Administering Oracle Content Manager
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Understanding Content Types
- Creating and Managing Content Types
- Setting Up Custom Attribute LOVs
- Mapping Stylesheets to a Content Type
- Creating and Managing Content Type Groups
- Mapping File Extensions to Content Types
- Data Security Overview
Understanding Content Types
The content types define the structure of a content item through a set of attributes. They are the main tenet of Oracle Content Manager (OCM). Administrators create these content types to ensure that content items are consistent, wherever the same content types are used.
A content type can consists of simple attributes, subitems, and compound content types such as Product Name, Description, Feature Highlights, Overview, Product Information Guide (attachment), and Product Release Date.
Simple Attributes
Attributes can be of type Extended, Pull-down, and Attachment. For example, an Image Type can have attributes such as image attachment, image height, width, and alternate text.
-
The extended attributes are data types such as Boolean, Date, Number, HTML, Text, and URL. While creating a content item of attribute type:
-
Boolean - is displayed as a check box
-
Date - appears as a date picker
-
Number - accepts numbers
-
HTML - is displayed as rich text html editor
-
Text - accepts characters
-
Attribute URL - accepts a URL
-
-
The pull-down attributes appear as values in the drop-down list.
-
The attachment attribute enables you to upload attachments for the content item.
Subitems
Subitems are individual content items based on their corresponding content types. For example, a Sales Kit can consist of White Paper and Datasheet, as subitems.
Compound Content Types
Apart from extended, pull-down list, and attachment attributes, compound content type is another attribute. A content type can have other content type as its component. Such a content type is called a compound content type. For example, a Product Brochure content type can have other content types such as product presentation, product white paper, and product demo as its components. This makes the Product Brochure a compound content type.
Creating and Managing Content Types
Only System Administrators and Content Super Users can create and manage content types. Figure: Creating a Content Type depicts the process to create a content type.
Minimum and Maximum Instances
While creating a compound content type, you can specify the minimum and maximum number of content items that can be added to the compound content item.
If you specify the minimum value to be zero, then the subitem of this type is not mandatory. If you specify a number greater than zero, then while creating the compound content item, it is mandatory to add that many number of content items as subitems.
If you specify a number in the maximum field, then that many content items can be added for the compound content item. If you leave it blank, then while creating the compound content item, any number of content items can be added as subitems.
Important: It is recommended that you understand the requirements of your organization before you define the attributes for the content type. This is because, after a content type is used to create a content item, you cannot update it. If you have to update such a content type, you must first duplicate and update the duplicate copy.
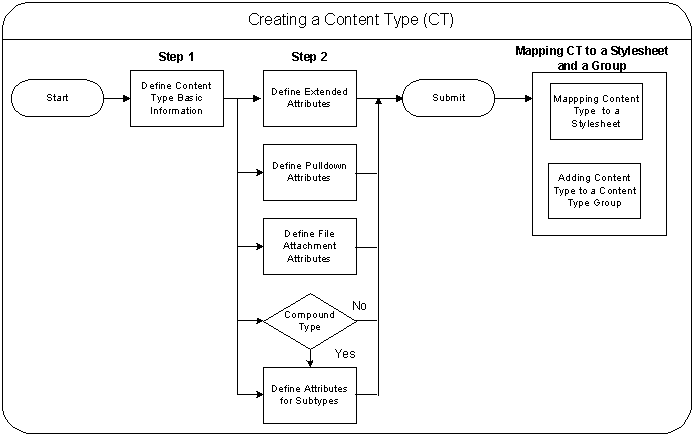
Creating a content type is a two step process:
-
In the first step, provide the basic details of the content type such as the name, owner, and the default stylesheet.
-
In the second step, define its attributes.
After creating a content type, you can map it to a stylesheet and also add it to a content type group. For details, see sections Mapping Stylesheets to a Content Type and Creating and Managing Content Type Groups.
Use the following procedure to create a content type.
Steps
-
Log into Oracle Content Manager as the Content Super User and navigate to Content Types tab.
-
Click Create Content Type.
-
Enter the required details such as name, description, and owner fields.
-
Select active from the Status menu.
Only if the content type is active, it is available for creating content items.
-
Enter an XML tag for the content type in the Content Type XML tag field.
The XML tag should not contain any spaces and must be unique. OCM stores this data in XML and uses it to present the content item.
