| C H A P T E R 8 |
|
Using Simple Network Management Protocol |
This chapter describes how to use Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). It includes the following sections:
The Sun server supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) interface, versions 1, 2c, and 3. SNMP is an open technology that enables the management of networks and devices, or nodes, connected to the network. SNMP messages are sent over IP using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Any management application that supports SNMP can manage your server.
Utilizing SNMP requires two components, a network management station and a managed node (in this case, the ELOM). Network management stations host management applications, which monitor and control managed nodes.
Managed nodes are any number of devices, including servers, routers, and hubs, that host SNMP management agents responsible for carrying out the requests from management stations. The management station monitors nodes by polling management agents for the appropriate information using queries. Managed nodes can also provide unsolicited status information to a management station in the form of a trap. SNMP is the protocol used to communicate management information between the management stations and agents.
The SNMP agent is preinstalled and runs on the ELOM, so all SNMP management of the server should occur through the ELOM. To utilize this feature, your operating system must have an SNMP client application. See your operating system vendor for more information. The SNMP agent on your ELOM provides inventory management and sensor and system state monitoring capabilities.
The base component of an SNMP solution is the management information base (MIB). MIB is a text file that describes a managed node’s available information and where it is stored. When a management station requests information from a managed node, the agent receives the request and retrieves the appropriate information from the MIBs. The Sun server supports the following MIB files. Download and install the MIB files from the Tools and Drivers CD. The files are located in the /SNMP/mib directory.
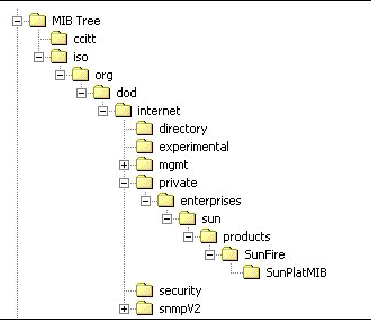
Use the MIBs to integrate the management and monitoring of the server into SNMP management consoles. The MIB branch is a private enterprise MIB, located at MIB object iso(1).org (3). dod (6) .internet (1) .private (4) .enterprises (1) .sun (42) .products (2). See FIGURE 8-1. The standard SNMP port, 161, is used by the SNMP agent on the ELOM.
FIGURE 8-1 Sun Server MIB Tree
SNMP is a protocol, not an operating system, so you need some type of application to use SNMP messages. Your SNMP management software might provide this functionality, or you can use an open-source tool like net-SNMP, which is available at http://net-snmp.sourceforge.net/.
Both management stations and agents use SNMP messages to communicate. Management stations can send and receive information. Agents can respond to requests and send unsolicited messages in the form of a trap. There are five functions that management stations and agent, use:
By default, port 161 is used for SNMP messages, and port 162 is used to listen for SNMP traps.
The ELOM has a preinstalled SNMP agent that supports trap delivery to an SNMP management application.
To use this feature, you must integrate the platform-specific MIBs into your SNMP environment, tell your management station about your server, then configure the specific traps.
Add your Sun server as a managed node using your SNMP management application. See your SNMP management application documentation for further details.
Configure a trap in your ELOM. See Managing Alerts, or Configuring E-mail Notification.
You can add, delete, or configure SNMP user accounts from the CLI. By default, SNMP v3 is enabled, and SNMP v1 and v2c are disabled.
To add an SNMP v3 read-only user account, enter the following command:
create /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/user/username authenticationpassword=password
To add an SNMP v1/v2c user account, enter the following command:
create /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/communities/communityname
To delete an SNMP v3 user account, enter the following command:
delete /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/user/username
To delete an SNMP v1/v2c user account, enter the following command :
delete /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/communities/communityname
To configure SNMP user accounts, use the set command
set target [propertyname=value]
These targets, properties, and values are valid for SNMP user accounts.
|
* If the PrivacyProtocol property has a value other than none, then PrivacyPassword must be set. |
|||
-> set /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/users/al privacyprotocol=DES
| Tip - To reduce the length of commands, navigate to the target first using the cd command. |
-> cd /SP/AgentInfo/SNMP/users/albert
-> set PrivacyPassword=password AuthProtocol=SHA AuthPassword=password
| Note - You can change SNMP user permissions without resetting the privacy and authentication properties. |
To show an SNMP user’s properties, Enter this command:
The result appears as follows:
Copyright © 2008, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.