| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Technical Overview |
1. Messaging Systems: An Introduction
Propagation of Information Across a Cluster
A. Message Queue Implementation of Optional JMS Functionality
Conventional and enhanced cluster models share the same basic infrastructure. They both use the cluster communication service to enable message delivery between producers and consumers across the cluster. However, as shown in the following figure and described in previous sections, these models differ in how destination and consumer information is synchronized across the cluster, in the mechanisms for detecting failure, in how client reconnect takes place.
Figure 4-5 Cluster Infrastructure
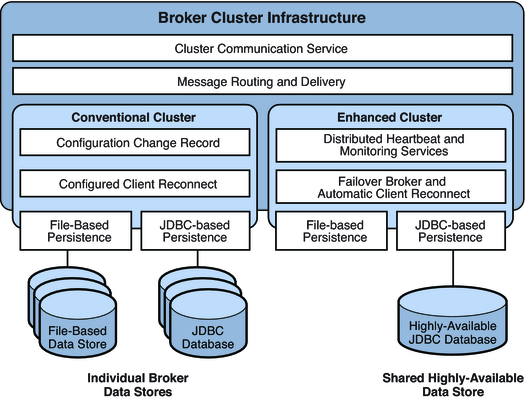
In addition, while both models rely on the broker's persistence interfaces (both flat-file and JDBC), in the case of enhanced clusters the shared data store must be a highly-available JDBC database (a highly-available file-based data store has not yet been implemented).
The following table summarizes the functional differences between the two cluster models. This information might help in deciding which model to use or whether to switch from one to another.
Table 4-1 Clustering Model Differences
|