The images below show you what your simulator will look like when you successfully complete the tutorial.
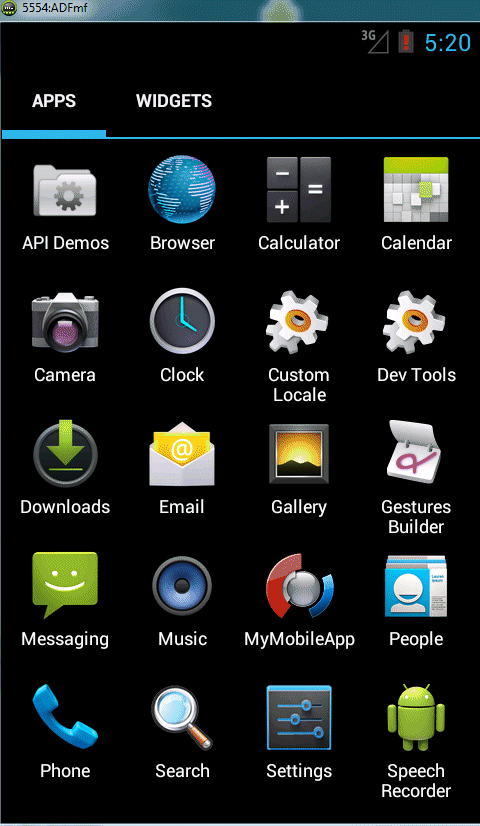
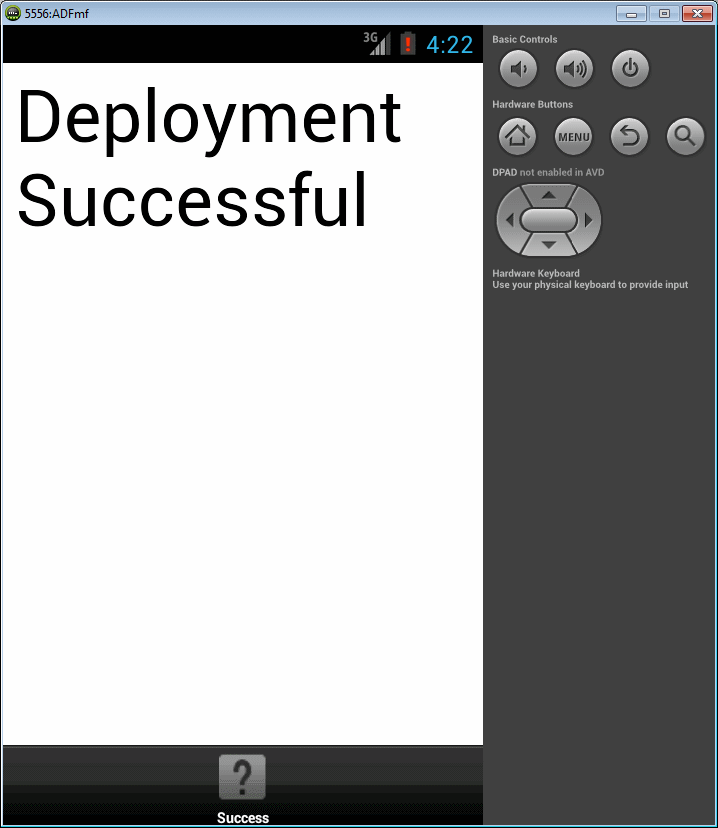
-
Download and install the Android SDK from http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html.

-
Unzip the adt-bundle-windows-x86_64.zip in a folder of your choice, for example AndroidSDK.
-
Find and double-click the SDK Manager.exe application. The Android SDK Manager is invoked. The Manager is what is used to install all the packages and emulators you use.
-
By default, the Android SDK Tools, Android SDK Platform-tools and several other packages are installed. You also need to install the Google Cloud Messaging for Android Library. To see this option you must select the Obsolete checkbox at the bottom of the window.
Then, scroll toward the bottom of the SDK Manager, select the Google Cloud Messaging for Android Library and click Install.

