Chapter 34 Serial Ports Test (sptest)
sptest checks the system's on-board serial ports (zs[0,1], zsh[0,1], se[0,1], se_hdlc[0,1]), as well as any multi-terminal interface (ALM2) boards (mcp[0-3]). Data is written and read in asynchronous and synchronous modes utilizing various loopback paths.
Intervention mode must be enabled to run this test. This test is non-scalable.
Table 34-1 Serial Port Tests
Synchronous Testing Software Requirements
If you have zs(7D) serial ports on your machine, the synchronous devices may not exist. Look in the /dev directory for zsh (where h=0 and/or 1). If they do not exist, you can create them. Verify that the following two lines are in the /etc/devlink.tab file. If they are not there, add them.
type=ddi_pseudo;name=zsh zsh\M0 type=ddi_pseudo;name=clone;minor=zsh zsh
The white spaces in the lines above must be a single tab character before and after the zsh variables; using spaces will not work.
When these lines have been added to the /etc/devlink.tab file:
If this command does not work:
sptest Options
Figure 34-1 sptest Option Menu
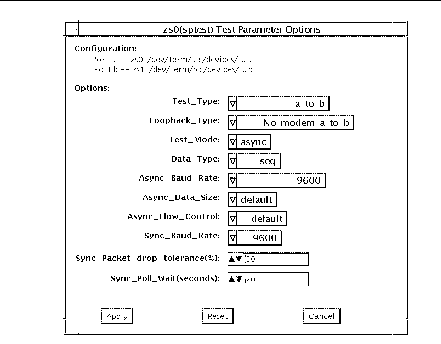
There are a variety of loopback paths available. The internal loopback paths do not require an external connector. Their availability depends on the device. The zs(7D) device has an internal path for synchronous mode and the se(7D) device has an internal path for asynchronous mode. The external loopback connectors are described in Appendix A. The exact type of loopback connector required depends on the system I/O panel.
Legend: In the following table, a represents port a of the CPU board (motherboard), b represents port b of the CPU board, and the device names of the ports for each CPU board are listed.
Table 34-2 sptest Serial Devices|
CPU |
Port |
Async Device |
Sync Device |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
a b |
zs0 or se0 zs1 or se1 |
zsh0 or se_hdlc0 zsh1 or se_hdlc1 |
|
1 |
a b |
zs2 zs3 |
zsh2 * zsh3 * |
|
2 |
a b |
zs4 zs5 |
zsh4 * zsh5 * |
|
* Currently, only zsh0 and zsh1 are supported by device drivers. |
|||
Table 34-3 sptest Options
|
sptest Options |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Test Type |
Selects how the test will run. Test options include: o a= runs the test on port a o b= runs the test on port b o a_b= runs the test on ports a and b sequentially o a_b_concurrent= runs the test on port a and port b concurrently. |
|
Test Mode |
Selects the mode to put the serial device into before running the test. The modes available are Asynchronous, Synchronous or Both. When Both is selected, the test runs in Asynchronous mode then Synchronous mode. |
|
Loopback Type |
Selects the loopback test. Options include: oInternal is an internal path for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types. oPlug_a_to_a__b_to_b is an external loopback plug for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types. ono_modem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable for a_to_b and a_to_b_concurrent test types. oModem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable with a modem attached to generate synchronous Transmit and Receive clocks in synchronous mode. The modem a_to_b external loopback type is intended for Sun internal use only. It requires custoe equipment that is not available. |
|
Data Type |
Selects the data pattern to transfer. The user can select: oRandom oSequential oAlphanumeric o0x00-0xff |
|
Async Baud Rate |
Selects the baud rate for Asynchronous mode testing. The valid rates are: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 76800, 115200, 153600, 230400, 307200, 460800, and ALL. The default rate is 9600 baud. Some platforms can only support up to 38400 or 76800. The test will return an error if you try to use a higher baud rate then is supported. For baud rates greater then 153600 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode. The RS-423 and RS-232 modes are usually selected by a hardware jumper on the motherboard. Consult your hardware installation manual for more information. |
|
Async Block Size |
Selects the size (in bytes) of each write. This can range from 1 to 10000. The default is 100. If it is larger than the async size it will be truncated to the async size. |
|
Async Data Size |
Selects the total number of bytes to transfer in Asynchronous mode. This can range from 1 to 10000. |
|
Async Parity |
Selects the parity to use in asynchronous mode. The user can select even, odd, or none. The default is none. |
|
Async Flow Control |
Selects the type of flow control to use in asynchronous mode testing. The user can select Hardware (RTS/CTS), Software (XON/XOFF) or None. The default depends on the loopback type. Software flow control is not allowed on a, b, a_b, or a_b_concurrent loopback types. |
|
Sync Baud Rate |
