Overview of Configure-to-Order Implementation
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Oracle Configure to Order
- Definitions
- Process Flows
- Feature Highlight
- Examples Used in This Manual
Overview of Oracle Configure to Order
Oracle Configure to Order Process Guide contains current information about how Oracle ERP products support configure to order capability. It provides detailed implementation consideration for every step of the process.
A Configure to Order environment is one in which the product or service is assembled or kitted on receipt of the sales order. Oracle Applications supports the Configure to Order environment with a range of features in order entry, demand forecasting, master scheduling, production, shipping, and financial accounting.
Configure to Order:
-
Includes Pick-to-Order (PTO) and Assemble-to-Order (ATO) items, models, and hybrids.
-
Supports building configurations using other configurations as subassemblies (multilevel configure to order)
-
Supports internal sourcing of ATO models at any level of Bill of Material (BOM)
-
Supports purchasing of ATO models and items at any level of the BOM
Definitions
Assemble-to-Order Model (ATO Configuration)
Assemble-to-Order model consists of:
-
Model bill of material with optional items and option selection rules
-
Configuration created from mandatory components and selected options
Assemble-to-Order Item
Assemble-to-Order item consists of:
-
Standard bill of material with standard components
-
Item manufactured from standard components
The three types of ATO items are:
-
AutoCreated Configuration Items: Configuration items created by CTO for a sales order that was placed for a model and options. These items have the following attributes:
-
Preconfigured Items: An item defined by the user with a "base model" and a configured bill of material. These items have the following attributes:
-
The ATO flag is selected on the OM tab of the item master
-
A Base Model defined on the BOM tab of the item master
-
-
Standard ATO Items: These are standard items with the ATO flag selected on the OM tab of the item master.
Configurations
Hybrid models or multilevel ATO models can also have multiple instantiations of a child model. Multiple instantiation is the ability to create and individually configure multiple occurrences of a model or model component, while configuring the model. A configuration model that contains models or model components that can instantiate multiple times is called a solution model.
While configuring using Oracle Configurator with the setup complete for multiple instantiation, you can access a configuration model instance, as well as an instance of each component model that is contained within the model. You can configure component model instances separately by selecting from the available options. For example, a computer system is represented by a solution model. A computer might contain a number of different servers, printers, and personal computer (PC) workstations. Each PC workstation in the system represents one instance of a configuration model, and each instance of the PC workstation can be configured differently. One instance of the PC workstation can be configured with a 21-inch flat screen monitor, 10 GB of disk space, and 512 KB RAM, whereas another instance of the PC workstation has a 17-inch screen, ergonomic keyboard, 256 KB RAM, and 4 GB of disk space. These two workstations are part of the computer system solution model.
For more information on how to do the necessary setup and use Configurator for multiple instantiated models, please refer to Oracle Configurator Developer User’s Guide.
Pick-to-Order Model (PTO Configuration)
Pick-to-Order model consists of:
-
Model bill of material with optional items and option selection rules
-
Pick slip used to kit included items and selected options
Pick-to-Order Item (Kit)
-
Standard bill of material with mandatory included items
-
Pick slip used to kit included items
Hybrid
-
Pick-to-Order models with optional Assemble-to-Order items
-
Pick-to-Order model containing Assemble-to-Order model
Multilevel Assemble-to-Order Model (Multilevel ATO Configuration)
Multilevel Assemble-to-Order model consists of:
-
A model bill of material with a nonphantom model as a component.
-
Configuration manufactured from mandatory components, selected options, and configured subassemblies.
Multilevel Assemble-to-Order Items
Multilevel ATO item consists of:
-
An autocreated or preconfigured or standard ATO item with another autocreated or preconfigured or standard ATO item as a component
-
Item manufactured from standard components and configured components
Multiorganization Assemble to Order Model (Multiorganization ATO)
Multiorganization Assemble-to-Order model consists of:
-
An ATO model that will be manufactured in and transferred from another organization
Process Flows
Three process flows are illustrated here:- one for single level, single organization make structures; one for multilevel, multiorganization make structures, and one for a purchased to order configuration.