-
Select a default stylesheet from the Search LOV.
Stylesheets enables you to preview the content item based on the stylesheet definition.
-
Optionally, to encrypt a URL, select the Encryption box.
-
Click Continue..
In the Create Content Type: <content type name>: Attributes page, the content type name and attributes are displayed with their order of display. You cannot modify the order.
-
To define extended and pull-down attributes, click Add Another Row in the respective regions.
-
The Field Length field defines the maximum number of characters that can be entered as a value for this attribute while creating content items.
-
The Default Value Updateble field indicates if the default value can be updated by the user while creating content items. To restrict users from updating the default value for this attribute, select No.
-
The Display Value field indicates the display priority. By default, the fields are displayed in a serial order.
-
-
In the Compound Content Type region:
-
Select a content type, which becomes the subitem of the compound content item.
-
Select a default content item from the Search LOV, which is displayed as a default subitem.
-
The Default Item Updateable field indicates if the default item can be updated by the user, while creating a content item.
-
-
Click Submit.
Setting Up Custom Attribute LOVs
While defining content type attributes, you can define custom lists of values (LOVs). For example, you can create custom LOVs for country, salutation, and so on.
Steps
-
Log in to the Oracle Applications login with Application Developer responsibility.
-
Create a custom value set.
-
Populate the value set.
-
Log into Content Manager.
-
Navigate to Content Types > Create Content Types.
-
Select Add Another Row from Pull Down List Attributes.
-
Populate the LOV Name field with your value set name.
Mapping Stylesheets to a Content Type
A stylesheet is a content type and tells the rendering engine how to display the content item on the Web. A stylesheet is like any other content type that can be selected to create a content item. You can create a content item using a content type of type stylesheet and store it in the content repository like another content item.
A stylesheet in OCM serves two purposes. Firstly, it defines how the content should be rendered on a Web site or any other device. Secondly, it enables you to preview a content item before it is released. Therefore, it is essential to map a content type to a stylesheet. Stylesheets must conform to the XSL format.
-
OCM cannot display an item in context with other content items that are used to build Web pages. To display the contents on the Web page, all the contents that are used to build the page must be stored in OCM. This is the responsibility of the application that calls the content item.
-
OCM only supports stylesheets that are of type Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL).
-
To create your own stylesheets, duplicate the seeded content types.
To map stylesheets to content types, log into Oracle Content Manager as the Content Super User.
Prerequisites: You must have content items of type Stylesheet in the repository.
Navigation: Content Type > Stylesheet Mapping.
Notes:
-
Mapped Stylesheets region: All the stylesheets mapped to the content type are displayed in this region. The Default Stylesheet column indicates the default stylesheet. You can change the default stylesheet setting.
-
To delete a stylesheet mapping, if you click the Delete icon, only the stylesheet is removed. But, the mapping is not deleted unless you click the Submit button.
Creating and Managing Content Type Groups
As more users use OCM, more custom content types are created and it becomes difficult to manage the content types. OCM supports the ability to group the content types into content type groups. By creating groups, you can restrict the users (while creating a content item) to select a content type only from the subscribed group.
To create and manage Content Type Groups, log into Oracle Content Manager with the Content Super User responsibility.
Navigation: Content Types > Content Type Group.
Notes:
-
When a content type group is inactive, all the content types in the group are not available to the users.
Mapping File Extensions to Content Types
The bulk upload feature enables you to map file extensions to content types. By using this feature, you can upload files to content types such as Image and File, which are seeded, and user defined file extensions. To enable files to map to user defined file extensions, you must map file extensions to content types.
Notes:
-
You can map file extensions only to content types with the file attachments attributes.
-
To check if a content type has file attachment attributes:
-
Click the Content Type tab.
-
Search for the content type by providing a content type name and click Go.
-
In the results displayed, click the link for the content type under the column Content Type Name. This displays a content type read only page.
-
Search for "File Attachment" on the page displayed. If some attribute rows appear under the File Attachment table header, then the content type has attachment attributes defined.
-
Data Security Overview
A folder hierarchy can consist of subfolders and content items. This helps the content creators to organize the content in folders and subfolders.