-
You will need to have installed JDeveloper version 11.1.2.4 or later. You can download JDeveloper from the Oracle ADF Mobile page. Click the Downloads tab to see the JDeveloper download.
-
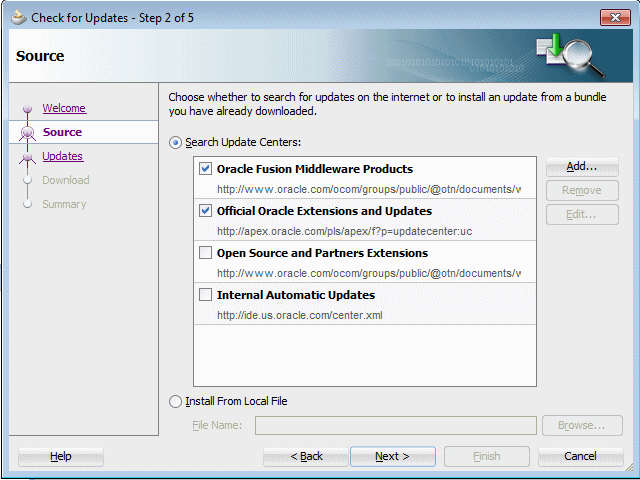
Install the ADF Mobile extension by using the JDeveloper Update Center. Start JDeveloper, and then select the menu item Help - Check for Updates.

-
Click Next at the Welcome dialog.
-
Select the Search Update Center radio button and click Next.
-
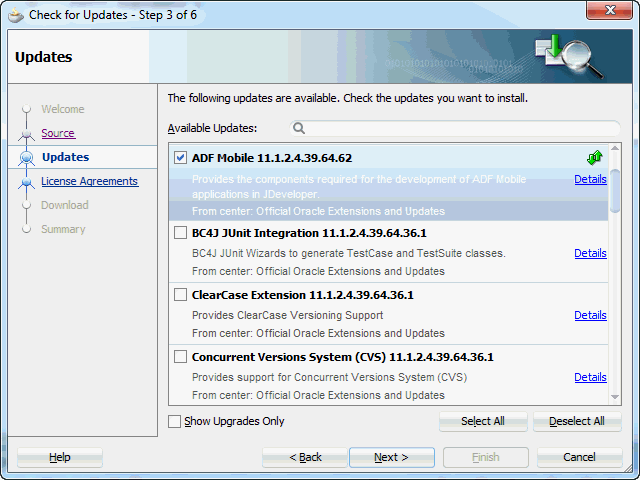
Enter mobile in the Available Updates: search box and select the ADF Mobile extension, then click Next
-
Accept the licensing agreements. Click Next and the download will start. Once complete, click Finish.

-
Restart JDeveloper as instructed.

-
When JDeveloper is restarted, select Studio Developer (All Features) to be able to use the ADF Mobile extension.
After JDeveloper is restarted, set the device SDK preferences as follows:
-
Select the menu item Tools > Preferences.

-
On the left side of the Preferences screen, click the ADF Mobile node. If you are using the ADF Mobile extension for the first time you may need to click the Load Extension button.

-
Next, expand the ADF Mobile node, and select Platforms. In the Supported Platforms list box, ensure Android is selected.
-
Update all entries with the correct directory locations. If you have installed the SDK to its default location, then you can click on the magnifying glass next to the input list, and navigate to the Android SDK Directory as recommended in the image or your installation location. Do the same for the Android Platform Location and Android Build Tools Location (even though it's greyed out, you can still use the magnifying glass to find the correct location).
There is a default password for the debug Key and Keystore. You can ignore those values for now.
-
Click OK to dismiss the Preferences pane.
-
Reopen the Android SDK Manager and create and start an Android emulator to use for your mobile deployment.

-
In the Android SDK Manager menu bar, select Tools - Manage AVDs...
The Android Virtual Device Manager dialog is displayed.

-
Click the New button and specify the following values to the properties.

AVD Name = ADFmf
Device = Nexus One
Target = Android 4.2 - API Level 17
Internal Storage = 500 MiB
SD Card = 500 MiB
Back Camera = Emulated
Memory Options Ram = 768
-
For the remainder, keep the defaults and click the OK button.
You may choose another device type, keeping in mind that newer devices have greater resource demands and you may run into RAM issues on your own machine.

-
A notification of the new AVD is displayed. Click OK to dismiss it.

-
Select the new AVD and click the Start button.