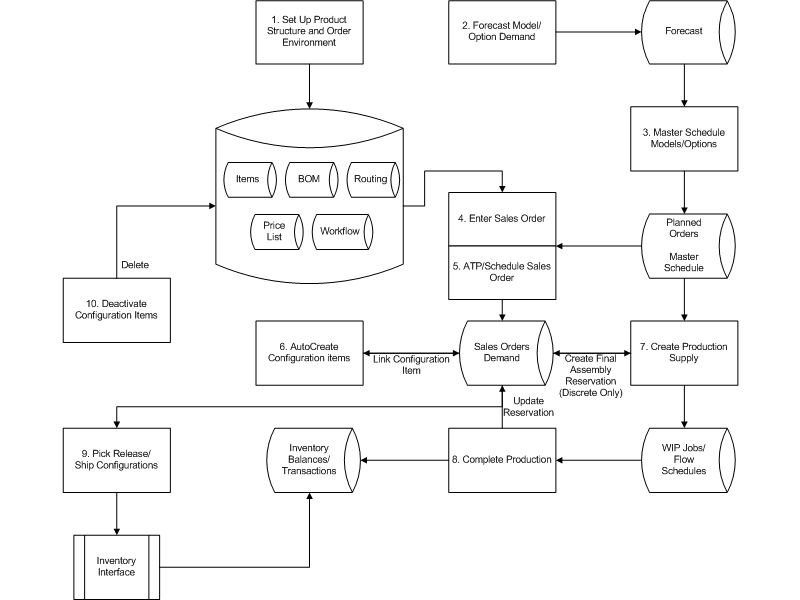
Example 1: Process Flow for Single Level, Single Organization ATO, and PTO
The following diagram illustrates the flow of a single level, single organization assemble-to-order sales order. Each numbered step is explained in the table following the diagram and will be covered in detail in the following chapters.
Process Flow for Single Level, Single Organization ATO, and PTO
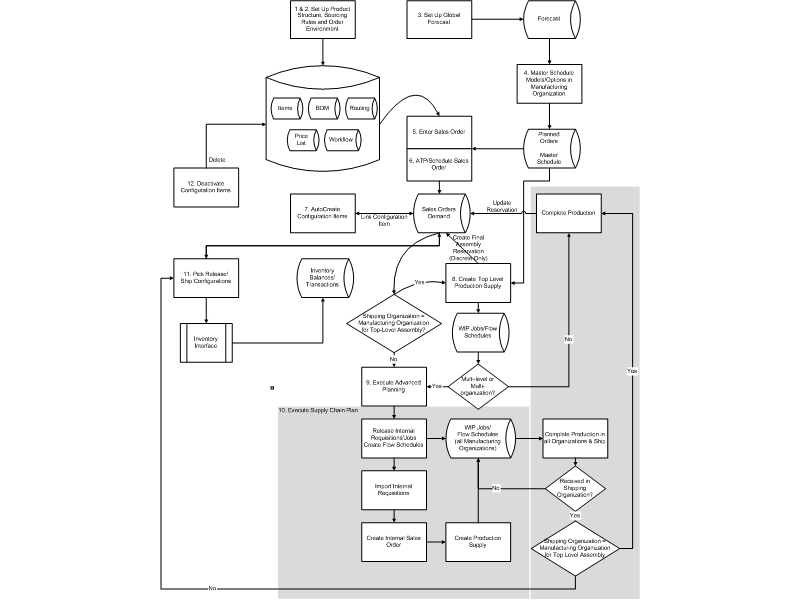
Example 2: Process Flow for Multilevel, Multiorganization ATO, and PTO
Note: Oracle Advance Planning and Scheduling (APS) must be installed to support multilevel and multiorganization ATO models and ATO items.
The following diagram illustrates the flow of a multilevel, multiorganization ATO sales order. Each numbered step is explained in the table following the diagram, and will be covered in detail in the following chapters.