Folders are associated with a set of meta-data and permissions. For more information on permissions, see
The IBC: Use Access Control (for data security) profile and the IBC: Default Home Folder (for setting home folder) profile enable security in OCM. They are essential for smooth functioning of OCM. By default, data security is enabled. The Content Super User must assign access control on the folders.
Access Control
For a folder hierarchy, it is necessary to have robust data security to provide fine grain access control to different users at different folder levels. Folder access control involves assigning a User or a Group the permissions to access the folder. Access control is a combination of permissions and exclusions.
Permissions for a folder are granted to Users, Group, Responsibility, or Global user levels.
The permissions for a folder can be set at the following levels:
-
Users - These are users who are defined in the FND APPLICATION as FND USERS
-
Responsibility - The permission can be granted to APPS Responsibilities. When a user logs in, based on the user’s login responsibility, the permissions are granted to the user.
-
Groups - These are resource groups that have been defined as JTF RESOURCE GROUPS. A user logging into the application must belong to the group to inherit the group permissions.
-
Global - Besides Users, Groups and Responsibility, permissions can also be granted at a Global level.
Table: Permissions List lists the permissions that you can grant or revoke to a user.
| Permissions | Description |
|---|---|
| Manage Folder | Allows you to update the folder properties including the access control. |
| Create Sub-Folder | Allows you to create subfolders under the given folder. |
| Manage Item | Allows you to create, update, restore, remove, and delete content items in the given folder. |
| Approve Item | Allows you to approve content items. |
| Translate Item | Allows you to translate content items. |
| Approve Translation | Allows you to approve translations. |
| Read Item | Allows you to read (view) the content items in the given folder. |
Exclusions
A folder can maintain an exclusion list to exclude certain users or groups by revoking their permissions.
Inheriting or Overriding Parent Access Control
The permissions of a folder play a role of a template while creating subfolders. The permissions that are granted for a parent folder can be inherited by its subfolder. However, these permissions can be changed anytime.
You can create and manage a folder if you have Create Sub-Folder and Manage Folder permissions. In the Folder Properties page, the Access Control region displays the access control (Permissions and Exclusions) for a folder. While creating a folder, if you select the option to:
-
Inherit parent access control, then the Permissions and Exclusions regions are disabled. This is the default selection.The subfolder inherits all the permissions from the parent folder. If you modify the parent folder access control, the subfolders also reflect the changes.
-
Override parent access control, then the Permissions and Exclusions regions are enabled.
You can assign permissions and exclusions for the subfolder. If you modify the parent folder access control, the subfolders do not reflect the changes.
Guidelines for Assigning Permissions to Users
In an organization, for users to successfully manage their assigned roles, it is recommended to assign the permissions, explicitly along with the assigned role. For OCM to work smoothly, the corresponding recommended permissions must be granted. See the following table for details.
| Permission/Role | Other Recommended Permissions |
|---|---|
| Manage Folder | Manage Folder, Create Sub-Folder, Manage Item, and Read Item |
| Create Sub-Folder | Create Sub-Folder |
| Manage Item | Manage Item and Read Item |
| Approve Item | Approve Item, Manage Item, and Read Item |
| Translate Item | Translate Item and Read Item |
| Approve Translation | Approve Translation, Translate Item, and Read Item |
| Read Item | Read Item |
Order of Priority for Access Control
The order of priority for access controls is listed below:
User settings override the Responsibility settings, Responsibility settings override Group settings, and Group settings override Global settings.
For a user, if the access controls conflict, then permissions override exclusions.
Setting Permissions and Exclusions for a Folder
When data security is enabled by setting the IBC: Use Access Control profile to Y, each user must be granted specific privileges that can be performed on each folder.
Understanding Access Control with a Scenario
In this scenario, it is assumed that the profile IBC: User Access Control is set to Y and the access control is with respect to the /Root/Common folder. This scenario also illustrates that the User settings override the Responsibility settings, Responsibility settings override Group settings, and Group settings override Global settings. In case of a conflict, permissions override exclusions.