-
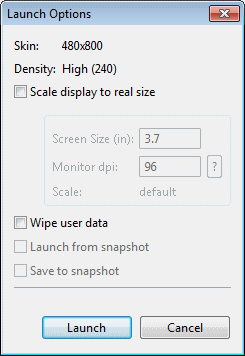
Accept the default values in the Launch Options pane, and click Launch.
-
It may take a while for the emulator to be invoked and start running. Depending on the speed of your CPU, 2 minutes is possible. Once it's running, you may continue and test your mobile deployment.

-
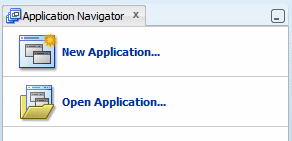
In the Application Navigator click New Application to start the New Gallery dialog box.
-
In the New Gallery expand the General - Applications nodes and select Mobile Application (ADF) and click OK.

-
In the Name your application page, enter MyMobileApp in the Application Name field, and click Next.

-
Click Next, and examine the Project Features for your second project, ApplicationController. The project includes the ADF Mobile Framework.

-
Click Next twice and in the Name your project page, leave the default project name. Examine the Project Features for the ViewController project. Notice that the project uses ADF Mobile Framework, HTML and CSS, Java, and JavaScript project features.

-
Click Next and Finish. In the Application Navigator, all the files associated with a new ADF Mobile application are viewable.
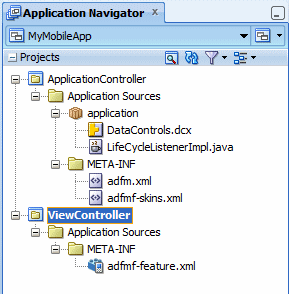
After you complete an ADF Mobile Framework application, JDeveloper adds both project and application level artifacts. Among these artifacts is an ADF Mobile framework model project and the view-controller project (with the default name, ViewController) that has the ADF Mobile framework feature application resources. These resources include the configuration file for applications features, adfmf-feature.xml. The configuration file is a stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define feature applications that will be seen when the application runs. The adfmf-feature.xml defines details of each feature - for example, its icon, content type, starting point, etc.
The adfmf-application.xml file defines the details of the application itself, including reference to features. These feature applications, when packaged into a JAR file known as a Feature Archive file (FAR), provide the reusable content that can be consumed by other ADF Mobile applications. One reason for this distinction is to allow developers to create feature archives (which may contain one or more features referenced in the adfmf-feature.xml), and then create applications by simply pulling in feature archives. Of course each app would only have one adfmf-application.xml.
A FAR is essentially a self-contained collection of everything that a feature requires, such as icon images, resource bundles, HTML, JavaScript, or other implementation-specific files. The FAR includes a single adfmf-feature.xml file, which identifies each of the packaged feature applications by a unique ID. You can edit this file to update feature properties. For example, you can specify the content implementation (local or remote HTML files, AMX pages, or a native application written in platform-specific language). You can also control the display of content based on such factors as user roles and privileges, or device properties. A mobile application can reference one FAR, several of them, or none at all. -
Right-click on the ViewController project and select New
In the New Gallery, select Web Tier - HTML and then the HTML Page item. Click OK.
-
Accept the default File Name and Directory, then click OK.

-
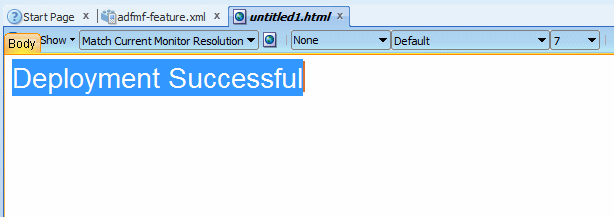
In the Editor, type the following text "Deployment Successful". Highlight the text and in the visual editor toolbar, select the fourth drop down list from the left, select 7. It might seem large, but it will appear smaller when running in the emulator.
-
Save your work.
In this part of the tutorial, you create and deploy a “Hello World” ADF Mobile application to the Android emulator.
Preparing ADF Mobile Framework applications for deployment is primarily comprised of creating platform-specific deployment profiles.
A deployment profile defines how an application is packaged into the archive that will be deployed to either an iOS or Android platform.
The deployment profile:
- Specifies the format and contents of the archive.
- Lists the source files, deployment descriptors, and other auxiliary files that will be packaged into the archive file.
- Describes the type and name of the archive file to be created.
- Highlights dependency information, platform-specific instructions, and other information.
-
In the Application Navigator, expand the ViewController project. Locate and expand the Application Sources folder. Then expand the META-INF folder. You will see the adfmf-feature.xml file as shown.
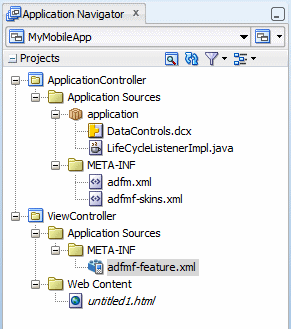
-
Double click on the adfmf-feature.xml file to open the Feature editor.