Process Flow for Multilevel, Multiorganization ATO, and PTO
| S. No. | ATO | PTO | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yes | Yes | Define Model and Option Class Bills of Material and routings (optional) | Define multilevel model and option class bills and routings (optional) to control order management, master scheduling/MRP, work in process, and costing. |
| 2 | Yes | Yes | Set up sourcing rules, shipping networks, assignments sets, APS plans | Define sourcing rule, shipping networks, assignment sets, ATP rules, and APS plans to control multiorganizational sourcing. |
| 3 | Yes | No | Set up global forecast | Set up global forecast for the model, options, or both using demand planning. |
| 4 | Yes | No | Master Schedule Models and Options | Master schedule ATO models, options, or both in the manufacturing organizations using the forecast set. |
| 5 | Yes | Yes | Enter Sales Order | Enter sales orders for models with options. |
| 6 | Yes | Yes | Check ATP | Optionally perform group ATP, based on planning output, to check for all supply-constrained components to find earliest possible ship date for configuration. If you are using ASCP, you can also perform a global availability check to determine the shipping warehouse on the order. |
| Yes | Yes | Book and Schedule the Order | - | |
| 7 | Yes | - | AutoCreate Configuration Items | Automatically generate a new item number, bill, and routing for all nonphantom models in the configuration structure in all potential sourcing organizations. The final configured assembly item is linked to the sales order. Advanced Planning does not recognize demand for an ATO model order, until this step. You can create a configuration for a scheduled order, before it is booked. See: AutoCreate Configuration Items. |
| 8 | Yes | - | Create Top Level Production Supply In a multilevel organization, you can create production supply in the shipping organization only if the final assembly is manufactured entirely in that organization. If the shipping organization does not manufacture the final assembly, and sources it entirely from another internal organization, you can create an internal requisition to transfer it from the source organization. If the shipping organization has more than one source (any combination of Make, Buy or Transfer), use Advanced Planning to recommend supply. |
If the final assembly is being shipped from the manufacturing organization itself : Discrete: Autocreate Final Assembly Orders Automatically open a discrete job for the top level item on each new ATO configuration order. These work in process jobs are reserved to the sales order. This process could also create supply for lower level configurations, if they are being built or bought from the same organization. Flow: Use the Line Scheduling workbench to schedule your line based on sales orders. The sales order number is referenced on the flow schedule. Internal Transfer: If the final assembly is entirely transferred from another manufacturing organization, the Autocreate Requisitions process automatically creates an internal requisition for this assembly and reserves it to the sales order. Note: You can also “progress the order” through Create Production Supply, which automatically opens a discrete job, creates a flow schedule, or creates an internal requisition for the final assembly item of the active configuration order line. For items that are manufactured in the shipping organization, this process can optionally create supply for lower level configurations if they are built or transferred in the same organization. |
| 9 | Yes | - | Plan lower level configuration supply | In a multiorganization environment: Use advanced planning to generate and implement planned orders across your supply chain. |
| 10 | Yes | - | Execute Supply Chain Plan | Complete required manufacturing in the respective source organizations, and ship to the shipping organization. If the shipping organization is the same as the manufacturing organization of the top-level configuration item, the work in process reservation or flow schedule reference is automatically converted into an inventory reservation when you complete the top-level configuration item to inventory. If the final assembly is transferred from another organization, the reservation to an internal requisition is automatically transferred to inventory, upon receipt of the assembly in the shipping organization. |
| 11 | Yes | Yes | Pick Release and Ship Configuration Orders | Pick release all configuration sales orders. |
| 12 | Yes | - | Deactivate Configuration Items | Deactivate autogenerated configuration item numbers in an organization whose orders are complete more than x days ago. A configuration item will be deactivated if there is no sales order demand, or open supply or transactions in that organization, |
Example 3: Process Flow for Purchase to Order Configurations
The following diagram illustrates the flow of a purchase to order sales order. Each numbered step is explained in the table following the diagram and will be covered in detail in the following chapters. Note that this assumes the top-level configuration is being purchased. If the top-level is made and a lower level configuration is bought, the flow would be similar to the multilevel multiorganization example, with the lower level production supply being replaced by a purchased supply.