In Table: Permissions and Exclusions for Manage Item, "P" indicates the permissions that are granted and "E" indicates the exclusions that are revoked for users with Manage Item permission.
| Type | Manage Item - Permissions and Exclusions |
|---|---|
| Global | P |
| User - John | P |
| User Harry | P |
| User - Scott | P |
| Group - Copyrighters | P |
| Responsibility - Content Creators | P |
| User - Nancy | E |
| Group - Contractors | E |
| Responsibility - Sales Reps | E |
The Table: Access Control Granted to Users lists the access controls details that are applicable for individuals, when they navigate to the /Root/Common folder.
| User Name | Responsibility | Group | Manage Item | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John | Media Manager | - | X | Granted through User Access |
| Mike | Content Creator | - | X | Granted through Responsibility Access |
| Joseph | Media Manager | Copyrighters | X | Granted through Group Access |
| Harry | Media Manager | Contractors | X | Granted as User overrides Group |
| Scott | Sales Rep. | - | X | Granted as User overrides Responsibility |
| David | Content Creator | Contractors | X | Granted as Responsibility overrides Group |
| Terry | Media Manager | Copyrighters Contractors | X | Granted through group access. Although the permission for Copyrighters is granted and revoked for Contractions, the user still gets the access as permissions override exclusions |
| Jack | External Use | - | X | Granted through Group Access. Although Copyrighters are granted and Contractors are revoked, Jack still gets access as permission overrides exclusions. |
| Nancy | Media Manager | - | - | Revoked through exclusions. Although Global grant is for all users, Nancy is explicitly excluded. |
| Henry | Sales Rep. | - | - | Revoked through responsibility exclusions |
| Nicole | Marketing User | Contractors | - | Revoked through group exclusions. |
The Table: Data Security Profiles explains the data security profiles. You must set these profile options for content items to be created and submitted properly.
| Profile Name | Default Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| IBC: Use Access Control | Y | Now, the data security is enabled. When a user logs in, the application verifies to see if the user has appropriate permissions to perform an action. |
| IBC: Default Home Folder | /COMMON | Specifies the default home folder for the user. |
Understanding Categories
A category is a specifically defined classification, which is used to logically group a set of content items together. While folders are work areas to organize content items, categories reflect more of a business group. Many organizations define content that can be classified into one or more categories. Categories also have a hierarchy of subcategories for finer classification. You can browse the library based on the categories.
Root Category
The Root category is the highest level in the category hierarchy. The Root category is seeded, and any seeded category cannot be deleted or renamed. You can create a category under the Root category depending on the permissions you have. The following figure represents a sample categories hierarchy.
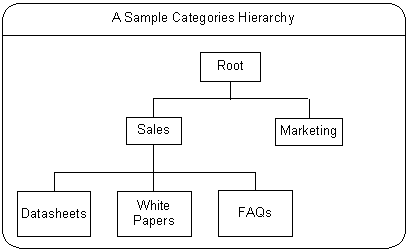
In the figure, Sales and Marketing are two categories under the Root category. Similarly, many such categories can exist under the Root category and subcategories under categories. Data sheets, White Papers, and FAQs are examples of subcategories under Sales.
Category Access Control
To maintain a category hierarchy, it is necessary to have robust data security to provide fine grain access control to different users at different category levels. Category access control involves assigning Users or Groups the permissions to access a category. Access control is a combination of permissions and exclusions.
Permissions
Permissions for a category are granted at Users, Group, Responsibility, or Global levels.
The following table lists the category permissions.
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Manage Category | Allows you to create, update, move, and delete a category. |
| Publish Content | Allows you to publish content to a category. |
| View Content | Allows you to view the published content. A library user must have this permission to view and browse the content in the library. |
Exclusions
A category can maintain an exclusion list to exclude certain users or groups by revoking their permissions.
Creating a Category and Setting Access Control
A category is a specifically defined classification, which is used to logically group a set of content items together. The Content Super User or an administrator must update the Root category for users to have Manage Category permission. Without this permission, no user will be able to create a subcategory under the Root category.
As an administrator, you can also assign content items to one or more categories. Only live versions of the content items can be assigned to the categories. Also, you can view, reject, or remove the content items from a category.
Managing Categories
You can perform the following tasks:
-
Move a category. You can move a category and alter the category hierarchy. The category being moved retains its original permissions.
-
Delete a category with subcategories. To perform this you must have Manage Category permission on the parent category and subcategories. If a category is deleted, then all content item mappings to the category are deleted.
-
Disable a category. By disabling a category, all its subcategories are disabled. A disabled category cannot be viewed in the library.
-
Enable a category only if the parent category is enabled.