-
Add a new feature by clicking the green plus sign on the Features table near top of the editor. If you cannot see the plus sign, scroll the Feature editor to the right (the plus sign is on the far right side of the Feature editor).
-
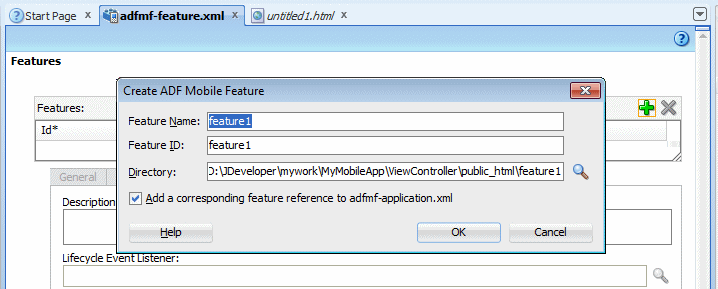
In the Create ADF Mobile Feature dialog, modify the following values:
- Feature Name: Success
- Feature ID: oracle.success
Accept the default directory value, and confirm the Add a corresponding feature reference to adfmf-application.xml check box is selected, and then click OK.

-
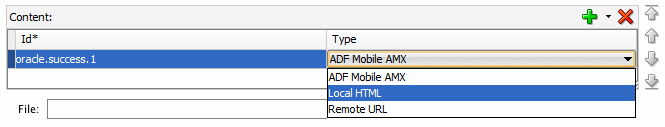
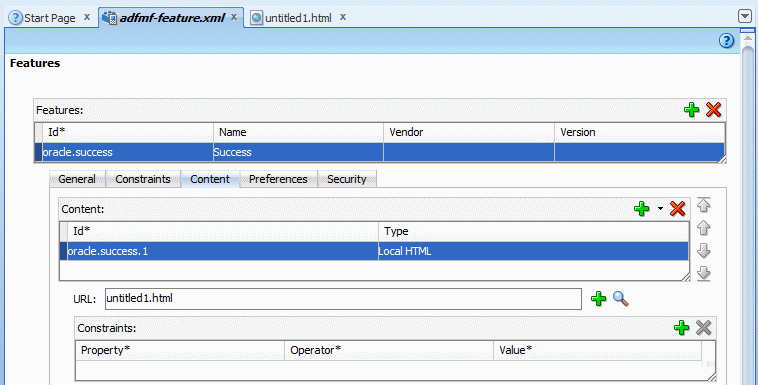
In the Features table, select the newly created feature oracle.success. Under the Features table, click the Content tab, and locate the Content table. Notice that the content item oracle.success.1 is created by default.
-
Save your work.
-
In the Content area, set the Type property is set to Local HTML.
-
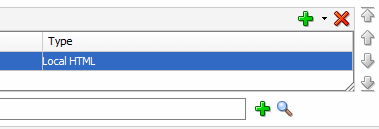
In the Content section, find the URL text box.
On the right side of the URL text box, click the magnifying glass icon.
-
In the Open window, select the html page you created earlier. In this case, untitled1.html. Then click Open.