Process Flow for Purchase to Order Configurations
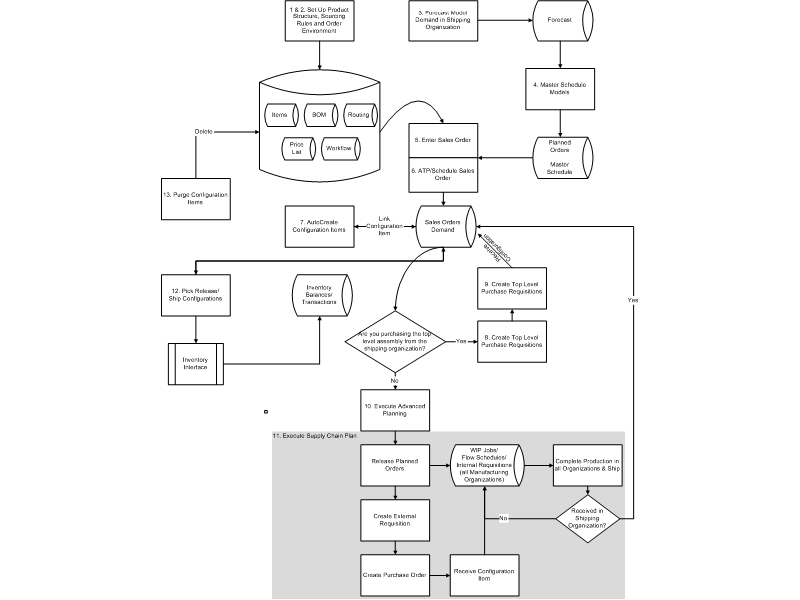
| S. No. | ATO | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yes | Define Model and Option Class Bills of Material and optionally routings | Define single or multilevel model and option class bills and optionally routings to control order management, master scheduling/MRP, work in process, and costing. The entire BOM for a purchased configuration should be created in the validation organizations and receiving organization. Routings for all models and option classes should be created in the receiving organization. |
| 2 | Yes | Set up sourcing rules | Define a buy type sourcing rule for the models you will procure and assign it the assignment set specified in "MRP: default sourcing assignment set" profile. |
| 3 | Yes | Forecast Model Demand | Forecast demand for the ATO model. All components and option classes should have their forecast control set to Null if you intend to buy the model configuration. |
| 4. | Yes | Master Schedule the Top model | Master Schedule your top ATO model. |
| 5 | Yes | Enter Sales Order | Enter sales orders for models with options. |
| 6 | Yes | Check ATP, Book and Schedule the Order | Perform group ATP based on planning output to back off the lead time of the model for a promise date. |
| 7 | Yes | AutoCreate Configuration Items | Automatically generate a new item number, bill, and routing for all nonphantom models in the configuration structure. The BOM and routing are created in the receiving organization if they do not exist in any other organization. The final configured assembly item is linked to the sales order. |
| 8 | Yes | Create Top Level Purchase Requisitions In multiorganization scenarios, you can create requisition supply only if the final assembly can only be purchased from that organization. If the shipping organization can partially make or transfer the assembly from another organization, use Advanced Planning to recommend planned orders. |
If the final assembly is being purchased directly from the shipping organization : Autocreate Purchase Requisitions automatically places a row in the req import tables for the top level purchased configuration or ATO item. Run Req import to create the requisitions. These requisitions are reserved to the sales order. Note:You could also “progress the order” through Create Supply Order Eligible, which will also place a line in the req import tables for the order line. |
| 9 | Yes | Create Purchase Orders | Create purchase orders or purchase order releases |
| 10 | Yes | Plan configuration supply | Use advanced planning to generate and implement planned orders if you are purchasing lower level configurations, or you are purchasing from an organization other than your shipping organization. |
| 11 | Yes | Execute Supply Chain Plan | Generate requisition and purchase order for the configuration item. Receive it into stock. |
| 12 | Yes | Pick Release and Ship Configuration Orders | Pick release all configuration sales orders. |
| 13 | Yes | Deactivate Configuration Items | Deactivate autogenerated configuration item numbers in an organization whose orders are complete more than x days ago. A configuration item will be deactivated if there is no sales order demand, or open supply or transactions in that organization. |
Note: Oracle APS must be installed to support purchasing of ATO items.
Feature Highlight
The following is a list of key Configure to Order features supported by Oracle Applications:
Product Definition
-
Support for ATO, PTO, and hybrid (PTO/ATO, ATO/ATO) product structures
-
Support for multilevel ATO and PTO-multilevel ATO hybrids structures, which enables building configured items that have other configured items as sub assemblies
-
Ability to ship configured items from a warehouse
-
Ability to purchase configurations at any level in your multilevel BOM structure.
-
Planning support for complex configurations where configurations are sourced across the supply chain.
-
Options specific sourcing
-
Mandatory and mutually exclusive option selection rules
-
Option dependent routings
-
Notification to the shipping organization when a change is made to the order request day, ship date, quantity, warehouse, configuration, or a line is split, after the configuration item has been created.
Planning Configurations
-
Forecast any planned item, anywhere on your bill of material, including models, options, and mandatory components, if your configurations are made in-house. Set up a global forecast using demand planning, if you use multilevel or multiorganizational models.
