Chapter 1 Product Overview
This chapter describes the purpose of SunTM Identity Manager and highlights the application's major features. It also briefly describes other identity management product offerings from Sun.
The chapter includes the following topics:
What is Identity Manager?
Sun Identity Manager makes it possible to automate the process of creating, updating, and deleting user accounts across multiple IT systems. Collectively, this process is known as provisioning (that is, creating and updating user accounts) and deprovisioning (deleting user accounts).
For example, when an employee joins a company, Identity Manager runs a workflow that retrieves the necessary approvals to grant the employee access. When these approvals are obtained, Identity Manager creates accounts for the employee in the company's human resources system (PeopleSoft), email system (Microsoft Exchange), and enterprise application (SAP). If the employee changes roles in the company, Identity Manager updates the user account and extends access to the necessary resources required in that new role. And when the employee leaves the company, Identity Manager automatically removes the user's accounts to prevent further access.
Identity Manager can also enforce audit policies on an ongoing basis. An audit policy specifies what types of access a user may or may not have. For example, in the United States it is a violation of Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) for the same user to have access to both Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable systems. This is known as a separation of duties violation. Identity Manager can conduct audit scanning to check for a variety of these types of violations and, depending on configuration, automatically remove access or send a notification to an administrator when a violation is detected. This process is known as remediation.
How Does Identity Manager Interface With Other IT Systems?
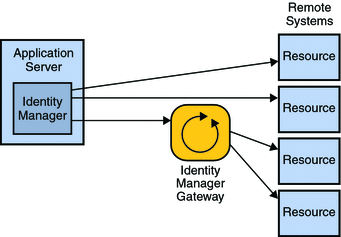
In Identity Manager, managed applications and other IT systems are called resources. Identity Manager uses either adapters or connectors to interface with resources.
Adapters and connectors are installed on the Identity Manager server. (Identity Manager does not require special software (called agents) to be installed on target resources.) Dozens of Identity Manager adapters and connectors are available, and new ones can be created to communicate with almost any resource using standard protocols or known application programming interfaces (APIs). Identity Manager ships with various adapters and connectors to communicate with many of the most common resources. In addition, templates and skeleton code is available to assist programmers in creating additional adapters and connectors.
Some resources cannot be communicated with directly and require the use of the Sun Identity Manager Gateway. Examples of resources that require the Gateway include Microsoft products, such as Exchange and Windows Active Directory, Novell products, such as eDirectory (formerly Netware Directory Services), and several others. In such cases, Identity Manager communicates directly with the Gateway and the Gateway interfaces with the resource.
Figure 1–1 Identity Manager Interfaces with Some Resources Directly, While Other Resources Require the Identity Manager Gateway
For a list of resources that Identity Manager supports, see Supported Resources in Sun Identity Manager 8.1 Release Notes.
How Do Users Connect to Identity Manager?
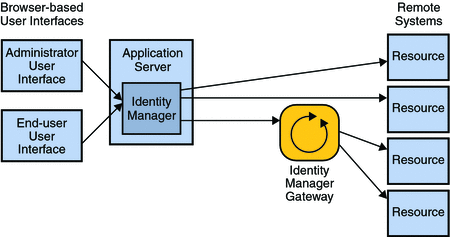
Identity Manager has a user interface (UI) for administrators, and a separate interface for end users. To use Identity Manager, administrators and end users use a web browser to log on to Identity Manager.
-
Administrators use the administrator interface to manage users, set up and assign resources, define rights and access levels, establish audit policies, manage compliance, and perform other business administrator and system administrator functions.
-
End users use the end-user interface to perform a range of self-service tasks, such as changing passwords, setting answers to authentication questions, requesting access to IT systems, and managing delegated assignments.
Figure 1–2 Users Can Connect to Identity Manager Using the Administrator Interface and the End-User Interface
Companies can also use SPML (Service Provisioning Markup Language) to either create their own user interface, or integrate an existing front-end system with Identity Manager.
Other Identity Manager interfaces include the following:
-
The IVR (Interactive Voice Response) telephone interface, which enables end users to perform Identity Manager functions using a telephone
-
The Identity Manager IDE (Integrated Development Environment), which is used by software developers to customize Identity Manager
-
The Identity Manager console, which is a command-line interface available to administrators
What is Identity Manager Service Provider?
Identity Manager Service Provider is a highly scalable, extranet-focused identity management feature that is capable of provisioning and maintaining millions of end user accounts that are stored on an LDAP directory server. The Service Provider feature can also manage thousands of administrator accounts and synchronize LDAP account data with other resources.
The Service Provider feature uses a subset of the features and functionality available in Identity Manager. For example, auditing functionality is not available because it is less useful in an extranet environment.
For a detailed accounting of the differences between standard Identity Manager and the Service Provider feature, see Service Provider Features in Sun Identity Manager Service Provider 8.1 Deployment.
Once available as a separate add-on product, Service Provider is now part of Identity Manager. Taking advantage of Service Provider functionality, however, requires special planning.
-
For information on how the Identity Manager Service Provider system architecture, see Understanding Identity Manager Service Provider System Architecture.
-
For information on planning a highly-available Identity Manager Service Provider architecture, see Understanding the Recommended Service Provider HA Architecture.
-
For information on deploying Identity Manager to take advantage of the Service Provider feature, see Sun Identity Manager Service Provider 8.1 Deployment.
Getting to Know Sun's Other Identity Management Products
In addition to Identity Manager, Sun's other identity management solutions include Sun JavaTM System Directory Server Enterprise Edition, Sun OpenSSO Enterprise, and Sun Role Manager. These products complement Identity Manager, and, in the case of Role Manager, can extend the capabilities of Identity Manager.
What is Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition?
Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition is a scalable, high-performance LDAP data store for identity information. Directory Server Enterprise Edition provides core directory services, as well as other complementary data services. Competing directory service offerings include Active Directory from Microsoft and eDirectory from Novell.
What is OpenSSO Enterprise?
Sun OpenSSO Enterprise (formerly Sun Java System Access Manager and Sun Java System Federation Manager) centralizes and enforces a comprehensive security policy for internal and external applications and web services. It provides secure and centralized access control and single sign-on (SSO) functionality. And it allows for federated identity management, which makes it possible to share applications with companies that have different directory services, security, and authentication technologies. Federated partners trust each other to authenticate their respective users and vouch for their right to access services.
What is Sun Role Manager?
Sun Role Manager (formerly Vaau RBACx) simplifies access control compliance by managing access based on a user's roles within a company and not on an individual, user-by-user basis. By creating roles based on usage and enterprise policies, companies can gain greater visibility into access and manage it in a more efficient, secure, and compliant manner.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
