination specification. If any of the specification elements from the source specification have already been created on the destination specification, these specification elements and the specification limits you have entered for them are not overwritten. You can delete specification elements that are copied if they are not required.
To define specification elements
-
From the Specification Elements window, select the Collection Element (Specification Element).
-
Change the UOM (Unit of Measure), if desired.
You can either accept the default unit of measure or change the unit of measure. You enter quality results in the unit of measure defined here, in the Specification Elements window.
-
Check the Enabled check box to enable the specification element.
Specification elements must be enabled before you they can be used in the data collection process.
Caution: You may need to enable specification elements that were copied from a source specification.
-
The target value represents the preferred value.
Important: If your specification elements correspond to collection plan elements, you can choose to use specification element target values as the default values when you enter quality results. See: Default Specification Limit Values.
-
On the Spec Range tab, enter the lower and upper Specification Range limits.
The lower and upper specification range limits can represent engineering tolerances. The upper limits must exceed the lower limits.
-
On the User-Defined Range tab, enter the lower and upper User-Defined Range limits.
The lower and upper user-defined range limits can be used to represent process control limits. Your user-defined limits can be inside of, outside of, or overlapping your specification range limits. The upper limits must exceed the lower limits.
-
On the Reasonable Range tab, enter the upper and lower values Reasonable Range limits.
The lower and upper reasonable range limit ensures that you collect values that make sense. The upper limits must exceed the lower limits.
-
Save your work.
To select specifications
-
Navigate to the Specifications window.
-
Select the Specification Name.
To copy specification elements from an existing specification
-
From the Specifications window, choose the Spec Elements button. The Specification Elements window opens.
-
Choose the Copy button. The Copy From Specification list appears.
-
Select the name of the source Specification.
You can copy specification elements from any specification even those that are not effective. You can copy specification elements from more than one specification. You can delete specification elements that are copied if they are not required.
Note: Oracle Quality permits you to copy specification elements across organizations.
When you copy specification elements from another specification, the specification limits (target value and range limits) are defaulted from the source. These values can be changed.
Caution: If you copy specification elements that are disabled on the source specification, they are copied to the destination specification as disabled.
To add individual collection elements to specifications
From the Specification Elements window, select the Collection Element from the Collection Elements list of values.
You can add any enabled user-defined or predefined reference information collection element.
When you add individual collection elements, the specification limits (target value and range limits) are defaulted from the source. These values can be changed.
Related Topics