Selects the device generated clock rate for synchronous mode testing. The valid rates are from 110 to 230400. The rate does not have to be a specific value as required for async mode baud rates. The default rate is 9600. Some platforms can only support up to 38400 or 76800. The test will return an error if you try to use a higher rate then is supported. For rates greater then 100000 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode. The RS-423 and RS-232 modes are usually selected by a hardware jumper on the motherboard. Consult your hardware installation manual for more information. |
|
Sync Packet Drop Tolerance |
Selects the tolerance level of Synchronous mode dropped packets during the many_packets subtest. The default is 20 percent. The valid range is from 0 percent to 99 percent. Some packet drops are expected especially at higher clock rates and on a heavily loaded system. |
|
Sync Poll Count |
Selects the number of seconds in additional time to wait for a Synchronous mode packet to be sent. Additional time may be needed when there is heavy system activity and time-outs are being detected. In general, the user can decrease the value to 0 when the system load is light or increase the value when there is a heavy system load. |
sptest Test Modes
sptest supports all three SunVTS test modes.
Table 34-4 sptest Test Modes|
Test Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection Test |
In this mode, the sptest tries to open the port to determine if the device is connected. If it fails and the port is not busy, the test exits with an error. If it is successful or fails with a busy or exclusive use error, then the port is considered connected, and the test passes. |
|
Functional Test |
In Functional test, sptest performs the selected loopback test. |
| Functional mode through SyMON |
If you invoke SunVTS through SyMON, the following test description applies: sptest tries to minimize the impact on the applications that are running. The Online test runs in synchronous and asynchronous modes. If the device supports an internal loopback then the functional test is run utilizing the internal loopback. The zs(7D) device supports an internal synchronous loopback and the se(7d) device supports an internal asynchronous loopback. |
sptest Command Line Syntax
/opt/SUNWvts/bin/sptest standard_arguments -o dev=device_name,porta=first_port_name,T=port,L=loopback_type,M=mode,D=data_pattern,AB=async_baudrate,BS=async_write_size,S=async_total_size,PAR=parity,F=flow_control,B=sync_speed,DP=sync_drop_tolreance,P=sync_timeout
Table 34-5 sptest Command Line Syntax
Note -
64-bit tests are located in the sparcv9 subdirectory: /opt/SUNWvts/bin/sparcv9/testname. If a test is not present in this directory, then it may only be available as a 32-bit test. For more information refer to "32-Bit and 64-Bit Tests".
sptest Error Messages
Table 34-6 sptest Error Messages|
|
Error Message |
Probable Cause(s) |
Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
6003 |
data miscompare, cnt = number, exp = value, obs = value, receive device = name, source device = name, baud rate = value |
System load too heavy for selected baud rate. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection defective. |
Lower the baud rate. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
System software error. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
6011 |
name: packet read failed, error = error_message, speed = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6012 |
name: packet write failed, error = error_message, speed = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error |
|||
|
6013 |
Device 'device_name' not responding. No data detected after number seconds. Received number bytes out of number sent. Baud rate = number |
System load too heavy for selected baud rate. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Lower the baud rate. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
Check the loopback connection. |
||
|
System software error. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
6014 |
name: expected text got text |
|
|
|
6015 |
Incomplete write on Port name, len number should be number, speed = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6016 |
Incomplete read on Port name, len number should be number, speed = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6018 |
name: port not ready for writing after number seconds, speed = number |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6020 |
packet data miscompare, cnt = number exp = value, obs = value, device = name, speed = number |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6021 |
name: port not ready for reading after number seconds, no data available, speed = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error. |
|||
|
6022 |
name: port not ready for writing after number seconds, wrote number bytes out of number. Baud rate = number |
System load too heavy. |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective. |
Check loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware. |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8001 |
