Role-Based Access Control
Role-based access control (RBAC) was updated in the Solaris 8 1/01 software release. RBAC databases can now be managed through the User tool in the Solaris Management Console graphical interface. A terminology change has made the term execution profiles obsolete. The term has been replaced with rights profiles, also referred to as rights (in the graphical interface) and profiles (on the command line and in files).
In addition to authorizations and commands with security attributes, a rights profile can now include other rights profiles. If the same command appears in more than one subordinate rights profile, the first occurrence in the file assumes precedence.
The policy.conf(4) file now recognizes the keyword PROFS_GRANTED, which lets you assign rights profiles by default.
The following figure illustrates how the extended user attributes are supplied to the user.
Figure 5-1 Extended Attribute Databases
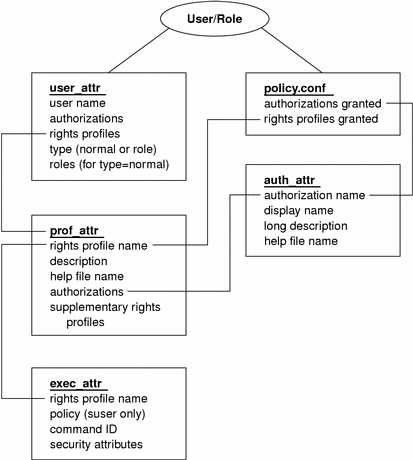
The user_attr database contains the attributes that are shown, including a comma-separated list of profile names. The contents of the profiles are split between the prof_attr file and the exec_attr file. The prof_attr file contains rights profile identification information, authorizations that are assigned to the rights profile, and rights profiles that are nested. The exec_attr file identifies the policy and contains commands with their associated security attributes. The auth_attr file supplies authorization information to the Solaris Management Console tools.
Note -
Although you can assign authorizations directly to users through user_attr, this practice is discouraged.
The policy.conf file supplies default attributes to be applied to all users. For example, if the Printer Management rights profile is assigned to a user or role, the user_attr entry for that user or role contains the keyword/value pair: profiles=Printer Management. The prof_attr file defines this profile, which also specifies the help file and authorizations, with the following line:
Printer Management:::Manage printers, daemons, spooling:help=RtPrntAdmin.html;auths=solaris.admin.printer, / solaris.admin.printer.modify,solaris.admion.printer.delete |
In the exec_attr file, the following line assigns an effective user ID = lp to the command /usr/sbin/accept within the Printer Management profile:
Printer Management:suser:cmd:::/usr/sbin/accept:euid=lp |
The following table lists commands that use authorizations.
Table 5-1 RBAC Commands|
Command |
Associated Authorizations |
|---|---|
|
at(1) |
solaris.jobs.user |
|
atq(1) |
solaris.jobs.admin |
|
crdw(1) |
solaris.device.cdrw |
|
crontab(1) |
solaris.jobs.user, solaris.jobs.admin |
|
allocate(1M) |
solaris.device.allocate, solaris.device.revoke |
|
deallocate(1M) |
solaris.device.allocate, solaris.device.revoke |
|
list_devices(1M) |
solaris.device.revoke |
|
smcron(1M) |
solaris.jobs.admin, solaris.jobs.user |
|
smdiskless |
solaris.admin.dcmgr.clients, solaris.admin.dcmgr.read |
|
smexec(1M) |
solaris.profmgr.read, solaris.profmgr.write |
|
smgroup(1M) |
solaris.admin.usermgr.read, solaris.admin.usermgr.write |
|
smmultiuser(1M), smuser(1M) |
solaris.admin.usermgr.pswd, solaris.admin.usermgr.read, solaris.admin.usermgr.write, solaris.profmgr.assign, solaris.profmgr.delegate, solaris.role.assign, solaris.role.delegate |
|
smmaillist(1M) |
solaris.admin.usermgr.read, solaris.admin.usermgr.write |
|
smosservice |
solaris.admin.dcmgr.admin, solaris.admin.dcmgr.read |
|
smprofile(1M) |
solaris.profmgr.read, solaris.profmgr.write |
|
smrole(1M) |
solaris.admin.usermgr.pswd, solaris.admin.usermgr.read, solaris.admin.usermgr.write, solaris.profmgr.assign, solaris.profmgr.delegate, solaris.role.assign, solaris.role.delegate |
For more information on the Solaris Management Console, see "System Administration Tools".
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