-
The resulting definition should look like the image below.
-
Save all your work.
In this section, you configure a new feature so the user can access the newly defined local HTML page from the native application container. You will need to perform this task whenever you add pages or task flows to your application.
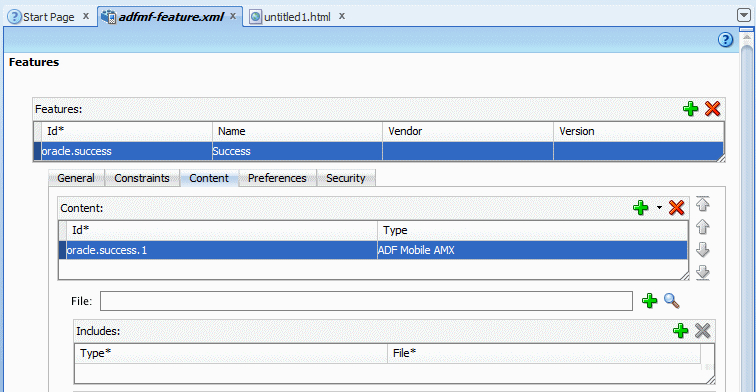
-
Confirm your emulator is still running. At the bottom of the emulator, click the Applications icon and all the installed applications will be visible.
Keep the emulator open and return to JDeveloper and the MyMobileApp application. -
In the Application menu, select Deploy - New Deployment Profile to start the Create Deployment Profile dialog box.

-
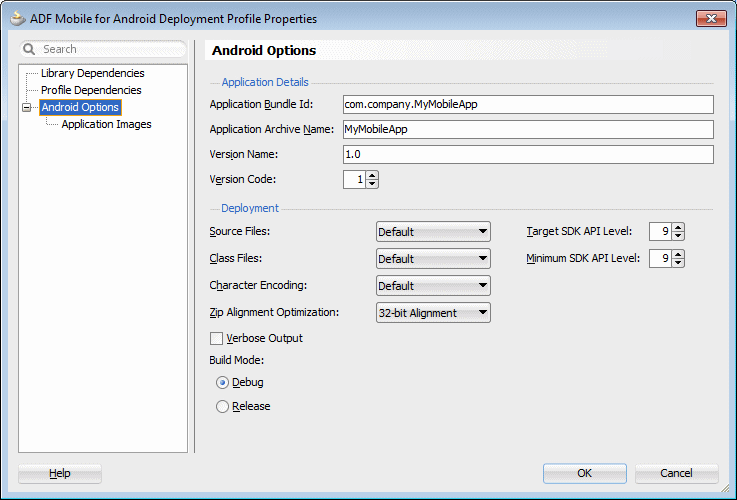
In the Profile Type drop-down list, ensure ADF Mobile for Android is selected. Enter Android_Mobile_Native_archive1 as the Deployment Profile Name and click OK.

-
Select the Android Options node and confirm your values look like the ones below.
-
Click OK, and then save all your work.
-
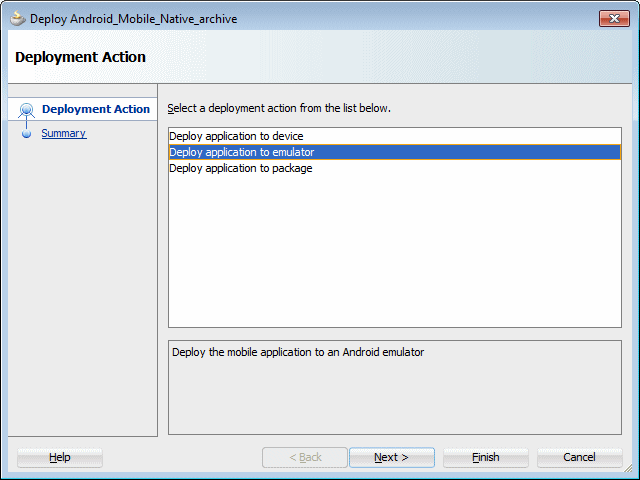
In the Application menu, select Deploy > Android_Mobile_Native_archive….

-
In the subsequent dialog box, select Deploy application to emulator, and click Finish.
-
Watch the Deployment Log window for any errors. If the compilation and deployment process completes as expected, you should see the Deployment Log window as shown below.

-
Navigate back to the emulator. Click the Home button...

...and then the Application icon to refresh the applications.