-
Use forecast sets as demand schedule for the manufacturing plan and use a manufacturing plan for ATP/Scheduling and planning supply
-
Use APS to check availability, determine a shipping organization using global availability, and schedule and plan supply across organizations. Promise based on matching configurations and option specific sources.
-
Use constraint based planning to generate feasible plans based on material and capacity constraints
-
Master schedule models and options in the manufacturing organizations
-
Define multiple sources for models and options at any level in the BOM
Ordering Configurations
-
Interactive option validation or autoselection using Oracle Configurator
-
Multiply instantiate ATO models and sub-models using Oracle Configurator
-
Support for ordering options in decimal quantities
-
ATP inquiry across the supply chain based on option material and resource availability
-
Match and reuse an ordered configuration or a configured subassembly
-
Reserve to available on-hand configuration (partial or full)
-
Automatic configuration pricing calculation taking discounts account
-
Order capture from any source (for example, your Web store)
-
Workflow based order processing
Manufacturing Configurations
-
Automatic creation of unique configuration item, BOM, and routing for the top-level model, as well as lower level models.
-
Option to create items, BOMs, and routings, based on sourcing rules, or the base model setup.
-
Discrete manufacturing and flow manufacturing environment support for building all levels of the configuration.
-
Supply chain cost roll up support for all sourced configurations.
-
Automatic configuration lead time and cost calculation for all configured subassemblies and top level assemblies.
-
Automatic final assembly work order creation for the top-level configuration.
-
Constraint based finite scheduling of final assembly work orders within each manufacturing organization.
-
Automatic flow schedule creation for the top-level configuration.
-
Automatic sales order reservation of top-level configuration upon production completion (single organization environment only).
-
Automatic internal requisition creation for the top-level configuration, with support to reserve the internal requisition to the sales order with automatic conversion to on-hand on receipt.
-
Multiple level supply creation support to create supply for all levels of configurations (in the shipping warehouse only).
-
Supply chain planning support to create supply for configurations at all levels across the supply chain.
Procuring Configurations
-
Automatic creation of unique configuration item, BOM, and routing for the top-level model as well as lower level models
-
Calculation of list price and blanket price for the configuration based on prices for the model and options
-
Transmission of configuration details through item attachments or the iSupplier Portal
-
Automatic requisition creation for the top-level purchased configuration
-
Automatic transfer of the reservation from the requisition to the purchase order
-
Automatic sales order reservation of top-level purchased configuration upon receipt into inventory
-
Supply chain planning support creation of supply for configurations at all levels across the supply chain
-
Support for drop-shipped configurations
Integration
The following Oracle Application products are integrated to provide Configure to Order features:
-
Bills of Material
-
MRP/MPS, SCP
-
APS (required for multilevel or multiorganization configurations)
-
Order Management products
-
Configurator products
-
Work in Process
-
Inventory
-
Flow Manufacturing
-
Cost Management
-
Purchasing
-
iSupplier Portal
Examples Used in This Manual
Two examples are used in this manual to illustrate the difference between single level/single organization and multilevel/multiorganization configure to order. Follow the example that best suits your manufacturing environment.
Example 1: A hybrid (PTO/ATO) in the single level, single organization environment
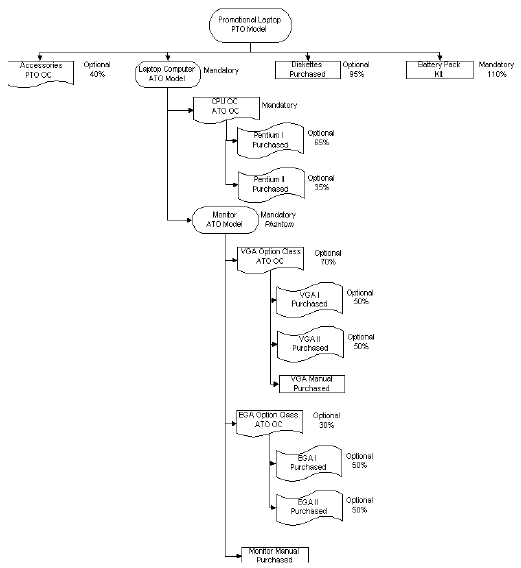
The following is an example of a hybrid (PTO/ATO) in the single level, single organization environment. It is for a PTO model Promotional Laptop that has three pickable items: diskettes, a battery pack, and the laptop computer ATO model. The laptop computer model is comprised of a phantom model for a monitor, option classes for CPUs, VGAs, and EGAs, and the actual options. The example is first shown as a diagram, then in a tabular format. This example is used throughout the entire book for illustration.
