Backing Up Your Namespace With nisbackup
The nisbackup command backs up one or more NIS+ directory objects or an entire namespace to a specified UNIX file system directory.
Note -
The nisbackup command is always run on a master server. Never run it on a replica server.
The nisbackup command copies the NIS+ namespace data set as of the time the backup command is run. This recording includes all current NIS+ data and also any changes entered into the NIS+ namespace by an authorized network administrator but not yet checkpointed (posted) to the NIS+ tables. The backup operation does not check or correct NIS+ data. If data in a table is corrupt, the corrupt data is backed up as if it were valid data.
The nisbackup command only backs up those directory objects that the machine is master server for. In other words, you can only use nisbackup on a master server. You cannot use nisbackup on a replica server.
-
If a machine is a master server for both a domain and a subdomain's NIS+ directory objects, you can run nisbackup on that machine to back up both domain and subdomain directory objects.
-
However, if a machine is a master server for one directory object, and a replica server for a different directory object, you can run nisbackup to back up the directory object that the machine is master server for, but it will not back up any objects that the machine is only a replica server for.
If the backup process is interrupted or unable to successfully complete its operation, it halts and restores all previous backup files that were stored in the target directory.
nisbackup Syntax
The nisbackup command uses the following syntax:
nisbackup [-v][-a] backupdir objects |
Where:
-
Backupdir is the target directory where the backup files are to be stored. For example, /var/master1_bakup.
-
Objects are the NIS+ directory objects that you want to back up. For example, org_dir.doc.com. Multiple NIS+ directory objects can be listed separated by spaces.
The nisbackup command takes the following options:
Table 16-1 Options for the nisbackup Command|
Option |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
-v |
Verbose mode. This mode provides additional information |
|
-a |
All. Backs up all NIS+ directory objects that the server is master of. This includes any sub-domain directory objects that this server is the master for. Note that directory objects of subdomains that have their own master servers will not be backed up. |
The nisbackup command must be run on the master server for the NIS+ directory objects you are backing up.
When specifying NIS+ directory objects to be backed up, you can use full or partially qualified directory names.
When you back up multi-level directories, the backup files for lower level directories are automatically placed in subdirectories of the target backup directory.
What nisbackup Backs Up
When using nisbackup, keep in mind that nisbackup is server specific. Regardless of whether or not you use the -a option, nisbackup only backs up those directories that the server you are running it on is master of. NIS+ directory objects that have some other master server will not be backed up.
For example, suppose the submaster1 server is master server for the sales.doc.com. directory objects and also a replica for the west.sales.doc.com. directory objects. When you run nisbackup on submaster1, only the sales.doc.com. directory objects will be backed up.
Some of the implications of this server specific principle are:
-
Entire NIS+ namespace. If you want to perform an NIS+ back up for an entire multi-domain namespace, and your root master server is also the master server of all subdomains, you can run nisbackup on the root master with the -a option. However, if the root master server is not the master server of all subdomains, you must also run nisbackup on each of the other master servers in order to obtain a complete back up of your entire namespace.
-
Sub-domains. If you are performing an NIS+ back up for one or more sub-domains, you must run nisbackup on the subdomain's master server. If one machine, such as the root master, is also master of one or more subdomains, you can run nisbackup on that machine with the -a option.
-
FNS ctx_dir. If you are running FNS, nisbackup will only back up your ctx_dir directories if you run it on the ctx_dir master server and either specify that the ctx_dir be backed up or use the -a option. If, as is common practice, your ctx_dir and NIS+ directory objects are served by different master servers, you must run nisbackup on both machines to back up all directories.
The Backup Target Directory
While the backup target directory must be available to the server being backed up, it is good practice to use a target directory that is not physically mounted on the server. That way you ensure that if the server is damaged the backup directory is still available.
A separate target directory must be used for each master server being backed up. It is good practice to avoid confusion by including the master server's machine name in the target directory name. For example, the target directory for a nisbackup run on the master1 machine might be named /var/master1_bakup
Never back up more than one master server to a given target directory. Always use different target directories for different master servers. This is because each time you backup one or more NIS+ directory objects to a given target directory, previous backup files for those NIS+ directory objects in that directory are overwritten.
