Messaging Server Use Cases
Use cases help identify the relationships among the logical components in an architecture. By mapping the interactions between the components according to the use cases, you get a visual picture of component interaction that is helpful in deployment design.
Typically, you analyze each use case to determine the interaction of components prior to deployment design. The following three use cases are typical for Messaging Server and show interactions among the logical components.
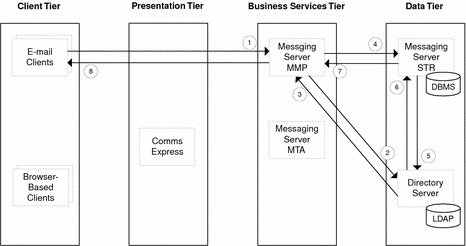
 Use Case 1: User Logs in Successfully to Messaging Server
Use Case 1: User Logs in Successfully to Messaging Server
-
Email client sends login information to Messaging Server Multiplexor (MMP)
-
MMP requests verification of user ID and password from Directory Server.
-
Directory Server returns verification to MMP.
-
MMP requests message list from Messaging Server Message Store (STR).
-
STR requests user’s LDAP record from Directory Server.
-
Directory Server returns user’s LDAP record to STR.
-
STR returns message list to MMP.
-
MMP forwards message list to email client.
 Use Case 2: Logged-In User Reads and Deletes Mail
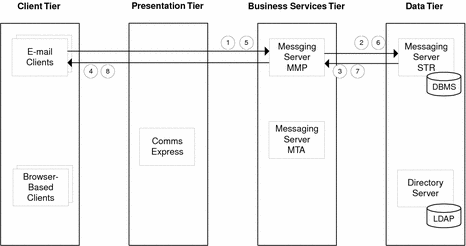
Use Case 2: Logged-In User Reads and Deletes Mail
-
Email client requests message to read from Messaging Server Multiplexor (MMP).
-
MMP requests message from Messaging Server Message Store (STR).
-
STR returns message to MMP.
-
MMP forward message to email client.
-
Email client sends deletes message action to MMP.
-
MMP forwards delete message action to STR.
-
STR deletes message from database and sends confirmation to MMP.
-
MMP forwards delete confirmation to email client.
 Use Case 3: Logged-In User Sends Email Message
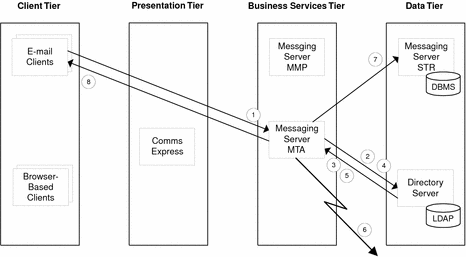
Use Case 3: Logged-In User Sends Email Message
-
Email client sends message composed in client to Messaging Server Message Transfer Agent (MTA).
-
MTA requests verification of user ID and password from Directory Server.
-
Directory Server returns verification to MTA.
-
MTA checks Directory Server for the destination domain for each recipient.
-
Directory Server returns to MTA the destination domain for each recipient.
-
MTA forwards message to each recipient.
-
MTA forwards message to Messaging Server Message Store (STR) to store message in outbox.
-
MTA sends confirmation to email client.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