You should see the MyMobileApp application you have just created and deployed. -
Click the MyMobileApp icon to start the application.
-
If you are finished, then close the emulator, but remember to restart it before you want to deploy to it again.
Now that you have an environment installed and have created an application, you're ready to deploy the application to the emulator.
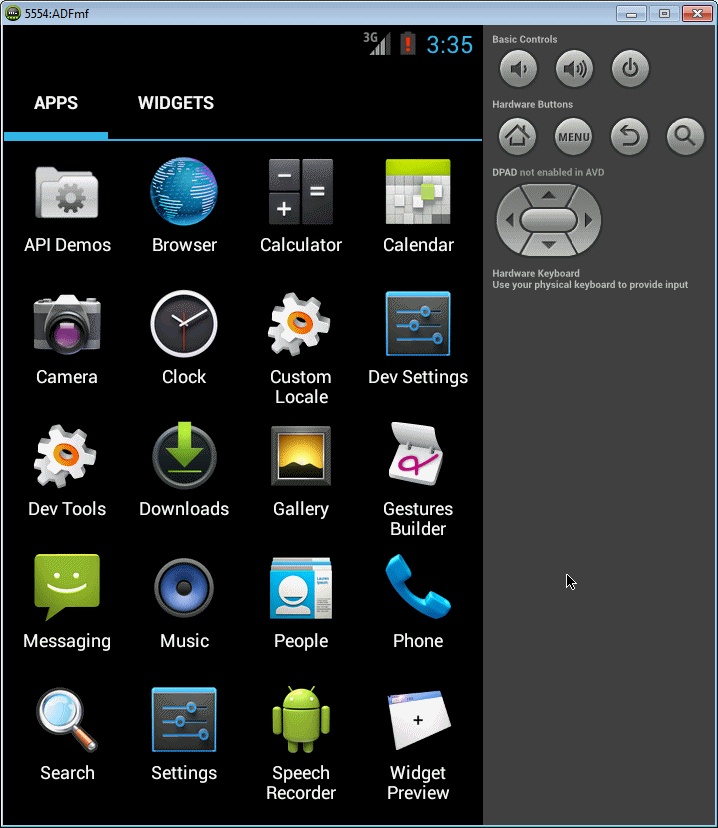
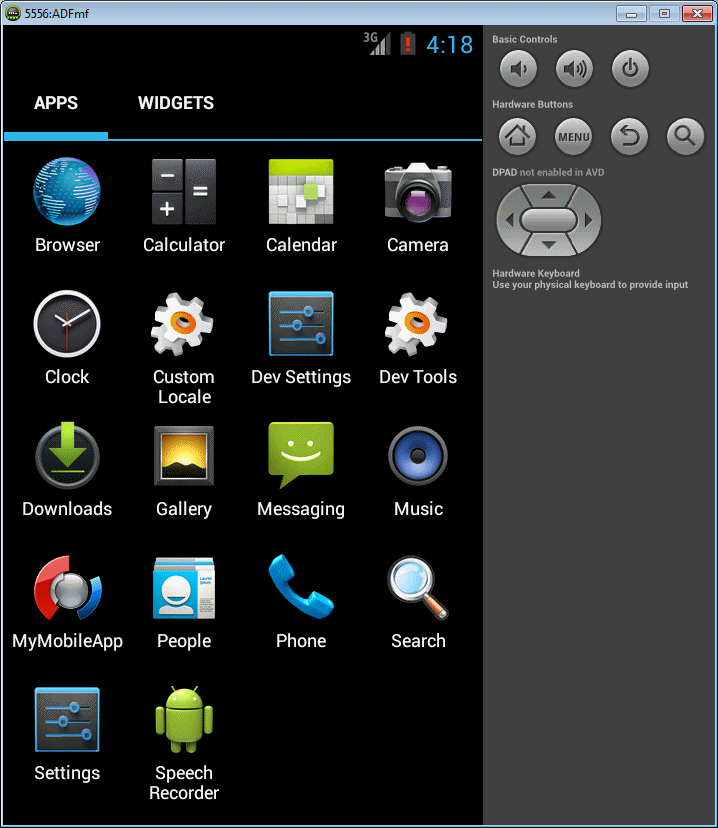
The MyMobileApp application currently contains your HTML
page running inside the ADF Mobile application.


 Part 1: Set Up and Configure the iOS Environment
Part 1: Set Up and Configure the iOS Environment