Test Type a_to_b is not allowed on Quick Test! |
|
|
|
8002 |
name: open() failed, error = error_message |
|
|
|
8003 |
Invalid Data Type: I=text |
|
|
|
8004 |
name: poll() error, (revents & (POLLERR | POLLHUP | POLLNVAL)) = value |
|
|
|
8005 |
Siemens serial device (se) does not support synchronous internal loopback test |
|
|
|
8006 |
Invalid port parameter: name |
|
|
|
8007 |
Invalid device name 'name', must specify either zsX or seX, where X is the first instance number of a device pair (ex., zs0) |
|
|
|
8009 |
Failed ioctl name, device = name, error = error_message |
|
|
|
8010 |
name: Not able to push Tty compatibility STREAMS module |
|
|
|
8011 |
Invalid Test Type: T=name |
|
|
|
8012 |
Invalid Mode: M=name |
|
|
|
8013 |
name device does not exist |
|
|
|
8014 |
Invalid baud_rate: number |
|
|
|
8015 |
write() to name failed: error_message, baud rate = number |
|
|
|
8016 |
read() to name failed: error_message, baud rate = number |
|
|
|
8017 |
Invalid size, requested = number bytes, min = number, max number |
|
|
|
8018 |
Could not open name after waiting number seconds |
Another process is using the port |
Stop other process using the port. |
|
Port is hung |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
|||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8021 |
name: No valid packets returned after number attempts, last error = error_message, wrote number packets, read number packets, device accounting shows number packets sent and number packets received |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Timeout too short |
Increase Sync_Poll_Count from pop menu. |
||
|
Loopback connection missing or defective |
Check the loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8022 |
printdlprim: unsupported primitive type value |
|
|
|
8023 |
stringtoaddr: invalid input string: text |
|
|
|
8025 |
dlinfoack: response ctl.len too short: number |
|
|
|
8026 |
dlinfoack: DL_INFO_ACK was not M_PCPROTO |
|
|
|
8027 |
dlokack: response ctl.len too short: number |
|
|
|
8028 |
dlokack: DL_OK_ACK was not M_PCPROTO |
|
|
|
8029 |
dlerrorack: response ctl.len too short: number |
|
|
|
8030 |
dlerrorack: DL_OK_ACK was not M_PCPROTO |
|
|
|
8031 |
dlbindack: response ctl.len too short: number |
|
|
|
8032 |
dlbindack: DL_OK_ACK was not M_PCPROTO |
|
|
|
8033 |
sigalrm: TIMEOUT |
|
|
|
8037 |
invalid packet length: number |
|
|
|
8038 |
name: poll() failed, error = error_message |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Bad serial port hardware |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8039 |
Failed I_STR ioctl, cmd = name, device = name, error = error_message |
|
|
|
8040 |
name: No packets sent, last error = error_message, wrote number packets, read number packets, device accounting shows number packets sent and number packets received |
No transmit clock present |
Reduce the system load. |
|
System load too heavy |
Increase Sync_Poll_Count from the pop menu. |
||
|
Timeout too short |
Check the loopback connection. |
||
|
Loopback connection missing or defective |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
|||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8041 |
Sporadic packets detected on name. The port must be quiescent before running test |
Another process is generating activity on the port |
Stop other process using the port. |
|
Bad serial port hardware |
Stop other process using the port. |
||
|
System software error |
|||
|
8042 |
syncinit: name missing minor device number |
|
|
|
8046 |
Test requires local or remote modem loopback (external data loop, external clocking) |
|
|
|
8047 |
name loopback type not allowed on Connection test |
|
|
|
8048 |
name loopback type not allowed on online mode |
|
|
|
8049 |
Invalid baud rate for device name, select between number and number |
|
|
|
8050 |
name internal loopback test not allowed on name device |
|
|
|
8051 |
Thread creation failed, error_message |
|
|
|
8054 |
name: At least number packets dropped (tolerance = number), last error = error_message. Wrote number packets, read number packets. Device statistics shows number packets sent and number packets received. number packets dropped in outbound queueing, number packets dropped in inbound queueing |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective |
Increase the drop tolerance option. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
Check the loopback connection. |
||
|
System software error |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
8055 |
name: number bad packets received, last error = error_message, wrote number packets, read number packets, device accounting shows number packets sent and number packets received |
System load too heavy |
Reduce the system load. |
|
Loopback connection missing or defective |
Check the loopback connection. |
||
|
Bad serial port hardware |
If the problem persists, contact your authorized Sun service provider. |
||
|
System software error |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