A Hybrid (PTO/ATO) in the Single Level, Single Organization Environment
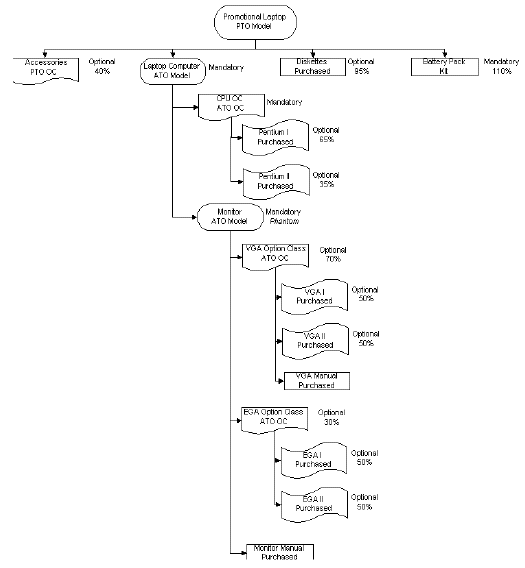
| Level | Item | Item Type | Optional | Supply Type | Planning % | Qty | Mutually Exclusive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Promotional Laptop | PTO Model | - | - | - | - | - |
| .2 | . Battery Pack | Kit | No | Assembly Pull | 110% | - | - |
| .2 | . Accessories | PTO Option Class | Yes | Assembly Pull | 40% | - | No |
| .2 | . Diskettes | Purchased Item | Yes | Assembly Pull | 95% | - | - |
| . 2 | . Laptop Computer | ATO Model | No | Assembly Pull | 100% | - | - |
| . . 3 | . . CPU | ATO Option Class | No | Phantom | 100% | - | Yes |
| . . . 4 | . . . Pentium I | Purchased | Yes | Assembly Pull | 65% | - | - |
| . . . 4 | . . . Pentium II | Purchased | Yes | Assembly Pull | 35% | - | - |
| . . 3 | . . Monitor | ATO Model | No | Phantom | 100% | - | No |
| . . . 4 | . . . VGA | ATO Option Class | Yes | Phantom | 70% | - | No |
| . . . . 5 | . . . . VGA Manual | Purchased Item | No | Assembly Pull | 100% | - | - |
| . . . . 5 | . . . . VGA1 | Purchased Item | Yes | Assembly Pull | 50% | - | - |
| . . . . 5 | . . . . VGA2 | Purchased Item | Yes | Assembly Pull | 50% | - | - |
| . . . 4 | . . . EGA | ATO Option Class | Yes | Phantom | 30% | - | No |
| . . . . 5 | . . . . EGA1 | Product | Yes | Assembly Pull | 55% | - | - |
| . . . . 5 | . . . . EGA2 | Product | Yes | Assembly Pull | 45% | - | - |
| . . . 4 | . . . Monitor Manual | Purchased Item | No | Assembly Pull | 100% | - | - |
Example 2: A multilevel ATO in a multiorganization environment
The following is an example of a hybrid (PTO/ATO) in a multilevel, multiorganization environment. It uses the same PTO model Promotional Laptop that has three pickable items: diskettes, a battery pack, and the laptop computer ATO model. However, now the laptop computer model is sourced from another organization, and the monitor model has been made nonphantom and is sourced from a third organization.
The original structure is changed in the following ways:
-
The orders are placed in organization W1 (your warehouse).
-
The laptop computer is made in organization M1.
-
The monitor sub model is changed to Assembly Pull (from phantom) and is made in organization M2.
-
There are sourcing rules set up such that W1 gets the laptop from organization M1, and M1 gets its monitors from M2.
The illustration is of the BOM in the three organizations: W1, M1, and M2. The BOM in the OM validation organization would contain all models and options. This example is used throughout the entire book for easy illustration.
A Multilevel ATO in a Multiorganization Environment
Note: If the monitor model was bought instead of made, the entire monitor model BOM should reside in the receiving organization (M1).