Maintaining a Chronological Sequence of NIS+ Backups
There are at least two ways to maintain an historic sequence of backup files:
-
Different target directoriess. You can maintain separate target directories for each date's backup. For example, /var/master1_bakup/July14, and /var/master1_bakup/July15, and so on. While this method is simple it wastes disk storage space.
-
File system backup. The most common method of maintaining an historical sequence of NIS+ backups is to simply include the backup target directory in whatever regular file system backup method that you use. To facilitate this, the nisbackup command can be run from a crontab file, or from within the Solstice backup routine. See your Solstice documentation for information on how to specify that commands like nisbackup be automatically run as part of the system backup procedure.
Backing Up Specific NIS Directories
To back up specific NIS+ directory objects, you list those directories after the target backup directory.
For example, to backup the three org_dir directory objects for the root, sales, and manf domains to a /master1_bakup directory, you would run nisbackup on the master1 machine as follows:
master1# nisbackup /var/master1_bakup org_dir org_dir.sales org_dir.manf |
Backing Up an Entire NIS+ Namespace
To back up an entire NIS+ namespace you run the nisbackup command on the root master server with the -a option.
When you use the -a option, you do not specify the NIS+ directory objects to be backed up. All NIS+ directory objects on the server and all those of subdomains below it will be automatically backed up.
For example, to backup the doc.com. namespace to a /master1_bakup directory, you would run nisbackup on the root master as follows:
rootmaster# nisbackup -a /var/master1_bakup |
Backup Directory Structure
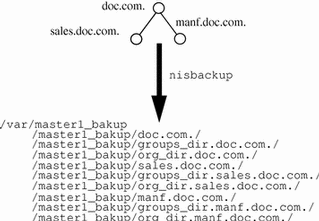
When you perform a back up on a domain, a subdirectory for each NIS+ directory object is created in the backup target directory. The names of these subdirectories match the fully qualified NIS+ directory object name including the trailing period.
If you perform a full backup of an entire NIS+ object using the -a option, then all three of the associated directory objects (domain. org_dir.domain., and groups_dir.domain.) are backed up and three target subdirectories are created. If you are backing up multiple objects, subdirectories are created for every object that you are backing up.
Note that the backup subdirectories for multiple NIS+ directory object are all subdirectories of the parent target backup directory regardless of whether or not they are subdomains. In other words, nisbackup does not reproduce a domain hierarchy under the parent backup target directory, instead all of the back up subdirectories are simple subddirectories of the target directory.
For example, if you backed up the root, sales, and manf directory objects of doc.com. to a /var/master1_bakup directory, nine subdirectories would be created in the /var/master1_bakup directory as shown in Figure 16-1:
Figure 16-1 Example directories created by nisbackup
Backup Files
The backup target directory contains a backup_list file that lists the NIS+ directory objects most recently backed up to this target directory.
Each of the subdirectories contain two files and a /data subdirectory. The three files are:
-
data.dict. An XDR encoded file containing an NIS+ data dictionary for the NIS+ directory objects backed up to this directory.
-
last.upd. A binary file containing time-stamp information about the NIS+ directory object backed up to this directory.
Each of the /data subdirectories contain one or more of the following files:
-
root.object. An XDR encoded data file containing a description of the NIS+ root directory object. For example, /master1_bakup/doc.com/data/root.object.
-
root_dir. An XDR encoded file containing a description of NIS+ objects contained in the root directory and server information for those objects. For example, /master1_bakup/doc.com/data/root_dir.
-
table.directory. An XDR encoded file containing the data that was present in an NIS+ table at the time the backup was performed and also any data contained in any associated NIS+ log files. If there is an NIS+ table in the NIS+ directory object being backed up, a corresponding table.directory backup file will be created in the /data subdirectory for that directory object.
For example, every NIS+ org_dir directory contains a hosts table so there will be a hosts.org_dir file in each target/org_dir.domain/data subdirectory. For example, /master1_bakup/org_dir.doc.com./data/hosts.org_dir
User-created NIS+ tables present in a given directory object are backed up in the same way as the standard NIS+ tables.
-
groups_dir. An XDR encoded file containing NIS+ groups information. This file is stored in the corresponding NIS+ groups_dir target directory.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
