Policy Evaluation and Enforcement
After a session token has been validated, the policy agent determines if the user can be granted access to the server by evaluating it's defined policies. The following illustration and accompanying text describes the process.
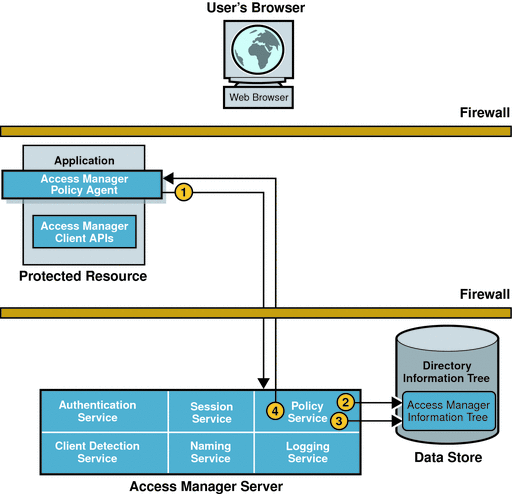
Figure 2–3 Policy Evaluation
-
The policy agent sends a request to the Policy Service.
The request asks for decisions regarding resources in the policy agent’s portion of the HTTP namespace. The request also includes additional environmental information. For example, IP address or DNS name could be included in the request because they might impact conditions set on a configuration policy.
-
The Policy Service checks for policies that apply to the request.
Policies are cached in Access Manager. If the policies have not been cached already, then the policies are loaded from the Access Manager information tree in the Identity Repository.
-
If policies that apply to the request are found, the Policy Service checks if the user identified by the session token is a member of any of the Policy Subjects.
-
If no policies that match the resource are found, the user is denied access. Skip to step 5.
-
If policies are found that match the resource, and the user is a valid subject, the Policy Service evaluates the conditions of each policy. For example, Is it the right time of day? or Are requests coming from the correct network?
-
If the conditions are met, the policy applies.
-
If the conditions are not met, the policy is skipped.
-
-
-
The Policy Service aggregates all policies that apply, encodes a final decision to grant or deny access, and responds to the policy agent with the appropriate decision.
The next part of the user session is logging the policy evaluation results.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
